Unit - 3
Pavement Design
Q1) What is pavement design?
A1)
- Requirements of a pavement A perfect pavement ought to meet the subsequent requirements:
Sufficient thickness to distribute the wheel load stresses to a secure cost at the sub-grade soil Structurally sturdy to resist all forms of stresses imposed upon it Adequate coefficient of friction to save you skidding of pavement.
- A toll road pavement is a shape which include superimposed layers of processed substances above the herbal soil sub-grade, whose number one characteristic is to distribute the implemented car hundreds to the sub-grade. The pavement shape must be capable of offer a floor of proper using quality, ok skid resistance, favorable mild reflecting characteristics, and coffee noise pollution.
- The final goal is to make certain that the transmitted stresses because of wheel load are sufficiently reduced, in order that they may now no longer exceed bearing ability of the sub-grade. Two kinds of pavements are usually diagnosed as serving this purpose, specifically bendy pavements and inflexible pavements.
- This bankruptcy offers a top level view of pavement types, layers, and their functions, and pavement failures. Improper layout of pavements ends in early failure of pavements affecting the using quality.
- Requirements of a pavement A perfect pavement must meet the subsequent requirements: Sufficient thickness to distribute the wheel load stresses to a secure fee at the sub-grade soil, Structurally robust to resist all kinds of stresses imposed upon it, Adequate coefficient of friction to save you skidding of vehicles, Smooth floor to offer consolation to street customers even at excessive speed
- Produce least noise from shifting vehicles, Dust evidence floor in order that visitors protection isn't impaired through lowering visibility, Impervious floor, in order that sub-grade soil is properly protected, and Long layout existence with low renovation price.
- Types of pavements: The pavements may be categorised primarily based totally at the structural overall performance into two, bendy pavements and inflexible pavements. In bendy pavements, wheel hundreds are transferred through grain-to-grain touch of the combination via the granular shape. The bendy pavement, having much less flexural energy, acts like a bendy sheet (e.g. Bituminous street). On the contrary, in inflexible pavements, wheel hundreds are transferred to sub-grade soil through flexural energy of the pavement and the pavement acts like a inflexible plate (e.g. Cement concrete roads). In addition to these, composite pavements also are available.
- A skinny layer of bendy pavement over inflexible pavement is a super pavement with maximum acceptable characteristics.
- However, such pavements are hardly ever utilized in new production due to excessive price and complicated evaluation required. Flexible pavements Flexible pavements will transmit wheel load stresses to the decrease layers through grain-to-grain switch via the factors of touch withinside the granular shape.
Q2) Write a note on types of pavement.
A2)
Types of pavements:
- The pavements may be categorised primarily based totally at the structural overall performance into two, bendy pavements and inflexible pavements. In bendy pavements, wheel hundreds are transferred through grain-to-grain touch of the combination via the granular shape. The bendy pavement, having much less flexural energy, acts like a bendy sheet (e.g. Bituminous street).
- On the contrary, in inflexible pavements, wheel hundreds are transferred to sub-grade soil through flexural energy of the pavement and the pavement acts like a inflexible plate (e.g. Cement concrete roads). In addition to these, composite pavements also are available.
- A skinny layer of bendy pavement over inflexible pavement is a super pavement with maximum acceptable characteristics. However, such pavements are hardly ever utilized in new production due to excessive price and complicated evaluation required. Flexible pavements Flexible pavements will transmit wheel load stresses to the decrease layers through grain-to-grain switch via the factors of touch withinside the granular shape
- The wheel load appearing at the pavement might be allotted to a much broader vicinity, and the strain decreases with the intensity.
- Taking gain of this strain distribution characteristic, bendy pavements usually has many layers. Hence, the layout of bendy pavement makes use of the idea of layered system. Based on this, bendy pavement can be built in some of layers and the pinnacle layer needs to be of quality excellent to preserve most compressive strain, similarly to put on and tear.
- The decrease layers will enjoy lesser importance of strain and occasional excellent cloth may be used. Flexible pavements are built the usage of bituminous substances.
- These may be both withinside the shape of floor remedies (together with bituminous floor remedies usually observed on low quantity roads) or, asphalt concrete floor courses (usually used on excessive quantity roads together with countrywide highways).
Q3) Give the characteristics of pavement.
A3)
- Flexible pavement layers mirror the deformation of the decrease layers directly to the floor layer (e.g., if there may be any undulation in sub-grade then it will likely be transferred to the floor layer). In the case of bendy pavement, the layout is primarily based totally on universal overall performance of bendy pavement, and the stresses produced have to be stored nicely beneath the allowable stresses of every pavement layer.
- Types of Flexible Pavements: The following sorts of creation were utilized in bendy pavement: Conventional layered bendy pavement, Full - intensity asphalt pavement, and Contained rock asphalt mat (CRAM).
- Conventional bendy pavements are layered structures with excessive excellent luxurious substances are positioned withinside the pinnacle wherein stresses are excessive, and occasional excellent reasonably-priced substances are positioned in decrease layers. Full - intensity asphalt pavements are built through putting bituminous layers at once at the soil sub-grade. This is greater appropriate whilst there may be excessive site visitors and neighborhood substances aren't available.
- Contained rock asphalt mats are built through putting dense/open graded combination layers in among asphalt layers. Modified dense graded asphalt concrete is positioned above the sub-grade will extensively lessen the vertical compressive pressure on soil sub-grade and shield from floor water. Typical layers of a bendy pavement Typical layers of a traditional bendy pavement consists of seal coat, floor path, tack coat, binder path, top coat, base path, sub-base path, compacted sub-grade, and herbal sub-grade (Figure 2).
- Seal Coat: Seal coat is a skinny floor remedy used to water-evidence the floor and to offer skid resistance.
- Tack Coat: Tack coat is a totally mild utility of asphalt, generally asphalt emulsion diluted with water. It presents right bonding among layer of binder path and should be thin, uniformly cowl the complete floor, and set very fast.
- Prime Coat: Prime coat is an utility of low viscous cutback bitumen to an absorbent floor like granular bases on which binder layer is positioned. It presents bonding among layers. Unlike tack coat, top coat penetrates into the layer beneath, plugs the voids, and paperwork a water tight floor.
- Typical move segment of a bendy pavement begincenterline{epsfig{file=p02-bendy-pavement-move-segment,width=12cm}}end Surface path Surface path is the layer at once in touch with site visitors masses and usually includes advanced excellent substances.
- They are generally built with dense graded asphalt concrete(AC). The features and necessities of this residue are: It presents traits together with friction, smoothness, drainage, etc. Also it'll save you the doorway of immoderate portions of floor water into the underlying base, sub-base and sub-grade, It should be difficult to face up to the distortion below site visitors and offer a easy and skid- resistant driving floor, It should be water evidence to shield the complete base and sub-grade from the weakening impact of water. Binder path This layer presents the majority of the asphalt concrete shape.
- It's leader motive is to distribute load to the bottom path The binder path usually includes aggregates having much less asphalt and would not require excellent as excessive because the floor path, so changing part of the floor path through the binder path effects in greater good value layout. Base path The base path is the layer of cloth without delay below the floor of binder path and it presents extra load distribution and contributes to the sub-floor drainage
- It can be composed of beaten stone, beaten slag, and different untreated or stabilized substances. Sub-Base path The sub-base path is the layer of cloth below the bottom path and the number one features are to offer structural support, enhance drainage, and decrease the intrusion of fines from the sub-grade withinside the pavement shape If the bottom path is open graded, then the sub-base path with greater fines can function a filler among sub-grade and the bottom path A sub-base path isn't continually wished or used.
- For example, a pavement built over a excessive excellent, stiff sub-grade won't want the extra capabilities presented through a sub-base path. In such situations, sub-base path won't be provided. Sub-grade The pinnacle soil or sub-grade is a layer of herbal soil organized to get hold of the stresses from the layers above.
- It is important that at no time soil sub-grade is overstressed. It have to be compacted to the applicable density, close to the best moisture content. Failure of bendy pavements The foremost bendy pavement screw ups are fatigue cracking, rutting, and thermal cracking.
- The fatigue cracking of bendy pavement is because of horizontal tensile pressure at the lowest of the asphaltic concrete.
- The failure criterion relates allowable quantity of load repetitions to tensile pressure and this relation may be decided withinside the laboratory fatigue check on asphaltic concrete specimens. Rutting happens best on bendy pavements as indicated through everlasting deformation or rut intensity alongside wheel load path.
- Two layout strategies were used to govern rutting: one to restrict the vertical compressive pressure at the pinnacle of subgrade and different to restrict rutting to a tolerable amount (12 mm usually). Thermal cracking consists of each low-temperature cracking and thermal fatigue cracking. Rigid pavements Rigid pavements have enough flexural energy to transmit the wheel load stresses to a much broader vicinity beneath. A ordinary move segment of the inflexible pavement.
- Compared to bendy pavement, inflexible pavements are positioned both at once at the organized sub-grade or on a unmarried layer of granular or stabilized cloth. Since there may be best one layer of cloth among the concrete and the sub-grade, this residue may be known as as base or sub-base path.
- Failure standards of inflexible pavements Traditionally fatigue cracking has been taken into consideration because the primary, or best criterion for inflexible pavement design.
- The allowable range of load repetitions to reason fatigue cracking relies upon at the pressure ratio among flexural tensile pressure and urban modulus of rupture. Of late, pumping is recognized as an critical failure criterion. Pumping is the ejection of soil slurry through the joints and cracks of cement concrete pavement, induced throughout the downward motion of slab below the heavy wheel loads. Other primary sorts of misery in inflexible pavements consist of faulting, spalling, and deterioration.
Q4) What are design parameters of pavement?
A4)
- When designing pavements (each blend layout and structural layout), there are 3 essential outside layout parameters to consider: the traits of the subgrade upon which the pavement is placed, the implemented hundreds and the environment.
- When designing pavements (each blend layout and structural layout), there are 3 essential outside layout parameters to consider: the traits of the subgrade upon which the pavement is positioned, the implemented hundreds and the surroundings.
- First, the subgrade upon which the pavement is positioned may have a huge effect on structural layout. Subgrade stiffness and drainage traits assist decide pavement layer thickness, the wide variety of layers, seasonal load regulations and any viable upgrades to subgrade stiffness and drainage itself. Second, the anticipated site visitors loading is a number one layout input (each in blend layout and structural layout).
- Traffic hundreds are used to decide pavement composition, layer kind and thickness, all of which have an effect on pavement existence. Third, the surroundings has a huge effect on pavement cloth performance. Environmental elements including temperature, moisture and ice formation can have an effect on pavement durability, binder rheology, structural help and in the long run pavement existence and failure.
- General: Criteria for figuring out the pavement (flexible) Thickness is vertical compressive pressure involves the subgrade because of the same old axle weighted down of significance 8.17 kN (8170 kg) , if extra than this reasons everlasting deformation in shape of rutting.
- The most rutting may be conventional in village avenue as 50 mm earlier than preservation and the analytical assessment may be achieved consistent with IRC:37. For inflexible and semi-inflexible pavement tensile pressure is taken because the layout criteria. There are surfacing contractors like Harris Surfacing who can assist you.
- Traffic: As in line with the IRC:37 layout site visitors have to be 0.1 msa to two msa (million widespread axles). Weight of industrial vehicle (weighted down) is taken into consideration as three tonnes or extra. For layout site visitors we don't forget the present site visitors and charge of boom. Traffic observe have to be achieved as in line with the IRC:9. Design existence: The no. Of years to be taken till the primary reconstruction. Design existence rely on the environmental conditions, substances used ,preservation etc.
- For rural roads layout existence of 10 years is taken into consideration. In low quantity roads for the skinny bituminous surfacing layout existence of five years is taken into consideration. Computation of layout site visitors: a=p(1+r)^(n+x)
Where, a=no. Of industrial vehicles/day for layout
p=no. Of industrial vehicles/day at closing matter
r=annual boom charge of industrial site visitors
n=no. Of years among closing matter and yr crowning glory of construction x=layout existence in years
- Pavement components Subgrade: To offer guide to the pavement as its foundation. Top 30 cm of the reducing or embankment at formation stage in rural roads don't forget as subgrade.
- A minimal of one hundred% of widespread proctor compaction have to be obtain in subgrade. For clayey soil 95% and moisture content material of 2% in extra of ideal fee. Soil beneathneath subgrade have to be compacted to 97% of widespread proctor compaction.
- CBR: Conduct on pattern which remoulded at OMC and dry density. Test have to be achieved in line with km depend upon soil type. If CBR much less than 2% for one hundred mm thickness then minimal CBR of 10% is to be furnished to the sub-base for CBR of 2%.
- If CBR extra than 15%, no want to offer sub-base. Sub-base direction: Selected substances positioned on subgrade that is compacted to 98% of IS heavy compaction. Function of sub-base is to distribute the stresses over a huge region of the subgrade imposed via way of means of the site visitors. Materials: CBR of 15% Passing through 425 micron IS sieve L.L<25 and P.I<6 Waste fabric which includes Fly ash, Iron and metallic slag Recycled concrete Municipal waste also are used.
- When subgrade is silty or clayey soil and annual rainfall of region is extra than one thousand mm, a drainage layer of one hundred mm then formation width have to be furnished. Base direction: to with stand excessive pressure concentrations which expand because of site visitors beneathneath the carrying floor.
- Different styles of base direction used are: WBM Crusher-run macadam Dry lean concrete Soft mixture base direction Lime-fly ash concrete Surface direction: Thickness of floor direction rely on the site visitors quantity and form of fabric used for it.
- For gravel roads more thickness have to be furnished due to misplaced in thickness because of the site visitors action. Bituminous carrying guides have to be made of top first-rate aggregate with aggregate effect fee now no longer exceeding 30 % which will lessen degradation of aggregates via way of means of crushing.
Q5) What is axel and wheel load?
A5)
- The axle load of a wheeled automobile is the full weight bearing at the roadway for all wheels related to a given axle.
- The axle load of a wheeled automobile is the entire weight bearing at the roadway for all wheels linked to a given axle. Axle load is an vital layout attention withinside the engineering of roadways and railways, as each are designed to tolerate a most weight-per-axle (axle load); exceeding the most rated axle load will motive harm to the roadway or rail tracks.
- One of the number one capabilities of a pavement is load distribution. Therefore, as a way to safely layout a pavement something need to be regarded approximately the anticipated hundreds it's going to encounter. Loads, the car forces exerted at the pavement (e.g., with the aid of using trucks, heavy machinery, airplanes), may be characterized with the aid of using the subsequent parameters: Tire hundreds Axle and tire configurations Repetition of hundreds Distribution of visitors throughout the pavement Vehicle speed
- Loads, together with the environment, harm pavement over time. The best pavement structural version asserts that every man or woman load inflicts a sure quantity of unrecoverable harm.
- This harm is cumulative over the existence of the pavement and while it reaches a few most cost the pavement is taken into consideration to have reached the quit of its beneficial carrier existence.
- Therefore, pavement structural layout calls for a quantification of all anticipated hundreds a pavement will come across over its layout existence. This quantification is normally performed in one in all ways: Equivalent unmarried axle hundreds (ESALs). This technique converts wheel hundreds of diverse magnitudes and repetitions (“combined traffic”) to an equal wide variety of “standard” or “equal” hundreds. Load spectra. This technique characterizes hundreds without delay with the aid of using wide variety of axles, configuration and weight.
- It does now no longer contain conversion to equal values. Structural layout calculations the usage of load spectra are commonly greater complicated than the ones the usage of ESALs. Both tactics use the equal kind and high-satisfactory of facts however the load spectra technique has the capability to be greater correct in its load characterization
Q6) What is tyre pressure?
A6)
- The "right" tyre strain or the business enterprise endorsed tyre strain is a selected cost of air strain that need to be maintained to your tyres to permit for max functioning of your car in addition to tyres. Every car synthetic in India undergoes extreme R&D throughout improvement to discover the quality tyre strain that completely fits your car.
- All our strain values were gathered from reputable tyre strain stickers that accompany any car this is synthetic withinside the country. We advocate which you observe handiest those reputable endorsed pressures to get the quality from your car in phrases of Performance, Safety, Efficiency and Tyre Life.
- In almost 15 acident cases, tyre blow-outs, overturning and skidding because of tyre strain extra than permissible limits had been observed to be the primary reasons, discovered a current look at executed with the aid of using Ahmedabad site visitors police.
- Project director of the parkway H C Modi said, “At excessive speeds, friction among tyres and the street effects in air strain increasing. If tyres have a strain of 32-35 PSI, it is going as much as 40-forty five PSI. This ends in immoderate warmth technology ensuing in accidents. Nearly 15 accidents are due to incorrect tyre strain.”
- The metropolis site visitors branch will now method the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) with the findings. It plans to advise putting in place cubicles a good way to compulsorily degree tyre strain of all automobiles earlier than permitting them to go — a strain of 26 PSI, or kilos according to rectangular inch, will handiest be allowed.
Q7) What is ESWL for dual wheel?
A7)
- In order to restriction the most load on unmarried wheel inside the precise restriction and to hold more load it's miles important to offer twin wheel meeting at the rear axles of heavy street vehicles.
- Equivalent Single Wheel Load (ESWL) of the twin wheel load meeting on the depth, ‘z’ can be described because the unmarried wheel load substitute of the twin wheel load meeting with the intention to motive the equal value of vertical deflection or equal price of compressive strain at that depth, z. Hence ESWL at any decided on depth, z can be decided primarily based totally on both equal deflection or equal strain criterion.
Q8) Write a note on westerguaards theory.
A8)
Westerguaard’s theory
- Westerguaard’s evaluation or principle is used for inflexible pavement that's manufactured from cement concrete with reinforcement or without reinforcement. High tensile power of inflexible pavement develops the slab action. Because of the weight spreading capacity, the stresses withinside the sub-grade beneath a inflexible pavement are substantially decreased. Over-stressing of the concrete typically reasons the failure of inflexible pavement, however failure of inflexible pavement isn't always because of the over stressing of the sub-grade. Hence the thickness is normally decided with the aid of using thinking about the calculation of stresses advanced withinside the concrete. Westerguaard’s principle is used to decide the stresses advanced withinside the concrete slab due to wheel loads.
Assumption made by Westerguaard’s Theory
Following are the critical assumptions taken into consideration with the aid of using Westerguaard’s Theory.
- The inflexible pavement is thought as a skinny elastic plate resting on soil sub-grade.
- The upward response at any factor is taken into consideration to be proportional to the deflection at that factor. upward response at any factor α deflection at that factor.
- Vertical subgrade response is thought to be proportional to the deflection. Cement concrete slab is homogeneous and isotropic (i.e. having uniform elastic residences).
- The slab deflection relies upon upon the flexural energy of the slab and the stiffness of the subgrade concluding that the stress deformation residences of a inflexible pavement relies upon upon the relative stiffness and the subgrade under the inflexible pavement.
Q9) Write a note on Repetitions
A9)
- Flexible pavements are so named due to the fact the full pavement shape deflects, or flexes, beneathneath loading. A bendy pavement shape is commonly composed of numerous layers of materials.
- Each layer gets hundreds from the above layer, spreads them out, and passes on those hundreds to the subsequent layer below.
- Thus the stresses could be reduced, which might be most on the pinnacle layer and minimal at the pinnacle of subgrade. In order to take most gain of this property, layers are normally organized withinside the order of descending load bearing capability with the very best load bearing capability material (and maximum expensive) at the pinnacle and the bottom load bearing capability material (and least expensive) at the bottom.
Q10) Write a note on Group Index & IRC method of flexible pavement design
A10)
- Group Index is a variety of assigned to the soil primarily based totally on its bodily residences like particle size, Liquid restriction and plastic restriction. It varies from a fee of zero to 20, decrease the fee better is the best of the sub-grade and extra the fee, negative is the sub-grade. By sieve evaluation take a look at we are able to decide Group index fee of soil subgrade from underneath equation
GI = 0.2a + 0.005 ac + 0.01bd
Where, a= percentage of soil passing 0.074 mm sieve in excess of 35 per cent, not exceeding 75.
b= percentage of soil passing 0.074 mm sieve in excess of 15 per cent, not exceeding 55.
c= Liquid limit in per cent in excess of 40. d= Plasticity index in excess of 10.
Data Required for Flexible Pavement Design
1. Group index of soil subgrade: Group index value range of different soils is given below
- For good soil – 0 to 1
- For fair soil – 2 to 4
- For poor soil – 5 to 9
- For very poor soil – 10 to 20
2. Traffic volume: It is the measure of Annual average daily traffic, peak-hour traffic. It is denominated by commercial vehicles/day or CVPD. It is classified in three categories. Based on number of vehicles per day. If no. Of vehicles per days is
- <50 - light traffic
- 50-300 - medium traffic
- >300 - Heavy traffic
Q11) What is Flexible Pavement Design Procedure?
A11)
- Before going to design the pavement we must know the structure of flexible pavement
- Calculation total thickness (T): From the below chart for given group index of soil subgrade and traffic volume value select appropriate thick curve value of “combined thickness of surface, base and sub-base line” which will give the total thickness of pavement.
- (Note: thick line suggests the entire thickness price and the dotted line suggests thickness of floor and base) Calculation thickness of sub-base course (tsb): From the beneath chart for given organization index of soil subgrade pick suitable curve price of “thickness of sub base only” in order to supply the thickness of the sub-base course.
- Calculation of thickness of base and surface course (tb & ts): Thickness of surface and base course = total thickness – sub-base thickness
= T - tsb
- The combined value of thickness of base and surface course can be found out from above chart form dotted curve with the help of group index value and traffic volume. Or otherwise assume the thickness of surface course (ts) = 5 cm Then we can easily calculate the value of thickness of the base course,
Tb = T-tsb-ts
Q12) Which types of loads occurs on pavement?
A12)
- Rigid pavements reply to loading in a lot of methods that have an effect on performance (each preliminary and long-term). The 3 predominant responses are: Curling stress. Differences in temperature among the pinnacle and backside surfaces of a PCC slab will motive the slab to curl. Since slab weight and make contact with with the bottom limition its movement, stresses are created.
- Load stress: Loads on a PCC slab will create each compressive and tensile stresses withinside the slab and any adjoining one (so long as load switch performance is > 0). Shrinkage and expansion. In addition to curling, environmental temperatures will motive PCC slabs to expand (whilst hot) and contract (whilst cool), which reasons joint movement.
- These 3 predominant responses commonly decide PCC slab geometry (commonly defined with the aid of using slab thickness and joint design). As slabs get longer, wider and thinner, those responses, or a aggregate of them, will ultimately exceed the slab’s capability and motive failure withinside the shape of slab cracking, joint widening or blowup. Note that extra issues, considerably load switch stresses and deflections, have to additionally be accounted for in design.
Q13) What are temperature stresses?
A13)
Temperature Stress:
- The stresses of number one difficulty are related to slab bending both because of temperature gradients, loading or a mixture thereof. Curling Since PCC is a lot more potent in compression than tension, tensile stresses have a tendency to manipulate PCC pavement design.
- Therefore, slab curling calculations are seeking for to discover the factors of most tensile strain because the slab curls because of temperature gradients within. In 1935, measurements said via way of means of Teller and Southerland of the Bureau of Public Roads confirmed that the most temperature differential (hence, most curling and most tensile stresses) is a lot large at some stage in the day than at some stage in the night. Therefore, the sunlight hours curling stresses are typically maximum limiting.
Q14) Write a note on Jointed Plain Concrete Pavement
A14)
Because of their cost-effectiveness and reliability, the vast majority of concrete pavements constructed today are JPCP designs.
They do not contain reinforcement.
They have transverse joints generally spaced less than 5 to 6.5 m apart.
They may contain dowel bars across the transverse joints to transfer traffic loads across slabs and may contain tie bars across longitudinal joints to promote aggregate interlock between slabs.
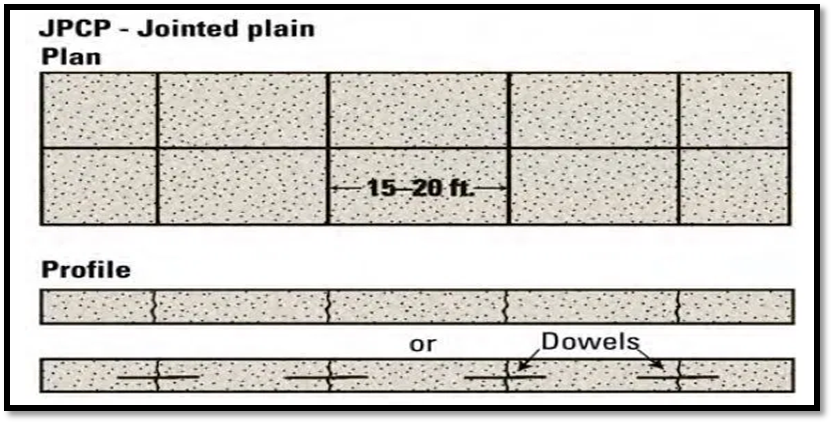
Fig.: Jointed Plain Concrete Pavement
Q15) What is Jointed Reinforced Concrete Pavement
A15)
Although reinforcements do not improve the structural capacity significantly, they can drastically increase the joint spacing to 10 to 30m.
Dowel bars are required for load transfer.
Reinforcement’s help to keep the slab together even after cracks.
The reinforcement, distributed throughout the slab, composes about 0.15 to 0.25 percent of the cross-sectional area and is designed to hold tightly together any transverse cracks that develop in the slab.
It is difficult to ensure that joints are cut where the reinforcement has been discontinued.
This pavement type is not as common as it once was on State highways, but it is used to some extent by municipalities.
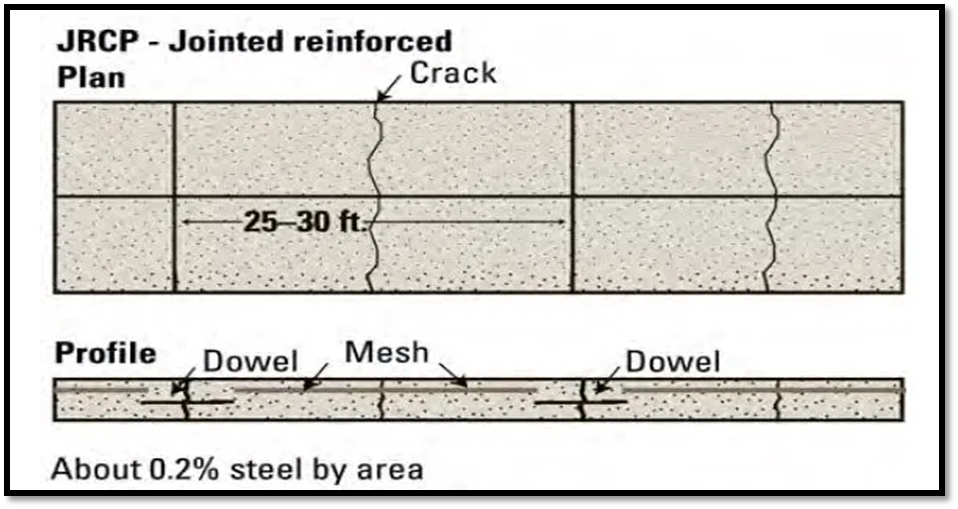
Fig.: Jointed Reinforced Concrete Pavement
Q16) What is Continuous Reinforced Concrete Pavement?
A16)
CRCP designs have no transverse joints, but contain a significant amount of longitudinal reinforcement, typically 0.6 to 0.8 percent of the cross-sectional area.
Transverse reinforcement is often used.
The high content of reinforcement both influences the development of transverse cracks within an acceptable spacing (about 0.9 to 2.5 m apart) and serves to hold cracks tightly together.
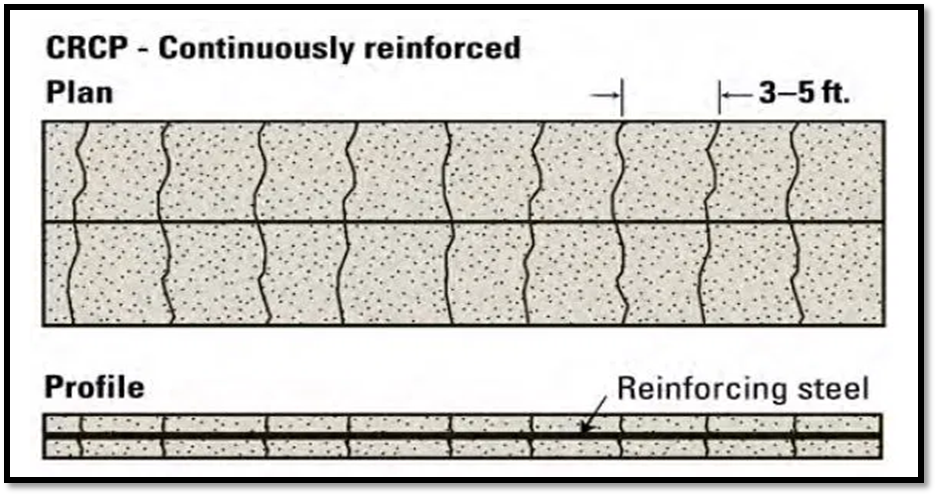
Fig.: Continuous Reinforced Concrete Pavement
Q17) What is periodic maintenance?
A17)
Periodic maintenance
- Since all kinds of motorway are uncovered to the unfavourable weather circumstance and transferring traffic, they might definitely put on out. Thus for economy, they want renovation earlier than similarly deterioration.
- Routine street renovation works are typically non-structural in nature and are supposed to increase the existence of the pavement, to beautify the overall performance and to lessen consumer delays in street use e.g. Re-graveling of unpaved roads, resealing (with floor dressing, extremely skinny asphalt, etc.) of paved roads, and re-graveling of shoulders.
- Non-preventive renovation also can be defined as ordinary, recurrent and pressing in which ordinary refers to the “fixed-cost” sports consisting of grass cutting, drainage renovation and street signal renovation; in conjunction with sports required in the course of the 12 months consisting of pothole patching, crack sealing, and grading, and pressing to the restore of defects resulting from disasters (e.g., floods) or accidents.
- Under this class of preservation usually following works are carried out:
Up hold of carriage way
Maintenance of aspect drains as clearing of silt and preserve right slope.
Maintain of shoulders and sub grade.
Of different ancillary paintings together with bridge etc
Improvement of motorway geometric and visitors controls etc.
Q18) Write a note Urgent Maintenance / Emergency Highway Repairs
A18)
- It is one of the styles of toll road renovation wherein unique maintenance are accomplished for unique issues and while arise because of the failure of pavements. Sometimes maintenance are wanted for a few sub floor drainage machine and move structures. Urgent maintenance are required to hold the highways open, guard assets and street users.
- Adequate toll road drainage machine need to be supplied that has a layout glide that might closing for the existence time of the assignment. On the Ring Road Hayatabad Peshawar, there's no such provision, which at times, purpose the water desk to upward push up and have an effect on the pavement foundations.
- Also the place contains of area and crop lands, so the water enter is extra which wishes to be removed, in any other case it will likely be risk to the sub grade. Proper sloping need to be supplied on the street floor which will cast off the rain water efficiently.
- Material of use need to be withinside the close by of the assignment place, in order that there need to be no put off in creation period. To make certain that the cloth attain to the web page withinside the time while wished and neither in advance nor later than that. In case of asphalting, the temperature on the time of the laying of cloth need to be inside limits and accordance to the standards.
Q19) What are earthen roads?
A19)
- An earth street is the most inexpensive sort of street organized from herbal soil. The pavement segment is definitely created from regionally to be had soil. These roads require very steep camber ranging among 1 in 25 and 1 in 33 to empty off the rain water fast from the pavement surface.
- These roads are commonly built with normal soil or stabilized soil. In our country, those roads are roads built as village roads. Gravel Road Gravel roads are built with one or compacted layers of gravel combined with sand and clay. The camber can be among 1 in 25 and 1 in 30. These roads are taken into consideration higher than the earth roads as they could deliver heavier traffic. These roads are taken into consideration low-value roads. These roads are commonly built as village roads and different district roads.
Types of Earthen Road
a) Ordinary Earthen Road: The earthen street whose basis and the carrying floor includes one or greater compacted layers of herbal soil to be had alongside its alignment is an everyday earthen street. The floor of this sort of form of street is normally dusty and ruts are fashioned quickly.
b) Stabilized Earthen Road: The avenue whose basis and the sporting floor are made from one or greater compacted layers of stabilized soil ( Stabilized with physical, chemical, or organic marketers to boom electricity and durability) is Stabilized Earthen Road. It consists of more traffic, load and additionally offers higher provider compared to regular earthen roads. 1.2. Materials Required The cloth required for the earthen avenue is well-graded soil with a liquid restriction of much less than 35% and a plasticity index of 4-10%.
Q20) Write a note on WBM road?
A20)
Water Bound Macadam (WBM)
- Water bound macadam road is a road in which the wearing course consists of clean crushed aggregates which are mechanically interlocked by rolling. These aggregates bound together with filler material and water laid on a well-compacted base course.
- Water bound macadam road is the most commonly used road construction procedure for over more than 190 years and in the first phase in most of the road projects, water-bound macadam road is constructed, and the surfacing is done with the premix carpet bituminous macadam or cement concrete.
Materials for water bound macadam road
- Coarse Aggregate
- Screenings (Filler Material)
- Binding Material
- Coarse aggregate:
Coarse aggregates consist of a mixture of hard and durable crushed aggregates and broken stones, and aggregate should be properly graded for each layer of the WBM road construction.
It should be hard and durable.
The coarse aggregate should be free from elongated particles and flaky particles.
2. Screenings: (filler material)
Screenings are the material that is used up to fill up the excess voids present in the compacted layer of course aggregate and these materials are the aggregates of a smaller size than the coarse aggregates.
3. Binding material
Binding material should be properly approved by engineer and it should have a plasticity index value less than 6 for the construction of water bound macadam road.
Construction procedure of water bound macadam road
There are the following steps in the construction procedure of WBM road as given below;
Preparation of foundation for WBM road
For the required grade and camber of WBM road, the subgrade or base course is properly prepared and the potholes and the depressions on the surface of the road is properly filled up & compacted.
Provision for lateral confinement
The shoulders having a thickness as that of compacted WBM layer should be constructed before laying of aggregates and with the proper quality of earth, they should be constructed.
The purpose of constructing shoulders is that the road surface to be constructed retains in between them and for the further laying of course aggregates, it becomes easy.
Spreading of coarse aggregates
After the construction of the shoulders, the coarse aggregates are uniformly spread on the prepared base and the total number of layers and thickness of water bound macadam road depends upon the details of pavement design.
Single-layer of compacted thickness 75 mm may be sufficient for ordinary roads and 2 layers of 150 mm each compacted thickness may be provided for special roads.
Rolling operation
For compacting the coarse aggregates, the rolling operation is carried out and it is done with the help of vibratory rollers or with the help of 3-wheeled power rollers weighing 6 to 10 tones.
For driving the rollers, skilled operators should be used because the fault rolling operations cause the formation of corrugations, the unequal finish of road surface, etc.
Application of screenings
The screenings are applied to properly fill the voids remained after the rolling operation is properly finished and in 3 or more layers as per the site conditions screening may be applied.
For each layer of screenings, compaction is carried out with the help of dry rollers, and to remove the un compacted screening material, brooming of each layer should be properly done after compaction.
The sprinkling of water and grouting
The road surface is properly sprinkled with plenty of water after the application of screening and brooming is done to sweep the wet screening properly into the voids after the water is sprinkled.
Application of binding material
As screenings, the same procedure is used in this step and rolling operation is carried out after each layer of water is sprinkled.
To washout, the binding material that gets stuck to the wheels of the rollers, the wheels of the roller should be constantly watered at the time of rolling operation.
Setting and drying of surface
The road is allowed to cure or set over-night after the final rolling operation and the next day again sufficient amount of screenings or binding materials can be used and compaction is done if the depressions or voids are visible.
Preparation of shoulders
The shoulders are constructed alongside by filling earth to specified cross slope at the time of the curing of the road and compacted properly.
Open for traffic
The road is then made open for traffic after proper drying and without any depressions. By placing obstacles longitudinally in the form of drums, barricades, etc the traffic should be well distributed over the full width of the road.
Maintenance of WBM road
- By the period of time when the potholes and ruts occur on the road, they should be filled with adequate materials and properly compacted.
- By means of dragging, the corrugations that occurred on the roads should be removed and by fresh materials, broken materials of the roads should be properly restored.
- In 2-5 years or based according to the traffic volume, the surface of the road should be renewed.
- The loose aggregates start coming on the top of the surface of the road so they should be removed and leveled surface should be added by fresh binding material.
Q21) Give advantages and disadvantages of WBM road.
A21)
Advantages of water bound macadam road
There are the following advantages of water bound macadam road such as;
- The construction cost is comparatively low in WBM road.
- No skilled laborers are required in the construction of WBM road.
- From locally available materials they are constructed.
- It can resist a load of traffic of about 900 tons per lane per day if these roads are maintained properly and from time to time.
Disadvantages of water bound macadam road
There are also some disadvantages of water bound macadam road such as;
- There is a high cost for maintenance on this road.
- There is a very less overall life span of these roads.
- The WBM roads can cause inconvenience and danger to traffic if they are not properly maintained.
- It leads to softening and yielding of subsoil because WBM roads are permeable to rainwater.