AEE
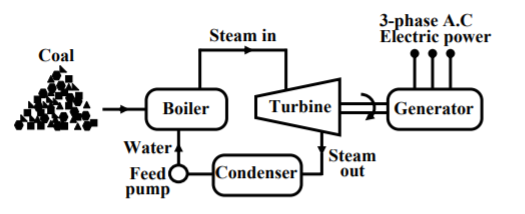
Unit – 1Introduction to Electrical Power System Q1) How power is generated through thermal power plant?Sol: In these plants coal is burnt to produce high temperature and pressure steam in boiler. The steam produces a rotational motion when it passes through turbine. This turbine rotates and produces electricity. In India coal is present in abundance so they are commonly used. The resources used are easily available and cheap so they require less cost in installation. The main drawback of these plants is that they pollute the environment. As the coal is burnt to produce energy the leftover ash and the chimneys adds to the cost in the plant.
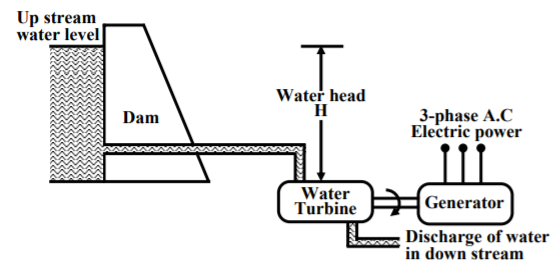
Fig 1 Thermal Plant Block diagramWe conclude the working of thermal plant by noticing that chemical energy from coal is converted to heat and steam which the turbine converts to mechanical energy to rotate and produce electricity. Q2) Draw the block diagram and explain the working of hydro power plant?A2) In these stations water is used to run the turbine which is coupled to the generator. The water head needed for running the generator may be available naturally in some areas or they can also be created artificially in form of dams. These plants are eco-friendly because no fuel is required to run them.
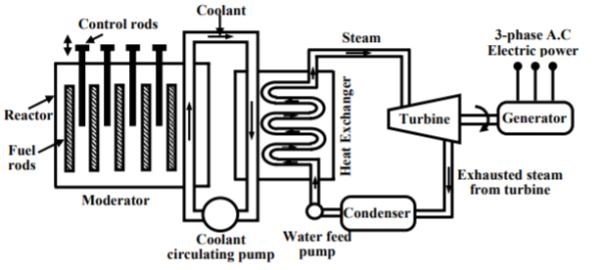
Fig 2 Hydro Power Plant block diagramThe above figure shows a hydro plant. The water from the dam is supplied to the water turbine, the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy making the turbine run. This kinetic energy from the turbine is converted to the electrical energy through generator. Water turbines generally operate at low rpm, so number of poles of the alternator are high. Q3) Explain the working of nuclear power plant?A3) The radioactive elements like U235 and thorium are used as fuel. The nuclear reactors and heat exchanger tubes are used in place of boilers as in thermal plants.
Fig 3 Nuclear Power Plant block diagramThere is fission reaction takes place in the radioactive elements within the nuclear reactors. The fission reaction is a chain reaction producing huge amount of energy in the form of heat. This heat is passed to the heat exchanger tubes producing steam of very high temperature. This steam drives the turbine to produce the electricity. Q4) Explain the significance of earthing with any two types?A4) It means connecting electrical equipment to earth with very low resistance wire. This ensures safe discharge of electrical energy due to failure of the insulation line coming in contact with the casing, etc. Earthing brings the potential of the body of the equipment to zero.The main purpose of Earthing is to protect the operating personnel from shock. Under unbalanced load maintain the line voltage. To avoid risk of fire due to leakage currents. For protecting the equipment. Methods of Earthing: Plate earthing:
|
|
|
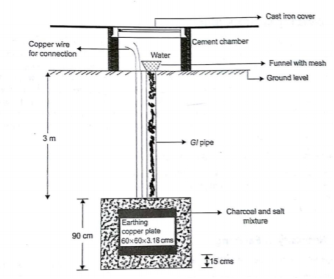
A copper plate of dimension 60cm x 60cm x 3.18 is used for earthing. The plate is buried in ground and layered with coal and salt. Then water is poured to maintain the earth’s electrode resistance below maximum value. The earth wire is bolted to the earth plate.
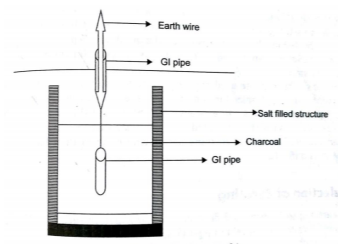
Fig 4 Plate earthingPipe earthing:The earth’s electrode made of galvanized iron pipe with holes on surface is placed upright in wet ground. In order to maintain the earth’s resistance, the pipe is filled with mixture of salt and coal.
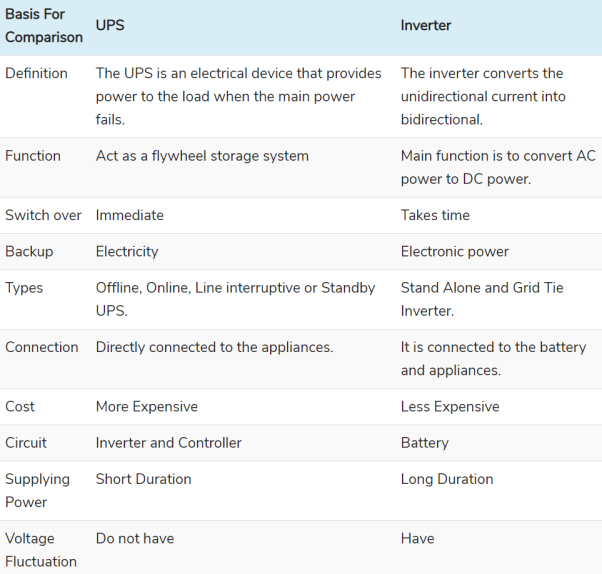
Fig 5 Pipe EarthingThis system can carry larger leakage currents compared to plate earthing method. Q6) List the safety precautions to be taken while working with electrical equipment?A6) The primary measures required to keep ourself and the equipment Safe are listed belowThe hands or the equipment to be repaired or checked should not have any trace of water on it. The equipment should not be of damaged insulation or broken chords. The equipment before installation should be tested first. The instruments should be identified and checked properly before fitting. The site of work should have a board to notify that work is in progress. The site where work is going on installation or any repair should be done after the site is earthed properly. During heavy lighting and storm avoid working with electrical equipment. The tools used while working should not be tossed it should be delivery by hand to the other person. The shoes with rubber soles should be worn during work. Insulated tools should be used. If we have to repair anything at home always turn off the mains first. Proper insulated rubber gloves and googles should be used. Always a wooden ladder should be used, avoid using steel ladders during work. Remember wire code of the country. Never repair energised equipment, take and tester check first than use. Q7) How solar electric energy can be used? Explain briefly.A7) Here PV cells are used which are made of silicon. Solar Photovoltaic: As soon as PV cells are exposed to light the electrons are released and current is produced. The cell is covered with metal grid to direct the flow of current. These cells connected in a panel are also used. These PV panels are installed above the roof. These panels are connected in series or parallel. The generation of power depends upon the amount of heat received from sun. Solar water pumps: The motor required to run the pump uses electricity generated by solar panels. It consists of a photovoltaic array mounted on a stand and a motor-pump set compatible with the photovoltaic array. It converts the solar energy into electricity, which is used for running the motor pump set. The pumping system draws water from the open well, bore well, stream, pond, canal etc Q8) Explain the difference between overhead and underground distribution system?A8)
Q9) What are miniature circuit breakers explain briefly?
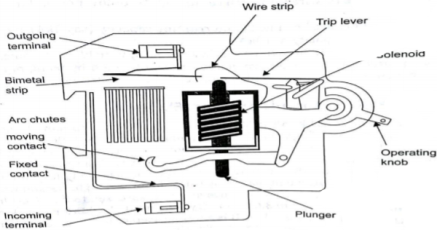
A9) MCB is a switch which automatically turns off when the current flowing through it passes the maximum allowable limit. Generally, MCB is designed to protect against over current and over temperature faults. In MCB there are two contacts one movable and other non-movable. When the current exceeds the predefined limit, a solenoid forces the moveable contact to open and the MCB turns off, thereby stopping the current from flowing in the circuits. It mainly consists of one bi- metallic strip, one trip coil and one hand operated on-off lever. The current in MCB flows from left side of circuit to bimetallic strip further going into the current coil, moving contact and at last through right side of circuit. When circuit is overloaded the bimetallic strip is overheated.
Fig 6 MCB This deformation of bimetallic strip causes displacement in the latch. This displacement releases the spring through which the MCB is connected to the moving contact. This spring makes moving contact to open MCB. The current coil or trip coil placed in such a manner that during SC faults, the MMF of that coil causes its plunger to hit the same latch point and force the latch to be displaced. Hence, the MCB will open in the same manner.They are frequently used in domestic and industrial purposes. The MCB detects faults like switching, overload, short circuit protection and overload protection. Q10) Compare and list the difference between UPS and Inverters?A10)
|
|
S.No. | Particulars | Overhead system | Underground System |
1 | Public Safety | Less Safe than Under ground | Safer |
2 | Initial Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
3 | Faults | Frequent | Rare |
4 | Appearance | Not good | Good as wires are not visible |
5 | Flexibility | It is more flexible as new conductor can be laid along the existing conductors. | It is not flexible as new conductors are to be laid in new channels |
6 | Location of fault | Easy to locate | Difficult to locate |
7 | Repair | Easy | Difficult |
8 | Working Voltage | Up to 400kV | Up to 66kV |
A9) MCB is a switch which automatically turns off when the current flowing through it passes the maximum allowable limit. Generally, MCB is designed to protect against over current and over temperature faults. In MCB there are two contacts one movable and other non-movable. When the current exceeds the predefined limit, a solenoid forces the moveable contact to open and the MCB turns off, thereby stopping the current from flowing in the circuits. It mainly consists of one bi- metallic strip, one trip coil and one hand operated on-off lever. The current in MCB flows from left side of circuit to bimetallic strip further going into the current coil, moving contact and at last through right side of circuit. When circuit is overloaded the bimetallic strip is overheated.
|
|
0 matching results found