Unit - 1
Introduction
Q1) What is the meaning of Management?
A1) Business management refers to functions that aim at the effective use of individuals and resources in a corporation to realize business objectives. So, it's a way to an end. Basically, there are five functions in business management, and that they are:
Planning is that the start line. During this phase, you create your business plan and the way you're getting to achieve it. But it's not as easy because it seems. You would like to form a sensible assessment of your business objectives and map the detailed strategies (with full back up plans just in case those strategies fail) through which your company are able to do its business objectives.
The organization follows the design. Here you organize all of your resources like employees, machines and finances in one well-oiled unit. You would like to urge of these combinations and timing correctly. Organizing helps you define "who goes to try to what". Established well-defined job roles, organizational hierarchies, and streamlined coordination between them.
Staffing cares with acquiring, deploying, and retaining the proper skilled workforce to deliver business results. The goal of staffing is to make the proper positive impacts on the effectiveness of the organization. Through staffing, you get the proper people within the right jobs who do the proper things. In short, this is often a correct delegation.
Leading is that the most vital function of the management process. Without a motivated workforce, you'll never be ready to achieve your business goals. Leading is about how you'll align employee tasks with the general goals of the organization. Leading is how you'll motivate, influence, and encourage your employees to perform at their best at work. Leading is how you'll involve your employees voluntarily within the growth and development of the corporate.
Control is a lively and constant monitoring of the people, processes and other resources of your company. Here you track the performance of all the resources in your company and confirm they're on the proper track. Through monitoring, you'll accurately assess whether all company resources are optimally used for desired business tasks. And make corrections whenever and wherever there are deviations, errors and gaps.
For a nation's economy, business growth is extremely important. However, the processes involved in a company are complex. It is the way in which the administration of a business is managed, which governs the parameters of a business's success. There are numerous factors that must be considered when running a business. It is important that there is a person who has experience.
Q2) What is Business Management?
A2) Companies have a tray of activities that must be kept in line for the proper functioning of the business so that it grows in all aspects and achieves a name in the market. In a country like India, where many start-ups live but can never stay in the market, one of the main reasons for the downfall of many companies may be a failure in managing the business and its activities.
The dynamics and success factors are extremely difficult to understand according to different markets, where the frequency of changing market demands is very high.
BM deals with the management and handling of all commercial activities that include and pertain to clients, the supervision and administration of the financial, accounting and marketing aspects of a company.
Business management has become one of the top career choices over the usual career prospects such as engineering and medicine.
Q3) What is the concept related business management?
A3) There are several concepts related to business management which are listed below:
Business operations:
Business operations are a set of activities that are repeated and improve business operations, generating better investment value for the company's stakeholders. Business operations involve a group of business processes that aim to realize a specific goal.
Business processes:
Business processes would mean a set of activities directed towards a particular objective to provide a service or product. There are separate business processes for operations, administration, and support.
Helps achieve group objectives: order factors of production, gather and organize resources, integrate resources effectively to achieve objectives. Directs the group's efforts toward achieving predetermined goals. By clearly defining the objective of the organization, there will be no loss of time, money and effort. These resources are coordinated, directed and controlled in such a way that the company works to achieve the objectives.
Optimal use of resources: Management uses all physical and human resources productively. This leads to efficient handling. Management provides the maximum utilization of scarce resources by selecting its best possible alternative use in the industry among various uses. It makes use of experts, professionals and these services lead to the use of their skills, knowledge and proper use and avoid waste. If employees and machines are producing at their best, there is no underutilization of any resources.
Reduce costs - Get maximum results through minimal input through proper planning, and using minimal input and getting the most out of it. Management uses physical, human and financial resources in such how on end in the simplest combination. This helps in reducing costs.
Establish a solid organization: no overlapping efforts (fluid and coordinated functions). Establishing a solid organizational structure is one of the objectives of the administration that is in tune with the objective of the organization and for the fulfilment of this, establishes an effective relationship of authority and responsibility, that is, who is responsible to whom, who can give instructions to who, who are the superiors. And who are subordinates. Management occupies various positions with the right people, with the right skills, training and qualifications. All jobs must be authorized for everyone.
Establishes the balance: allows the organization to survive in a changing environment. Keeps in touch with the changing environment. With the change in the external environment, the initial coordination of the organization must be changed. Therefore, it adapts the organization to the changing demand of the market / changing needs of societies.
Essential for the prosperity of society: efficient management leads to better economic production which in turn helps increase people's well-being. Increase profit which is beneficial for businesses and society you will get the most out of it at the least cost by creating income-generating employment opportunities in your hands.
Q4) What are the characteristics of management?
A4) It is almost impossible to understand the concept of management in a nutshell. The best way to understand the management concept, nature and scope by describing its features
1. Management may be a process: continuous, social and unique:
Management is a continuous process because an organization continues perpetually and needs solutions to problems continuously. A process features a beginning and an end, and management begins with planning and ends with control and restarts with planning. It is a social process because it is managed by people (employees and managers) for people (clients) and by people (investors and society in general).
It is a unique process because it involves group activities; It is integrative in nature since it interlaces different resources in a coordinated way; and intangible in appearance (since the presence of management is felt solely through performance).
2. Management is a science, an art and also a profession:
A science is a systematized body of knowledge, accumulated through the use of the scientific method (through observation and research), has a cause-and-effect relationship, can be formally imparted, and has universal application.
Management has all the makings of being a science, but it is a soft science rather than a hard science (where 2 + 2 may not always be 4) because it is about human beings, whose behaviour is more difficult to predict.
Art refers to practical application, through creative use of the body of knowledge to obtain desired results through personal possession of skill where there is room for personal judgment. In this way, management is definitely an art, since it is a social process.
Two doctors who prescribe the same drugs to two different patients with the same disease may have different results with different doses. Management is rightly called the art of the arts. Since management is both a science and an art, it is correct to call it artistic science (art-based science) or scientific art (science-based art).
A profession is an occupation that requires a significant body of knowledge, which is formally acquired and applied with the ethical standards declared by the main body whose certification is essential for service to society.
Management is not a profession like accounting, law or medicine, which are thousands of years older than management, because no qualification is essential to be a manager, there is a main body, All India Management Association, but its membership it is not mandatory.
However, management is becoming a profession as management education expands and businesses demand managers who are fully professional. With liberalization, globalization and privatization, the demand for professional managers will increase even more.
3. Management influences and is influenced by the environment:
Management does not work in a vacuum. It has to deal with the internal (controllable) and external (non-controllable) environment. The internal environment consists of employees, processes, and systems. The external environment comprises STEEPLE (social, technological, economic, ecological, political, legal and ethical environments).
The internal environment indicates strengths and weaknesses and the external environment indicates opportunities and threats. Management tries to turn threats into opportunities and weaknesses into strengths; but sometimes it changes depending on the environment.
4. The core of management is making decisions:
When Peter F. Drucker said that "everything a manager does, he does through decision making," he was very clear that the core of management was decision making.
Since management is interdisciplinary (management has borrowed concepts from economics, psychology, sociology, anthropology, law, mathematics, statistics, etc.), it makes use of multiple and interdisciplinary knowledge to make decisions and makes use of authority to obtain them. Enforceable decisions.
5. Management is goal-oriented:
The management process is a purposeful activity and begins and ends with goals. All organizations, both for-profit and non-profit, are goal oriented. It is the responsibility of management to achieve these objectives.
Without goals, an organization would be like a ship without rudders. Management always starts with goals and remains aware of their achievement. If there are any gaps in performance and goals, management tries to harmonize them with each other. Management cares as much about efficiency as it is about its effectiveness.
6. Managers bring the organization to life:
"Good managers can propel an organization into unprecedented realms of success, while bad managers can devastate even the strongest companies." It is the management that can give life through its dynamism to the management process in this turbulent business environment. When things go well, the credit goes to management and when it is the other way around, the first victim is management.
7. Management is a multidisciplinary and multifaceted activity:
It is multidisciplinary because it is a young discipline and has borrowed most of the concepts from other disciplines such as economics, sociology, psychology, anthropology, mathematics, law, politics, etc.
However, it has begun empirical research to develop itself. It is multi-faceted because managers have to play different types of roles, many of them at the same time.
Q5) What are the basic functions of management?
A5) Regardless of the size, nature and type of organization, all managers must perform some basic functions which are as follows:
(a) Planning:
Planning is always the first function that every manager performs. Planning refers to “deciding beforehand what to try to, the way to roll in the hay, when to try to it, and who goes to try to it. Planning bridges, the gap between where we are today and where we want to go”. Every manager begins by deciding in advance the objectives of a company and how to achieve them. Planning is that the foundation of all other management functions.
(b) Organize:
After establishing the plans, the next role of each manager is to organize the activities and establish an organizational structure to execute the plan. Establishing the organizational structure means deciding the framework how many units and subunits or departments are needed, how many positions or designations are needed in each department, how to distribute authority and responsibility among different people. Once these decisions are made, an organizational structure is established.
(c) Staffing:
Third step or function of a manager is Staffing. It refers to recruiting, selecting, appointing employees, assigning functions to them, maintaining cordial relationships, and handling employee complaints. It also includes training and developing employees, deciding their compensation, promotion, raises, etc., evaluating performance, keeping personal records of employees.
(d) Lead:
Once employees are appointed, they need to be trained and the job done. Leading refers to giving directions or instructions to employees motivating them, supervising the activities of employees, communicating with them. Managers act as leaders and guide them in the right direction, so the management function includes, supervising, motivating, communicating and leading.
(e) Control:
This is the last function of the managers. In this role, managers try to match actual performance with planned performance, and if there is no match between the two, managers try to find out the reasons for the deviation and suggest corrective measures to get on track. Control functions refer to all performance measures and follow-up actions that keep actual performance on track.
Q6) State the objectives of departmental organisations?
A6) They integrate the objectives of the organization with the objectives of the departments and harmonize the departmental goals with the organizational goals. It helps each managerial function and every departmental activity contribute to organizational goals.
1. Coordination during planning:
When plans are made, managers make sure that the various sorts of plans (long and short term, strategic and routine), policies, rules and procedures operate consonant and coordination with one another in order that various departments follow these plans. Effective way.
2. Coordination during the organization:
The division of labor into departments on the idea of the similarity of activities, the appointment of individuals to manage these departments, the definition of their authority and responsibility and therefore the creation of the organizational structure is aimed toward coordinating departmental activities with organizational objectives. If activities are randomly divided without coordination, some activities might not be assigned to people et al. Could also be assigned to quite one person.
3. Coordination during staffing:
After jobs are created, managers make sure that people fill different jobs consistent with their skills and skills. This ensures that you simply place the proper person at the proper job to realize coordination between your work activities.
4. Coordination during management:
When a manager directs his subordinates through motivation, leadership and communication, he tries to coordinate the activities of the organization. It's also an effort to harmonize individual goals with the goals of the organization. Management maintains unity and integrity among the activities of the members of the organization.
5. Coordination while controlling:
Control ensures that actual performance is in accordance with planned performance. The aim of control through budgets or information systems is to coordinate the various organizational activities. All management activity is, therefore, coordinated to contribute to the organization's objectives. Coordination is required throughout the organization.
Management principles like unity of command and scalar chain facilitate the task of managers within the effective coordination of managerial functions.
Coordination because the essence of management is, therefore, intrinsic to management. Aligning the interior environment with the external environment, human with non-human resources to realize the objectives of the organization, is that the task of all people in the least levels of all departments. Coordination gives meaning and purpose to every task and promotes the group's effort to realize the goal.
Coordination isn't department or function specific. All management functions (planning, organization, staffing, direction and control) of all departments must be coordinated to realize the general objectives. However, the intensity of managerial functions may vary at different times for various departments.
Sometimes coordinated efforts should focus more on planning, while at other times, the main target should be more on control. No matter the degree of care, the essence of coordination highlights its need, which is omnipresent altogether departments, in the least levels, in the least times.
Contemporary organizations are open systems. Their active and continuous interaction with the environment presupposes the presence of a robust coordination system in organizations. Coordination is that the force of organizational success.
Q7) State the Evolution of the management concept.
A7) Evolution of the management concept
The evolution of managerial thinking is a process that began in the early days of man. It started from the time when man saw the need to live in groups. Powerful men were able to organize the masses, share them in various groups. The exchange was made according to the strength, mental capacity and intelligence of the masses.
The point is, management has been practiced in one form or another since civilization began. If you want a good example where advanced management principles were applied, consider the organization of the ancient Roman Catholic Church, military forces, and ancient Greece. These are all excellent examples. But the industrial revolution brought a drastic change. And suddenly, the necessity to develop a more holistic and formal management theory became a necessity.
- Explain the evolution of managerial thinking
- Stages in the evolution of managerial thinking
You cannot understand what it implies or appreciate how it happened without looking at the various areas where it happened. For a better understanding, the evolution of management thinking will be shared in four different stages. These include:
- Prescientific management period
- Classical theory
- Neoclassical theory or behavioural approach
- Max Weber's Bureaucratic Model
- The prescientific management periods
The industrial revolution that happened within the 18th century had a big impact on management as an entire. It changed the way companies, as well as individuals, raised capital; organize work and the production of goods. Entrepreneurs had access to all factors of production such as land, labor, and capital. Theirs was to make an effort to combine these factors to successfully achieve a specific goal.
However, the new dimension that management took after the industrial revolution cannot be discussed without mentioning notable personalities who contributed their quarter. They were ready to introduce useful ideas and approaches to offer management a particular and universally acceptable direction. Here are some of them.
Q8) Explain the theories during the evolution of management.
A8) Classical theory
But its contribution to the evolution of management is limited. The beginning of what is known as management science began in the last decade of the 19th century. Names like Emerson, F.W. Taylor, H.L. Grant et al. Paved the way for the establishment of what's called scientific management.
During the classical period, managerial thinking focused on work content, standardization, division of labor, and a scientific approach to organization. It was also closely related to the industrial revolution, as well as the rise of large-scale companies.
Neoclassical theory
This period of evolution of management thinking is an improvement on classical theory. In other words, he modified and improved the classical theory. For example, classical theory focused more on the area of job content, including the management of physical resources, while neoclassical theory placed a deeper emphasis on employee relationships in the work environment.
The bureaucratic model
A German sociologist named Max Weber proposed this model. And it includes a system of rules, the division of labor that depends on functional specialization, legal authority and power, the hierarchy of authority, and the location of employees based on their technical competence.
The evolution of management theories
Organizations have been formed and through the writings of various writers. Its writing consisted of the government of the kingdoms and the management of humans. And these formed the literature that aided in the development of management theories. And these management models were also offered by military, political and religious organizations.
For example, Sun Tzu's book "The Art of War" was written in the 16th century BC. C. Sun was also a general in the Chinese Army. However, Sun's book writings were also used for management purposes.
The book emphasizes that it is possible to achieve success by using the strength of the organization to exploit the weakness of rivals. Another great book was Chanakya's Arthashastra. It was written in the 3rd century BC. C. And focused on the government of the kingdom in regards to the formulation of government policies and people management.
Conclusion
The evolution of management started from civilization. So, what we have now are refined and improved management thoughts and theories. It will help to improve the knowledge of the process and will effectively use the management principles for the improvement of the organization.
Q9) What is Henry Fayol's fourteen management principles?
A9) He developed the subsequent principles underlying the management of all kinds of organizations:
HENRY FAYOL'S FOURTEEN MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES:
1 Authority and responsibility goes hand in hand Fayol argued that authority flows from responsibility. Managers who exercise authority over others must take responsibility for both decisions and results. He viewed authority as a corollary of responsibility. Authority is both official and private. Official authority springs from the manager's position within the organizational hierarchy and private authority is formed from intelligence, experience, moral worth, past service, etc. A corollary of the principle that no manager should tend authority unless he assumes responsibility is that those that have responsibility should even have corresponding authority so as to enable them to initiate action over others and command the resources necessary for the performance of their functions.
2. Unity of command: This principle holds that an employee should have just one boss and receive instructions from him only. Fayol discovered that if this principle is disobeyed, authority is going to be undermined, discipline is going to be jeopardized, order is going to be disturbed and stability are going to be threatened. Dual control may be a permanent source of conflict. Therefore, in every organization, each subordinate must have a superior whose mandate he must obey.
3. Unity of direction: this suggests that each one the executive and operational activities that relate to a special group with an equivalent objective must be directed by “a boss and an idea. However, it doesn't mean that each one decision must be made up of above. It just means all related activities should be led by one person. For instance, all marketing activities like product strategy and policy, advertising and advertisement, channel policy, product pricing policy, marketing research, etc., should be under the controlled by a manager and directed by an integrated plan.
4. Scalar chain of command: consistent with Fayol, the scalar chain is that the chain of superiors that goes from the very best authority to rock bottom ranks. The road of authority is that the route followed through each link within the chain by all communications that start from or attend the last word authority.
5. Division of labor: this is often the principle of specialization that, consistent with Fayol, applies to all or any sorts of work, both managerial and technical. It helps an individual acquire a skill and precision with which he can do more and better work with an equivalent effort. Therefore, the work of everyone within the organization should be limited the maximum amount as possible to the performance of one leadership role.
6. Discipline: Discipline may be a sine qua non condition for the right functioning of a corporation. The members of a corporation must perform their functions and behave in reference to others in accordance with rules, norms and customs. Consistent with Fayol, the simplest thanks to maintain discipline is: (i) to possess good superiors in the least levels; (ii) agreements (entered into with individual employees or with a union, because the case may be) that are the foremost clear and fair as possible; and (iii) sanctions imposed with criteria.
7. Subordination of the individual interest to the general interest: The interest of the organization is above the interests of the individual and the group. It can only be achieved when senior managers in the organization set an example of honesty, integrity, fairness and fairness. It will involve an attitude and a spirit of sacrificing your own personal interests whenever it is evident that those personal interests are in conflict with the interests of the organization. However, it can be emphasized that social and national interests must take precedence over organizational interests whenever the two are opposed to each other.
8. Remuneration: Employees must receive fair and equitable remuneration. Differences in pay should be based on job differences, in terms of employee qualities, application, responsibility, working conditions, and job difficulty. You must also take into account factors such as cost of living, general economic conditions, demand for labor, and the economic status of the business.
9. Centralization: Fayol believed in centralization. However, he did not contemplate the concentration of all decision-making authority in senior management. However, he argued that centralization and decentralization is a matter of proportion. In a small business with a limited number of employees, the owner-manager can give orders directly to everyone. However, in large organizations, where the worker is separated from the CEO through a long scalar chain, decision-making authority must be distributed among several managers to varying degrees. Here one generally encounters a situation of decentralization with centralized control. The degree of centralization and decentralization also depends on the quality of the administrators.
10. Order: Order, in Fayol's conception, means the right person in the right job and everything in its proper place. This type of order depends on a precise knowledge of the human and resource requirements of the concern and a constant balance between these requirements and resources.
11. Fairness: Means that subordinates should be treated fairly and kindly. This is essential to awaken your devotion and loyalty to the company. Therefore, it is the CEO's duty to instil a sense of fairness at all levels of the scale chain.
12. Stability of staff tenure: Management policies should provide a reasonable sense of job security. The hiring and firing of personnel should not depend on the whims of superiors but on well-conceived personnel policies. He points out that it takes time for an employee to learn his job; If they drop out or are discharged in a short time, the learning time is lost. At the same time, those deemed inappropriate should be eliminated and those deemed competent should be promoted. However, "a middle manager who stays is infinitely preferable to top managers who come and go."
13. Initiative: focuses on the ability, attitude and resourcefulness to act without being asked by others. Managers must create an environment that encourages their subordinates to take initiative and responsibility. Since it provides a sense of great satisfaction to smart employees, managers must sacrifice their personal vanity to encourage their subordinates to show initiative. However, it should be limited, according to Fayol, by respect for authority and discipline.
14. Esprit de Corps: Cohesion and team spirit should be fostered among employees. One of the main characteristics of organized activity is that several people work together in close cooperation to achieve common goals. An environment must be created in the organization that induces people to contribute to the efforts of others in such a way that the combined effort of all together promotes the achievement of the general objectives of the company. Fayol warns against two enemies of the esprit de corps, viz. (i) divide and conquer, and (ii) abuse of written communication. It may be to the company's benefit to divide its enemy, but it will surely be dangerous to divide the workers themselves. Rather they should be soldiers in cohesive and highly interactive task forces. Over-reliance on written communication also tends to disrupt team spirit. Written communication, when necessary, should always be complemented by oral communication because face-to-face contacts tend to promote speed, clarity, and harmony.
Q10) What are Scientific management 5 principles that were proposed by Taylor?
A10) His thoughts about management came from his ample workings with three companies: Midvale Steel Works, Simonds Rolling Mills, and Bethlehem Steel Co.
Taylor concluded that scientific management implies a more complete mental revolution on the part of workers and management, without this mental revolution, scientific management does not exist.
Scientific management 5 principles proposed by Taylor:
1. Science, not a golden rule 2. Harmony, not discord 3. Mental revolution 4. Cooperation, not individualism 5. Development of each and every person towards their greater efficiency and prosperity.
1. Science, not a rule of thumb:
To increase organizational efficiency, the "rule of thumb" method must be replaced by methods developed through scientific work analysis.
Golden rule means the decisions made by the manager based on his personal judgment. Taylor says that even a small manufacturing activity, such as loading iron sheets into rail cars, can be scientifically planned. This will help save time and human energy. Decisions must be based on scientific research with cause-and-effect relationships.
The work assigned to any employee must be observed and analyzed with reference to each element or a part of it and therefore the time involved in it to make a decision the simplest way to perform that work and determine the standard performance for it.
2. Harmony, not discord:
Taylor emphasized that there must be complete harmony between the workers and the management since if there is any conflict between the two, it will not be beneficial to either the workers or the management.
Both management and workers must realize the importance of each. To achieve this level, Taylor proposed that an entire mental revolution on a part of both management and workers.
He means that there must be a complete change in the attitude and perspective of workers and management towards each other. It should always be kept in mind that prosperity for an employer cannot exist for long unless it is accompanied by prosperity for the employees of that organization and vice versa.
It is possible to (a) share a part of the surplus with the workers (b) the training of the employees, (c) the division of labor (d) the team spirit (e) the positive attitude (f) the sense of the discipline (g) sincerity, etc.
The management must always be willing to share the profits of the company with the workers and the latter must give their full cooperation and hard work to achieve the organizational objectives. Group action with mutual trust and understanding must be perfect to understand the focus of work. This principle requires that there's an ideal understanding between management and workers which both feel a part of an equivalent family. It helps to produce a synergistic effect as both management and workers work in unison.
3. Mental revolution:
It involves a change in the behaviour of workers and management towards each other. Both must realize the importance of the other and work with full cooperation. Both management and workers should aim to increase the profits of the organization.
To do this, the workers must do their best to make the company profit and, on the other hand, the management should share part of the profits with the workers. Therefore, the mental revolution requires a complete change in the perspective of both the management and the workers. There should be a spirit of union between workers and management.
4. Cooperation, not individualism:
This principle is an extension of the "harmony, not discord" principle and emphasizes mutual cooperation between workers and management. Cooperation, mutual trust, and a sense of goodwill must prevail among both managers and workers. The main motive is to replace internal competition with cooperation.
Both "management" and "workers" must realize the importance of each other. Workers should be considered part of management and allowed to participate in management's decision-making process. Management should always accept their proposal and should also reward them if their suggestions prove beneficial to the organization, viz. Cost reduction or production increase, etc.
At the same time, workers must also resist the strike or make unnecessary demands on management. Workers must be treated as an integral part of the organization and all-important decisions must be made after proper consultation with workers. Both must see themselves as two pillars whose strength alone can guarantee the achievement of the common objectives of the organization.
Taylor also suggested that there should be a proper division of labor and responsibility between the two. Management must always guide, encourage and assist workers.
5. Development of each and every one of the people towards their greater efficiency and prosperity:
The efficiency of any organization also largely depends on the skills and abilities of its employees. Therefore, it was considered essential to provide training to workers to learn the best method developed using the scientific approach. To achieve efficiency, steps must be taken from the employee selection process. Employees must be scientifically selected.
Q11) Write short note on neoclassical theory.
A11) movement in which Elton Mayo had pioneered. Mayo and his collaborators carried out the Hawthorne experiments that formed the basis for this theory. In this article, we will talk about the Neoclassical Theory of Organizations.
Introduction to neoclassical theory
Hawthorne's experiments revealed that an informal organization, as well as socio-psychological factors, exert a much greater influence on human behaviour than psychological variables.
Therefore, these findings focused on human beings and their behaviour in organizations.
Therefore, neoclassical theory is also called the behaviour theory of organizations or human relations approach.
The main propositions are the following:
- Generally speaking, an organization is a social system. Also, it has several interacting parts.
- There is an informal organization within each formal organization. More importantly, the two affect each other.
- Human beings are interdependent. Therefore, the organization can predict its
- Behaviour if you look at social and psychological factors.
- Motivation is a very complex process. Several socio-psychological factors work together to motivate people at work.
- Human beings don't always act rationally. In fact, the most irrational behaviour is when they seek rewards at work.
- Normally, the objectives of the organization conflict with the objectives of each individual. Therefore, it is important to reconcile these objectives.
- Another important aspect of running an organization is teamwork. However, organizations must work to achieve this.
Furthermore, neoclassical writers offered an organizational design as follows:
- Flat structure: the scalar chain is shorter. Therefore, communication and motivation are more effective.
- Decentralization: a decentralized structure allows initiative and autonomy at lower levels.
- Informal organization: a formal organization represents the official channels of interaction. However, it has many weaknesses. Therefore, an informal organization can fill these gaps and meet people's social and psychological needs.
Weaknesses of Neoclassical theories
While neoclassical theory improves on its predecessors, it has the following weaknesses:
- Neoclassical theory offers several structures. However, you cannot apply them to all situations. Furthermore, a single structure does not serve the purposes of all organizations.
- This theory lacks a unified approach. In simpler terms, it is just a modification of classical organizational theory.
- The Noe Classical theory is based on several assumptions that may not be true. To give you an example, the assumption that it is always possible to find a solution to a problem that satisfies everyone is not true.
Q12) Explain numerous basic principles of the Human Relations Approach.
A12) There are numerous basic principles of the Human Relations Approach listed below:
Decentralization: The concept of hierarchy employed by classical management theorists is replaced by the thought that individual workers and functional areas (i.e., departments) should have greater autonomy and decision-making power. This needs a greater emphasis on lateral communication so that coordination of efforts and resources can occur. This communication occurs through informal communication channels rather than formal and hierarchical ones.
Participatory Decision Making: Decision making is participatory in the sense that those who make day-to-day decisions include line workers who are not normally considered "management." The greater sovereignty granted to individual employees and the consequent reduction in the "height" and increased scope of control of the organizational structure requires that they have the knowledge and ability to make their own decisions and the communication skills to coordinate their efforts with others without close staff. Supervisor.
Concern for the development of self-motivated employees: The importance of a decentralized and autonomous decision-making system by the members of the organization requires that these members be extremely "self-motivated." The goal of managers in an organization of this type is to design and implement organizational structures that reward that self-motivation and autonomy. Another is negotiating working relationships with subordinates that foster effective two-way communication.
Therefore, the human relations approach implies modifications in the structure of the organization itself, in the nature of the work and in the association between manager and assistant. Each of these changes depends on assumptions about the individual, the organization, and communication, like any other theory of organizations. Elton Mayo and others organized an experiment that came to be known as Hawthorne experiments and explored informal groupings, informal relationships, communication patterns, and internal leadership patterns. Elton Mayo is often popular as a parent at the School of Human Relations. Human relationships defend various factors after performing the Hawthorne experiments mentioned below:
- Social system: The organization in general is a social system that consists of numerous interacting parts. The social system established individual roles and establishes norms that may differ from those of the formal organization.
- Social environment: The social climate of work affects workers and is also affected.
- Informal organization: The informal organization also exists within the framework of the formal organization and affects and is affected by the formal organization.
- Group dynamics: In the workplace, workers often do not act or react as individuals but as members of a group.
- Informal Leader: There is an appearance of informal leadership as opposed to formal leadership and the informal leader sets and enforces group norms.
- Non-financial reward: money is an encouraging element, but not the only motivator of human behaviour. Men have various motivations and socio-psychological factors act as important motivators.
Q13) Define the need for management by objectives.
A13) Need for management by objectives (MBO)
- The Management by Objectives process assist the members to understand their duties in the workplace.
- KRAs are designed for each employee based on her interest, specialization, and educational qualification.
- Members of work force are crystal clear about what is expected of them.
- The management by objectives process leads to satisfied employees. Avoid job mismatch and unnecessary confusion later on.
- Members in their own way participate in order to the achieve the goals and objectives of the organization. Each employee has her own role in the workplace. They tend to stay in the organization for a longer period of time and contribute effectively. They enjoy the workplace and don't treat work as a burden.
- Management by objectives ensures effective communication between employees. It leads to a positive environment in the workplace.
- Management by objectives leads to well-defined hierarchies in the workplace. Ensures transparency at all levels. A supervisor from any organization would never interact directly with the Managing Director in case of inquiries. First, she would meet with her chief reporting officer, who would then pass the message on to his superior and so on. Everyone is clear about their position in the organization.
- The MBO process leads to highly motivated and engaged employees.
- The MBO process establishes a benchmark for each employee. The superiors establish objectives for each of the team members. Each employee receives a list of specific tasks.
Q14) What are the advantages and disadvantages of Management by objectives?
A14) Management by objectives has the following limitations:
- It involves setting individual goals and responsibilities. But all work in an organization is a group effort in which the activities are so closely interrelated that no individual can be blamed or rewarded for any end result.
- It is difficult to make comparative evaluations of individuals because the objectives of each individual are different from those of others in terms of complexity, etc.
- It is difficult to assess and identify the potential. MBO is only concerned with current job performance.
- The method is time consuming.
- MBO assumes a certain level of trust throughout the hierarchy. But organizational life teaches people to be cautious. This inhibits honest dialogue and proper goal setting.
- MBO is not much suitable to routine worker-level jobs, such as an assembly line. In these types of situations, the more traditional performance appraisal tends to be used. The technique is especially suitable for managerial, professional and sales personnel and for those who work independently.
Advantages of management by objectives (MBO)
- MBO forces managers not only to plan activities, but to plan for results. Managers define objectives while formulating plans. Once the objectives are clearly established, they act as incentives and standards for control purposes.
- MBO allows managers to focus on really important and profit-impacting tasks rather than tasks that might have little impact on overall results.
- MBO establishes clear organizational goals and structures. Identify the key result areas and hold the people in charge of achieving the objectives.
- Employees commit to perform the work assigned to them as agreed and expected. They clearly know their goals and they also know how to move towards their achievements. Therefore, they do not need to wait for instructions, directions or guidance from their superiors.
- Helps develop effective control. Control involves setting your own standards, evaluating performance and taking the necessary corrective measures if there is any deviation.
- Helps management formulate better management training programs based on performance evaluations.
- People become willing and enthusiastic masters of their own destiny.
Q15) Briefly explain the concept of Management.
A15) Business management refers to functions that aim at the effective use of individuals and resources in a corporation to realize business objectives. So, it's a way to an end. Basically, there are five functions in business management, and that they are:
Planning is that the start line. During this phase, you create your business plan and the way you're getting to achieve it. But it's not as easy because it seems. You would like to form a sensible assessment of your business objectives and map the detailed strategies (with full back up plans just in case those strategies fail) through which your company are able to do its business objectives.
The organization follows the design. Here you organize all of your resources like employees, machines and finances in one well-oiled unit. You would like to urge of these combinations and timing correctly. Organizing helps you define "who goes to try to what". Established well-defined job roles, organizational hierarchies, and streamlined coordination between them.
Staffing cares with acquiring, deploying, and retaining the proper skilled workforce to deliver business results. The goal of staffing is to make the proper positive impacts on the effectiveness of the organization. Through staffing, you get the proper people within the right jobs who do the proper things. In short, this is often a correct delegation.
Leading is that the most vital function of the management process. Without a motivated workforce, you'll never be ready to achieve your business goals. Leading is about how you'll align employee tasks with the general goals of the organization. Leading is how you'll motivate, influence, and encourage your employees to perform at their best at work. Leading is how you'll involve your employees voluntarily within the growth and development of the corporate.
Control is a lively and constant monitoring of the people, processes and other resources of your company. Here you track the performance of all the resources in your company and confirm they're on the proper track. Through monitoring, you'll accurately assess whether all company resources are optimally used for desired business tasks. And make corrections whenever and wherever there are deviations, errors and gaps.
For a nation's economy, business growth is extremely important. However, the processes involved in a company are complex. It is the way in which the administration of a business is managed, which governs the parameters of a business's success. There are numerous factors that must be considered when running a business. It is important that there is a person who has experience.
Today's modern economic units cannot afford to make random decisions like they did in the past. Each economic decision needs to be well-studied and balanced. One wrong decision can have a huge impact on a business unit. As a result, more scientific and logical ways to handle business have evolved over time. This is nothing but "business science".
Q16) Define Management. Explain its features.
A16) In other words, setting up and running a company using scientifically proven methods and logical and systematic processes is called "management" (or business management).
Management is the philosophy that economic units continue to operate to achieve their goals in a cost-effective manner.
Management is "the power to run a business and take responsibility for its success or failure."
Meaning: -
According to George Terry, "management is a separate process of planning, organization, operation and control that is carried out using humans and other resources to determine and achieve a defined purpose. Increase".
According to Mary Parker Foret, "management is the art of accomplishing things through others."
According to Henry Fayol, "Managing is predicting, planning, organizing, directing, coordinating, and managing."
Nature of Management
As we have already established, different people have different views on management. Therefore, it is very difficult to define the nature and scope of management. Let's look at each of these terms individually to see how they work in the context of management.
The nature of management
Managing as a systematic process helps identify a group of people who perform a particular activity, thereby improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization. Here is a striking feature that emphasizes the nature of management in the business.
- Universal
Management is a universal process and is essential for all organizations. If there's act, there's management. Management principles apply regardless of the size or location of the business. The universal principle also means that management skills are developed and transferable over time.
2. Social process
The nature of management involves organizing and managing people in groups. It requires different levels of empathy, understanding and dynamism. This process involves developing, motivating, and retaining employees, in addition to caring for social and emotional well-being.
3. Purpose
Management always has the ultimate goal of achieving the goals, missions and visions of the organization. Management success can be measured by how well an organization achieves its goals. It has the fundamental purpose of improving efficiency and productivity. Goals need to be realistic, achievable, and time-limited.
4. Intangible
There is no physical evidence of the management process. Its success can be measured by the result of that effort. For example, low turnover indicates high employee engagement and job satisfaction. This further indicates that managers or individuals in management are taking proactive steps to improve employee retention.
5. Adjustment
Administrators coordinate all functions of an organization by bringing together different teams and departments. Without adjustment, there will be ambiguity and confusion. Therefore, by gathering people on the same page, communication is possible and duplication of work is minimized.
6. Creativity
Management consists of individual components and is a complex process. All independent components contribute in their own way. For example, the group's efforts encourage creative ideas and imagination. The sum of the individual efforts creates a synergistic effect and something new is born.
7. Dynamic function
Business must be dynamic in nature, as businesses are often influenced by economic, social, political and technical factors. The flexibility and adaptability allow individuals to function well in stressful situations. Appropriate training and promotion are required within the process.
Q17) What is the scope of Management?
A17) Well-defined responsibilities, concepts, theories, and principles associated with management functions define the scope of management.
1. Financial management
All companies prioritize financial management because it can be very unwieldy if it is not properly managed. Effective financial management ensures fair interests to stakeholders, good estimates of capital requirements, and optimal capital setting. This includes preparing and reviewing financial statements, developing appropriate dividend policies, and negotiating with external stakeholders.
2. Marketing management
Marketing control extends to planning, organizing, directing, and managing activities in the marketing department. Identifying customer requirements is important to providing a business solution. Managers achieve better results when they are fully aware of the benefits of the products and services that their organization offers. Marketing management ensures that the available resources are used properly and the best possible results are achieved.
3. Personnel management
HR management, as the name implies, deals with people or individuals in a business environment. This includes hiring, transferring, dismissing, benefits and social security for employees. This aspect of management is very important because employees form a team and the team drives the goals of the organization. Personal productivity also contributes to overall efficiency. Organizations can struggle if they don't meet the needs and desires of their employees.
4. Production control
This type of management refers to the process of creating a utility. Engage in production control when converting raw materials into finished products and overseeing planning and regulation. Without production, there are no finished products or services. Without it, an organization cannot generate profits or profits. The final product must meet the customer's requirements. This process includes quality control, R & D, planning layout, and simplification.
5. Office management
This includes managing and coordinating the goals of the organization and all office activities to achieve those goals. For example, management efficiency has a significant impact on the business. The more organized departments and responsibilities, the more effective the organization.
Q18) Do you think proper Management is an important part of an organization?
Or
Explain the importance of management.
A18) (1) Management is versatile: Management is used not only by businesses but also by non-profit / non-profit organizations. Non-profits use business science to achieve our social goals. Organizations, as well as individuals like us, use management to achieve professional and personal goals. To some extent, management is used by most people in everyday life. The positive force behind successful business, non-business, social or personal activities is effective management. In this way, management can be found in all areas of work and life.
(2) There is no substitute for management. Management is so basic and basic in nature that it cannot be replaced by anything else. The management philosophy when applied to any activity / task gives great results. No other philosophy can replace (alternative) management in its ability to produce the desired results in the most cost-effective way.
(3) Management brings order in the turmoil: many activities need to be performed to achieve a given goal / goal. If they are not properly planned and coordinated, they will only cause confusion and no results. Management is necessary for smooth activity without collisions, dropouts and repetitions. Management streamlines or harmonizes individual efforts. Therefore, when things move in a systematic (orderly) way, we can say that management exists. And when there is unordered and confusing turmoil, we can say that there is a lack of control.
(4) Management is focused on goals, which enhances the effectiveness of our efforts. Management remains focused on the ultimate goal. All activities, large and small, need to bring us closer to our goals. In other words, management has an effect on our efforts. If you don't keep your goals in mind, you can go off the right track and waste your efforts. Management believes in achieving goals by constantly (continuously) setting goals and networking. These goal-oriented efforts are almost always successful. Therefore, management has an impact on our efforts.
(5) Economic and social development requires management: Today's world is plagued by resource shortages, fierce competition and explosive population growth. During these critical times, economic and social development and progress can only occur if the available resources are used in the best possible way. The only way to do this is to use resources wisely. Intelligent management of resource usage can save the world from crisis situations in the near future. This means that business science can be used at the "macro" level to handle economic or country-wide problems.
In other words, developing countries are not necessarily in short supply of resources. They are just "controlled" countries. By wisely managing national resources, we can achieve appropriate and sustainable economic development.
(6) Reduction of waste: Management guarantees reduction of waste within the organization. Today, waste reduction is essential for any organization. By reducing waste, your organization is more productive.
(7) Reduction of absenteeism: Proper management makes it easier to reduce absenteeism in an organization. Absence occurs when an employee remains absent without prior permission. Absenteeism causes some problems for the organization.
(8) Higher efficiency: To produce higher efficiency in an organization, management is required. Efficiency is the relationship between revenue and cost. The more revenue you make at the same or lower cost, the more efficient your organization is said to be.
(9) Better Relationships: Management enables better relationships within an organization. You need to build good relationships across your organization, that is, between the different people and departments within your organization. Good relationships create teamwork and bring success to the organization.
(10) Promote growth and expansion: Successful managers are responsible for the growth and expansion of the company. No organization can grow and expand without the active involvement and commitment of his boss and his subordinates. In many cases, slowing the growth and expansion of an organization is inefficient management.
Q19) Management is a series of continuous inter-related functions. Comment.
A19) Regardless of the size, nature and type of organization, all managers must perform some basic functions which are as follows:
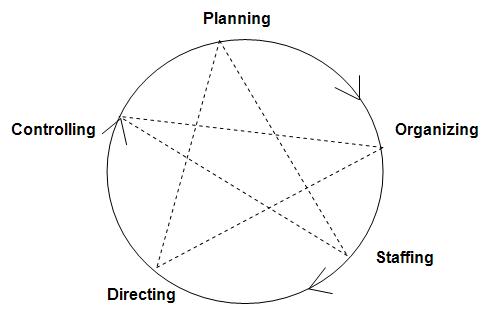
(a) Planning:
Planning is always the first function that every manager performs. Planning refers to “deciding beforehand what to try to, the way to roll in the hay, when to try to it, and who goes to try to it. Planning bridges, the gap between where we are today and where we want to go”. Every manager begins by deciding in advance the objectives of a company and how to achieve them. Planning is that the foundation of all other management functions.
(b) Organize:
After establishing the plans, the next role of each manager is to organize the activities and establish an organizational structure to execute the plan. Establishing the organizational structure means deciding the framework how many units and subunits or departments are needed, how many positions or designations are needed in each department, how to distribute authority and responsibility among different people. Once these decisions are made, an organizational structure is established.
(c) Staffing:
Third step or function of a manager is Staffing. It refers to recruiting, selecting, appointing employees, assigning functions to them, maintaining cordial relationships, and handling employee complaints. It also includes training and developing employees, deciding their compensation, promotion, raises, etc., evaluating performance, keeping personal records of employees.
(d) Lead:
Once employees are appointed, they need to be trained and the job done. Leading refers to giving directions or instructions to employees motivating them, supervising the activities of employees, communicating with them. Managers act as leaders and guide them in the right direction, so the management function includes, supervising, motivating, communicating and leading.
(e) Control:
This is the last function of the managers. In this role, managers try to match actual performance with planned performance, and if there is no match between the two, managers try to find out the reasons for the deviation and suggest corrective measures to get on track. Control functions refer to all performance measures and follow-up actions that keep actual performance on track.
Q20) “A successful enterprise has to achieve its goals effectively and efficiently” Explain.
A20) “A successful enterprise has to achieve its goals effectively and efficiently”. Thus, management has to see that task are completed and goals are achieved with the minimum resources.
Management is thus getting things done with the aim of achieving goals effectively and efficiently. Being effective or doing work effectively basically means finishing the given task. It is concerned with end result; it is achieved or not. Efficiency means doing the work correctly and with minimum cost. If by using less resources more benefits are derived then efficiency has increased. It is thus essential for any organisation to focus on efficiency as well as effectiveness. It is not only important to complete the work correctly but equally important to complete it with minimum cost. In the same manner, it is not only important to reduce cost but equally important to complete the work correctly.