Unit – I
Basic Computer Concept
Q.1) What are the characteristics of computer?
A1: The following are the characteristics of the computer system:
- Speed
When it comes to conducting mathematical computations, a computer outperforms humans in terms of speed and accuracy. Millions (1,000,000) of instructions can be processed every second by computers. Microseconds and nanoseconds are the lengths of time that computers take to do their tasks.
2. Accuracy
Computers are 100 percent accurate in their calculations. Data inconsistency or inaccuracy can cause errors.
3. Diligence
A computer can consistently and accurately do millions of jobs or calculations. There are no signs of exhaustion or a lack of concentration. It also has a memory that is superior to that of humans.
4. Memory
Data is stored in primary memory, which is built into a computer. Secondary storage refers to removable media such as CDs, pen drives, and other similar devices that are used to store data.
5. Versatility
Versatility refers to a computer's capacity to do a variety of tasks with the same accuracy and efficiency.
6. Reliability
A computer is dependable because it produces consistent results for similar sets of data, i.e., we will obtain the same result no matter how many times we input the same data.
7. Automation
The computer does all functions automatically, that is, without the need for human interaction.
8. Power of remembering
A computer has the ability to store any quantity of data or information. Any information can be stored and retrieved for as long as you need it, for as many years as you like. How much data you want to store in a computer and when you want to lose or retrieve that data is totally up to you.
9. No IQ
A computer is a dumb machine that can't do anything unless the user tells it to. It follows the instructions at a breakneck pace and with pinpoint accuracy. It is up to you to select what you want to do and how you want to do it. As a result, unlike you, a computer cannot make its own decisions.
10. No Feelings
It lacks sensations and emotions, as well as flavor, knowledge, and experience. As a result, even after long hours of work, it does not become exhausted. It doesn't differentiate between users.
Q.2) Describe input devices?
A2: Input Devices are the devices that are used to provide data and instructions to the machine. Depending on the type of data you want to enter in the computer, you can use a variety of input devices, such as a keyboard, mouse, joystick, light pen, and so on.
Devices like keyboard and mouse that are used to input data and instructions to the computer are called input unit.
Keyboard
It's the most widely used input method. It is used to directly insert data and instructions into a computer. On the keyboard, there are 104 buttons known as keys.

Fig 1: keyboard
Mouse
Another input device that is usually used with computers is the mouse. It's essentially a pointing system that operates on the Point and Click principle. When the mouse is pushed over the mouse pad, a light beam reflects under it, causing the cursor on the screen to turn.
The mouse is used in Windows-based applications, where the user can execute commands by using the pointer to point to objects and pressing the mouse buttons. We also use the mouse to draw in paint and take pictures of the kids.

Fig 2: mouse
Most modern mice now have a wheel in the center of two buttons that allows us to scroll through documents more quickly. To scroll up or down in a book, we use our forefinger to turn the wheel. The optical mouse tracks the movement of the mouse to shift the cursor on the computer screen using red light.
Joystick and Game Pad
Joysticks and gamepads are examples of input devices that are used to guide the movement of objects on a computer screen. These, like the mouse, are pointing instruments. They are mostly used to play video games.
A vertical stick with a track ball at the bottom of the joystick. The user needs to shift the items on the screen quickly when playing video games. Objects can be easily pushed in all directions with the movement of this vertical stick.
A game-pad is a type of game controller that is held in two hands and feedback is provided by pressing buttons on it with the fingers (especially the thumbs). Control Pad is another name for it.

Fig 3: joystick and gamepad
Light pen
Another pointing type input device is the light pen. It's a pen-shaped interface that lets you aim directly at objects on the screen. It can also be used to draw directly on the computer display.
Scanner
With the aid of a scanner, we can save images, photos, and diagrams to the screen. The picture is read by the scanner and saved as a file on the disk.

Fig 4: scanner
Touchscreen
A touchscreen is a type of computer display that detects the touch of a human finger, gloved hand, stylus, pen, or other pointing device. By pressing the button, the user gives the machine instructions.
Q.3) Explain output devices?
A3: Output Devices are the devices that are used to show the results or details. The display can be seen on a monitor or printed on paper using a printer. The monitor and printer are the most popular output devices.
Monitor
The most popular output device connected to a computer for displaying processed data is this. It has the appearance of a television and is also known as VDU (Visual Display Unit). Pixels are a large number of very tiny dots on a projector that are used to view pictures. The resolution of a monitor refers to the amount of pixels that can be displayed on its screen.
The following are the two most popular monitor types:
- Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)Monitor
- Liquid crystal Display (LCD)Monitor
Since the display on the computer cannot be saved for a long time, it is referred to as Soft Copy Output.
LCD monitors are becoming more common as a result of their sharp picture quality. They are flat-screen displays with a light weight.

Fig 5: monitor
Printer
This is a vital computer system output unit. It prints out the results that are shown on the computer screen. Printed output is also known as hard copy output because, unlike display output, it can be saved even when the screen is turned off.

Fig 6: types of printers
There are various styles of printers. Printers are classified as follows based on their printing techniques:
● Character printer
● Line printer
● Page printer
- Character Printer
The character printer prints one character at a time, at a rate of 30 to 600 characters per second. A character printer is an example of a dot matrix printer.
Dot matrix printer
This printer functions similarly to a typewriter. It presses the end of pins fixed in its print heads against an inked ribbon to make an impression on the page. This printer is noisy and produces low-quality prints. CPS is the unit of measurement for its speed (Characters Per Second).
2. Line printer
This printer has a fast print speed and prints one line at a time. It is used when a large amount of production is needed because it produces results quickly. Drum printers and Chain printers are examples of Line printers. These printers produce a lot of noise and run at speeds ranging from 200 to 2000 LPM (Lines Per Minute).
3. Page printer
The Paper Printer prints a whole page at once. Inkjet printers and line printers are examples of these printers since they must store each page in memory before printing it.
Inkjet printer
This printer prints on the paper by spraying tiny ink droplets. It has the ability to print in color as well as black and white. This printer produces better print quality than a Dot Matrix printer and does so without producing any noise. PPM is the unit of measurement for its speed (Pages Per Minute).
Laser printer
Laser beam technology is used to print text or graphics on paper in this form of printer. This printer has a fast print speed and produces prints of excellent quality. Its rate is also expressed in PPM.
Speaker
Output devices, such as speakers, are classified as such. These are used to listen to the computer's music and sound effects. They typically come in pairs and are of varying shapes and sizes.

Fig 7: speaker
Plotter
A plotter may be used to print a photograph, drawing, or picture stored on a screen. It's a printer output system that produces high-quality printed output. Engineers and architects are the most popular users.

Fig 8: plotter
Q.4) What do you mean by storage units?
A4: All input data, instructions and data interim to the processes are stored in the memory. Memory is of two types – primary memory and secondary memory. Primary memory resides within the CPU whereas secondary memory is external to it.
A memory is just like a human brain. It is used to store data and instructions.
Computer memory is the storage space in the computer, where data is to be
Processed and instructions required for processing are stored. The memory is
Divided into a large number of small parts called cells. Each location or cell has a
Unique address, which varies from zero to memory size minus one. For example, if
The computer has 64k words, then this memory unit has 64 * 1024 = 65536 memory
Locations. The address of these locations varies from 0 to 65535.
Memory is primarily of three types −
● Cache Memory
● Primary Memory/Main Memory
● Secondary Memory
Cache Memory
Cache memory is a very high-speed semiconductor memory which can speed up the
CPU. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory. It is used to hold
Those parts of data and program which are most frequently used by the CPU. The
Parts of data and programs are transferred from the disk to cache memory by the
Operating system, from where the CPU can access them.
Advantages
The advantages of cache memory are as follows −
● Cache memory is faster than main memory.
● It consumes less access time as compared to main memory.
● It stores the program that can be executed within a short period of time.
● It stores data for temporary use.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of cache memory are as follows −
● Cache memory has limited capacity.
● It is very expensive.
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary memory holds only those data and instructions on which the computer is
Currently working. It has a limited capacity and data is lost when power is switched
Off. It is generally made up of semiconductor device. These memories are not as fast
As registers. The data and instruction required to be processed resides in the main
Memory. It is divided into two subcategories RAM and ROM.
Characteristics of Main Memory
● These are semiconductor memories.
● It is known as the main memory.
● Usually volatile memory.
● Data is lost in case power is switched off.
● It is the working memory of the computer.
● Faster than secondary memories.
● A computer cannot run without the primary memory.
Secondary Memory
This type of memory is also known as external memory or non-volatile. It is slower
Than the main memory. These are used for storing data/information permanently.
CPU directly does not access these memories, instead they are accessed via input-
Output routines. The contents of secondary memories are first transferred to the main
Memory, and then the CPU can access it. For example, disk, CD-ROM, DVD, etc.
Characteristics of Secondary Memory
● These are magnetic and optical memories.
● It is known as the backup memory.
● It is a non-volatile memory.
● Data is permanently stored even if power is switched off.
● It is used for storage of data in a computer.
● Computer may run without the secondary memory.
● Slower than primary memories.
Q.5) What is CPU?
A5: The central processor unit (CPU) is the computer's most important component. It's also known as a microprocessor or processor. Inside the Computer, it is the brain that runs the show. The processor performs all functions and processes on a computer, either directly or indirectly. The computer processor is, without a doubt, one of the most crucial components of the computer system.
The central processing unit (CPU) is made up of transistors that receive and process data. Processors are transistors that conduct logical processes. It is also, scientifically, one of the most incredible devices in the world of technology, not just one of the most fantastic aspects of the PC.
Parts of CPU
Arithmetic logic units (ALU) - It is a component of a computer processor that performs arithmetic and logic tasks. The (AU) arithmetic unit and the (LU) logic unit are the two halves of an arithmetic-logic unit (ALU).
Control unit (CU) - The program instruction is decoded. Silica is utilized as part of the CPU chip in a computer. In other words, a microprocessor is a silicon device utilized for data processing.
Registers - It refers to the computer processor's temporary storage locations. The control unit is in charge of it (CU). Registers that hold data, instructions, and addresses needed by the program while it is operating.
Q.6) What do you mean by computer system?
A6: A computer system is a collection of interconnected components that work together to produce a desired outcome.
A computer is an electronic device that can be configured to accept, process, and generate results from data (input) (output). a computer with a printer
A computer system is a collection of additional hardware and software.
A central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output devices, and storage devices are the main components of a computer system. To give the desired output, all of these components work together as a single unit. A computer system is available in a variety of shapes and sizes. It could be anything from a high-end server to a personal computer, laptop, tablet, or smartphone.
Components of computer system
Let's have a look at the essential components of a computer system
● Input unit
● Output unit
● Control unit
● Arithmetic logic unit
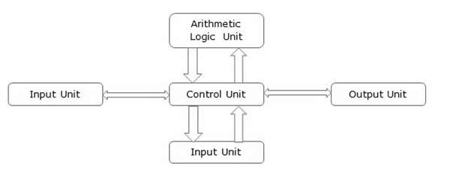
Fig 9: components of computer
The basic parts of a computer are as follows −
● Input Unit − Devices like keyboard and mouse that are used to input data and instructions to the computer are called input unit.
Input devices are the devices that allow control signals to be sent to a computer. These devices convert the data into a digital format that the computer system can understand. Keyboards, mice, scanners, touch screens, and other input devices are examples.
● Output Unit − Devices like printer and visual display unit that are used to provide information to the user in desired format are called output unit.
The output device is the device that receives data from a computer system for display, physical production, and other purposes. It turns digital data into a human-readable format. Monitor, projector, headphones, speakers, printer, and so on.
● Control Unit − As the name suggests, this unit controls all the functions of the computer. All devices or parts of the computer interact through the control unit.
● Arithmetic Logic Unit − This is the brain of the computer where all arithmetic operations and logical operations take place.
After data is input into the primary unit, the Arithmetic Logical Unit is employed to process it. Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, logic, and comparison are the major operations of the Arithmetic Logical Unit.
● Memory − All input data, instructions and data interim to the processes are stored in the memory. Memory is of two types – primary memory and secondary memory. Primary memory resides within the CPU whereas secondary memory is external to it.
Control unit, arithmetic logic unit and memory are together called the central
Processing unit or CPU. Computer devices like keyboard, mouse, printer, etc. that
We can see and touch the hardware components of a computer. The set of
Instructions or programs that make the computer function using these hardware
Parts are called software. We cannot see or touch software. Both hardware and
Software is necessary for working on a computer.
Q.7) Write the difference between primary memory and secondary memory?
A7: Difference between primary and secondary memory
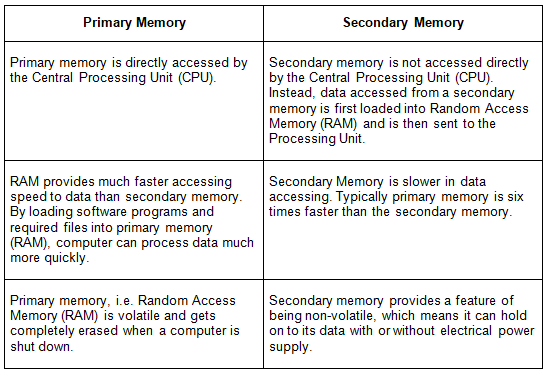
Q.8) Write the difference between input device and output device?
A8: Difference between input device and output device
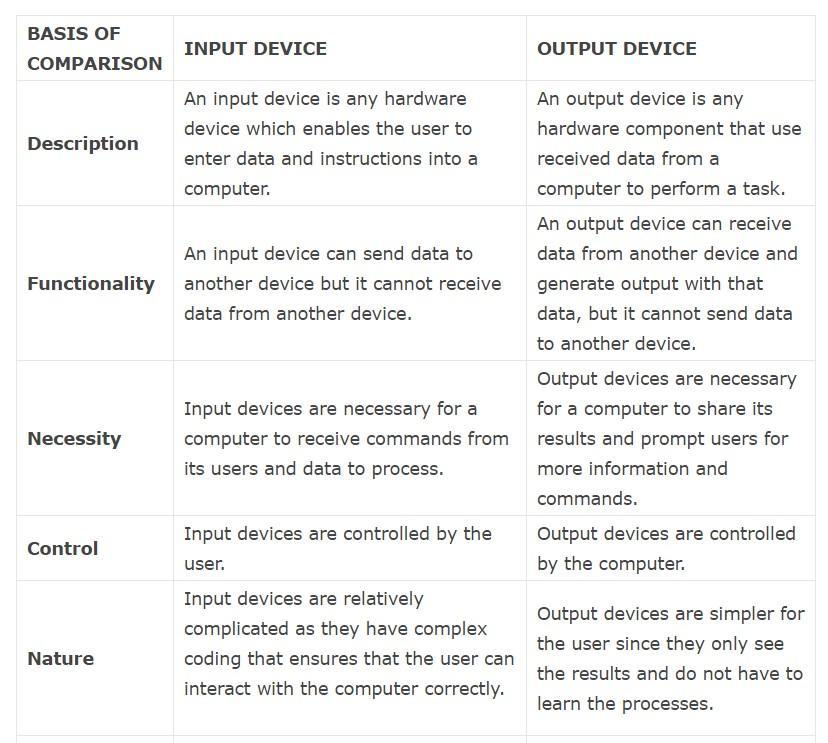
Q.9) Write the difference between printer and plotter?
A9: Difference between plotter and printer
S.No. | PLOTTER | PRINTER |
1 | It can read files in the DWG, CDR, Al and other vector formats. | It can read BMP, PDF and JPG TIFF formats. |
2 | It is a device that draws pictures on the page with the help of commands given through a computer. | It is a device that brings images and texts on the page with the help of commands given through a network. |
3 | It is expensive. | It is less costly as compared to plotters. |
4 | It can draw continuous lines. | It cannot draw continuous lines. |
5 | It works on slow speeds. | It works on fast speeds. |
6 | Its software includes Adobe Illustrator, Corel, Flexi and CAD. | Its software includes Photoshop and any other image-editing program. |
7 | It gives the output in a format that is similar to a vector graphic. | It gives the output file data in a format such as bitmap or pixels. |
8 | Examples are Drum plotters, Flatbed plotters, Pen plotters, Electrostatic plotters, Inkjet plotters. | Examples are Laser Printers, Solid Ink Printers, LED Printers., Business Inkjet Printers, Home Inkjet, Printers, 3D Printers. |
Q.10) Write the difference between printer and scanner?
A10: Difference between printer and scanner
Printers | Scanners |
It is a device whose work is to acquire the text and graphics output from the computer and generate a hard copy of it. | It is a device that scans documents then convert them into a digital format. |
Output Device | Input Device |
Digital document is rendered over the paper by creating an impact or charges on a photosensitive material. | Illuminating lamp is used on the scan head to reflect the light on to the lens, which is then focussed over a CCD array. |
Examples are Laser Printers, Solid Ink Printers, LED Printers., Business Inkjet Printers, Home Inkjet, Printers, 3D Printers. | Examples are Flatbed, Sheet-fed, Handheld, and Drum scanners. |