UNIT 2
Question Bank
Q1- Define Corrosion.
A- The destruction of metal by chemical or electrochemical attack of environment this process starting at the surface of metal known as corrosion. Corrosion is the twostep process that requires three things i.e., a metallic surface, an electrolyte and oxygen.
Q2- Write down the consequences of corrosion?
A- Corrosion has many consequences on economic, health, safety, to our society.
Economic Effects: To determine the economic cost on the country’s economy there are several studies conducted by different country. Among all the most extensive study was carried out by United State in 1975 and gathered that it cost about $70 billion.
Health Effects: Recent years have seen an increasing use of metal prosthetic devices in the body, such as pins, plates, hip joints, pacemakers, and other implants. New alloys and better techniques of implantation have been developed, but corrosion continues to create problems. E.g.- inflammation caused by corrosion products in the tissue around implants, fracture of weight-bearing prosthetic devices.
Technological effects: Technology sector is also very badly affected by the corrosion. A great deal of the development of new technology is held back by corrosion problems because material is required to withstand in many cases simultaneously higher temperature, higher pressure. Corrosion problems that are less difficult to solve affect solar energy systems, which require alloys to withstand hot circulating heat transfer fluids for long periods of time, and geothermal systems, which require materials to withstand highly concentrated solutions of corrosive salts at high temperatures and pressures.
Q3- Write down the major factors responsible for corrosion.
A-
(i)Nature of metal
(ii)Potential Difference
(iii)Purity of metal
(iv)Relative areas of cathode and anode parts
(v)Nature of corrosion Product
(vi)Temperature
(vii)Presence of moisture
(viii)Effect of pH
(ix)Concentration of electrolytes
(x)Over Voltage
Q4- Write down the difference between EMF series and Galvanic Series.
A- EMF series and galvanic series
EMF series | Galvanic series |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q5- Write down the different type of oxide layers.
A- 4 types of oxide layers: -
Porous oxide layer (non – protective)
Non – porous oxide layer (protective)
Unstable oxide layer
Volatile oxide layer
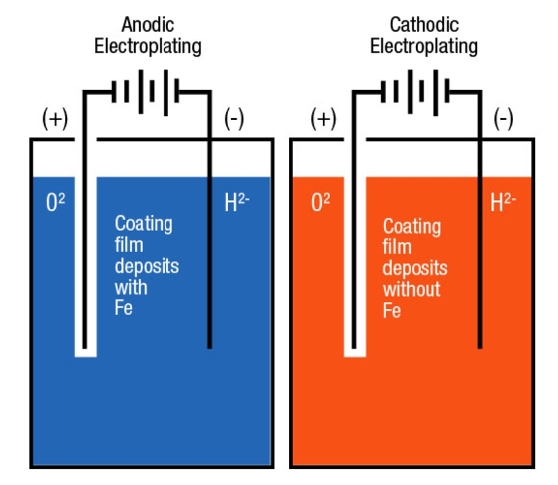
Q6- What are anodic and cathodic coatings? Explain with diagram.
A- Anodic coating: -
Coating metal is higher placed than the base metal then it is called as anodic coatings.
e.g.: -galvanizing
Cathodic coatings: -
If coating metal is lower placed in galvanic series than base metal then it is called as tinning.
Methods of applying metallic coatings: -
- Hot dipping
- Electroplating
- Cementation’
- Metal cladding