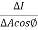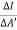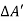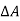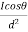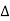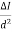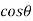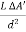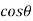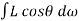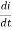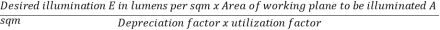AEE
Unit – 3Utilization of Electrical Energy Tariff Q1) Calculate the electricity bill amount for a month of 31 days, if the following devices are used: 3bulbs of 40W for 6hr, 4 tube-lights of 50W for 8hr and a TV of 120W for 6hr. Given the rate of electricity is Rs.2.50 per unit?A1) It has been given that the following devices are used as specified 3bulbs of 40W for 6hr, 4 tube-lights of 50W for 8hr and a TV of 120W for 6hr. Total power consumed by 3 bulbs = 40x3 = 120Wh=0.12kWhElectrical units for 1 day = 0.12x6=0.72unitsElectrical units for 31 days = 0.72 x 31 = 22.32 unisTotal Power the four tube-lights consume in a day = 50x4 = 200Wh=0.2kWh Electrical units for one day = 0.2 x 8 =1.6 unitsElectrical units for 31 days= 1.6 x 31 =49.60 unitsTotal power the TV consumes in a day = 120x6 =720Wh=0.720kWhElectrical units for one day = 0.720x6 = 4.32unitsElectrical units for 31 days = 4.32x31=133.92unitsTotal units consumed = Electrical units consumed by bulb for 31 days+ Electrical units consumed by tube-light for 31 days+ Electrical units consumed by TV for 31 days = 22.32+49.06+133.92 = 205.84unitsThe rate per unit is given as 2.50 per unit. So, the total bill is = 205.84x2.50 = Rs 514.60 Q2) Calculate the electricity bill amount for a month of April, if 4 bulbs of 40 W for 5 h, 4 tube-lights of 60 W for 5 h, a TV of 100 W for 6 h, a washing machine of 400 W for 3 h are used per day. The cost per unit is Rs 1.80.A2) Electric energy consumed per day by 4 bulbs = 4x40 x5 = 800Wh
Electric energy consumed per day by 4 lights = 4x60x5 =1200 W-h
Electric energy consumed per day by TV = 100x6 = 600 W-h
Electric energy consumed per day by washing machine = 400x3 =1200 W-h
.’. Total electric energy consumed by all electric appliances = (800+ 1200 + 600+ 1200) W-h = 3800 W-h = 3.8 kWh =3.8 units
Total electric energy consumed in the month of April (30 days) = 3.8 x 30 = 114units
Cost of one unit = Rs. 1.80
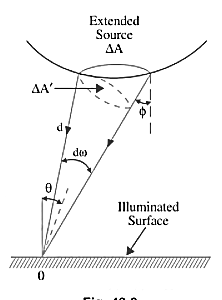
Cost of 114 units = 114 x 1.80 =Rs 205.20Electricity bill amount = Rs 205.20 Q3). A consumer has a maximum demand of 200 kW at 40% load factor. If the tariff is Rs. 100 per kW of maximum demand plus 10 paise per kWh, find the overall cost per kWh?A3) Units consumed/year = maximum demand x load factor x hours in a year = (200x0.4) x 8760 = 7,00,800 kWhAnnual charges = Annual M.D charge+ Annual Energy charges = Rs(100x200+0.1x700800) = Rs. 90,080Overall cost/kWh = Rs90080/700800 = Rs 0.1285 = 12.85 paise. Q4). The maximum demand of a consumer is 20 A at 220 V and his total energy consumption is 8760 kWh. If the energy is charged at the rate of 20 paise per unit for 500 hours use of the maximum demand per annum plus 10 paise per unit for additional units, calculate: (i)annual bill (ii) equivalent flat rate.A4) Let load factor and power factor be unityMaximum demand = (220x20x1)/1000 = 4.4kWUnits consumed in 500hrs = 4.4 x 500 = 2200kWhCharges for 2200kWh = Rs 0.2 x 2200 = Rs 440Remaining Units = 8760-2200 = 6560kWhCharges for 6560kWh = Rs 0.1 x 6560 =Rs 656Total annual bill = Rs (440+656) = Rs 1096Equivalent flat rate = 1096/8760 = Rs 0.125 = 12.5 paise Q5) Define luminance and also derive its expression?A5) Let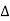 A be an element of area of an extended source and
A be an element of area of an extended source and 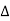 t its luminous intensity when viewed in a direction making angle
t its luminous intensity when viewed in a direction making angle 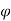 with the perpendicular to the surface of the source, them luminance of source element is given by
with the perpendicular to the surface of the source, them luminance of source element is given by
Fig 1 Luminance Calculation
Q6) Draw and explain the working principle of Fluorescent lamp?A6) It uses fluorescence to deliver visible light and is a low weight mercury vapour lamp. When electric current passed energises the mercury vapours and they deliver UV radiations causing the phosphor coating of the inner wall of lamp to radiate visible light. The circuit is shown below.
Fig 2 Fluorescent Lamp Circuit When the switch is turned on the lamp and the ballast have full supply voltage across them. There is glow discharge formed in the starter at full supply voltage. This also ionises the gas inside the starter and in turn heats the bimetallic strip. The bimetallic strip then bends and is connected to the fixed contact. This establishes the flow of current from the starter and when the current flows through the neon bulb of starter the voltage across the neon bulb is reduced. The current flow is reduced near neon bulb as there is voltage drop across the ballast. There will not be any gas discharge in the neon bulb when there is no voltage across the starter of neon bulb. At the time of breaking of the contacts in the neon bulb of the starter, the current gets interrupted, and hence at that moment, a large voltage surge comes across the ballast.
Gas discharge process gets started and continues and hence current again gets a path to flow through the fluorescent lamp tube itself. During discharging of penning gas mixture, the resistance offered by the gas is lower than the resistance of starter. The discharge of mercury atoms produces ultraviolet radiation which in turn excites the phosphor powder coating to radiate visible light.Starter gets inactive during glowing of fluorescent lamp because no current passes through the starter in that condition Q7) Explain LPSVL with its working principle?A7) The outer envelope is made of borosilicate glass and the inner surface of outer glass is coated with indium oxide. The indium oxide layer is heat reflective coating and reflects IR radiation back inside the tube as a result of which both light and temperature inside the tube increases. The arc tube contains a mixture of metallic sodium and inert gasses argon and neon.
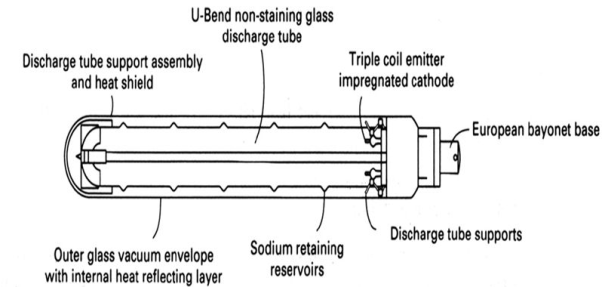
Fig 3 Low Pressure Sodium Vapour LampWhen power is supplied the lamp is energised and the electrodes produce an arc and this arc strikes through the conductive gas and lamp produces a reddish-pink light. The heat is generated due to the current flowing through argon and neon mixture and heat vaporizes the metallic sodium. Q8) Explain working of mercury vapour lamp?A8)
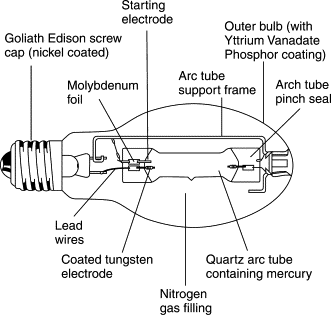
Fig 4 Mercury Vapour Lamp It has an inner quartz arc tube and outer borosilicate glass envelope. The nitrogen gas is filled between the tubes for insulation.so that the metal can be protected from oxidation. Due to the quartz, it can withstand the temperature up to 1300K. The arc consists of two electrodes and starting electrodes. The electrodes are dipped into mixture of thorium, calcium and barium carbonates. The electrodes hold a tungsten rod upon which a double layer of coiled tungsten wire is wound. They are heated to convert these compounds into oxides after dipping. Thus, they get thermally and chemically stable to produce electrons. The electrodes are connected through a quartz tube by molybdenum foil leads. The supply voltage when applied reaches to the starting electrode and the bottom electrode. The voltage gradient in the gap between the starting electrode and main electrode is high. A local argon arc is created due to the high voltage gradient across the starting electrode and the bottom electrode. This initial arc heats up the mercury and vaporizes it and this mercury vapor helps to strike the main arc soon. But the resistance for the main arc current control resistor is somewhat less than the resistance of the resistor used in the initial arc current control purpose. For this reason, initial arc stops and main arc continues to operate. The mercury vapor arc gives visible spectra of green, yellow and violet. But there may be still some invisible ultraviolet radiation during discharging process of mercury vapour so phosphor coating may be provided on outer glass cover to improve efficiency of the mercury lamp. Q9) The illumination in a drawing office 30 m x 10 m is to have a value of 250 lux and is to be provided by a number of 300-Watt filament lamps. If the coefficient of utilization is 0.4 and depreciation factor is 0.9, determine the number of lamps required. The luminous efficiency of each lamp is 14 lm/W. A9)
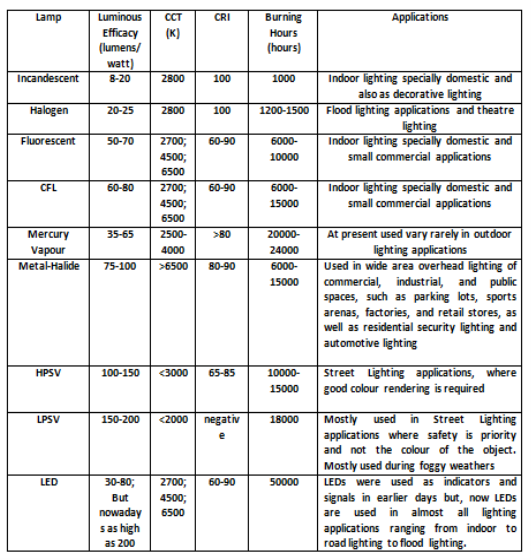
Q10) Compare CFL, Mercury vapour lamp, Sodium vapour lamp and fluorescent lamps?A10)
Electric energy consumed per day by 4 lights = 4x60x5 =1200 W-h
Electric energy consumed per day by TV = 100x6 = 600 W-h
Electric energy consumed per day by washing machine = 400x3 =1200 W-h
.’. Total electric energy consumed by all electric appliances = (800+ 1200 + 600+ 1200) W-h = 3800 W-h = 3.8 kWh =3.8 units
Total electric energy consumed in the month of April (30 days) = 3.8 x 30 = 114units
Cost of one unit = Rs. 1.80
Cost of 114 units = 114 x 1.80 =Rs 205.20Electricity bill amount = Rs 205.20 Q3). A consumer has a maximum demand of 200 kW at 40% load factor. If the tariff is Rs. 100 per kW of maximum demand plus 10 paise per kWh, find the overall cost per kWh?A3) Units consumed/year = maximum demand x load factor x hours in a year = (200x0.4) x 8760 = 7,00,800 kWhAnnual charges = Annual M.D charge+ Annual Energy charges = Rs(100x200+0.1x700800) = Rs. 90,080Overall cost/kWh = Rs90080/700800 = Rs 0.1285 = 12.85 paise. Q4). The maximum demand of a consumer is 20 A at 220 V and his total energy consumption is 8760 kWh. If the energy is charged at the rate of 20 paise per unit for 500 hours use of the maximum demand per annum plus 10 paise per unit for additional units, calculate: (i)annual bill (ii) equivalent flat rate.A4) Let load factor and power factor be unityMaximum demand = (220x20x1)/1000 = 4.4kWUnits consumed in 500hrs = 4.4 x 500 = 2200kWhCharges for 2200kWh = Rs 0.2 x 2200 = Rs 440Remaining Units = 8760-2200 = 6560kWhCharges for 6560kWh = Rs 0.1 x 6560 =Rs 656Total annual bill = Rs (440+656) = Rs 1096Equivalent flat rate = 1096/8760 = Rs 0.125 = 12.5 paise Q5) Define luminance and also derive its expression?A5) Let
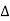 A be an element of area of an extended source and
A be an element of area of an extended source and 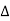 t its luminous intensity when viewed in a direction making angle
t its luminous intensity when viewed in a direction making angle 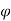 with the perpendicular to the surface of the source, them luminance of source element is given by
with the perpendicular to the surface of the source, them luminance of source element is given by
|
L =
By illuminance E =
dω = E = |
|
V= L
|
|
|
Given E= 250 lm/sqm, A=30x10= 300 sq m, D.F. = 0.9, U.F. = 0.4. Total lumens = Total lumens = (250 x 300)/(0.9 x 0.4) = 208333 lm Flux emitted per lamp = 300x14= 4200 lm. ∴ Number of lamps required = 208333/4200 = 50. |
|
0 matching results found