Unit – VII
Operating system – Windows
Q.1) Write short notes on the operating system and window?
A1: An OS (OS) is associate degree interface between a soul and hardware. Associate degree OS is software package that performs all the fundamental tasks like file management, memory management, method management, handling input and output, and dominant peripheral devices like disk drives and printers.
Some in style OSs embody UNIX operative System, Windows OS, VMS, OS/400, AIX, z/OS, etc.
Definition
An OS could be a program that acts as associate degree interface between the user and therefore the hardware and controls the execution of every kind of programs.
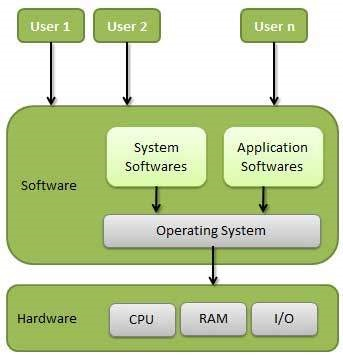
Fig 1 – operating system
Following are a number of necessary functions of associate degree OS.
• Memory Management
• Processor Management
• Device Management
• File Management
• Security
• Control over system performance
• Job accounting
• Error detection aids
• Coordination between different software package and users
Basics of Window
A2: Microsoft's Windows operating system is a graphical operating system. It lets users view and save files, run applications, play games, and watch videos, as well as connect to the internet. It was made available for both personal and professional use.
The original version, 1.0, was released by Microsoft.
On November 10, 1983, it was published for both home computer and professional functions of Windows. It was later available on a variety of Windows platforms, including the current version, Windows 10.
The first business-oriented version of Windows, known as Windows NT 3.1, was introduced in 1993. The next versions, Windows 3.5, 4/0, and Windows 2000, were thereafter released. Microsoft created the various versions of Windows XP for a home and commercial context when it was released in 2001. It was built using common x86 hardware, such as Intel and AMD processors. As a result, it may run on a variety of hardware, including HP, Dell, and Sony systems, as well as custom-built PCs.
Q.2) What do you mean by user interface?
A2: The part of an operating system, application, or device that allows a user to enter and receive information is referred to as the user interface (UI). Text is shown on a text-based user interface (see image to the left), and commands are often input on a command line using a keyboard. The operations of a graphical user interface (see right-hand image) are performed by clicking or moving buttons, icons, and menus with a pointing device.
Text user interface
Text-based user interfaces have evolved into modern graphical user interfaces. A text-based user interface can still be utilized with some operating systems. The commands are entered as text (e.g., "cat story.txt") in this example.
Open the Start menu and type cmd to bring up the text-based Command Prompt on Windows. To open the command prompt in a new window, press Enter on the keyboard. Instead of using the mouse, you can type commands into the command prompt using the keyboard.
Fig 2: text user interface
Graphical user interface
Most operating systems have a graphical user interface, which means that instead of inputting commands, you use a pointing device to handle various graphical objects (such as icons). Because the core principles of many graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are largely the same, understanding how to use a Windows UI will almost certainly lead to learning how to use Linux or another GUI.
The following are the basic components of most graphical user interfaces:
● a start menu with program groups,
● a taskbar showing running programs,
● a desktop,
● various icons and shortcuts.
Fig 3: graphical user interface
Q.3) Write the use of the mouse?
A3: You can use the numeric keypad to press and hold the active mouse button and to release it. This is helpful if you want to drag an item.
To | Do this |
Drag an item | Point to the item and then press zero (0) |
Drop an item | Point to the location where you want to move the item and then press the decimal point (.) |
Clicking items using Mouse Keys
After you choose a button, you can click items on your screen.
To | Do this |
Click an item | With the left button selected as your active button, point to the item, and then press 5 |
Right-click an item | With the right button selected as your active button, point to the item and then press 5 |
Double-click an item | With the left button selected as your active button, point to the item and press the plus sign (+) |
Q.4) What is my computer?
A4: Many Windows users who have been with the operating system since its early versions, such as Windows XP, have grown accustomed to using apps and accessing files in specific ways. If you're one of those people who relied on a certain icon to access your critical folders and files, you might be wondering where the My Computer icon in Windows 7 can be found.
One popular approach for browsing the folders and files on your Windows 7 computer is to use the computer button from the Start menu. If, on the other hand, you prefer to access your files from your Desktop, you may be seeking for a means to get to the “My Computer” area from there.
You can customize your Desktop in Windows 7 by adding a variety of icons that will transport you to a variety of popular locations. Our instructions below will show you how to add a computer icon to your desktop, giving you another way to access your files.
Display my computer icon on desktop
● Go to your computer's desktop.
● Personalize by right-clicking in an empty spot and selecting Personalize.
● Change the desktop icons option.
● Click Apply, then OK after checking the box to the left of Computer.
How to Show the My Computer Icon on the Desktop
The instructions below will show you how to add a computer icon to your desktop. When you double-click that icon, a Windows Explorer window appears, displaying your computer's disks and associated devices. You can then browse the folders and files on any of those drives by double-clicking on them.
- Navigate to your computer’s Desktop.
This can be accomplished by minimizing or closing all open windows, or by right-clicking the taskbar and selecting the Show the desktop option.
2. Click the Personalize option after right-clicking on an empty spot on the desktop.
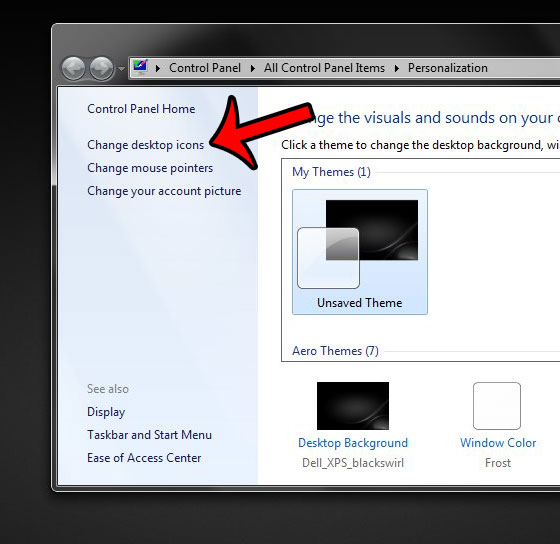
3. In the left-hand column of the window, click the Change desktop icons link.
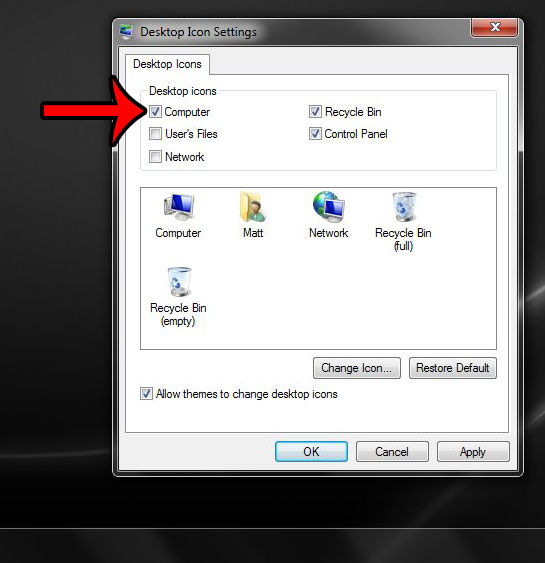
4. Under Desktop icons, check the box to the left of Computer, then click Apply at the bottom of the window, then OK.
Q.5) Write about recycle bin?
A5: When items, such as files and folders, are no longer needed, you can delete them in Windows 7. However, when you delete objects, they are stored in the Recycle Bin rather than being permanently deleted. The Recycle Bin serves as a temporary storage area for removed items until you are ready to permanently delete them. If necessary, deleted items can be recovered from the Recycle Bin, however there are several exceptions.

Fig 4: recycle bin
Purpose
The Recycle Bin serves as a sort of ‘holding pen' for deleted files and folders (and even shortcuts!). When you delete a file or folder, it is not permanently removed from your computer. Instead, Windows 7 recycles the deleted items. It's almost like being in limbo with these files. The files you've deleted will remain in the Recycle Bin until you decide they're no longer needed, at which point you can opt to permanently delete them.
The Recycle Bin's purpose is to allow you to retrieve lost objects in the event that you accidentally lose an important document, photo, or folder.
The Recycle Bin is located on your desktop and may also be reached using Windows Explorer's Desktop favorite.
How recycle bin work
Permanently deleting files and directories necessitates some effort on the side of the computer. As a result, rather than destroying a file or folder every time you hit the delete key on your keyboard, Windows 7 sends them to the Recycle Bin.
The Recycle Bin takes up a certain amount of space on your computer's hard drive (which can be adjusted). Items in the Recycle Bin are deleted once storage capacity is depleted. This means that, in order to make room for them, the Recycle Bin will begin to overwrite the oldest deleted objects with the most recently removed things.
The frequency with which objects are purged is determined by the Recycle Bin's assigned storage capacity, how frequently you delete items, and the size of the files you delete.
Q.6) Write the advantages and disadvantages of recycle bin?
A6: Advantages
The ability to recover deleted things is the obvious benefit of the Recycle Bin. However, depending on how long ago you deleted the item and whether it was purged to make way for more recently deleted items, there is a time restriction.
Disadvantages
When you run out of space on your computer, you'll frequently need to delete unneeded files and folders. Using standard delete activities, such as placing data in the Recycle Bin, will, however, have no effect on the amount of storage space available on your computer. This is because, as previously said, the material isn't actually wiped; it's merely marked for deletion, but it's still taking up space on your hard drive.
To reclaim storage space on your computer, empty the Recycle Bin; this will mark the space held by flagged things as free to use, allowing you to reclaim extra storage space.
Q.7) Describe status bar?
A7: A status bar is a horizontal window at the bottom of a parent window that displays several types of status information. The status bar can be broken into sections to display different types of data. The status bar in the Microsoft Windows Paint application is seen in the image below. The words "For Help, click Help Topics on the Help Menu" appears in the status bar in this situation. The status bar is a section of the window at the bottom that includes Help text and coordinate information.
Types and Style
A status bar appears at the bottom of the parent window by default, but you can specify the CCS TOP style to have it display at the top of the client area of the parent window.
To include a sizing grip at the right end of the status bar, use the SBARS SIZEGRIP style.
Size and Height
The status bar's window method sets the window's initial size and position automatically, ignoring the parameters supplied in the CreateWindowEx function. The client area of the parent window has the same width as the client area of this window. The height is determined by the metrics of the font currently selected in the device context of the status bar, as well as the width of the window's borders.
When the window method receives a WM SIZE message, it automatically modifies the size of the status bar. When the parent window's size changes, the parent usually sends a WM SIZE message to the status bar.
By sending the window an SB SETMINHEIGHT message with the minimum height, in pixels, an application can set the minimum height of a status bar's drawing area. The window's edges are not included in the sketching area. When drawing in an owner-drawn status bar, a minimum height is useful.
Multiple - part status bar
A status bar can be divided into several sections, each of which displays a separate line of text. Sending the window an SB SETPARTS message with the number of parts to produce and the address of an integer array divides a status bar into parts. Each member of the array specifies the client coordinate of a part's right edge, and each element contains one element for each part.
The maximum number of elements in a status bar is 256, though most apps utilize significantly fewer. By giving the window an SB GETPARTS message, you can get a count of the parts in a status bar, as well as the coordinates of the right edge of each part.
Q.8) Explain the start menu?
A8: The Microsoft Windows Start menu is where you'll discover your installed apps and any files or folders in Windows. The Start menu is accessed by default by pressing the Start button in the bottom-left corner of the Windows desktop screen. The image depicts an example of the Start menu in Windows 7.
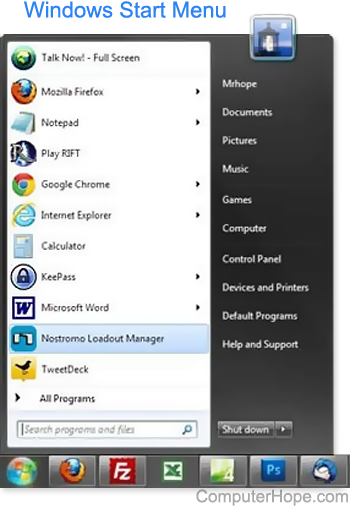
Fig 5: start menu
Where is the start menu?
The Start menu is discovered by clicking Start and is displayed in the bottom left corner of the screen by default in versions of Microsoft Windows that support it. If the Taskbar is moved from the bottom of the screen, its location may change.
A Start menu is not available on computers that do not run Microsoft Windows (for example, Linux and Apple systems). A Windows Start menu is also not available on cell phones or tablets.
What is accessible in the Start menu?
The Windows Start menu in Microsoft Windows XP and Windows 7 is described here. If you're using Windows 10, Scroll down to the section on the Windows 10 Start menu.
Left pane
The left pane displays any pinned program shortcuts as well as recently opened programs. One pinned program is separated by a line from the recently run programs in the example above.
All programs
The All-Programs option is located at the bottom of the left pane and displays all of the computer's installed programs.
Search
The "Search" bar is located directly beneath the All Programs option. You can enter in the name of the program or file you're looking for and have the results displayed above.
Right pane
The right pane displays each of the computer's most frequently used components, including your Computer, Control Panel, Documents, Music, and Pictures.
Shut down
The Shutdown button is located at the bottom of the right pane and allows you to turn the computer off. You can also swap users, log off, restart, sleep, or hibernate the computer by clicking the arrow next to the Shutdown button.
Q.9) How to start the applications?
A9: Computers exist for a single purpose: to run programs. A program that performs a useful function is referred to as an application. There are apps for creating spreadsheets, playing games, editing images, and accessing email, to mention a few. The apps you have installed on your computer determine the practical activities you may do with it as well as the enjoyment alternatives you have (games, movies, music, and so on).
In Windows 8.1, there are two types of programs: desktop applications and web applications. Desktop applications are traditional-style applications built to operate on the Windows desktop in resizable windows. Apps designed for Windows 8 and 8.1 are known as Windows 8 apps.
Starting an application
If the app you wish to launch appears on the Start screen, simply click or tap its shortcut to launch it. If it doesn’t appear there, click the down-pointing arrow at the bottom of the Start screen to see the Apps list. This is a list of all the applications that have been installed.
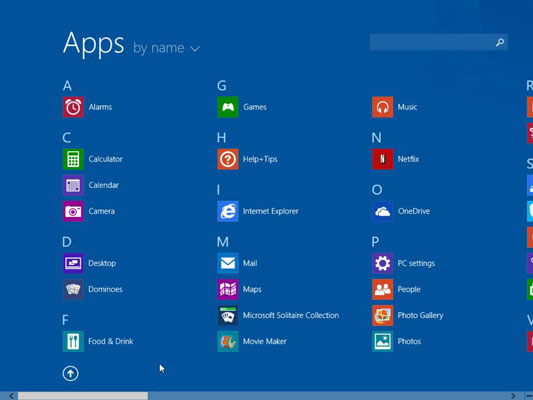
Applications can also be launched via pinned shortcuts on the taskbar or the desktop. To start the application, click a pinned taskbar shortcut icon or double-click a pinned desktop shortcut icon.
Depending on the sort of application, one of two types of interfaces appears after you launch it. Traditional desktop apps operate in a window with the background set to the desktop. You can move and resize the window, and you can have lots of windows open at once, arranged so you can see all of them.
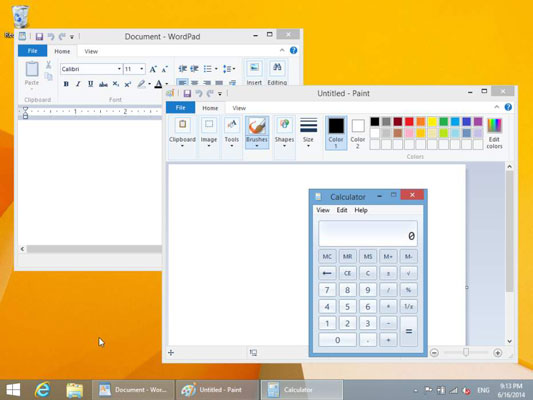
To issue commands, most desktop applications have a menu system, toolbars, or a ribbon at the top of the window.
In contrast, a Windows 8 software often takes up the full screen and may not have any visible controls. Right-click to bring up a command bar with commands at the top or bottom of the screen. A command bar can be found at the top and bottom of the image below.
The controls and commands in Windows 8 apps are larger and simpler than those in desktop applications, and they are designed to function well with touch screens.
Q.10) Write about file explorer?
A10: The file management application used by Windows operating systems to browse folders and files is called File Explorer. It gives the user a graphical interface to navigate and access the files on the computer.

The File Explorer can be accessed by clicking the folder icon in the Taskbar. The File Explorer window will open after you click the icon.
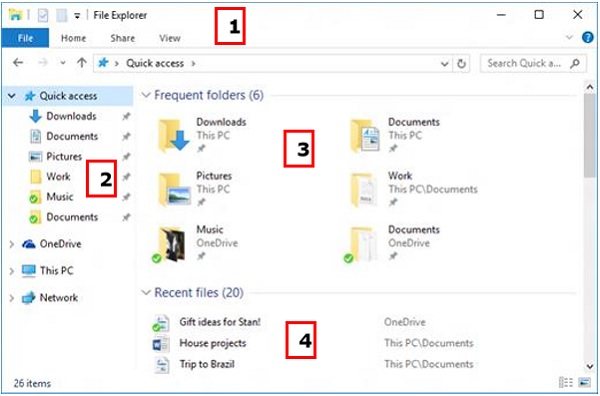
The following parts make up the basic File Explorer window:
● The File Explorer ribbon, which is similar to the Microsoft Office ribbon. The ribbon has buttons for doing typical actions with your files and folders.
● The Navigation Pane allows you to access your document and image libraries, as well as your storage devices. It also has folders and network devices that are commonly used.
● On the right, the Frequent folders section lists the folders you've worked with recently so you can get to them quickly.
● In the lower area of the window, the Recent Files section displays files and documents that you've recently opened.
The File Explorer Ribbon
The File Explorer in Windows 10 now has a new ribbon toolbar, similar to the one found in current versions of Microsoft Office. The most common tasks are represented by buttons and commands on this ribbon.
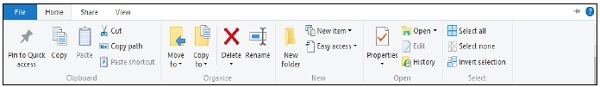
There are four tabs on the Ribbon, each with its own set of commands. Copying and pasting files and folders from one location to another is one of the operations available from the home tab.
● Transferring files and folders to a different location.
● Transferring files and folders to a different location.
● Sending a file or folder to the Recycle Bin or permanently deleting it.
● Changing the name of a file or folder.
● Adding a new folder or other new things to your collection.
● Verifying or changing a document's or folder's properties.
● Opening a file or folder.
● Different options to select one or various files and folders.
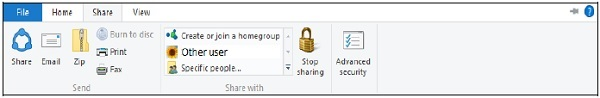
The Share ribbon provides a variety of choices for sharing files and folders. For instance,
● Sending a file via email or text message.
● Compressing (or “Zipping”) a folder to reduce its size.
● Documents are printed or faxed.
● Users or networks can share with each other.
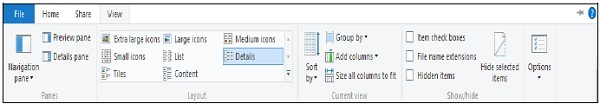
You can modify how Windows displays your files and folders using the View ribbon. Here are some of the adjustments you can make:
● Adding more panes to offer a preview or more information about your files.
● Changing the file and folder layout from icons to lists, and so on.
● Sorting and structuring your folder's contents.
● Hide certain directories or files.
The File tab brings up a menu with many options, such as
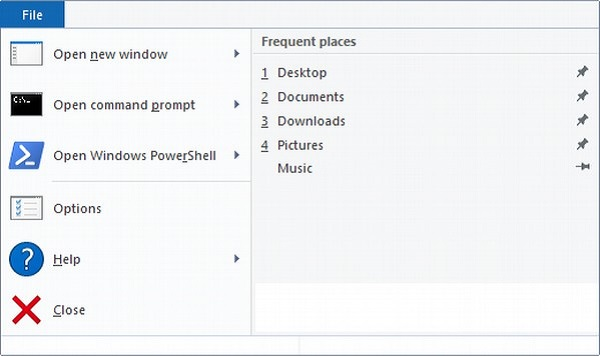
● A second File Explorer window is opened.
● Advanced users can open command windows.
● Changing or modifying File Explorer's behavior choices.
Q.11) Explain the folder and directories?
A11: The operating system is stored in a hard disk folder (directory). It's usually the Windows or Winn folder in Windows.
Consider your hard disks to be gigantic filing cabinets. Consider them to be enormous filing cabinets with no drawers and no manila folders on the inside. Instead, if you have a piece of paper or a document to file, you just toss it into your huge cabinet. After a few hundred documents have been thrown into this cabinet in a haphazard manner, you will quickly discover that identifying any one document inside that vast pile of papers is time-consuming and difficult. Instead, most of us label a series of manila folders and then file them away in our filing cabinet. You may have a folder for academic transcripts, a folder for tax paperwork, a folder for old poems you've written, and a folder for the warranties that came with your new computer.
The same can be said about your hard drive. A folder (also known as a directory) in Windows is similar to the yellow folders found in file cabinets. On your hard drive, make a folder called "school essays," another called "scanned photos," and yet another called "215 homework." You'll amass a number of different folders over time, but you'll be pleased you did because finding and organizing your papers will be much easier.
Actually, you'll find that a huge number of directories have already been created for you. When you install a new software on your computer, it normally creates one or more new folders in which to keep the necessary files.
Directory
A directory is an area on your computer where you can store files. A hierarchical file system, such as Linux, MS-DOS, OS/2, and Unix, uses directories.
The output of the Windows/DOS tree command is shown below. It displays the contents of all local and subdirectories (e.g., the "big" directory in the "cdn" directory). When viewing this overview, the current directory is the C: drive's root directory. Because there is nothing beneath it and the other directories "branch" from it, it is called the "root" directory. The directory may also be referred to as a home directory if you're using an operating system with numerous user accounts.
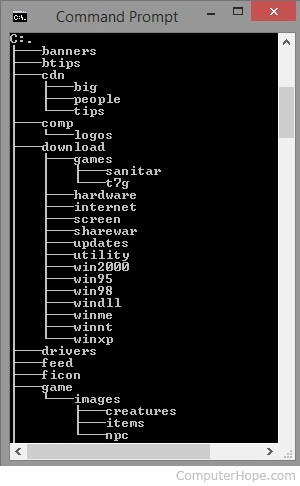
Change a directory
The "cd" command is used to change a directory in MS-DOS, Linux, Unix, and most other command-line operating systems.
Make directory
Use the "mkdir" command to create a directory in MS-DOS, Linux, Unix, and most other command-line operating systems.
Remove directory
Use the "rmdir" command in MS-DOS to delete a directory. Use the "rm -r" command in Linux and Unix.
Purpose of directory
On a computer, a directory is used to store, organize, and segregate files and folders. You may, for example, create a directory for images and another for all of your documents. You could quickly access the sort of file you wanted to view by saving specified types of files in a folder. In other words, finding a photo in a directory containing only pictures is easier than finding a picture in a directory containing all types of files.
In addition to storing programs, directories are also used to store them. When you install a program, for example, its files are saved in a separate directory that may contain subdirectories and tens, hundreds, or thousands of files. It helps prevent files with the same name from being overwritten, edited, or deleted by other programs by storing them in their own directory.
Q.12) How to create and rename the file and folder?
A12: The keys to properly arranging files and folders inside a hierarchy are to keep comparable objects together and to give folders descriptive names. Creating a new folder can aid in the organization and tracking of files and folders. To make a folder, first choose a place for it, then create the folder, and last give it a name. You should give each folder a meaningful name so that you can tell what it contains just by looking at it. You can rename a folder or file at any moment after you've given it a name.
Create a folder
● Open the drive or folder where the folder will be created.
● On the toolbar, click the Organize button, then New folder.
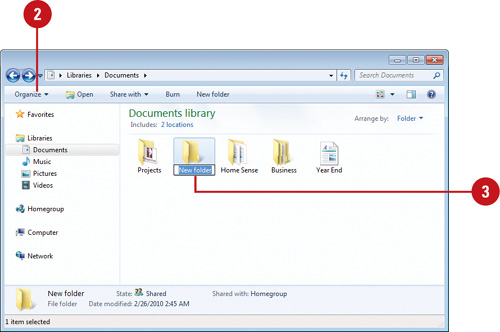
● Type a new name in the New Folder name field.
● Press enter.
Rename a file or folder
● To choose a file or folder, click it.
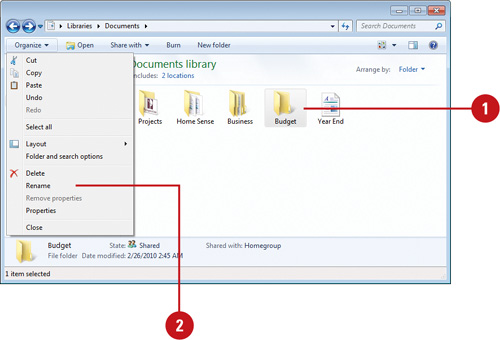
● On the toolbar, click the Organize button, then Rename.
● Type a new name, or click to set the insertion point, and then edit the name with the name chosen.
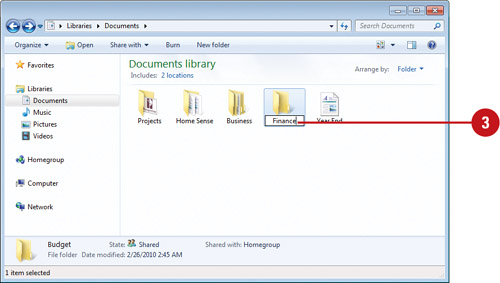
● Press enter.
Q.13) How to open and close the window?
A13: From the Front Panel:
● To bring the keyboard focus to the Front Panel, press Alt+Tab.
● To move the highlight within the Front Panel and choose a control, use the arrow keys.
● To select the control and open the application's window, press Return or Spacebar.
From Application Manager:
● As explained above, open the Application Manager window by selecting the Front Panel control.
● Within the Application Manager window, use the arrow keys to transfer the highlight to an application group icon.
● To open the application group, press Return twice.
● To start an application, move the highlight to an application or action icon with the arrow keys, then hit Return twice.
From a terminal emulator window:
● As mentioned above, choose the Front Panel control to open a terminal emulator window.
● When the window appears, input the command to launch the program.
Closing the window
When you close a window, it disappears from all workspaces.
Q.14) What is window setting and control panel?
A14: You may need to change the settings on your computer at some point. You could want to alter your desktop backdrop or your Internet settings, for example. The Control Panel allows you to adjust these and other options.
In Windows, however, the Settings app has largely supplanted the Control Panel. The Control Panel is still available, but the Options app now contains the majority of the tasks and settings.
Open the setting app
Click the Start button, then select the gear icon.
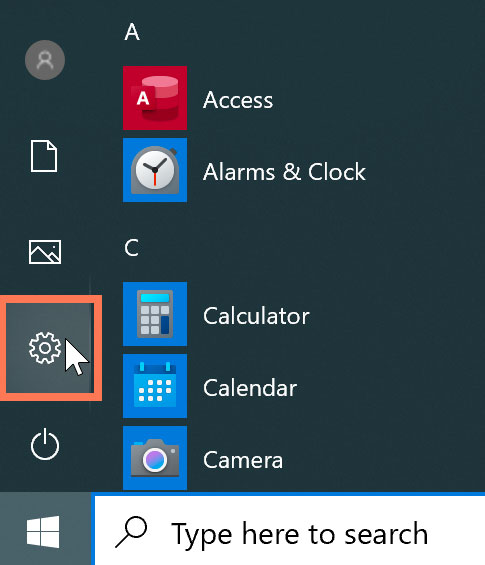
Open the control panel
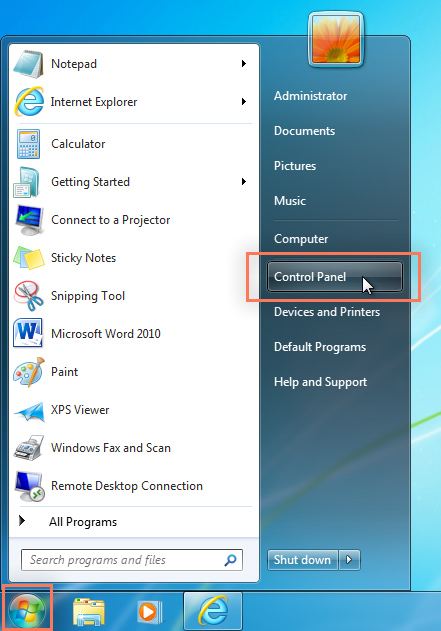
- Then pick Control Panel from the Start menu.
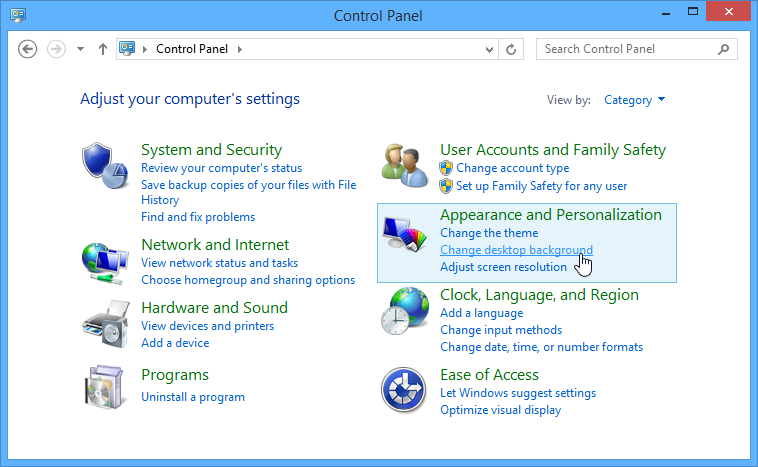
2. The Control Panel will appear on the screen. To change a setting, simply click it. In this case, we'll select a new wallpaper for our desktop by clicking Change desktop background.
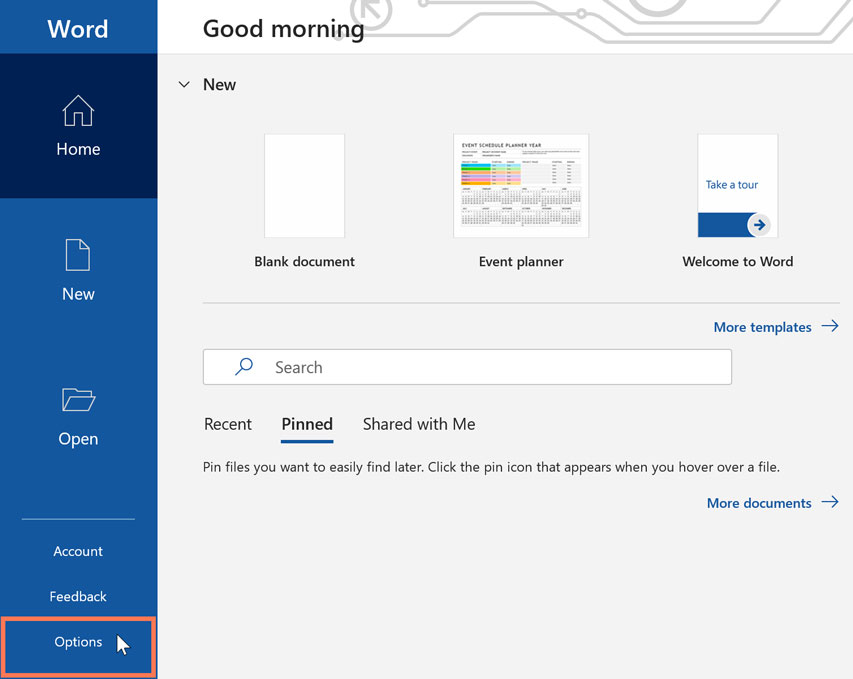
Adjusting application setting
You'll be able to customize the settings for several applications on your computer as well. Typically, application settings can be found under File > Options, Tools > Options, or a separate Settings menu. Keep in mind that the location may differ, and some apps may not have any settings you may modify.
Control panel
The Control Panel is where you may make changes to Windows settings. These options affect practically every aspect of how Windows appears and functions, and you may use them to customize Windows to fit your needs.
Find control panel items
When you’re in the Control Panel:
● Use search - Type a word or phrase in the search box to find a setting or task you're looking for. For instance, type "sound" to get settings for your sound card, system sounds, and the taskbar volume icon.
● Browse - Select several categories (for example, System and Security, Programs, or Ease of Access) and view common tasks listed under each area to learn more about Control Panel.
When browsing Control Panel by icons, type the initial letter of the item's name to easily locate it in the list. To find Keyboard, type K into the search box, and the first Control Panel item that starts with the letter K—in this case, Keyboard—is selected from the list.
To scroll through the list of icons in Control Panel, use the arrow keys (Up Arrow, Down Arrow, Left Arrow, and Right Arrow).
Select the Start button > Settings if you can't find an option in Control Panel. Settings now has access to several Control Panel options.
Q.15) Write the short on the wallpaper and screensaver?
A15: The terms "wallpaper" and "screensaver" are often used in computer jargon. You come across sites that promise free wallpapers and screensavers even when exploring the web. These are visuals that are used to personalize the look of a computer monitor, laptop, notebook, or even a smartphone today. Normally, the operating system provides a limited amount of photographs for use as wallpaper or screensaver on all such devices. People can easily edit the image to make it a background or screensaver if they so wish.
Wallpaper
The wallpaper is the image that appears on the monitor when a PC or laptop is turned on and the operating system begins to run. To avoid boredom while working on the system, the user has the option of using a picture or photograph of his choice. It's similar to the system's cover when it's in use and no files have been opened by you. Wallpaper is also known as the desktop background, despite the fact that it is in the foreground because it appears on the computer all the time, even when you are not using it. You may use the internet to get photographs of nearly anything and set them as your background. All folder and word file icons are visible above the backgrounds. Wallpapers have no purpose other than to relax your eyes.
Screensaver
You've probably seen your computer monitor going dark after a period of inactivity on your part. Normally, there is an animated graphic on the monitor that you can see that continuously shifting its position. This is known as a screensaver, and if you haven't set one, the OS will provide one by default. If you're running Microsoft XP, you'll notice an animated image displaying this name and leaping across the screen. However, screensavers can be downloaded from the internet and programmed to appear when the system is left idle for a length of time that the user specifies.
Q.16) Write the difference between wallpaper and screensaver?
A16: Difference between wallpaper and screensaver
● The screensaver is animated, while the wallpaper is static.
● A wallpaper is a background image that appears when no files are open, whereas a screensaver is a graphic that appears when the computer is left idle for a period of time.
● A wallpaper is a single image, but a screensaver is a collection of several images.
● Wallpapers use very little power; however, screensavers are larger and use more.
● A wallpaper appears all of the time, whereas a screensaver appears just after the monitor has been idle for a period of time.
Q.17) How to set a date and time?
A17: Windows 7 typically keeps precise track of the current date and time, but you may need to alter the Windows time zone to match your region if you have a new computer.
- To get started, press the Windows key on your keyboard.
The key with the Windows logo on it is the Windows key. If it isn't already visible, the taskbar appears. The taskbar is the blue area at the bottom of your computer screen.
2. From the shortcut menu that appears, right-click the Date/Time display on the far-right end of the taskbar and select Adjust Date/Time.
The dialog window for setting the date and time appears.
3. Change the date and time by clicking the Change Date and Time button.
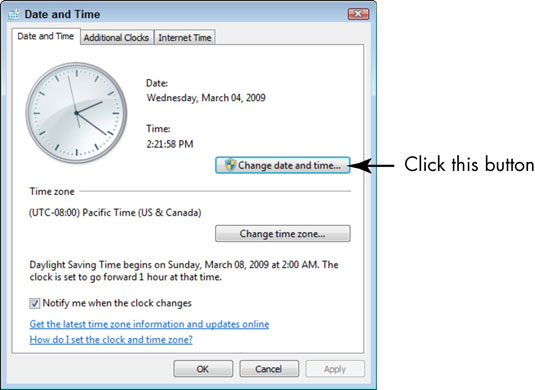
The Date and Time Settings dialog box appears.
4. Enter a new time in the Time field, or modify the time by clicking the up and down arrows next to it.
To change the date, click a new date in the calendar.
5. Click OK once you've completed altering the date and time settings.
The Date and Time dialog box appears again.
6. Click the Change Time Zone button, select an option from the Time Zone drop-down list, then click OK to change the time zone.
7. Click ok.
The changes are saved, and the dialog box is closed.
Q.18) Explain notepad?
A18: Notepad is one of the most widely used text-editing tools in Windows 7. It's a simple text editor that may be used to create simple text documents or website code. Read this little tutorial to learn how to open Notepad in Windows 7.
Open Notepad Using Search
● To find notepad, go to the Start menu and put notepad into the search box.
To open notepad on Windows 7, select Notepad with notepad icon from the results.
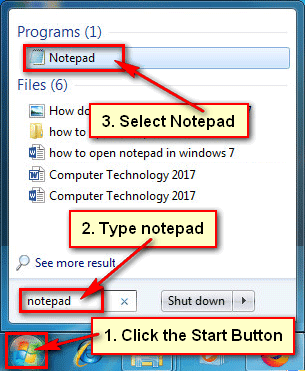
● The notepad program will launch. You can now utilize notepad to help you with your job.
Manually Open Notepad on Your Computer
● To get a list of all programs, click the Start button and select All Programs.
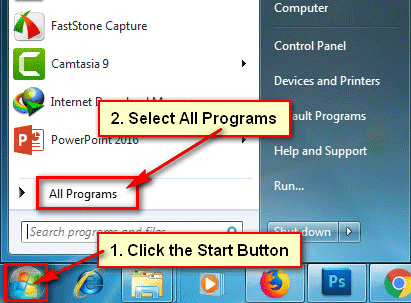
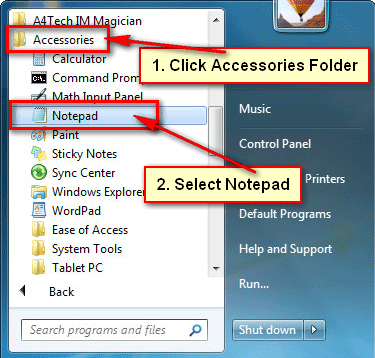
● To open Notepad in Windows 7, click the Accessories folder icon and pick Notepad.
Open Notepad Creating Text Document
● Up to your desktop, press the mouse-right button.
To create a new text document, move your mouse pointer up to New and pick Text Document.
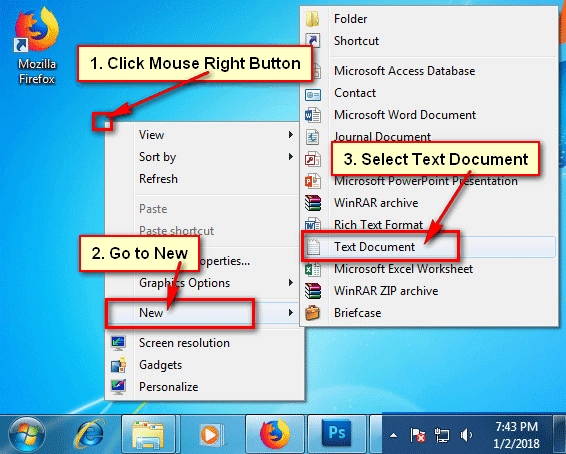
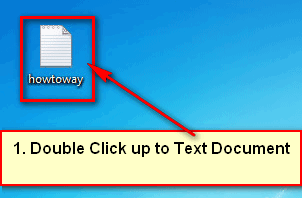
● Your recently created document will appear on your desktop.
To open the text document, double-click it.
Q.19) Explain window accessories?
A19: Windows includes a number of add-ons and built-in programs that are extremely useful for completing daily tasks.
The ability to use data created in one file in another file, even if the two files were created in different Windows programs, is one of the most useful features Windows provides. To work with multiple programs or files at the same time, simply open them on your desktop. Any window open on the desktop is represented by a program button on the taskbar. When you want to switch from one open window to another, click the program button on the taskbar.
Frequently used windows accessories
Program | Description |
Calculator | Performs arithmetic calculations |
Command Prompt | Executes MS-DOS commands |
Internet Explorer | Displays web (HTML) pages |
Notepad | Creates, edits, and displays text only documents |
Paint | Creates and edits bitmap pictures |
Snipping Tool | Captures different parts of the screen |
Sound Recorder | Creates and plays digital sound files |
Sticky Notes | Creates color notes on the screen |
Windows DVD Maker | Burns pictures and videos to DVDs |
Windows Fax and Scan | Sends and receives faxes or scanned pictures and documents |
Windows Live Messenger | Sends and receives instant messages to online contacts; you need to download the program from the web (http://download.live.com). |
Windows Live Mail | Provides e-mail, newsgroup, and directory services; you need to download the program from the web (http://download.live.com). |
Windows Live Movie Maker | Creates movies using audio and video files; you need to download the program from the web (http://download.live.com) |
Windows Live Photo Gallery | Views, edits, organizes, and shares photos and videos; you need to download the program from the web (http://download.live.com) |
Windows Live Writer | Creates blogs with text, photos, and videos; you need to download the program from the web (http://download.live.com) |
Windows Media Center | Provides entertainment options for digital and on-demand media |
Windows Media Player | Plays sound, music, and video |
WordPad | Creates, edits, and displays text, Rich Text Format, and Word documents |
Q.20) Write the basics of window setup?
A20: The following are the three basic types of clean installation procedures:
● Use a brand-new disk or computer system to install.
● Erase, format, and install the disk.
● For dual-booting, install into a new directory.
Make sure your computer can boot from a DVD if you plan to utilize one of the first two ways (most newer computers support booting from a DVD drive). Changing the drive boot order in the BIOS or CMOS may be necessary, but test it as-is first. Next, test the DVD drive with no floppy disk inserted and a clean hard disk. The Windows 7 DVD is bootable and should automatically begin the Setup application.
Depending on the speed of your computer, installation takes 15 to 30 minutes. If you have any questions regarding any of the processes in this procedure.
During a clean installation, Windows 7 applies the NTFS format to any disk partition that it is installed on.
Setup procedure
If you're installing into an empty partition and can boot into a supported operating system for Setup (Windows Vista or XP), simply start up, insert the DVD, and select Install Now from the dialog box that appears. Then you can follow the installation instructions step by step.
If Windows fails to recognize the DVD upon insertion, you must launch the Setup software, setup.exe, from the Start, Run dialog box (type D:/setup.exe after opening the Run dialog box; on Vista, use the Start menu Search box instead [using the correct letter for your DVD drive if it isn't D]). The setup.exe program can be found in the DVD's Sources directory. After the Setup routine has started, you can proceed to the next step in the installation process.
This procedure changes if your machine has a blank hard disk or if your present operating system isn't supported. The installation process must be started from the Windows 7 DVD (this works only if you can boot from the DVD drive). Setup automatically runs if you boot from the DVD.
A network is used in yet another technique of setup. To begin a network installation, make a network share of the distribution DVD or a hard drive copy of the DVD. The target system must be connected to the internet, and the user account must have read access to the installation files at the very least. Setup can be started by running setup.exe from a network share. For example, type this path into the Start, Run command, or the Vista Start menu Search box: sources Setup. Before the first reboot, Setup detects an over-the-network installation and moves all files from the network share to the local machine.
The single DVD contains all versions of Windows 7, 32-bit and 64-bit. After the installation is complete, the product key you enter during setup determines which version of Windows 7 you get. After you've completed your installation, store your Windows 7 DVD and product key somewhere safe. It can be used for a variety of repairs.