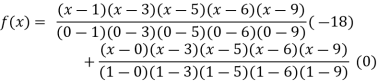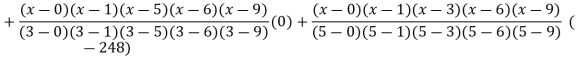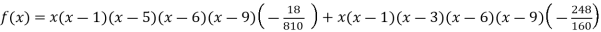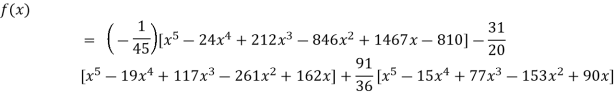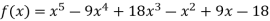Unit - 6
Statistics and finite differences
Q1) Find the best values of a and b so that y = a + bx fits the data given in the table
x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
y | 1.0 | 2.9 | 4.8 | 6.7 | 8.6 |
A1)
y = a + bx
x | y | Xy |  |
0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 2.9 | 2.0 | 1 |
2 | 4.8 | 9.6 | 4 |
3 | 6.7 | 20.1 | 9 |
4 | 8.6 | 13.4 | 16 |
 |  |  |  |
Normal equations,  y= na+ b
y= na+ b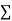 x (2)
x (2)
On putting the values of 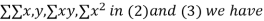
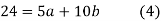

On solving (4) and (5) we get,

On substituting the values of a and b in (1) we get
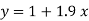
Q2) By the method of least squares, find the straight line that best fits the following data )
X | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Y | 14 | 27 | 40 | 55 | 68 |
A2)
Let the equation of the straight line best fit be y = a + bx. (1)
x | y | x y | 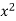 |
1 | 14 | 14 | 1 |
2 | 27 | 54 | 4 |
3 | 40 | 120 | 9 |
4 | 55 | 220 | 16 |
5 | 68 | 340 | 25 |
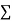 | 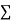 | 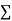 |  |
Normal equations are 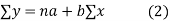
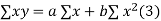
On putting the values of 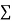 x,
x, 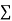 y,
y, 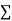 xy and
xy and 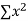 in (2) and (3) we have
in (2) and (3) we have
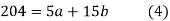
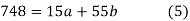
On solving equations (4) and (5) we get
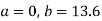
On substituting the values of (a) and (b) in (1) we get,
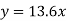
Q3) Find the least squares approximation of second degree for the discrete data
x | 2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
y | 15 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 19 |
A3)
Let the equation of second degree polynomial be 
x | y | Xy | 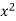 |  | 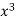 | 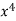 |
-2 | 15 | -30 | 4 | 60 | -8 | 16 |
-1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
2 | 19 | 38 | 4 | 76 | 8 | 16 |
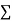 | 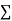 | 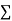 | 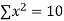 | 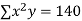 |  |  |
Normal equations are 
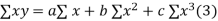
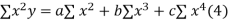
On putting the values of 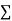 x,
x, 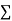 y,
y, xy,
xy,
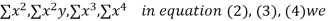 have
have
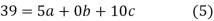
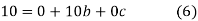
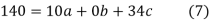
On solving (5),(6),(7), we get, 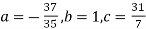
The required polynomial of second degree is
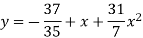
Q4) Fit a second degree parabola to the following data by least square method:
x | 1929 | 1930 | 1931 | 1932 | 1933 | 1934 | 1935 | 1936 | 1937 |
y | 352 | 356 | 357 | 358 | 360 | 361 | 365 | 360 | 359 |
A4)
Taking 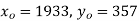
Taking 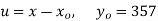
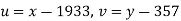
The equation 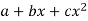 is transformed to
is transformed to 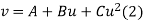
x | 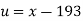 | y | 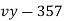 | Uv |  | 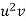 | 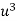 | 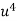 |
1929 | -4 | 352 | -5 | 20 | 16 | -80 | -64 | 256 |
1930 | -3 | 360 | -1 | 3 | 9 | -9 | -27 | 81 |
1931 | -2 | 357 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | -8 | 16 |
1932 | -1 | 358 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 |
1933 | 0 | 360 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1934 | 1 | 361 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
1935 | 2 | 361 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 16 | 8 | 16 |
1936 | 3 | 360 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 27 | 27 | 81 |
1937 | 4 | 350 | 2 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 256 |
Total |  |
| 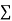 | 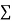 | 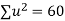 | 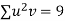 |  | 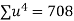 |
Normal equations are
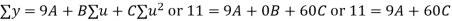

On solving these equations we get 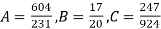
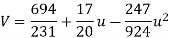
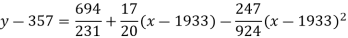
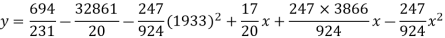

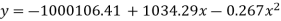
Q5) Find the least squares approximation of second degree for the discrete data
x | 2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
y | 15 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 19 |
A5)
Let the equation of second degree polynomial be 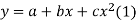
x | y | Xy | 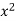 | 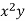 | 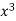 | 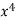 |
-2 | 15 | -30 | 4 | 60 | -8 | 16 |
-1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
2 | 19 | 38 | 4 | 76 | 8 | 16 |
 | 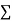 | 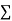 | 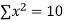 | 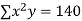 |  | 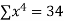 |
Normal equations are 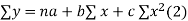

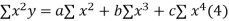
On putting the values of 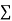 x,
x, 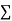 y,
y,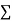 xy,
xy,
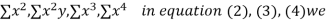 have
have

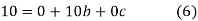

On solving (5),(6),(7), we get, 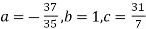
The required polynomial of second degree is
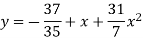
Q6) Fit a second degree parabola to the following data.
X = 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 |
Y = 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 2.7 | 3.4 | 4.1 |
A6)
We shift the origin to (2.5, 0) antique 0.5 as the new unit. This amounts to changing the variable x to X, by the relation X = 2x – 5.
Let the parabola of fit be y = a + bX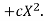 The values of
The values of 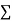 X etc. Are calculated as below:
X etc. Are calculated as below:
x | X | y | Xy | 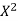 | 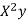 | 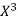 | 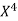 |
1.0 | -3 | 1.1 | -3.3 | 9 | 9.9 | -27 | 81 |
1.5 | -2 | 1.3 | -2.6 | 4 | 5.2 | -5 | 16 |
2.0 | -1 | 1.6 | -1.6 | 1 | 1.6 | -1 | 1 |
2.5 | 0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 |
3.0 | 1 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 1 | 2.7 | 1 | 1 |
3.5 | 2 | 3.4 | 6.8 | 4 | 13.6 | 8 | 16 |
4.0 | 3 | 4.1 | 12.3 | 9 | 36.9 | 27 | 81 |
Total | 0 | 16.2 | 14.3 | 28 | 69.9 | 0 | 196 |
The normal equations are
7a + 28c =16.2; 28b =14.3;. 28a +196c=69.9
Solving these as simultaneous equations we get


Replacing X bye 2x – 5 in the above equation we get
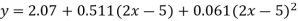
Which simplifies to y =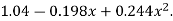
This is the required parabola of the best fit.
Q7) Estimate the chlorine residual in a swimming pool 5 hours after it has been treated with chemicals by fitting an exponential curve of the form
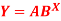 of the data given below-
of the data given below-
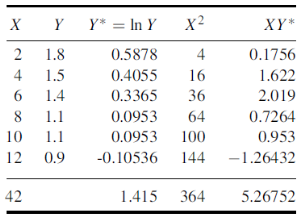
Hours(X) | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
Chlorine residuals (Y) | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 |
A7)

Taking log on the curve which is non-linear,
We get-
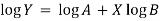
Put
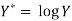
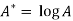
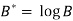
Then-
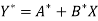
Which is the linear equation in X,
Its nomal equations are-
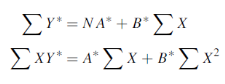
Here N = 6,
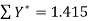
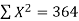
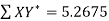
Thus the normal equations are-
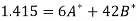
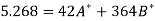
On solving, we get

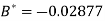
Or
A = 2.013 and B = 0.936
Hence the required least square exponential curve-
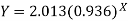
Prediction-
Chlorine content after 5 hours-
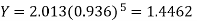
Q8) What do you understand by positive correlation and negative correlation?
A8)
Positive Correlation:
Correlation between two variables is said to be positive if the values of thevariables deviate in the same direction i.e. if the values of one variable increase (or decrease) then the values of other variable also increase (or decrease). For example:
1. Heights and weights of group of persons;
2. House hold income and expenditure;
3. Amount of rainfall and yield of crops
Negative Correlation:
Correlation between two variables is said to be negative if the values of variables deviate in opposite direction i.e. if the values of one variable increase (or decrease) then the values of other variable decrease (or increase). Some examples of negative correlations are correlation between
1. Volume and pressure of perfect gas;
2. Price and demand of goods;
3. Literacy and poverty in a country
Q9) What is Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation?
A9)
Coefficient of correlation measures the intensity or degree of linear relationship between two variables. It was given by British Biometrician Karl Pearson (1867-1936).
Karl Pearson’s Coefficient of Correlation is widely used mathematical method is used to calculate the degree and direction of the relationship between linear related variables. The coefficient of correlation is denoted by “r”.
If X and Y are two random variables then correlation coefficient between X and Y is denoted by r and defined as-
Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation-
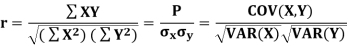
Here-  and
and 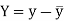
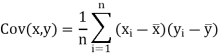
Q10) Find the correlation coefficient between Age and weight of the following data-
Age | 30 | 44 | 45 | 43 | 34 | 44 |
Weight | 56 | 55 | 60 | 64 | 62 | 63 |
A10)
x | Y | 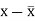 | 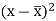 | 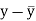 | 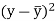 | ( 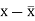  |
30 | 56 | -10 | 100 | -4 | 16 | 40 |
44 | 55 | 4 | 16 | -5 | 25 | -20 |
45 | 60 | 5 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
43 | 64 | 3 | 9 | 4 | 16 | 12 |
34 | 62 | -6 | 36 | 2 | 4 | -12 |
44 | 63 | 4 | 16 | 3 | 9 | 12 |
Sum= 240 |
360 |
0 |
202 |
0 |
70
|
32 |
Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation-
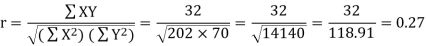
Q11) Find the correlation coefficient between the values X and Y of the dataset given below by using short-cut method-
X | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
Y | 90 | 85 | 80 | 60 | 45 |
A11)
X | Y | 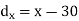 | 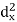 |  | 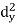 | 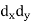 |
10 | 90 | -20 | 400 | 20 | 400 | -400 |
20 | 85 | -10 | 100 | 15 | 225 | -150 |
30 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 100 | 0 |
40 | 60 | 10 | 100 | -10 | 100 | -100 |
50 | 45 | 20 | 400 | -25 | 625 | -500 |
Sum = 150 |
360 |
0 |
1000 |
10 |
1450 |
-1150 |
Short-cut method to calculate correlation coefficient-

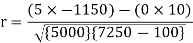
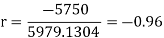
Q12) Psychological tests of intelligence and of engineering ability were applied to 10 students. Here is a record of ungrouped data showing intelligence ratio (I.R) and engineering ratio (E.R). Calculate the co-efficient of correlation.
Student | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J |
I.R | 105 | 104 | 102 | 101 | 99 | 98 | 96 | 92 | 93 | 92 |
E.R | 101 | 103 | 100 | 98 | 96 | 104 | 92 | 94 | 97 | 94 |
A12)
We construct the following table:
Student | Intelligence ratio 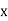 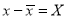 | Engineering ratio 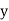 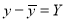 | 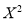 |  | 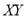 |
A B C D E F G H I J | 100 6 104 5 102 3 101 2 100 1 99 0 98 -1 96 -3 93 -6 92 -7 | 101 3 103 5 100 2 98 0 95 -3 96 -2 104 6 92 -6 97 -1 94 -4 | 36 25 9 4 1 0 1 9 36 49 | 9 25 4 0 9 4 36 36 1 16 | 18 25 6 0 -3 0 -6 18 6 28 |
Total | 990 0 | 980 0 | 170 | 140 | 92 |
From this table, mean of 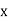 i.e.,
i.e., 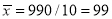 and mean of
and mean of 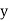 , i.e.,
, i.e., 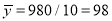
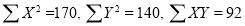
Substituting these values in the formula (1), we have

Q13) Calculate coefficient of correlation between X and Y series using Karl pearson shortcut method
X | 14 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 16 | 17 | 16 | 15 |
Y | 13 | 11 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 9 | 14 | 17 |
A13)
Let assumed mean for X = 15, assumed mean for Y = 14
X | Y | Dx | Dx2 | Dy | Dy2 | Dxdy |
14 | 13 | -1.0 | 1.0 | -1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
12 | 11 | -3.0 | 9.0 | -3.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 |
14 | 10 | -1.0 | 1.0 | -4.0 | 16.0 | 4.0 |
16 | 15 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
16 | 15 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
17 | 9 | 2.0 | 4.0 | -5.0 | 25.0 | -10.0 |
16 | 14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
15 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0 |
120 | 104 | 0 | 18 | -8 | 62 | 6 |
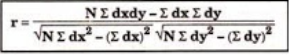
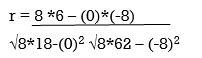
r = 48/√144*√432 = 0.19
Q14) Two variables X and Y are given in the dataset below, find the two lines of regression.
x | 65 | 66 | 67 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 | 71 |
y | 66 | 68 | 65 | 69 | 74 | 73 | 72 | 70 |
A14)
The two lines of regression can be expressed as-
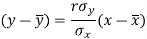
And
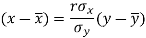
x | y | 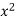 | 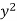 | Xy |
65 | 66 | 4225 | 4356 | 4290 |
66 | 68 | 4356 | 4624 | 4488 |
67 | 65 | 4489 | 4225 | 4355 |
67 | 69 | 4489 | 4761 | 4623 |
68 | 74 | 4624 | 5476 | 5032 |
69 | 73 | 4761 | 5329 | 5037 |
70 | 72 | 4900 | 5184 | 5040 |
71 | 70 | 5041 | 4900 | 4970 |
Sum = 543 | 557 | 36885 | 38855 | 37835 |
Now-

And
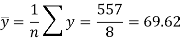
Standard deviation of x-
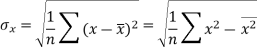
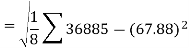
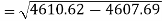
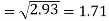
Similarly-
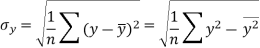
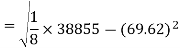
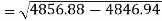
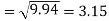
Correlation coefficient-
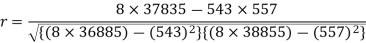

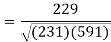

Put these values in regression line equation, we get
Regression line y on x-
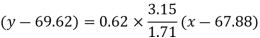
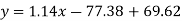

Regression line x on y-
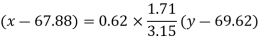
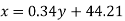
Q15) Compute the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient of the dataset given below-
Person | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J |
Rank in test-1 | 9 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 1 | 3 |
Rank in test-2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
A15)
Person | Rank in test-1 | Rank in test-2 | d =  | 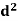 |
A | 9 | 1 | 8 | 64 |
B | 10 | 2 | 8 | 64 |
C | 6 | 3 | 3 | 9 |
D | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
E | 7 | 5 | 2 | 4 |
F | 2 | 6 | -4 | 16 |
G | 4 | 7 | -3 | 9 |
H | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
I | 1 | 9 | -8 | 64 |
J | 3 | 10 | -7 | 49 |
Sum |
|
|
| 280 |
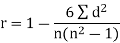
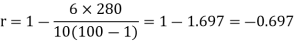
Q16)
Test 1 | 8 | 7 | 9 | 5 | 1 |
Test 2 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 5 |
A16)
Here, highest value is taken as 1
Test 1 | Test 2 | Rank T1 | Rank T2 | d | d2 |
8 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
7 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
9 | 7 | 1 | 3 | -2 | 4 |
5 | 4 | 4 | 5 | -1 | 1 |
1 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
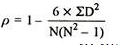
R = 1 – (6*8)/5(52 – 1) = 0.60
Q17) Deduce Lagrange’s formula for interpolation. The observed values of a function are respectively 168,120,72 and 63 at the four position3,7,9 and 10 of the independent variable. What is the best estimate you can for the value of the function at the position6 of the independent variable.
A17)
We construct the table for the given data:
X | 3 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 10 |
Y=f(x) | 168 | ? | 120 | 72 | 63 |
We need to calculate for x = 6, we need f(6)=?
Here 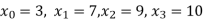
We get 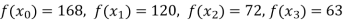
 By Lagrange’s interpolation formula, we have
By Lagrange’s interpolation formula, we have

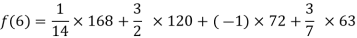
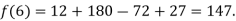
Hence the estimated value for x=6 is 147.
Q18) Find the polynomial of fifth degree from the following data
X | 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 9 |
Y=f(x) | -18 | 0 | 0 | -248 | 0 | 13104 |
A18)
Here 
We get 
 By Lagrange’s interpolation formula
By Lagrange’s interpolation formula