Unit - 3
Question Bank
Q1- What are the different parts of cement on the basis of classification?
A- There are 4 types of cement on the basis of classification:
(i) Natural Cement
(ii) Puzzolona Cement
(iii) Slag Cement
(iv) Portland Cement
Q2-Define Portland Cement. Explain its composition.
A- Hydraulic cement produced by pulverizing clinkers that consists of calcium silicate, usually containing one or more of the forms of calcium sulfate as a inter ground station. A good sample of Portland cement consists of:
(i) Silica(SiO2): - 20-24%
(ii) Calcium Oxide: -60-70%
(iii) Alumina (Al2O3): -5-7%
(iv) Magnesia(MgO): -2-3%
(v) Ferric Oxide (Fe2O3): -1-2.5%
(vi) Sulphur trioxide (SO3): -1-1.5%
(vii) Sulphur Oxide: -1%
(viii) Potassium Oxide (K2O): -1%
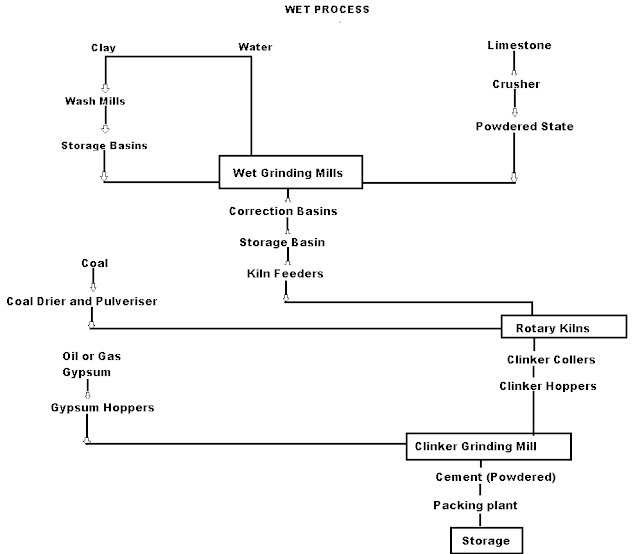
Q3 -Make a flow chart of Wet Process Cement Manufacturing.
A- On using the calcareous as a raw material then chalk must be crushed into minute particles and hence dispersed it in water in a wash mill. Wash mill used to break the solid materials into lumps/slurry. In similar wash mill clay is also broken up and mixed with water. Then this slurry is stored in the silo called as slurry silo where it is consistently stirred. The composition of raw material is checked again and if required corrected by adding clay or chalk materials as per requirement.
Q4 -Mention the role of Tricalcium Aluminate and Tetracalcium Aluminoferrite.
A-
Tricalcium Aluminate
- It turns out higher heat of hydration and contributes to faster gain in strength.
- Cements with low Tricalcium Aluminate contents usually generate less heat, develop higher strengths and show greater resistance to sulfate attacks.
- It has high heat generation and reactive with soils and water containing moderate to high sulfate concentrations so it’s least desirable.
Tetracalcium Aluminoferrite
- Assist in the manufacture of Portland Cement by allowing lower clinkering temperature.
- Tetra calcium Aluminoferrite act as a filler
- Contributes very little strength of concrete eventhough it hydrates very rapidly.
Q5 -Write down the function of gypsum cement.
A-Function of gypsum in cement :-
Tri calcium aluminate combines with water very rapidly.

After the initial setting, the paste becomes soft and the added gypsum retards the dissolution of tri calcium aluminate by forming insoluble calcium sulpho aluminate.
Q6 -Write down the factors which effects the Heat of Hydration.
A-
(i) According to the requirement the material selection should be done.
(ii) Cements with higher tricalcium silicate, tricalcium aluminate influence the rate of heat generation.
(iii) The cement content, water-cement ratio, placing and curing temperature.
(iv) The higher cement content generates more heat.
Q7-What are the different types of cement?
A-There are major thirteen types of cements:
(i) Ordinary Portland Cement
(ii) Portland Pozzolana Cement
(iii) Rapid hardening cement
(iv) Quick Setting Cement
(v) Low Heat Cement
(vi) Sulfates Resisting Cement
(vii) Blast Furnace Slag Cement
(viii) High Alumina Cement
(ix) White Cement
(x) Colored Cement
(xi) Air Entraining Cement
(xii) Expansive Cement
(xiii) Hydrographic Cement
Q8- Explain Rapid Hardening Cement and Portland Pozzolana Cement.
A-Portland Pozzolana Cement: This cement is prepared by grinding pozzolanic clinker with Portland cement. It can also be produced by the mixing up of pozzolana with gypsum or calcium sulfate. It is used in marine structures, seawage works, laying underwater concrete etc.
Rapid Hardening Cement: This cement is used in concrete where formworks are removed at an early stage and are similar to ordinary Portland cement. This cement has increased lime content. The strength of rapid hardening cement at three days is similar to 7 days strength of OPC with the same water cement ratio. Hence, it increases the rate of construction with decreasing the cost of construction by saving formwork cost.
Q9-What are the advantages of Ready Mix Concrete?
A-Advantage of Ready Mix Concrete:
(i) Ready Mix Concrete (RMC) allows speedy construction through programmed delivery at site.
(ii) RMC reduces the labour cost and site supervising cost.
(iii) RMC comes with consistency in quality through accurate & computerized control of sand aggregates and water as per mix designs.
(iv) Production of RMC helps in minimizing cement wastage due to bulk handling.
(v) Production of RMC is relatively pollution free.
(vi) Reduced project time resulting in savings in all aspects.
Q9- Define Fly Ash.
A- Fly ash is the byproduct of burning pulverized coal in electric generation power plants. Fly ash consists of aluminous and siliceous material that form the cement in the presence of water. On mixing up of fly ash with lime and water then it form the compound that is very similar to the Portland Cement. This makes the fly ash suitable as prime material in blended cement, mosaic tiles, and other building material.
Q10 -Mention the applications of Fly Ash.
A-
(i) Fly Ash can be used as the prime material in many cement based products.
(ii) Fly Ash is most commonly used in Portland Cement Concrete Pavement.
(iii) Fly Ash usage is economically beneficial.
(iv) This is also used as embankment and mine fill.
Q11- Explain the advantages of Fly Ash.
(i) These are cold weather resistance
(ii) Fly can be used as an admixture
(iii) Fly Ash are high strength gains, depending on use
(iv) They reduces crack problems, permeability and bleeding