UNIT 4
Question Bank
Q1-Mention the important principles of Green Chemistry.
A- There are following 12 major principles of green chemistry:
(i) Preventing Waste
(ii) Maximize atom economy
(iii) Less hazardous chemical syntheses
(iv) Designing safer chemicals
(v) Safer solvents and Auxiliaries
(vi) Increases Energy efficiency
(vii) Uses renewable feedstock
(viii) Reduce derivatives
(ix) Use catalysts, not stoichiometric reagent
(x) Design chemicals and products to be degraded after use
(xi) Real time analysis to prevent pollution
(xii) Minimize the potential for accidents
Q2- What are super critical fluids?
A- This technology is involved in the wide variety of industrial applications. There are many sectors like food, cosmetics, pharmaceutics, waste treatment which are involved in this. The related superficial fluid processes include extraction, impregnation, formulation and waste treatment among others. Super critical CO2 is a fluid state of CO2 where it is held or above the critical temperature and pressure.CO2 shows the dual property in the nature i.e., it behaves like gas and dry ice as a solid.
Q3-Industrial application of super critical fluids.
A- CO2 is highly used by coffee manufacturers; they are looking forward from classic decaffeinating solvents, because of real or perceived danger related to their use in food preparation. CO2 are forced through the green coffee beans which are then sprayed with water at high pressure to remove caffeine’s further the same can be resold by distillation.
This CO2 can be used as more environment friendly solvent for dry cleaning over traditional solvents. This CO2 is used as the extraction solvent for the creation of essential oils and other herbal distillates.
Q4- Explain in brief about Nickel Cadmium battery.
A- Nickel-Cadmium: Nickel cadmium battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes. The maximum recharge rate for Ni-Cd battery varies by size.
Voltage: Zinc carbon primary cells and Nickel cadmium cells are not preferably exchangeable as because the potential of Zinc Carbon primary cells are greater than that of Ni-Cd cells. As many electronic devices are designed to work with primary cell that may discharge as low as 0.90 to 1.0V per cell.
Charging: Depending on the cell manufacturing Ni-Cd batteries can be charged in different ways. The charge rate is measured based on the percentage of the amp-hour capacity the battery is fed as the steady current over the duration of charge.
On fully charging the Ni-Cd batteries the batteries consist a nickel oxide hydroxide positive electrode plate, a cadmium negative electrode plate, a separator and an alkaline electrolyte. Nickel Cadmium consist of nickel wire gauze and electrode grids. The anode grid consists of a mixture of spongy cadmium with 78% cadmium hydroxide, 18% iron, 1% nickel and 1% graphite. The cathode grid contains nickel hydroxide (80%), cobalt hydroxide (2%), graphite (18%) and traces of barium compound. Graphite increases the conductivity, the cobalt and barium compounds increase the efficiency of active material and also the cycle life. 6M KOH is the electrolyte.
Electrode Reaction:
 On anode,Cd + 2OH- Cd(OH)2 + 2e-
On anode,Cd + 2OH- Cd(OH)2 + 2e-
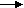 On cathode end, 2Ni(OH)3 + 2e- 2Ni(OH)2 + 2OH-
On cathode end, 2Ni(OH)3 + 2e- 2Ni(OH)2 + 2OH-
 Cd + 2Ni(OH)3 2Ni(OH)2 + Cd(OH)2
Cd + 2Ni(OH)3 2Ni(OH)2 + Cd(OH)2
Applications: These are used in pocket calculators, photo flash units, cordless garden tools, alarm, emergency lighting, instrument etc.
Q5- Mention the advantage of Alkaline Fuel Cells.
A-
(i) Activation over voltages at the cathode is usually less than acid electrolyte fuel cell.
(ii) Electrode are made of normal materials, there is no use of precious metal or costly material in it.
(iii) Good Power density
(iv) Low temperature operation
(v) Mobile electrolyte fuel cell can easily cooled by circulated hydrogen.
Q6- What are the different type of batteries?
A-