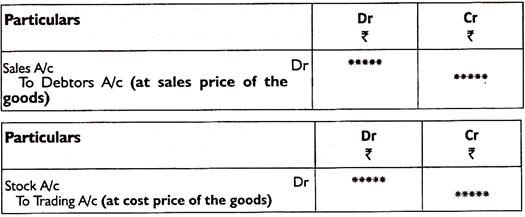
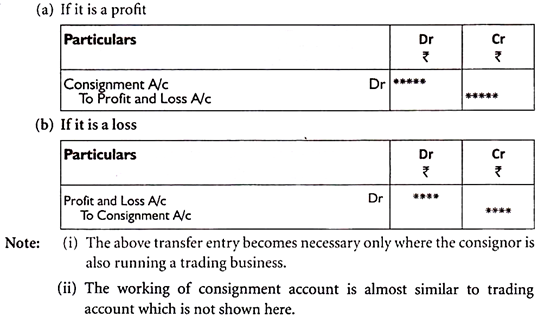
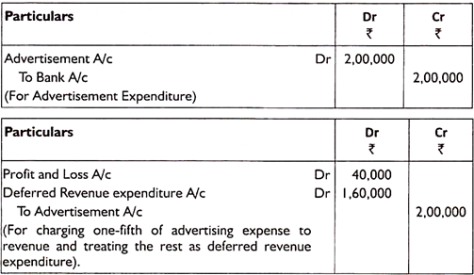
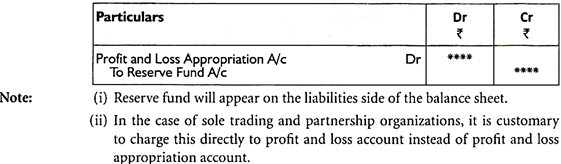
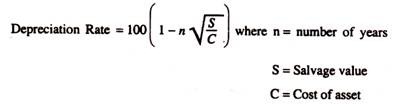Q1) Explain trading account.A1) Trading accountTrade and manufacturing operating companies deal with the sale and purchase of goods. Therefore, only the manufacturing and trading entities prepare the trading account. Service providers do not prepare for this.Advantages of preparing a trading account format
Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount |
To opening stock | xxx | By sales | xxx |
To purchase | xxx | Less: Returns | xxx |
Less: returns | xxx | By Closing stock | xxx |
To direct expenses: | xxx | By Gross loss c/d |
|
Freight & carriage | xxx |
|
|
Custom & insurance | xxx |
|
|
Wages | xxx |
|
|
Gas, water & fuel | xxx |
|
|
Factory expenses | xxx |
|
|
Royalty on production | xxx |
|
|
To Gross profit c/d | xxx |
|
|
Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount |
To Gross loss b/d | xxx | To Gross profit b/d | xxx |
Management expenses: | xxx | Income: | xxx |
To salaries | xxx | By Discount received | xxx |
To office rent, rates, and taxes | xxx | By Commission received | xxx |
To printing and stationery | xxx | Non-trading income: | xxx |
To Telephone charges | xxx | By Bank interest | xxx |
To Insurance | xxx | By Rent received | xxx |
To Audit fees | xxx | By Dividend received | xxx |
To Legal charges | xxx | By Bad debts recovered | xxx |
To Electricity charges | xxx | Abnormal gains: | xxx |
To Maintenance expenses | xxx | By Profit on sale of machinery | xxx |
To Repairs and renewals | xxx | By Profit on sale of investments | xxx |
To Depreciation | xxx | By Net Loss(transferred to Capital A/c) | xxx |
Selling distribution expenses: |
|
|
|
To Salaries | xxx |
|
|
To Advertisement | xxx |
|
|
To Godown | xxx |
|
|
To Carriage outward | xxx |
|
|
To Bad debts | xxx |
|
|
To Provision for bad debts | xxx |
|
|
To Selling commission | xxx |
|
|
Financial expenses: |
|
|
|
To Bank charges | xxx |
|
|
To Interest on loan | xxx |
|
|
To Discount allowed | xxx |
|
|
Abnormal losses: | xxx |
|
|
To Loss on sale of machinery | xxx |
|
|
To Loss on sale of investments | xxx |
|
|
To Loss by fire | xxx |
|
|
To Net Profit(transferred to capital a/c) | xxx |
|
|
TOTAL |
| TOTAL |
|
Section of the balance sheetTo be widely considered about the balance sheet of the division part of assets part of liabilities main capital. For each department: Assets section In the balance sheet, assets with similar characteristics are grouped. The mainly adopted approach is to divide assets into current and non-current assets. Liquid assets include cash and all assets that can be converted into cash or expected to be consumed in a short period of time–usually one year. Examples of current assets include cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, prepayment costs or prepayment, short-term investments and inventories. All assets that aren't listed as current assets are grouped as non-current assets. A common feature of such assets is that they continue to provide profit for a long time-usually more than one year. Examples of such assets include long-term investments, equipment, plants and machinery, land and buildings, and intangible assets. Debt DivisionA debt is an obligation to a party other than the owner of the business. They are grouped as current and long-term liabilities in the balance sheet. Current liabilities are obligations that are expected to be met within a one-year period by using current assets of the business or by providing goods or services. Owner's equity divisionThe owner's interest is the obligation of the business to its owner. The term owner's equity is mainly used in the balance sheet of a business in the form of a sole proprietor and partnership. In the balance sheet of the company the term “ownership interest “is often replaced by the term “shareholder interest".When the balance sheet is created, the liabilities section appears first, and the owner's equity section appears later.Balance sheet format there are two formats on the balance sheet that present Assets, Liabilities and owner's ' equity–the account format and the report format.
Assets | $ | Liabilities & Stockholder’s equity | $ |
Current assets: Cash Account receivable Prepaid building rent Unexpired insurance Supplies
Total current assets
|
85,550 4,700 1,500 3,600 250
| Liabilities: Notes payable Accounts payable Salaries payable Income tax payable Unearned service revenue
Total liabilities |
5,000 1,600 2,000 3,000 4,400
|
95.600 | 16,000 | ||
Non-current assets: Equipment 9,000 Acc. dep. –Equipment 3,600
Total assets |
5,400
| Stockholder’s equity: Capital stock 50,000 Retained earnings 35.000
Total liabilities & stockholder’s equity
|
85,000
|
101,200 | 101,000 | ||
|
|
|
|
Assets Current assets:
Cash Account receivable Prepaid building rent Unexpired insurance Supplies
Total current assets
|
85,500 4,700 1,500 3,600 250
|
95,600
| |
Non-current assets: Equipment 9000 Acc. Dep- Equipment 3600
Total assets
|
5,400
|
101,000
| |
Liabilities & Stockholder’s Equity Liabilities Notes payable Accounts payable Salaries payable Income tax payable Unearned service revenue
Total liabilities
|
5,000 1,600 2000 3000 4,400
|
16,000 | |
Stockholder’s equity: Capital stock Retained earning
Total stockholder’s equity
Total liabilities and stockholder’s equity |
50,000 35,000
|
85,000
| |
101,00 |
Rs | |
| By Sales |
| By Trading Stock |
Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs |
|
| Closing Stock |
|
|
|
| Rs |
TO Rent Account Add: Outstanding | [11 month rent] [December] | 11,000 1,000 |
12,000 |
Liabilities | Rs | Assets |
|
Outstanding Expenses: Rent |
1,000 |
|
|
Balance Sheet | ||||||||
|
| By Interest on investment Add: Interest accrued | …… 1,200 |
|
Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs |
|
| Interest accrued | 1,200 |
|
| Rs | Rs |
| By Apprentice Premium Less: Received in advance | 6,000 4,000 |
2,000 |
Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs |
Apprentice Premiu received in advance | 4,500 |
|
|
| Rs. |
|
To Depreciation a/c Furniture | 2,500 |
|
Liabilities | Rs | Assets |
| Rs |
|
| Furniture Less: Depreciation | 50,000 2,500 |
47,500 |
| Rs |
|
TO Bad Debts To Reserve for doubtful Debts | 1,000 1,000 |
|
Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs |
|
|
| Sundry Debtors Less: Bad Debts
Less: Provision for Doubtful Debts | 21,000 1,000 |
19,000 |
20,000 | ||||
1,000 |
| Rs |
|
To ad Debts To Reserve for Doubtful Debts To Reserve for Discount on Debtors |
1,000 380 |
|
Liabilities | Rs | Assets |
| Rs |
|
| Sundry Debtors Less: Provision for Doubtful on Debts
Less: Provision for Doubtful Debts | 20,000 1,000
19,000 380 |
18,620 |
| Rs |
| Rs |
|
| By Reserve for Discount on Creditors | 300 |
Liabilities | Rs |
|
|
|
Sundry Debtors Less: Reserve for Discount | 10,000 300 |
9,700 |
|
|
So, the interest charged is a loss to the business and a profit to the owner. Thus, it is debited to profit and loss a/c and added to the capital of the balance sheet. Adjusting entries: a) Interest on Capital a/c Dr. To Capital a/cb) Profit and Loss a/c Dr. To Interest on Capital a/c 10. Interest in drawing:The drawing is the money that the owner has withdrawn from the capital. It charges interest on the drawing so that it allows business interest on capital. It's a profit to the business and a loss to the owner. Thus, it is credited to profit and loss a/c and deducted from the capital on the balance sheet.Profit and Loss Account
| Rs |
| Rs |
To Interest on Capital |
| By Interest on Drawings |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital Add: Interest on Capital Less: Drawings Interest on Drawings |
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 7. Committee of managers:Business companies sometimes offer profit incentives to managers in the form of commissions to motivate people to increase business profits. This fee is given as a percentage of net profit. There are two ways to provide this percentage of net profit.(a) The percentage of the commission against net profit before charging such fees;(b) The percentage of fees to net income after invoicing such fees; 8. Specific hidden tweaks:The adjustments are not given explicitly under the array of adjustments, but they need to be placed and adjusted. For example,the balance displays the subsequent items alongside other items at the top of Dec31, 2009: DR Cr10% loan January 1, 2009 - - Interest on loan 3,000 -(Paid during the year) If we carefully observe loans are obtained in March 1, 2009 at a rate of interest of 10%. That is, the interest paid on a one-year loan in December31, 2009 (Rs.50, 000×10/100) rupees.5, 000. But the interest paid is only Rs.3, 000 as shown in the trial balance. This indicates that interest is not paid (Rs.5, 000-3,000-2,000. Therefore, this should be considered as an adjustment. The entry is – Profit and Loss A/c Dr 2,000TO Interest payable A/c 2,000 Here, the total interest charged to the profit and loss account is Rs.Will you be given 3,000 trial balances plus interest expense? 2,000, which is completely equivalent to Rs.5,000. Interest expense Rs.2,000 will appear as liabilities on the balance sheet.Please note that there are many adjustments to different types of courses and preparations for the final. Their treatment is explained when they appear. WorksheetWhen all the necessary information for financial reporting is ready (that is, information on the trial balance and adjustment, officially aggregated without errors), the accountant prefers to draft a work sheet. The worksheet is a rough work and is not part of the financial statements. The worksheet is provided for convenience to ensure that the financial statements prepared in the debit and credit columns representing the trial balance, adjusted, adjusted trial balance, trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet are in order. Q5) From the following ledger balance presented by Sen. on 31st March, 2016 prepare a trading account:
7. Committee of managers:Business companies sometimes offer profit incentives to managers in the form of commissions to motivate people to increase business profits. This fee is given as a percentage of net profit. There are two ways to provide this percentage of net profit.(a) The percentage of the commission against net profit before charging such fees;(b) The percentage of fees to net income after invoicing such fees; 8. Specific hidden tweaks:The adjustments are not given explicitly under the array of adjustments, but they need to be placed and adjusted. For example,the balance displays the subsequent items alongside other items at the top of Dec31, 2009: DR Cr10% loan January 1, 2009 - - Interest on loan 3,000 -(Paid during the year) If we carefully observe loans are obtained in March 1, 2009 at a rate of interest of 10%. That is, the interest paid on a one-year loan in December31, 2009 (Rs.50, 000×10/100) rupees.5, 000. But the interest paid is only Rs.3, 000 as shown in the trial balance. This indicates that interest is not paid (Rs.5, 000-3,000-2,000. Therefore, this should be considered as an adjustment. The entry is – Profit and Loss A/c Dr 2,000TO Interest payable A/c 2,000 Here, the total interest charged to the profit and loss account is Rs.Will you be given 3,000 trial balances plus interest expense? 2,000, which is completely equivalent to Rs.5,000. Interest expense Rs.2,000 will appear as liabilities on the balance sheet.Please note that there are many adjustments to different types of courses and preparations for the final. Their treatment is explained when they appear. WorksheetWhen all the necessary information for financial reporting is ready (that is, information on the trial balance and adjustment, officially aggregated without errors), the accountant prefers to draft a work sheet. The worksheet is a rough work and is not part of the financial statements. The worksheet is provided for convenience to ensure that the financial statements prepared in the debit and credit columns representing the trial balance, adjusted, adjusted trial balance, trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet are in order. Q5) From the following ledger balance presented by Sen. on 31st March, 2016 prepare a trading account:Particulars | Rs | Particulars | Rs |
Stock(1-4-2015) Purchase Wages Carriage inwards Freight inward | 10,000 1,60,000 30,000 10,000 8,000 | Sales Returns inward Return outward Gas and Fuel | 3,00,000 16,000 10,000 8,000 |
Particulars | Rs | RS | Particulars | Rs | Rs |
To Opening Stock To purchase Less: Return outwards To wages Add: Outstanding To carriage inwards To freight inwards To Gas and fuel Less: Prepaid To Gross profit c/d |
1,60,000 10,000 | 10,000
1,50,000
34,000 10,000 8,000
7,000 85,000
| By Sales Less: Returns inward BY Closing Stock | 30,00,000 16,000 |
2.84,000 20,000
|
| |||||
30,000 4,000 | |||||
8,000 1,000 | |||||
| |||||
3,04,00 | |||||
3,04,00 | |||||
|
|
Particulars | Rs | Particulars | Rs |
Gross profit Rent paid Salaries Commissions (Cr.) Discount received Insurance Premium paid | 1,00,000 22,000 10,000 12,000 2,000 8,000 | Interest received Bad debts Provisions for bad debts(1-4-2016) Sundry debtors Buildings | 6,000 2,000 4,000 40,000 80,000 |
Particulars | Rs | RS | Particulars | Rs | Rs |
To Rent Add: Outstanding (22,000x1/11) To Salaries Add: Outstanding To Insurance premium
Less: Prepaid insurance To Provision for bad and doubtful debts(closing)
Add: Bad debts Add: Further bad debts
Less: Opening provisions for bad and doubtful debts To Depreciate on building (80,000 x 10%)
To Net profit (transferred to capital A/c)
| 22,000 2,000 |
24,000
14,000
6,000
2,900 8,000 | By Gross profit b/d By Commission
Less: Received in advance By Discount received By interest received Add: Accrued | - 12,000 2,000 | 1,00,000
10,000 2,000
8,000
|
10,000 4,000 | 6,000
2,000 | ||||
8,000 2,000 | |||||
1,900 2,000 3,000
| |||||
6,900
4,000 | |||||
| |||||
65,100 | |||||
1,20,000 | |||||
1,20,000 |
Particulars | Rs | Particulars | Rs |
Stock on 01.01.2016 Purchase Sales Expenses on purchase Bank charges paid | 9,000 22,000 42,000 1,500 3,500 | Bad debts Sundry expenses Discount allowed Expenses on sale Repairs on office furniture | 1,200 1,800 1,700 1,000 600 |
Particulars | Rs. | Particulars | Rs |
To Opening stock To Purchase To Expense’s on purchase To Gross profit c/d
To Bank charges To Bad debts To Sundry expenses To Discount allowed TO Expense on sale To Repairs on office furniture TO Manager’s commission To Net profit (transferred to capital A/c) | 9,000 22,000 1,500 14,000 | By Sales By Closing stock
By Gross profit b/d | 42,000 4,500
|
46,500 | 46,500 | ||
3,500 1,200 1,800 1,700 1,000 600 200 4,000
| 14,000
| ||
14,000 | 14,000 |
|
Particulars | Rs | Particulars | Rs |
Capital Drawings Cash in hand Loan from Bank Bank over draft Investment Bills receivables | 2,00,000 40,000 15,000 40,000 20,000 20,000 10,000 | Sundry creditors Bill payable Goodwill Sundry debtor Land and Building Vehicles Cash at bank | 40,000 20,000 60,000 80,000 50,000 80,000 25,000 |
Particulars | Rs | Rs | Particulars | Rs | Rs |
Capital Add: Net profit Add: Interest on capital
Less: Drawings Loan from bank
Add: Interest outstanding Bills payable Sundry creditors Bank overdraft Add: Interest outstanding
Outstanding liabilities Salaries Wages | 2,00,000 96,000 20,000 |
2,76,000
46,000 20,000 40,000
23,000
30,000
| Good will Land and Building Vehicles Less: Depreciation
Investment Stock in trade Sundry debtors Less: Bad debts
Less: Provision for bad and doubtful debts
Bills receivable Cash at bank Cash in hand |
80,000 8,000 | 60,000 50,000
72,000 20,000 1,20,000
63,000
10,000 25,000 15,000
|
3,16,000 40,000 | |||||
80,000 10,000 | |||||
40,000
6,000 | |||||
20,000 3,000 | 70,000
7,000 | ||||
10,000 20,000 |
| ||||
4,35,000 | |||||
| 4,35,000 |