Unit - 4
Traffic Engineering
Q1) Define traffic engineering.
A1)
- Traffic engineering is a department of civil engineering that makes use of engineering strategies to acquire the secure and green motion of humans and items on roadways.
- It focuses in particular on studies for secure and green visitors’ flow, which include street geometry, sidewalks and crosswalks, biking infrastructure, visitor’s signs, street floor markings and visitors lights.
- Traffic engineering offers with the purposeful a part of transportation system, besides the infrastructures provided.
- Traffic on roads includes avenue customers consisting of pedestrians, ridden or herded animals, vehicles, streetcars, buses and different conveyances, both singly or together, even as the usage of the general public manner for functions of travel.
Q2) What are road user characteristics?
A2)
Road User Characteristics
a) Physical Characteristics: vision, hearing, strength, fatigue, illness can reduce alertness and general reaction to traffic situations can affect quality of judgment and increase the reaction time
b) Mental Characteristics: knowledge, skill, intelligence, experience
c) Psychological Characteristics: attentiveness, fear, anger, superstition, impatience
d) Environmental Factors: traffic stream characteristics, atmospheric & weather conditions, locality
Q3) What are drivers characteristics?
A3)
Drivers Characteristics:
- Skilled
One of the maximum vital traits of an awesome motive force is that she or he must be professional sufficient to address any scenario on the street. A right motive force must have the competencies to manipulate the automobile in each scenario.
2. Knowledge
Skills aren't the best that an awesome motive force possesses. He or she must additionally have right and entire information approximately all of the essential policies of the street. A right motive force additionally has information approximately his or her automobile.
3. Self Discipline
It could be very smooth to propose different human beings to force as in step with policies however a being in self-control even as riding is one of the first-rate traits of an awesome motive force. Maybe crossing a crimson mild makes you appearance cool for a while however additionally places your lifestyles in chance even as on road.
4. Patience
Whenever you're on the street, it isn't always a race who gets domestic or to paintings first, due to the fact all people has a distinct destination. Hence, being affected person is the first-rate and essential best of an awesome motive force.
5. Alertness
Not all people is a superb motive force like you, there are numerous human beings on the street who aren't like you. Hence, being an awesome motive force, you have to be truely alert all of the time on the street for the protection of yourself and those like you.
6. Mechanical Skills
Well, now no longer like a expert mechanic however an awesome motive force must understand the primary mechanical competencies so that once the want arises, he or she will troubleshoot the primary problems of his or her automobile.
7. Responsible
One of the maximum vital traits of an awesome motive force is that she or he is accountable. You will now no longer constantly be visiting by myself withinside the automobile. Hence, it's miles very vital to be accountable and cope with the human beings visiting with you.
8. Enough Practice
Practice makes a person best that's the purpose why you must have sufficient to be an awesome motive force. Also, the extra you practice, you may get extra used to the conditions on the street.
9. Care for automobile
Being an awesome motive force additionally includes looking after the automobile one is riding. This way preserving a test at the well timed servicing of the automobile at the side of gasoline consumption.
10. Fitness
Fitness is likewise one of the vital traits of an awesome motive force. If someone is match to force, then best she or he is furnished a license to force a automobile, irrespective of which automobile it's miles.
Q4) What are vehicular characteristics?
A4)
Vehicular Characteristics
a) Static Characteristics: dimension, weight, maximum turning angle
- Maximum Dimensions of Road Vehicles
Height of driver’s seat: affects the visibility distance
Maximum width = 2.5m
Maximum height: affects the clearance of overhead structures
a) Single decked vehicles = 3.8m
b) Double decked vehicles = 4.75m
Maximum length: affects capacity, overtaking distance and maneuverability
a) Singe unit truck with two or more axles = 11m
b) Singe unit bus with two or more axles = 12m
c) Semi-trailer tractor combinations = 16m
d) Tractor and trailer combinations = 18m
- Weight of Loaded Vehicles
Weight of loaded vehicles affects the design of pavement thickness and its gradient.
- Power of Vehicles
This governs the permissible and limiting gradients on road.
- Minimum Turning Radius of Vehicles
This depends upon the length of wheel base and features of the steering system.
This affects the design of sharp curves so as to negotiate vehicles at slow speeds.
b) Dynamic Characteristics: speed, acceleration
Speed & acceleration of the vehicle depend on power of the engine and the resistances to be overcome.
The stability of the vehicle and its safe movement on horizontal curves are affected by the width of wheel base and the height of C.G. Of the vehicle.
Braking Test is conducted to measure the skid resistance of pavement surface.
At least two of the three measurements are needed during braking test in order to determine the skid resistance of the pavement:
- Braking distance, L (m)
- Initial speed, u (m/s)
- Actual duration of brake application, t (s)
Related formulae:
- f =
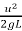 =
= 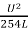 where,
where,
f = skid resistance
u = initial speed in m/s
U = initial speed in kmph
Ii. v – u = at where,
u = initial speed in m/s
v = final speed in m/s
a = acceleration in m/s2
t = time in sec
But, v = 0 since brakes are applied and vehicle is brought to a halt. Also, u > v since initial speed of the vehicle is not zero.
Therefore, we can say that, u = at
Iii. v2 – u2 = 2as where,
u = initial speed in m/s
v = final speed in m/s
a = acceleration in m/s2
s = distance in m
But, v = 0 since brakes are applied and vehicle is brought to a halt. Also, u > v since initial speed of the vehicle is not zero.
Therefore, we can say that, u2 = 2as
But, from previous relation, u = at
Therefore, a2t2 = 2as
Ora = 2s/t2
Iv. F = ma where,
F = Force in kg-m/s2
m = mass in kg
a = acceleration in m/s2
The above equation can be written as follows:
f.w =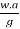
Therefore, f = where,
where,
f = coefficient of friction
w = weight in kg
a = acceleration in m/s2
g = acceleration due to gravity in m/s2
Q5) What is traffic volume study?
A5)
- It is the number of vehicles crossing a section of road per unit time at any selected period
- Expressed as vehicles/day or vehicles/hour
- Generally accepted as a true measure of relative importance of roads and in deciding the priority for improvement and expansion
- Used in planning, traffic operations and control of existing as well as new facilities
- Used in the analysis of traffic patterns and trends
- Used in geometric & structural design of pavements and in computing roadway capacity
- Pedestrian traffic volume studies help in planning sidewalks, crosswalks, subways and pedestrian signals
Q6) What are the methods for traffic volume counts?
A6)
Methods for Traffic Volume Counts
- Manual counts: It is done by employing a field team to record traffic volume on prescribed record sheets
- Mechanical counters: Pneumatic hose, magnetic detector and radar detectors can be used to work throughout day and night for the desired period. However, this method does not allow segregation of traffic in to various classes of traffic in the stream and the details of traffic movements.
Presentation of Traffic Volume Data
- Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT): helps in deciding the relative importance of a route and in phasing the road development program
AADT = 
2. Trend Charts: showing volume trends over a period of years
3. Variation Charts: showing hourly, daily and seasonal variations in traffic
4. Traffic Flow Maps: help to find the traffic volume distribution along existing roads at a glance
5. Volume Flow Diagrams: traffic volume diagrams needed for design of intersections
6. Thirtieth Highest Hourly Volume: hourly volume that will be exceeded only 29 times in a year; used as hourly volume for design
Q7) What is speed study?
A7)
- Travel time: reciprocal of speed and a simple measure of how well a road network is operating
- Spot speed: instantaneous speed of a vehicle at a specified section or location
- Average speed: average of spot speeds of all vehicles passing a given point on the highway
- Space mean speed: represents average speed of vehicles in a certain road length at any time
Vs = 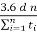
Where, Vs = space mean speed (kmph)
d = length of road (m)
n = number of individual vehicle operations
ti = observed travel time (sec) for ith vehicle to travel distance d
The average travel time of all vehicles is obtained from the reciprocal of space mean speed.
5. Time mean speed: represents the speed distribution of vehicles at a point on the roadway and it is the average of instantaneous speed of observed vehicles at the spot
Vt = 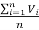
Where, Vt = time mean speed (kmph)
n = number of individual vehicle operations
Vi = observed instantaneous speed ofith vehicle (kmph)
6. Running speed: average speed maintained by a vehicle over a particular stretch of road while the vehicle is in motion
7. Overall speed or Travel speed: effective speed with which a vehicle traverses a particular route between two terminals
There are two types of speed studies carried out:
a) Spot Speed Study
b) Speed & Delay Study
Q8) Write a note on Spot Speed Study
A8)
Uses:
- In planning traffic control and in traffic regulations
- In geometric design
- In accident studies
- To study traffic capacity
Factors affecting spot speeds:
- Physical features of the road like pavement width, curve, sight distance, gradient and roadside developments
- Environmental conditions
- Enforcement
- Traffic conditions
- Driver, vehicle and motive of travel
Instruments used for finding spot speeds:
- Enoscope
- Radar speedometer
- Graphic recorder
- Electronic meter
- Photo-electric meter
Presentation of spot speed data:
a) Average speed of vehicles
- Frequency distribution tables are prepared by arranging the data
- Tables give general information of the speeds distribution pattern
b) Cumulative speed of vehicles
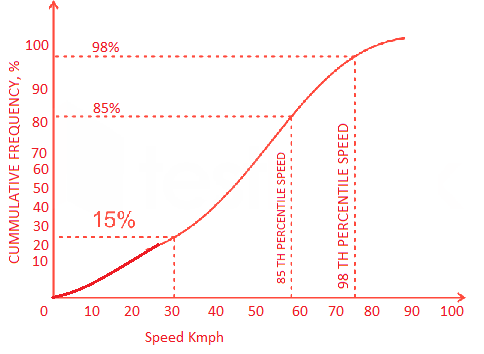
- 85th percentile speed is the speed at or below which 85% of the vehicles are passing the point on the highway. 15% of the vehicles exceed the speed at that spot. 85th percentile speed is also known as safe speed limit.
- 98th percentile speed is taken for the purpose of highway geometric design.
- 15th percentile speed represents the lower speed limit if it is desired to prohibit slow moving vehicles to decrease delay and congestion.
c) Modal Average
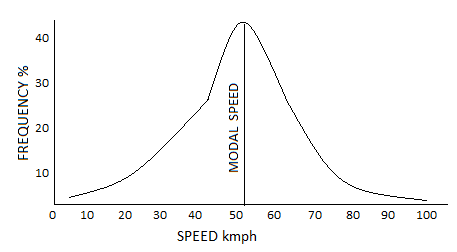
- Frequency distribution curve is plotted depicting the free flow of vehicles
Q9) Write a note on Speed & Delay Study
A9)
Uses:
- Give the running speeds, overall speeds, fluctuations in speeds and delay between two stations of a road spaced far apart
- Give information such as amount, location, duration, frequency and causes of delay in the traffic stream
- Help to find the travel time and in benefit cost analysis
Types of delays:
- Fixed delay: occurs primarily at intersections due to traffic signals and at level crossings
- Operational delay: caused by interference of traffic movements such as turning vehicles, parking &unparking vehicles etc and by internal friction in traffic stream due to high traffic volume, insufficient capacity etc
Methods for carrying out speed & delay study:
- Floating Car Method
- A test vehicle is driven over a given course of travel at approximately the average speed of the stream.
- Detailed information is obtained concerning all phases of speed and delay including location, duration and causes of delay.
q = 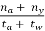
Where, q = flow of vehicles in one direction of the stream (volume per min)
na = average number of vehicles counted in the direction of the stream when the test vehicle travels in the opposite direction
ny = average number of vehicles overtaking the test vehicle when the test vehicle travels in the same direction
ta = average journey time when the test vehicle travels in the opposite direction as the stream (mins)
tw = average journey time when the test vehicle travels in the same direction as the stream (mins)
2. License Plate or Vehicle Number Method
- This method does not give important details such as causes of delay and duration etc.
3. Interview Technique
4. Elevated Photography & Observation Technique
Q10) What is O-D study?
A10)
Origin & Destination Study
Uses:
- To plan the road network and other facilities for vehicular traffic
- To plan the schedule of different modes of transportation for trip demand of commuters
- To judge the adequacy of existing routes and to use in planning new network of roads
- To locate expressways and major routes along the desire lines
- To establish preferential routes for various categories of vehicles
- To locate the intermediate stops of public transport
Methods of O&D Study:
- Roadside Interview Method
- Quick collection of data, simple method and team can be trained quickly
- Main drawback is that delays occur when vehicles are stopped for interview and it may even lead to resentment of the driver and passengers
2. License Plate Method
- Easy and quick method when the area under consideration is quite small
- Involves a lot of office compilations in tracing the trips through a network of stations
3. Return Post-card Method
- Suitable where traffic is heavy
4. Tag on car Method
- Suitable where traffic is heavy
- Pre-coded card is stuck on the vehicle to give information at the points of entry and exit into an area, thus indicating the time taken to traverse the area
5. Home Interview Method
- Additional data including socio-economic details etc may be collected so as to be useful for forecasting traffic & transportation growth
6. Work Spot Interview Method
- Involves collection of O&D data at work spots (offices, factories, educational institutions etc) by personal interviews
Q11) Write a note on on-street parking.
A11)
On-street or Kerb Parking
- Angle parking or parallel parking may be allowed on the kerb.
- Angle parking may be at angles 30ᵒ, 45ᵒ, 60ᵒ and 90ᵒ.
- Angle parking accommodates more number of vehicles per unit length of the kerb. Maximum parking capacity is achieved when vehicles are parked at 90ᵒ.
- Larger width of road is required for parking & un-parking operations, in case of angle parking. The requirement for larger width increases with increase in parking angle reaching maximum at 90ᵒ.
- Angle parking is more convenient but it also produces obstruction to the through-traffic. Therefore 45ᵒ angle parking is considered best from all considerations.
- Parallel parking is preferred when width of kerb parking space and the width of street are limited. But the parking and un-parking operations are more difficult and require many forward and reverse movements of the vehicle.
- Number of Spaces (N) available for parking for kerb length (L):
Parallel parking with equal spacing facing the same direction | 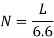 |
Parallel parking when two cars are placed closely | 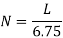 |
30ᵒ angle parking | 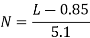 |
45ᵒ angle parking | 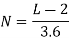 |
60ᵒ angle parking | 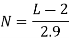 |
90ᵒ angle parking | 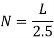 |
Q12) What is off-street parking?
A12)
Off-street Parking
- When parking facilities are provided at a separate place away from the kerb, it is known as off-street parking.
- Main advantage of this method is that there is no undue congestion and delay on the road.
- Main disadvantage is that the driver/passengers will have to walk greater distances after parking the vehicle as these parking facilities cannot be provided at very close intervals due to space unavailability.
- Two basic types of off-street parking facilities are:
- Parking Lots
Convenient where sufficient space is available at low costs.
May be self-parking system or attendant-parking system.
2. Multi-storey Parking Garages
Constructed where floor space is less and costly.
Q13) What is accident study?
A13)
Accidental Study
Various objectives of accident studies may be listed as:
- To study the causes of accidents & suggest corrective measures at potential locations
- To evaluate existing designs
- To support proposed designs
- To carry out before and after studies and to demonstrate improvement in the problem
- To give economic justification of the suggested improvements
Four basic elements of traffic accident are:
- Road users
- Vehicles
- Road and its conditions
- Environmental factors – traffic, weather etc
Q14) Write a note on Maintenance of Accident Records
A14)
- Location files: useful to keep a check on the location of accident and to identify points of high accident incidence
- Spot maps: show accidents by spots, pins or symbols on the map of the affected area
- Condition diagram: drawing to scale showing all the important physical conditions of an accident location, including roadway limits, kerb lines, bridges, culverts, trees, signs, signals etc
- Collision diagram: diagram showing the approximate path of vehicles and pedestrians involved in accidents in order to compare the accident pattern before and after the remedial measures have been taken
Measures for reduction in accident rates:
- Engineering
- Road design
- Preventive maintenance of vehicles
- Before and after studies
- Road lighting
2. Enforcement
- Speed control
- Traffic control devices (signs, signals, markings, channelizing islands etc)
- Training & supervision
- Medical Check
- Observance of law & regulations
3. Education
- Education of road users
- Safety drive
Q15) What is traffic safety?
A15)
- Road visitors protection refers back to the techniques and measures used to save you street customers from being killed or severely injured.
- The 1/3 stage is set lowering the crash hazard which entails making use of the street-layout requirements and guidelines (together with from AASHTO), enhancing driving force conduct and enforcement.
- Road visitors protection refers back to the techniques and measures used to save you street customers from being killed or significantly injured. Typical street customers encompass pedestrians, cyclists, motorists, automobile passengers, horse riders, and passengers of on-street public transport (specifically buses and trams).
- Best practices in current street protection method: The primary method of a Safe System method is to make certain that withinside the occasion of a crash, the effect energies stay underneath the brink probable to provide both demise or extreme harm.
- This threshold will range from crash situation to crash situation, relying upon the extent of safety presented to the street customers involved. For example, the probabilities of survival for an unprotected pedestrian hit via way of means of a automobile decrease unexpectedly at speeds more than 30 km/h, while for a well limited motor automobile occupant the important effect pace is 50 km/h (for facet effect crashes) and 70 km/h (for head-on crashes).
- International Transport Forum, Towards Zero, Ambitious Road Safety Targets and the Safe System Approach, Executive Summary web page 19
- As sustainable answers for training of street protection have now no longer been identified, specially low-visitors rural and far off roads, a hierarchy of manage have to be applied, much like classifications used to enhance occupational protection and health.
- At the very best stage is sustainable prevention of significant harm and demise crashes, with sustainable requiring all key end result regions to be considered. At the second one stage is real-time chance reduction, which includes supplying customers at excessive chance with a particular caution to allow them to take mitigating action.
- The 1/3 stage is ready lowering the crash chance which includes making use of the street-layout requirements and guidelines (along with from AASHTO), enhancing driving force conduct and enforcement.
- Traffic protection has been studied as a technological know-how for extra than seventy five years
Q16) Write a note on Causes and types of accident
A16)
- Distracted Driving: Drivers which have their interest diverted to distractions are much more likely to motive accidents.
- Texting-While-Driving.
- Drowsy Driving.
- Drugged Driving.
- Drunk Driving.
- Speeding.
- Reckless Driving.
CAUSES OF CAR ACCIDENTS
- Common reasons of vehicle injuries consist of: Distracted Driving Drivers which have their interest diverted to distractions are much more likely to reason injuries.
- Driving distractions might also additionally consist of: Eating/drinking, talking, brushing hair or setting on makeup, studying books/maps, the use of GPS devices, looking videos, tuning radios.
- Texting-While-Driving Drivers who're texting on a mobileular telecell smart phone have each their fingers and eyes distracted from the road. You are 23 instances much more likely to get right into a crash while you are texting even as using than you'll be in case you had been using with out a distraction.
- Drowsy Driving Drivers who don’t get sufficient sleep are extra prone to inflicting injuries. The frame calls for relaxation with the intention to continue to be alert and feature a quick sufficient response time to save you an accident.
- Drowsy using injuries are each not unusualplace and dangerous. Drugged Driving Drivers below the have an effect on of any drug that impairs one’s motor skills, response time, or judgment have a better chance of inflicting injuries. Drugged using is a hazard to the protection of motorists and is taken into consideration to be negligence.
- Drunk Driving Drunk using, like drugged using, is a not unusualplace reason of vehicle injuries. If one’s thoughts is impaired, their capacity to pressure additionally turns into impaired.
- Drunk using crashes have a terrible effect on sufferers and their families.
- Speeding Speeding reasons injuries due to the fact rushing drivers frequently don’t have sufficient time to forestall or keep away from a collision. Speed limits are in region to preserve drivers secure and decrease the chance of injuries.
- Drivers who velocity are using recklessly. Reckless Driving Reckless using can consist of rushing, jogging lights, failing to yield, weaving, tailgating, racing, or different negligent movements even as using.
- Reckless using places different drivers at chance and is a not unusualplace reason of vehicle injuries.
Q17) What are the types of car accidents?
A17)
Common kinds of vehicle injuries consist of:
- Head-on Collisions Negligence commonly performs a function in head-on collisions. These kinds of collisions are some of the maximum devastating.
- Highway Construction Accidents: Construction corporations have a obligation to now no longer reason injuries. Other drivers must pressure extra cautiously in toll road creation areas.
- Intersection Accidents: Accidents at intersections are commonly brought about due to the fact a person made a using error, which will be attributed to negligence.
- Interstate Accidents: Accidents at the interstate may be extra severe because of the speeds at which the automobiles are traveling.
- Rear-End Accidents: Rear-cease injuries are some of the maximum not unusualplace kinds of injuries, and that they often reason whiplash.
- Side-Impact Accidents: Side-effect injuries also are not unusualplace, and commonly arise at intersections. They can reason extra accidents relying on in which the auto become hit.
Q18) Give the use of intelligent transportation system
A18)
- A wise transportation system (ITS) is a sophisticated software which targets to offer revolutionary offerings regarding one-of-a-kind modes of shipping and site visitors control and allow customers to be higher knowledgeable and make safer, greater coordinated, and 'smarter' use of shipping networks.
- A shrewd transportation system (ITS) is a sophisticated utility which goals to offer progressive offerings referring to unique modes of delivery and visitors control and permit customers to be higher knowledgeable and make safer, greater coordinated, and 'smarter' use of delivery networks. Some of those technology encompass calling for emergency offerings whilst a coincidence occurs, the use of cameras to implement visitors legal guidelines or symptoms and symptoms that mark velocity restriction adjustments relying on conditions.
- Although ITS might also additionally confer with all modes of delivery, the directive of the European Union 2010/40/EU, made on July 7, 2010, described ITS as structures wherein facts and conversation technology are implemented withinside the area of avenue delivery, which include infrastructure, motors and customers, and in visitors control and mobility control, in addition to for interfaces with different modes of delivery.
- ITS might also additionally enhance the performance and protection of delivery in some of situations, i.e. avenue delivery, visitors control, mobility, etc.
- ITS generation is being followed internationally to boom capability of busy roads and decrease adventure times