Unit 2
Recruitment and Selection
Q1) Define recruitment. Also state the objectives of recruitment. 5
A1) Recruitment is a positive process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for the jobs in the organisation. When more persons apply for jobs then there will be a scope for recruiting better persons. In simple words, the term recruitment refers to discovering the source from where potential employees may be selected. The scientific recruitment process leads to higher productivity, better wages, high morale, reduction in labour turnover and enhanced reputation. It stimulates people to apply for jobs; hence it is a positive process.
According to Edwin B. Flippo, “It is a process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating and encouraging them to apply for jobs in an organisation.”
The purposes of recruitment are:
(i) To attract people with multi-dimensional skills and experiences those suit the present and future organisational strategies,
(ii) To induct outsiders with a new perspective to lead the company,
(iii) To infuse fresh blood at all levels of the organisation,
(iv) To develop an organisational culture that attracts competent people to the company,
(v) To search or head hunt/head pouch people whose skills fit the company’s values,
(vi) To devise methodologies for assessing psychological traits,
(vii) To seek out non-conventional development grounds of talent,
(viii) To search for talent globally and not just within the company,
(ix) To design entry pay that competes on quality but not on quantum,
(x) To anticipate and find people for positions that does not exist yet.
Q2) Explain about different sources of recruitment of an organisation. 12
A2) An organisation recruits suitable candidates from different sources. Such categories are grouped as internal sources and external sources. Such sources are discussed below-
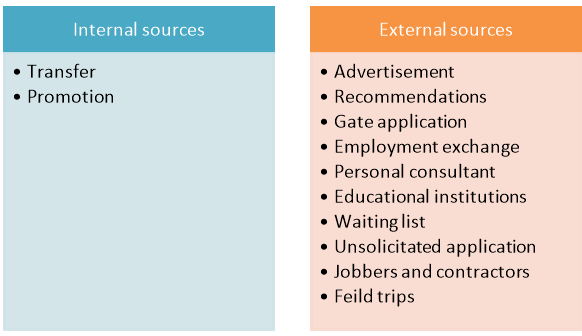
A. Internal Sources:
It is the source where employees are recruited within the organisation itself. Such sources are-
- Promotion:
It refers to the movement of employee with increase in position, responsibility, pay scale, authority etc. of an employee.
2. Transfer:
It refers to movement of employee from one position to another position with same responsibility, pay scale, authority etc. of an employee.
B. External Sources:
There are various external sources of recruitment.
1. Advertisement:
When a company wants to inform the public that it has a vacancy, it puts up an advertisement. The details of the job and the qualification of the candidates are briefly given. The company may receive the applications in response to the advertisement. After that, interview will be conducted.
2. Recommendations:
Here, recommendation means appointment of a person on getting a recommendation letter from a person reliable and well-known to the company. In certain cases, an employee of the company may bring the candidates to the company for the purpose of being appointed
3. Gate Applicants:
The educated unemployed youth may contact the company to get employment. These candidates may not have any recommendations. Even the company might not have issued any advertisement for the post. The candidate personally approaches the appointing authority of the company. If such candidate is found fit for any one of the posts which are vacant at that time, the candidate is appointed.
4. Employment Exchange:
The job seekers register their names with their qualifications with the employment exchange. The company can get a list of candidates who have requisite qualifications to fit in a job. Out of the listed candidates, any one of them can be selected. The employment exchange is of two kinds, i.e., public employment exchange and private employment exchange.
5. Personnel Consultant:
Private consultant is a separate specified agency doing the function of recruitment of the personnel on behalf of the company. In other words, the functions of personnel department of any company are performed by the personnel consultants. It receives the applications from the candidates, verifies the applications, conducts interviews and selects the candidates. The personnel consultant receives fees from the company for its service.
6. Educational Institutions – Campus Interview:
Universities, colleges and institutions are formed to offer specific courses. The educational institutions make an arrangement for campus interview. The business concerns come to the campus of educational institutions to recruit the students for various posts. The selected students are requested to join the post after completing the course.
7. Waiting List:
The business concern prepares a waiting list of candidates who have already been interviewed. But, they are not appointed for lack of vacancy. Whenever a vacancy arises, the vacancy may be filled up by the company out of the waiting list.
8. Unsolicited Applicants:
Unsolicited applications means the application received through mail from the candidate. The application brings the information regarding the name and address of the candidate, his age, educational qualification, experience, area of interest, etc. If there is any vacancy at that time, the candidate will be recruited for the specified post. Normally, this type of application is considered for the posts at the lower level.
9. Jobbers and Contractors:
The casual vacancy may be filled up by the company through the jobbers and contractors. Normally, unskilled candidates are appointed in this way. They are available at short notice and for a less salary. This type of candidate is brought by the jobbers and contractors to the place of work and they receive some commission from the company for this service.
10. Field Trips:
A company may send a group of experts to the towns and the cities where the various kinds of candidates required by the company are available. In this case, a prior advertisement may be issued in newspapers. The advertisement contains information regarding the date, venue and time of the interview. The interview is conducted in different places. This is procedure followed to recruit the candidates under field trips.
Q3) State the advantages and disadvantages of internal sources of recruitment. 5
A3) Advantages of internal sources of recruitment
1. It increases the morale among the staff members of the company.
2. Giving promotion keeps the employee happy.
3. It attracts efficient staff members.
4. The training expenses may be reduced, to some extent.
5. A person who has got a promotion, inspires the staff members to acquire a thorough knowledge of his job.
6. Internal promotion helps the staff members to derive job satisfaction.
7. A promoted staff member may make use of his past experience in the new post.
8. It increases the security of the job of the staff member.
9. A new responsibility can be entrusted safely to the promoted staff members on the basis of contents of Service Register.
10. It ensures the continuity of job to the staff members and stability of the organisation.
11. It induces the staff members to work hard to get promotion.
12. The expenses for advertisement, recruitment, test and interview are avoided.
Disadvantages of internal sources recruitment
1. If the higher post is filled internally, the company will not be able to get fresh and original ideas and initiative from the staff members.
2. The outsiders do not have a scope to show their ability in the performance of the work.
3. An under-qualified person may be appointed in the higher post.
4. If the promotion is guaranteed to the internal staff members after the expiry of a specific period, the concerned staff member does not care to work efficiently.
Q4) State the advantages and disadvantages of external sources of recruitment. 5
A4) Advantages of external sources of recruitment
1. Choice – A company can recruit a person out of a large number of applicants. Each and every candidate’s plus points and minus points are taken into consideration for the purpose of recruitment. Then, the best candidate can be selected by the company
2. New Outlook – If a new person is recruited by the company, a new way of approach may be used to solve the problem, which will give maximum benefits to the company.
3. Wide Experience – If the recruited new candidate has experience in various fields, the company can get the benefit of the candidate’s experience.
Disadvantages of external sources of recruitment
1. Grudging of old employment – If a candidate is recruited from external sources, the existing staff may have a grudge against him. It results in demoralisation of the staff members.
2. Lack of co-operation – The existing staff members do not extend their co-operation to the person who is selected from out of external sources. In addition to this, the existing staff members make the new recruit face the difficulties and try to disorient him in relation to his work.
3. Expensive – Recruitment of a person from outside the company requires a lot of formalities. The formalities include issuing advertisement, receiving the applications, screening the applications, dispatching the interview letters, fixation of interview date, time and place, formation of an interview committee etc. Completing all the above said procedure involves a lot of expenditure.
4. Trade union – If the trade union of the company is very strong, it is very difficult to convince the trade union and recruit a person from outside a company.
5. Danger of non-adjustment – If a newly recruited person fails to adjust himself to the working conditions of the company, it leads to more expenditure in looking for his replacement. Besides, it causes irritation and quarrel between the recruited person and the existing staff members.
Q5) Discuss the factors governing recruitment of an organisation. 10
A5) The factors governing recruitment process are discussed below-

Figure: Factors governing recruitment
1. Internal Factors:
(i) Organization Policies and Practices:
Policies and practices of the organization affect the system of recruitment of the organization. Some organizations may adopt the practice of recruiting from within the organization through promotion, transfer, lay-off etc., and others may go for external sources. Some organizations adopt the practice of recruiting the persons from backward castes and communities, physically handicapped persons etc., and others may give importance to merit irrespective of caste, creed and religion.
(ii) Image of the Organization:
Image or the impression that an organization gives to the public considerably influences on the recruitment process of the organization. Kind of job environment, benefit it provides to its employees, employer employee relation that prevails in the organization enhance the image of the organization. Better the image, better the quality of applicant and vice-versa.
(iii) Wage and Salary Policies:
Benefits provided by the organization to its employees have a great influence on its recruitment system. Higher salaries and wages consistent with the merit and experience of the employees will certainly attract meritorious and experienced employees towards the organization.
(iv) Promotion and Retirement Policies:
Company which provides better promotion prospects to its dedicated and meritorious employees and offers retirement benefits like pension or gratuity to those who are serving in the company for a minimum fixed period also affect the recruitment policy of the organization and in turn attract meritorious and able persons towards the organization.
(v) Working Conditions:
Good working conditions like proper lighting and ventilation, safety provisions, welfare measures like bonus, quarter’s facility, subsidized food, medical facility etc., influence positively on the recruitment system of the organization.
2. External Factors:
External factors like government regulations, trade union restrictions, labour market conditions, legal factors, economic factors, cultural factors, location of the organization etc., also influence the recruitment system of the organization.
(i) Government Regulations:
Government regulations towards Backward Caste, Scheduled Caste, Scheduled Tribes and women have a direct impact on recruiting practices and hence organisations have to observe these regulations while recruiting its employees.
(ii) Trade Union Restrictions:
Trade union always wants to protect the interest of its members and hence interfere in the recruitment process of the organization. Therefore, while making the recruitment, interest of the trade union should be kept in mind and process should be continued.
(iii) Labour Market Conditions:
Labour market conditions in India are always volatile i.e., changing. At any given point of time there may be a surplus or a shortage of well qualified candidate in a particular category of post for which vacancy is to be filled up. If well qualified candidates are in short supply recruitment becomes difficult and if the candidates are excess with suitable qualification, selection becomes difficult. Therefore, it is necessary to take a note of labour market condition while recruiting the employees.
(iv) Legal Factors:
Legal factors like prohibition of employment of children, prohibition of employment of women in night shift, provision of security to the workers in underground mines, abolition of bonded labour, regulation of employment of contract labour, safety of scheduled caste, scheduled tribe and other weaker sections of society, discrimination in employment on the basis of religion, caste, sex, etc., influence on the recruitment practice of the organization.
(v) Economic Factors:
Economic factors like cost of recruitment, capacity of recruiting competent persons, working conditions in other similar organizations etc., also affect the recruitment practice of the organization.
Q6) Define the term selection. Also state the internal sources of recruitment. 5
A6) Recruitment is the process of actively seeking out, finding and hiring candidates for a specific position or job. The recruitment definition includes the entire hiring process, from inception to the individual recruit’s integration into the company. Recruitment is a positive process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for the jobs in the organisation. When more persons apply for jobs then there will be a scope for recruiting better persons. According to Edwin B. Flippo, “It is a process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating and encouraging them to apply for jobs in an organisation.”
Internal Sources of Recruitment:
1. Promotions:
The promotion policy is followed as a motivational technique for the employees who work hard and show good performance. Promotion results in enhancements in pay, position, responsibility and authority. The important requirement for implementation of the promotion policy is that the terms, conditions, rules and regulations should be well-defined.
2. Retired employee:
The retired employees may be given the extension in their service in case of non-availability of suitable candidates for the post.
3. Former employees:
Former employees who had performed well during their tenure may be called back, and higher wages and incentives can be paid to them.
4. Transfer:
Employees may be transferred from one department to another wherever the post becomes vacant.
5. Internal advertisement:
The existing employees may be interested in taking up the vacant jobs. As they are working in the company since long time, they know about the specification and description of the vacant job. For their benefit, the advertisement within the company is circulated so that the employees will be intimated.
Q7) Explain briefly about different sources of recruitment. 12
A7) Different sources of recruitment are broadly divided into two parts- internal sources and external sources.
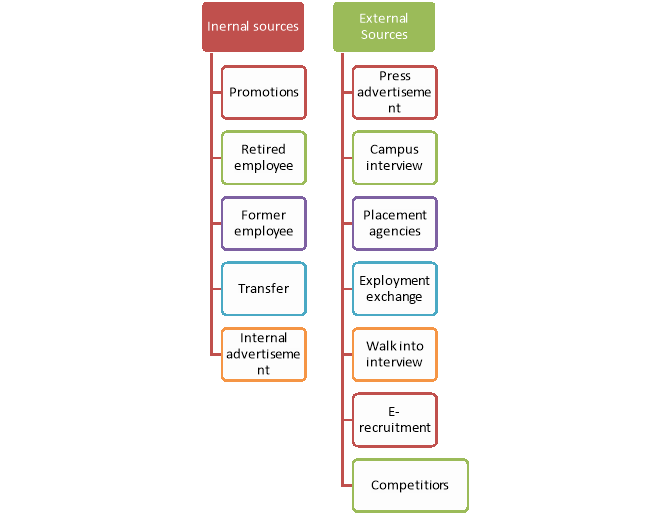
Figure: Sources of recruitment
Internal Sources of Recruitment:
1. Promotions:
The promotion policy is followed as a motivational technique for the employees who work hard and show good performance. Promotion results in enhancements in pay, position, responsibility and authority. The important requirement for implementation of the promotion policy is that the terms, conditions, rules and regulations should be well-defined.
2. Retired employee:
The retired employees may be given the extension in their service in case of non-availability of suitable candidates for the post.
3. Former employees:
Former employees who had performed well during their tenure may be called back, and higher wages and incentives can be paid to them.
4. Transfer:
Employees may be transferred from one department to another wherever the post becomes vacant.
5. Internal advertisement:
The existing employees may be interested in taking up the vacant jobs. As they are working in the company since long time, they know about the specification and description of the vacant job. For their benefit, the advertisement within the company is circulated so that the employees will be intimated.
External Sources of Recruitment:
1. Press advertisement:
A wide choice for selecting the appropriate candidate for the post is available through this source. It gives publicity to the vacant posts and the details about the job in the form of job description and job specification are made available to public in general.
2. Campus interviews:
It is the best possible method for companies to select students from various educational institutions. It is easy and economical. The company officials personally visit various institutes and select students eligible for a particular post through interviews. Students get a good opportunity to prove themselves and get selected for a good job.
3. Placement agencies:
A databank of candidates is sent to organizations for their selection purpose and agencies get commission in return.
4. Employment exchange:
People register themselves with government employment exchanges with their personal details. According to the needs and request of the organization, the candidates are sent for interviews.
5. Walk in interviews:
These interviews are declared by companies on the specific day and time and conducted for selection.
6. E-recruitment:
Various sites such as jobs.com, naukri.com, and monster.com are the available electronic sites on which candidates upload their resume and seek the jobs.
7. Competitors:
By offering better terms and conditions of service, the human resource managers try to get the employees working in the competitor’s organization.
Q8) State the importance of selection for an organisation. 5
A8) Selection is significant for an organisation as it brings employees to the organisation. Some of the significance of selection is discussed below-

Figure: Importance of selection
(i) Reduced labour turnover:
Properly selected candidates feel like staying in the organisation; as suitable work on matching jobs, assigned to them is a source of satisfaction to them. Hence, the phenomenon of unnecessary labour turnover is highly minimised – making for a stable labour force in the organisation. This benefits both the organisation and the worker.
(ii) Lesser need for training:
Properly selected personnel exhibit a lesser need for training; as their suitability for the jobs to be assigned to them, has already been verified through the selection-procedure. As such the necessity for arranging ‘routine-training programmes’ for such personnel is rules out – saving organisation’s time, efforts and costs involved in conducting such training programmes.
(ii) Self-motivation and high morale:
When suitable candidates (i.e. ‘best-fits’) are assigned to matching jobs; such personnel feel self-motivated towards the best performance of’ their jobs. The constant state of self-motivation over a period of time helps in building high morale of such personnel, for the organisation.
(iv) More and better production – leading to profit maximization:
A derivative advantage of the ‘self-motivation and high morale’ is that the production (or performance) turned out by ‘best fits’ is not only more in quantity; but is also of a superior quality. This phenomenon leads to profit maximisation, for the enterprise, in the long-run.
(v) Good human relations:
As a result of good selections, there is a better environment for working in the organisation. Such environment helps to promote good human relations in the organisation; which is one of the highly valued assets of the organisation.
Q9) Discuss about the selection process of an organisation. 10
A9) Selection is a process of choosing right person for the right job. Selection means weeding out unsuitable applicants and selecting those individuals with prerequisite qualifications and capabilities to fill the jobs in the organization. The selection process consists of a series of steps as follows:
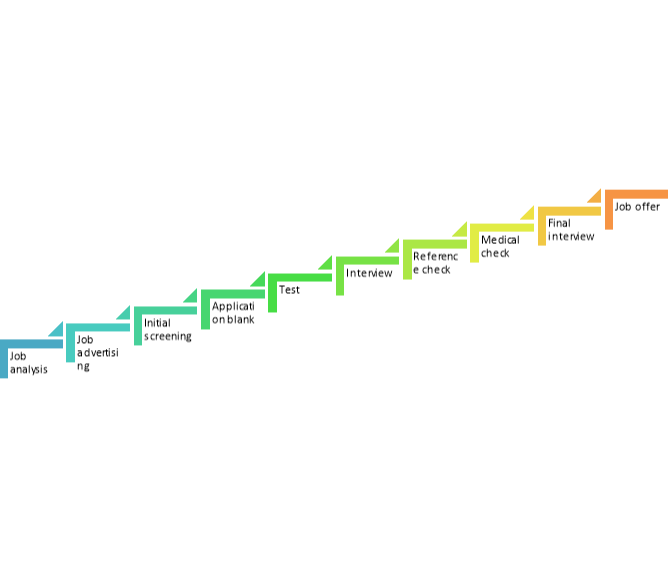
Figure: Selection process
1. Job Analysis:
The first step in selection process is analysing the job. Job analysis consists of two parts:
- Job Description, and
- Job Specification.
Proper job analysis helps to advertise the job properly by clearly stating the duties, qualifications, experience, salary, etc. Accordingly, the right candidates may apply for the job, thus saving time and effort of the selectors.
2. Advertising the Job:
The next step is to advertise the job. The job can be advertised through various media such as newspapers, internet, etc. The right details about the job and the candidate requirements must be given in the advertisement.
3. Initial Screening:
The initial screening can be done of the applications and of the applicant. Usually, a junior executive does the screening work The executive may check on the experience, age, qualifications family background of the candidate. The candidate may be informed of salary, working conditions, etc.
4. Application Blank:
It is a company's format to obtain standard information of every candidate in respect of biographic, academic, references, work experience, etc. The application blank provides:
- Inputs for the interview.
- The basis to reject candidates who do not meet eligibility criteria.
5. Tests:
Various tests are conducted to judge the ability and experience of the candidates. The type of tests depends upon the nature of job. An important advantage of tests is that large group of candidates can be tested at a time. The various tests are:
- Personality test
- Intelligence test
- Performance test
- Stress test, etc.
6. Interview:
It is face to face exchange of views, ideas and opinions between the candidate and interviewer(s). There are various types of interviews such as:
- Panel Interview
- Individual Interview
- Group Interview
- Exit Interview, etc.
7. Reference Check:
Candidate may be asked to provide references to confirm about the applicant s past life, character and experience. Reference check helps to:
- Know the character and other details of the candidate.
- Cross check false information supplied by candidate, if any.
8. Medical Check:
Medical check of the candidates is undertaken to:
- Check physical fitness of the candidate.
- Ensure the health and safety of other employees.
9. Final Interview:
Before making a job offer, the candidates may be subjected to one more oral interview to find out their interest in the job and their expectations. At this stage, salary and other perks may be negotiated.
10. Job Offer:
This is the most crucial and final step in selection process. A wrong selection of a candidate may make the company to suffer tor a good number of years. Company should make a very important decision to offer right job to the right person.
Q10) Distinction between selection and recruitment. 8
A10)
Basis of difference | Recruitment | Selection |
| It is an activity of establishing contact between employers and applicants. | It is a process of picking up more competent and suitable employees. |
2. Purpose | It encourages large number of Candidates for a job. | It attempts at rejecting unsuitable candidates. |
3. Process | It is a simple process. | It is a complicated process. |
4. Nature | It is positive process. | It is negative process. |
5. Hurdles | The candidates have not to cross over many hurdles. | Many hurdles have to be crossed. |
6. Sequence | It proceeds selection. | It follows recruitment. |
7. Economy | It is an economical method. | It is an expensive method. |
8. Time Consuming | Less time is required. | More time is required. |
Q11) What types of employment tests are followed by an organisation in its selection process. 8
A12) Employment test is conducted to find out the intelligence, maturity, skills, etc., of the candidates or prospective employees. Such test are discussed below-
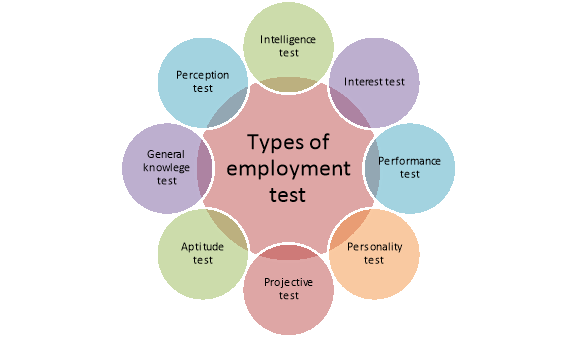
Figure: Types of employment test
1. Intelligence Test
Intelligence test is conducted to find out the intelligence of the candidate. It helps to measure their mental ability, numerical ability, presence of mind, memory, communication skills, etc. This test is used for selecting managers.
2. Interest Test
Interest test is conducted to find out whether the candidate is interested in a particular job or not. It finds out the likes and dislikes of a candidate about his occupation, hobbies, etc. This test helps the company to provide vocational guidance to their employees.
3. Performance Test
Performance test is conducted to measure candidate's performance in a particular job. It helps to find out the candidate's knowledge and skill required for a specific job. For e.g. Typing test can measure the speed and accuracy of a typist or a data entry operator.
4. Personality Test
Personality test is conducted to find out the maturity, inter-personal skills, emotional stability, capacity to get along, behaviours under stress and strain, etc. This test is used for selecting salesman, public relations staff, etc.
5. Projective Test
Projective test is conducted to find out how the candidate interprets (explains) the problem or situation. For e.g. A picture is shown to the candidate, and he is asked to give his views and opinions about it.
6. Aptitude Test
Aptitude test is conducted to find out:
- Whether the candidate has the talent to do a specific job, or
- Whether he has the ability to learn the job after giving him training.
In short, aptitude test is done to find out whether the candidate will be able to do a specific job or not. Some candidates have a good talent or aptitude for accounting jobs while others show smart skills in marketing jobs. Companies give more importance to the candidate's mental suitability for job.
7. General Knowledge Test
G.K. Test is conducted to find out the general awareness of the candidates. They are asked questions about politics, work affairs, current affairs, etc.
8. Perception Test
Perception test is conducted to check the beliefs, attitudes, intelligence, mental sharpness, wisdom, etc. of the candidate.