Unit - 1
Strings
Q1) Define finite automata?
A1) Finite Automata(FA) is the simplest pattern recognition machine. The finite automatic or finite state machine is an abstract machine with five components or tuples. It has a set of states and rules that switch from one state to another, but it depends on the input symbol that is added. It is essentially an abstract digital machine model.
Some important features of general automation are shown in the figure below:
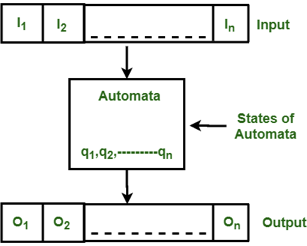
Fig 1: Features of finite automata
The figure above shows the following automated features:
● Input
● Output
● State of automata
● State relation
● Output relation
A Finite Automata consists of the following:
{Q, Σ, q, F, δ}.
Where,
Q: Finite set of states.
Σ: set of Input Symbols.
q: Initial state.
F: set of Final States.
δ: Transition Function.
Finite automata is divided into 2 types:
- Deterministic Finite Automaton (DFA)
In this, for each input symbol, the state to which the machine will move can be determined. As it has a finite number of states, the machine is called Deterministic Finite Machine or Deterministic Finite Automaton.
An automaton can be represented by a 5-tuple (Q, ∑, δ, q 0 , F),
Where −
Q is a finite set of states.
∑ is a finite set of symbols, called the alphabet of the automaton.
δ is the transition function.
q 0 is the initial state from where any input is processed (q 0 ∈ Q).
F is a set of final state/states of Q (F ⊆ Q).
2. Non-deterministic Finite Automaton (NDFA)
In NDFA, the machine can move to any combination of the states. Hence, it is called Non-deterministic Automaton as it has finite number of states.
Q → Finite non-empty set of states.
∑ → Finite non-empty set of input symbols.
∂ → Transitional Function.
q0 → Beginning state.
F → Final State
Q2) Describe the Chomsky hierarchy?
A2) The Chomsky Hierarchy describes the class of languages that the various machines embrace. The language group in Chomsky's Hierarchy is as follows:
- Type 0 known as Unrestricted Grammar.
- Type 1 known as Context Sensitive Grammar.
- Type 2 known as Context Free Grammar.
- Type 3 Regular Grammar.

Fig 2: Chomsky hierarchy
The above diagram shows the hierarchy of chomsky. Each language of type 3 is therefore also of type 2, 1 and 0 respectively. Similarly, every language of type 2 is also of type 1 and type 0 likewise.
● Type 0 grammar -
Type 0 grammar is known as Unrestricted grammar. The grammar rules of these types of languages are unregulated. Turing machines can model these languages efficiently.
Example:
- BAa → aa
- P → p
● Type 1 grammar -
Type 1 grammar is known as Context Sensitive Grammar. Context-sensitive grammar is used to describe language that is sensitive to context. The context-sensitive grammar follows the rules below:
● There may be more than one symbol on the left side of their development rules for context-sensitive grammar.
● The number of left-hand symbols does not surpass the number of right-hand symbols.
● The A → ε type rule is not permitted unless A is a beginning symbol. It does not occur on the right-hand side of any rule.
● The Type 1 grammar should be Type 0. Production is in the form of V →T in type1
Example:
- S → AT
- T → xy
- A → a
● Type 2 grammar -
Type 2 Grammar is called Context Free Grammar. Context free languages are the languages which can be represented by the CNF (context free grammar) Type 2 should be type 1. The production rule is:
A → α
Example:
- A → aBb
- A → b
- B → a
● Type 3 grammar -
Type 3 Grammar is called Regular Grammar. Those languages that can be represented using regular expressions are regular languages. These languages may be NFA or DFA-modeled.
Type3 has to be in the form of -
V → T*V / T*
Example:
A → xy
Q3) Explain deterministic finite automata?
A3) In this, for each input symbol, the state to which the machine will move can be determined. As it has a finite number of states, the machine is called Deterministic Finite Machine or Deterministic Finite Automaton.
● An automaton can be represented by a 5-tuple (Q, ∑, δ, q 0 , F), where −
● Q is a finite set of states.
● ∑ is a finite set of symbols, called the alphabet of the automaton.
● δ is the transition function.
● q0 is the initial state from where any input is processed (q 0 ∈ Q).
● F is a set of final state/states of Q (F ⊆ Q).
Transition function can be defined as:
δ: Q x ∑→Q
Graphical Representation of DFA
A DFA can be represented by digraphs called state diagram. In which:
- The state is represented by vertices.
- The arc labeled with an input character shows the transitions.
- The initial state is marked with an arrow.
- The final state is denoted by a double circle.
Advantages and disadvantages
● DFAs are used to model a Turing machine.
● They are used as ++ models of computation.
● The union/intersection of the languages recognized by two given DFAs.
● The complement of the language recognized by a given DFA.
Example
Q = {q0, q1, q2}
∑ = {0,1}
q0 = {q0}
F = {q2}
Solution:
Transition Diagram:

Transition Table:
Present State | Next State for Input 0 | Next state of Input 1 |
→q0 | q0 | q1 |
q1 | q2 | q1 |
*q2 | q2 | q2 |
Q4) What is nondeterministic finite automata?
A4) In NDFA, the machine can move to any combination of the states. Hence, it is called Non-deterministic Automaton.
It has a finite number of states.
● Q → Finite non-empty set of states.
● ∑ → Finite non-empty set of input symbols.
● ∂ → Transitional Function.
● q0 → Beginning state.
● F → Final State
Transition function can be defined as:
δ: Q x ∑ →2Q
Graphical Representation of NFA
An NFA can be represented by digraphs called state diagram. In which:
- The state is represented by vertices.
- The arc labeled with an input character show the transitions.
- The initial state is marked with an arrow.
- The final state is denoted by the double circle.
Example
- Q = {q0, q1, q2}
- ∑ = {0, 1}
- q0 = {q0}
- F = {q2}
Solution:
Transition Diagram:

Transition table:
Present State | Next State for Input 0 | Next State of Input 1 |
→q0 | q0, q1 | q1 |
q1 | q2 | q0 |
*q2 | q2 | q1,q2 |
In this figure, we can see that the current state is q0(input 0), and the next state will be q0,q1(input 1) so the next state is q1. When the current state is q1(input 0), the next state will be q2(input 1), the next state is q0. When the current state is q2(input 0), the next state is q2( input 1), the next state will be q1 or q2.
Q5) Write the difference between DFA and NFA?
A5) Difference between DFA and NFA
DFA | NFA |
The transition from a state is to a single Particular next state for each input symbol. Hence it is called deterministic. | The transition from a state can be to Multiple next states for each input symbol. Hence it is called non-deterministic. |
Empty string transitions are not seen in DFA. | NDFA permits empty string transitions. |
Requires more space. | Requires less space. |
Backtracking is allowed in DFA | In NDFA, backtracking is not always Possible. |
A string is accepted by a DFA, if it transits to a final state.
| A string is accepted by a NDFA, if at least one of all possible transitions ends in a Final state. |
Q6) Convert the given Moore machine into its equivalent Mealy machine?
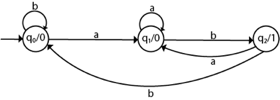
A6) The transition table of given Moore machine is as follows:
Q | a | b | Output((λ) |
q0 | q1 | q0 | 0 |
q1 | q1 | q2 | 0 |
q2 | q1 | q0 | 1 |
The equivalent Mealy machine can be obtained as follows:
λ' (q0, a) = λ(δ(q0, a))
= λ(q1)
= 0
λ' (q0, b) = λ(δ(q0, b))
= λ(q0)
= 0
The λ for state q1 is as follows:
λ' (q1, a) = λ(δ(q1, a))
= λ(q1)
= 0
λ' (q1, b) = λ(δ(q1, b))
= λ(q2)
= 1
The λ for state q2 is as follows:
λ' (q2, a) = λ(δ(q2, a))
= λ(q1)
= 0
λ' (q2, b) = λ(δ(q2, b))
= λ(q0)
= 0
Hence the transition table for the Mealy machine can be drawn as follows:

The equivalent Mealy machine will be
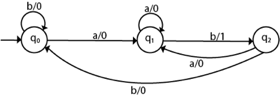
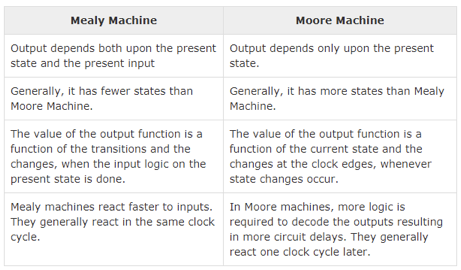
Q7) Write the difference between moore and mealy machine?
A7) Difference between mealy and moore machine
Q8) Explain Mealy Machine?
A8) A Mealy Machine is a machine in which the output symbol depends on the machine's current input symbol and current state. The output is expressed in the Mealy machine with each input symbol for each state, separated by /.
The Mealy machine can be described by 6 tuples (Q, q0, ∑, O, δ, λ') where
- Q: finite set of states
- q0: initial state of machine
- ∑: finite set of input alphabet
- O: output alphabet
- δ: transition function where Q × ∑ → Q
- λ': output function where Q × ∑ →O
Equivalence of moore and merely
Moore and the mealy machine appear differently from each other.
Designing a moore machine with a mealy machine is often possible.
Designing a mealy machine with a moore machine is often possible.
It is possible to transform any Moore machine into a mealy machine.
Moore machine or mealy machine may be used to describe each standard language.
All languages specified by a mealy machine or moore machine are standard.

Fig 3: Example of equivalent moore and mealy machine
A moore machine M can never be correctly equal to a mealy machine M 'since one greater than that of the mealy machine M' on the same input is the length of the output string of a moore machine M.
We can, however, overlook the reaction of the moore machine to input λ and say
For all inputs w, moore machine M and a mealy machine M 'are equivalent if
Where b for its initial state is the output of the Moore machine M
Theorem: If M1= (Q, Σ, Δ, δ, λ ,q0 ) is a moore machine then there is an M2 equivalent to M1 mealy machine.
Proof: Create a mealy machine M2 as (Q, Σ, Δ, δ, λ’ ,q0 )
λ’ is describe as-
λ’(q,a) = λ(δ (q,a)) For q and input symbols of all states a
Moore machine is on input 1010 output
0 1 2 2 1
Although the output from the mealy machine constructed is
1 2 2 1
By the equivalence state
In the beginning of output of mealy machine, we can add output of q0 0 of moore machine
The machine generated is therefore equivalent to the Moore machine defined.
Q9) Explain Moore Machine?
A9) The Moore machine is a finite state machine in which the current state and the current input symbol define the next state. At a given time, the output symbol depends only on the machine's current state.
Moore machine can be described by 6 tuples (Q, q0, ∑, O, δ, λ) where,
- Q: finite set of states
- q0: initial state of machine
- ∑: finite set of input symbols
- O: output alphabet
- δ: transition function where Q × ∑ → Q
- λ: output function where Q → O
Example:
The state diagram for Moore Machine is-

Transition Table for MM(moore machine) is
Current State | Next State(δ) | Output(λ) | |
0 | 1 | ||
q0 | q1 | q2 | 1 |
q1 | q2 | q1 | 1 |
q2 | q2 | q0 | 0 |
Q10) What is the equivalence of DFA and NFA?
A10) It would seem superficially that deterministic and non-deterministic finite state automata are totally distinct beasts. However, it turns out that they are equivalent. There is a DFA for every language recognized by an NFA that recognizes that language and vice versa.
The NFA to DFA conversion algorithm is relatively simple, even though the resulting DFA is substantially more complicated than the original NFA. I will illustrate this equivalence after the hop and also go through a brief example of converting an NFA to an equivalent DFA.
DFA and NFA Theorem proof -
Let's formally state the theorem we are proving before continuing:
Theorem:
Let the language L ⊆ Σ* be recognized by NFA N = (Σ, Q, q0, F, δ) and assume L.
A DFA D= (Σ, Q ', q'0, F', δ ') exists that also accepts L. (L(N)= L(D)).
We are able to prove by induction that D is equal to N by allowing each state in the DFA D to represent a set of states in the NFA N. Let's define the parameters of D: before we start proofing,
● Q’ is equal to the powerset of Q, Q’ = 2Q
● q’0 = {q0}
● F’ is the set of states in Q’ that contain any element of F, F’ = {q ∈ Q’|q ∩ F ≠ Ø}
● δ’ is the transition function for D. δ’(q,a) = Up∈ q δ(p, a)for q ∈ Q’ and a ∈ Σ
It's worth more explaining, I think δ '. Note that in the set of states Q 'in D, each state is a set of states from Q in N itself. Determine the transition δ (p,a) for each state p in state q in Q 'of D (p is a single state from Q). The union of all δ(q, a) is δ(q,a) .
Now we will demonstrate δ’(q0’, x) =δ’(q0 , x) that for every x i.e L(D) = L (N)
Q11) Design FA with ∑ = {0, 1} accepts even number of 0's and even number of 1's?
A11) For inputs 0 and 1, this FA will consider four possible phases. The phases could be as follows:

Here, q0 is both a start and a finish state. It's worth noting that the 0s and 1s are kept in a symmetrical pattern. Each state has its own set of connotations, such as:
q0: state of even number of 0's and even number of 1's.
q1: state of odd number of 0's and even number of 1's.
q2: state of odd number of 0's and odd number of 1's.
q3: state of even number of 0's and odd number of 1's.
Q12) Design a DFA L(M) = {w | w ε {0, 1}*} and W is a string that does not contain consecutive 1's?
A12) When three 1's appear in a row, the DFA is:
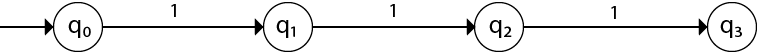
Two consecutive 1s or a single 1 are permitted here, so

The final states are phases q0, q1, and q2. The DFA will create strings that do not contain consecutive 1's, such as 10, 110, 101, and so on.
Q13) Design an NFA with ∑ = {0, 1} accepts all string in which the third symbol from the right end is always 0?
A13)

As a result, we always receive '0' as the third sign from the right end. The NFA can take the following forms:
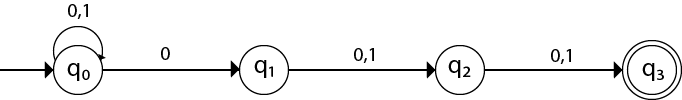
Because we can either proceed to state q0 or q1 in state q0 with input 0, the preceding graphic is an NFA.
Q14) Design a NFA for the transition table as given below?
Present State | 0 | 1 |
→q0 | q0, q1 | q0, q2 |
q1 | q3 | ε |
q2 | q2, q3 | q3 |
→q3 | q3 | q3 |
A14) The mapping function, as shown in the table, can be used to create the transition diagram.
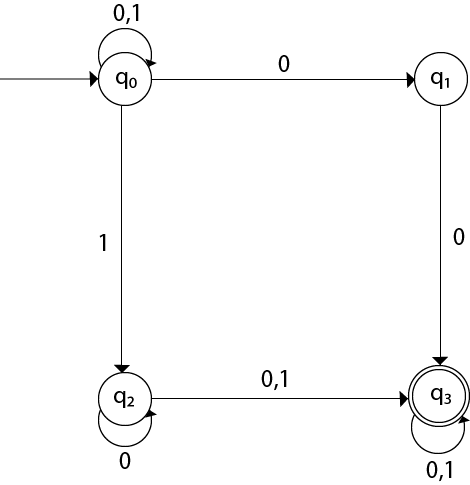
Here,
δ(q0, 0) = {q0, q1}
δ(q0, 1) = {q0, q2}
Then, δ(q1, 0) = {q3}
Then, δ(q2, 0) = {q2, q3}
δ(q2, 1) = {q3}
Then, δ(q3, 0) = {q3}
δ(q3, 1) = {q3}