CT
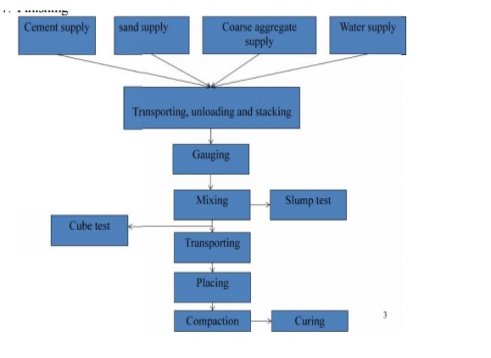
UNIT – 2PRODUCTION, PROPERTIES AND TESTING OF FRESH CONCRETEQ1) Explain production and properties of fresh concrete A1)NOMINAL MIXESIn concrete mix concrete, all ingredients and their size are determined by standard definitions. This ratio is specified in the cement ratio to the specific energy gain combination. Mixing ratios such as 1: 1.5: 3, 1: 2: 4, 1: 3: 6 etc. They were adopted by mixing concrete without a scientific basis, only on the basis of previous studies of solidarity. Therefore, acceptance of ordinary concrete or not to mention, the mixing of preference is preferred for simple, insignificant and minimal concrete works. According to the 'Indian Standard- IS 456: 2000', pre-mixed concrete can be used for M20 grade concrete or lower grade such as M5, M7.5, M10, M15. Proportion of nominal mix as per Indian StandardThe volume of composite materials under M20 grade concrete will comply with IS 456: 2000 According to IS 456: 2000, in the composition of the composition can be adjusted the estimated values if the water level will be increased to overcome the difficulty of laying and density of concrete so that the water level of the cement is maintained as specified. Automatic mixing usually consists of volumetric batching. The measurement is usually determined by weight, and in combination it is converted to a volume value, i.e. in the case of one bag of cement, i.e. 50 kg of standard measuring boxes are made on site, at the rate of one bag of cement. These measuring boxes are called box gauges. Advantages of nominal Mix Concrete01. A self-proclaimed mix is a pre-determined concrete because the scale is pre-determined.02. It is easy to do in the construction site.03. It does not take much time to determine the value because the size is already provided with the standard code.04. There is no need to find people who have the skills to make concrete mixing name.Disadvantages of nominal mix concrete01. The great recurrence of the mix of claims is that, it is based on past experience and studies of art, and has no scientifically proven method.02. It can create or build well-designed energy unless all other factors such as density, w / c ratio, concrete treatment are strictly adhered to.03. The amount of water cement is considered by thought and, if left unchecked, sometimes leads to bleeding and separation of the concrete which leads to poor performance and therefore impairs the strength of the concrete.04. No consideration of composite structures such as classification and quantity of composite items etc.05. In a word mix, cement content is sometimes used in excess, which increases the total cost of construction.06. No laboratory tests are performed to ensure the quality of the new concrete.07. This combination does not consider and evaluates the specific properties of each ingredient. For example, if we take cement as part, the softness of the cement, the quality of the cement and the type of cement, the size and layout of the composite etc. It is usually not counted individually when making this fake assertion mix.Q2) Explain water cement ratioA2)The water–cement ratio is the ratio of the load of water to the load of cement utilized in a concrete blend. A decrease ratio ends in better electricity and durability, however might also additionally make the combination hard to paintings with and form. Workability may be resolved with using plasticizers or super-plasticizers. Often, the ratio refers back to the ratio of water to cement substances, w/cm. Cement substances encompass cement and supplementary cement substances which include fly ash, floor granulated blast-furnace slag, silica fume, rice husk ash and herbal pozzolans. Supplementary cement substances are delivered to reinforce concrete. However, a combination with a ratio of 0.35 might not blend very well, and might not glide nicely sufficient to be positioned. More water is consequently used than is technically important to react with cement. Water–cement ratios of 0.45 to 0.60 are greater usually used. For better-electricity concrete, decrease ratios are used, in conjunction with a plasticizer to boom flow ability. Q3) Explain process of manufacturing of fresh concrete with all processes like batching, mixing, transportation, compaction, curing of concrete, curing methods .A3)Good quality concrete is actually a compact mixture of cement, composite and good mixing with water that mixes into a hard mass due to the chemical action between cement and water. Each of the four regions has a specific function. The coarser collection serves as a filler. A good collection fills the gaps between the attachment and the green combination. Cement by contact with water acts as a bond. The flow of the mixture is aided by the adhesion of cement, fines to this day, increasingly using mixtures. Most of the reinforced concrete materials depend on the care used in all stages of concrete production. The logical separation of concrete ingredients is the core of the mixing design. However, it may not guarantee the achievement of the goal of quality workmanship. The purpose of quality control is to ensure the production of concrete of the same power from batch to batch. This requires that certain rules be followed in the various stages of concrete production and discussed below. The stages of concrete production are:1. Batching and measurement of material2. Mixing3. Transport4. Placement5. Compacting6. Curing 7. Finishing
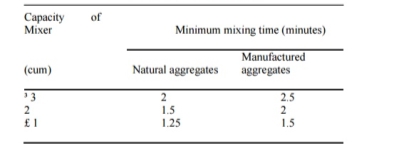
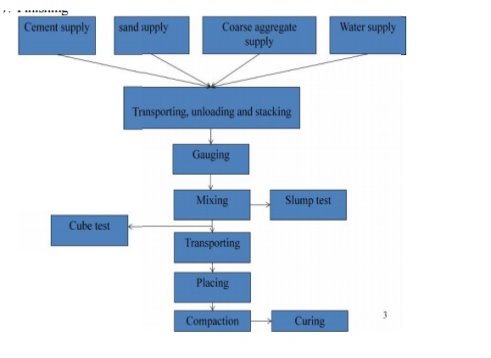
Fig no 1 Manufacturing process of concreteBATCHING OF MATERIAL For good quality concrete should be used the correct and accurate amount of all ingredients. Combined, cement and water must be measured with an accuracy of 3 percent of batch quantity and admixtures at 5 percent of the total value. There are two most common forms of baking material, batching volume and heavy batching. Factors affecting the choice of baking method by the size of the work, the required production rate, the required batching performance standards. It is recommended for the most important tasks. a) Volume batchingb) Weight batchingMIXING1. Hand Mixing2. Mixing Machinea) Tilting mixersb) Non- tilting mixerc) Reversing Drum mixerd) Pan type or stirring mixere) Transit mixerf) Charging Mixer and mixing timeThe order for the ingredients in the mixer is as follows:About 25 percent of the water needed for mixing is initially placed in the mixing tank to prevent any cement attachment to the rings and bottom of the drum. Then the ingredients are extracted in excess. To skip over the loading sequence should be to insert the first half of the coarse cement and then the composite half to be on top of this complete cement and the aggregate to balance. After adding the ingredients to the drum equal volume was introduced. The mixing time is calculated from the total water added to the mixture. The speed of the aggregates is usually 15 to 20 per minute. With proper mixing, the number of changes per minute required by the drum is 25 to 30. The mixing time also depends on the mixing capacity
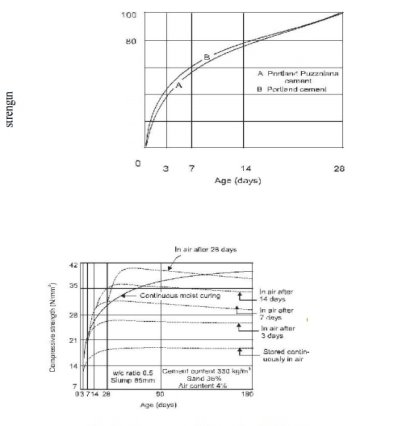
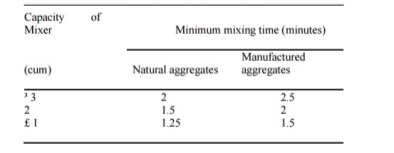
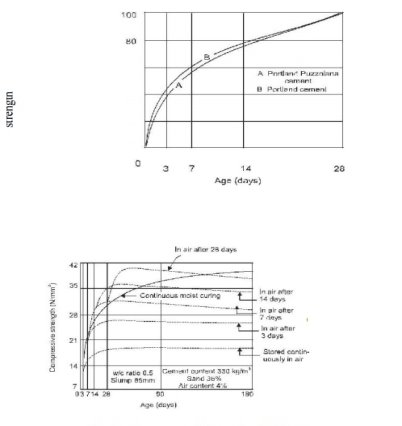
Fig no 2 Table of mixingPoor quality of concrete is obtained when mixing time is reduced. on the other hand if the mixing time is extended it is not economical. however, it is found that when the mixing time is extended to 2 minutes the compressive strength of the produced concrete is improved and beyond this time the improvement of the compressive strength is not significant. prolonged mixing can cause separation. Also, due to the long mixing times water can get in or out and lead to loss of function and energy. TRANSPORTINGThe concrete should be moved to the storage area immediately without the loss of homosexuality acquired during mixing. a maximum of 2 hours from mixing time is allowed if trucks have an agitator and 1 hour using trucks without stimulants to move the concrete. And it must be ensured that separation does not occur during travel and placement. The methods used to transport concrete depend on the quality and value of the work, the distance to the placement site, and the location. some of the concrete delivery methods are below:a. Mortar panb. wheel barrowc. Chutesd. Dumpere. Bucket and ropewayf. Belt conveyorg. skip and hoisth. PumpingPLACING Achieving quality concrete should be placed very carefully to protect the homosexuality achieved during mixing and to avoid transport segregation. studies have shown that delays in the installation of concrete results in gaining greater compressive strength as long as the concrete is not sufficiently compacted. in dry mixes in hot weather a delay of half an hour is allowed and in wet mixtures when it is cold it can be a few hours. the various conditions in which concrete is applied are discussed below. FoundationsConcrete foundations for walls and columns are provided underground. Before laying concrete on the foundation all open ground, tree roots etc., are removed. If the area is found dry it is made wet so that the soil does not absorb water from the concrete. On the other hand when the foundation bed is wet the water and mud are removed and the cement is sprinkled before laying the concrete. Beams, columns and slabsBefore laying the concrete, the forms must be inspected for proper alignment. They should be strong enough to withstand the weight of concrete and construction loads without undue damage. The forms should be light enough to avoid any mud loss that has resulted in concrete mixed with bees. the inside of the forms should be cleaned and oiled before use to avoid any adhesion to the concrete and forms and make it difficult to remove them. Concrete should not be discarded but should be placed in a place to protect against discrimination. it should be lowered as high as possible. it should be placed in one place on the formwork and allowed to flow in separate ways to take care of the bee colony. The formation of seas should be avoided. Can be tested by preventing concrete thickness by 150-300 mm with r c c function. Laitance, however, if constructed must be removed before laying the next layer of concrete. Several such layers form an elevator, as long as they follow each other fast enough to avoid cold joints. The top of the previous elevator is kept rugged and all the money spent is wiped out before setting the next elevator. Firmness should be checked for firmness and clean face. Rust or loose scales if present, are removed with a wire brush. Paint, oil or grease if found should be removed. a small tightening cover should be checked before assembly. Mass concretingWhere the concrete will be laid in bulk as a foundation for raft, dam, bridge, pier etc., the concrete is laid in sections of 350-450 mm in diameter. Several such layers arranged in quick succession form an elevator. before applying the concrete to the next lift, the front elevator area is thoroughly cleaned with water jets and scrubbing with a wire brush. in the case of dams, sand explodes. Laitance and lax matter are removed and cement mortar is applied. where the concrete is subjected to lateral thrust, binding bars or binding stones are provided to form the key between the various layers. Concreting Highways and RunwaysConcrete is placed in the areas of highway, open road, or floor slabs. First the soil on which the concrete is to be placed is prepared and all loose material and grass are removed etc. The ground is wet and compacted. The subgrades into which the concrete is to be placed should be well mixed and diamond-plated to avoid any moisture loss in the concrete. The concrete is then placed elsewhere. This allows the concrete to pass through enough and the cracks do not grow after that. Concrete is not placed in a pile in one place and then pulled out, instead it is placed in the same size. Concreting underwater2. Concrete can be placed under water with the help of dumping buckets. The concrete is soaked in water from a water-tight bucket. When you get to the floor the bucket is made open and the concrete is discarded. In this process a certain amount of cement is washed away resulting in a decrease in the strength of the concrete. Another way to make underwater concrete is to fill a bag of cement with a dry or dry mixture of cement and aggregates and lower it into the storage area. The downside to this approach is that the concrete will fill the gaps filled with the bags with the guns.3. A good way to put concrete under water is to use a termie pipe. Concrete is poured into it by a ditch. The lower edge of the pipe is covered with thick ploythene paper, below the pipe in the installation area. Concrete (150-200 mm fall) is poured into the mortar until the entire pipe is filled with cement. The pipe is slightly raised and given a jerk, the polythene metal cover falls off and the concrete is shown. It must be ensured that the end of the pipe stays inside the concrete so that water does not enter the pipe. The pipe is then filled with concrete along the border and the process is repeated to the concrete level above the water level. No reduction is required for underwater concrete as combined with hydrostatic water pressure. Concrete can also be placed under water with the help of pipes and pumps.COMPACTIONAfter the concrete has been applied to the desired location, the next step in the concrete production process is its assembly. The joint consists of new concrete inside the mold or frames and surrounding embedded parts with reinforcing steel. A lot of air is trapped in the concrete during its production and there may be partial separation. Both of these factors adversely affect the quality of the concrete. Concrete compression is the process of removing trapped air and voids, eliminating the separation and creating a uniform weight. It was found that 5 percent of the void in reinforced concrete reduced energy by more than 30 percent and 10 percent of voids reduced energy by more than 50 percent. Therefore, the density and consequence of the strength and durability of concrete depend largely on the degree of density. For maximum strength dry concrete should be mixed 100 percent. Voids increase the penetration of concrete. Impossible loss results in the easy penetration of moisture, oxygen, chlorides, and other harsh chemicals into the concrete. This causes metal corrosion and cracking (dispersion) of the concrete i.e., loss of strength. The easy penetration of sulphates from nature causes a strong reaction with tri calcium aluminate (C3A) present in the cement. This causes concrete damage and loss of strength. The infiltration of carbon dioxide causes the lightening of the concrete i.e., the loss of alkalinity of the concrete or the loss of protective energy provided by the concrete to the reinforcement or other metal embedded in it. When the depth of the carbon exceeds the size of the concrete cover of the embedded metal, the metal is exposed to moisture. This speed up the corrosion of metal as the protective concrete cover remains naturally alkaline. Voids also reduce the connection between the embedded metal and the concrete. This leads to the loss of the strength of the bond of the reinforced concrete joint and thus the member loses strength. Spaces such as honeycombs and blowholes on the exposed surface reveal a visible feature. Concrete surfaces are not good to look at in all such aspects. Concrete smoothly and perfectly, the finishing area not only looks good but is also durable and durable. The joints are obtained by providing external work over the concrete to overcome internal tensions between the particles that make up the concrete, between the concrete and the reinforcement and between the concrete and the forms and by reducing the air barrier to a minimum. Concrete congestion can be obtained in the following ways. 1. Hand compaction2. Compaction by vibrationa. Needle Vibrator:b. Formwork Vibrator3. Compaction by spinning4. Compaction by jolting5. Compaction by rollingCURING OF CONCRETECement gets stronger and harder due to the chemical action between cement and cement. This chemical reaction requires moisture, a good temperature and a period of time called treatment. Differences in compression strength and healing time. The healing of newly installed concrete is very important for its strength and durability. Most of the energy in the first phase is supplied by the clinker compound C3S and half is C2S, and is completed in about three weeks. Recent power Provided by C2S is slow and long lasting. Since enough water should be made of concrete to allow it to get full strength. The process of maintaining concrete moisture for this purpose is known as cooling. The purpose is to prevent moisture loss in concrete due to Evaporation for any other reason, provide extra moisture or heat and humidity to accelerate energy gain. Treatment should be done for at least three weeks and is not possible in less than ten days. About 14 liters of water is needed to irrigate each bag of cement. Immediately after the laying of the concrete, the increase in strength is very rapid (3 to 7 days) and then progresses slowly thereafter indefinitely. Wet concrete cured for 7 days is about 50 percent more than dry air produced all the time. If the concrete is kept wet for one month, the strength is almost twice as high as that of concrete exposed only to dry air.
Fig no 3 Development of strength with curingMETHOD OF CURING Concrete can be kept moist in many ways. The methods consist of supplying excess moisture to the concrete during the initial solidification by meditation, spraying, spraying, etc. Or by preventing moisture loss in concrete by sealing the concrete with a membrane formed by the applied treatment. The following are some of the earlier treatments. 1. Water curing2. Steam curing3. Curing by infra red radiation4. Electrical curing5. Chemical curingFinishingConcrete is used primarily because of its high compression strength. However, the end of the final product is not a good thing. In the last few decades efforts have been made to complete the construction of the land so that it can be seen better in concrete areas and is as follows.1. Formwork finishes 2. Surface treatment3. Applied finishes Q4) Explain influence of temperature and maturity of concrete A4)Temperature is something we can't control. Temperature fluctuations can affect the results of new residential or commercial concrete projects and are something to be aware of when laying it down. Concrete is originally a plastic object made of a mixture of cement, water, and composite. Water can be very hot or very cold thus affecting how the concrete appears when it hardens. This combination of precise size makes it harder for more time to provide the built-in power. Even during set-up, the concrete will emit a lot of heat and lose water, which needs to be controlled by a process known as treatment. The Effects of Heat on ConcreteTemperatures during the manufacture and installation of concrete may affect the setting time and storage capacity. When temperatures are high, this can lead to cracking, and many concrete works use cold water through the mixing process to control the concrete temperature and reduce the chances of cracking and damage. Once the concrete has been set and acquired its design strength, which is generally accepted as 28 days, the concrete will expand and operate according to the local temperature. This movement is determined by the coefficient of heat dissipation of concrete and changes in temperature when the building is exposed. The rate of development is mainly determined by the calculations used as they form 70 to 80 percent of the concrete volume. High temperatures can lead to an increase in concrete, and this can lead to cracking. The length of the concrete structure can also lead to additional stress in construction. This feature is especially important on bridges. Low temperatures, on the other hand, can lead to the reduction of concrete and this can be disrupted when water enters the cracks, leading to the formation of ice which can cause serious problems for the concrete due to the increase in volume. Impact of Temperature VariationTemperature variations can have a negative and positive impact on concrete and its strength. The temperature of the mixed area when it is first laid must be under controlled conditions so that the concrete gains the design strength it is intended to have. An increase in temperature affects the initial energy increase while reducing energy in the long run. Temperature variations can have an effect on a variety of concrete structures. The initial high temperature affects the recent strength of the concrete, as this increases the fuel and leads to uneven distribution of hydration products. This leads to product concentrations in the area of hydrating particles and this slows down hydration continuation and affects energy. High temperatures during laying can also increase voids in concrete, and this can significantly affect its durability. High temperatures also tend to reduce the performance of concrete, and this makes it very difficult for proper reinforcement. Rapid hydration leads to the concrete getting its original strength early and hard when stirred and set. This can lead to the formation of beehives in concrete, which can have a significant impact on concrete strength. Concrete is best placed at temperatures between 5 degrees Centigrade and 40 degrees Centigrade. Any temperatures above or below this require special care in the temperature of the water used in the mixing, and subsequent care while curing the concrete. This process can take years of experience to complete. If you have a big project and need experts, call us, Frederick's company with concrete. MATURITY RULEMaturityThe maturity of the concrete indicates how far the treatment has progressed. Growing the relationship between concrete temperature, time and energy gain. It is represented by a reference value that can be measured in real time in the field. How to MatureThe ripening method, often referred to as maturation, is a method of testing the strength of new local concrete by associating time measurements with temperature and actual energy values. To speed up schedules, increase safety, and improve construction methods, construction teams want to know the strength of their concrete in the workplace in real time. Since maturity is related to concrete strength, maturity method is a way of achieving this without relying solely on the standard specimens of testing and laboratory testing. Growth is calculated following the changes in the temperature of the new concrete over time. Since each concrete compound has its own solid-maturing properties, we can use maturation to measure the strength of that compound at any time after laying. Once we know the ripeness of a particular concrete, we can use special relationships of concrete with the strength of the maturity to make a reliable measure of its strength. Basic StepsMonitor internal temperatures during healing Use the internal temperature history tracked to calculate maturity Use maturity relationships to measure strength Q5) Explain workability and factors affecting workability A5)WHAT IS THE WORKABILITY OF CONCRETEConcrete performance is a broad and automated term that describes how freshly mixed concrete can be easily mixed, laid, assembled and finished with minimal loss of homosexuality. Performance is an asset that directly affects the power, quality, appearance, and even personnel costs of placement and completion. But ideas are not very important when testing and documenting concrete structures, so how are these quality factors explained in terms of measurement values. This will include everything you need to know about concrete operations, contact materials, descriptive tests, and downhill test kits to test you. The use of the word indicates the ease or difficulty with which concrete is handled, delivered and laid. The amount of water available in concrete should be at the right level. Generally, a high amount of cement water is required for it to work properly. In the real work of water is to lubricate the concrete. Easy concrete to manage and install active concrete. Types of workability1. Low workable concrete 2. Medium workable concrete3. High Workable concrete1. Low workable concrete Poor concrete can also mean rough concrete. Low-water concrete is known as underutilized concrete. It is difficult to mix the concrete by hand. Its water content of cement is less than 0.4, and the compaction factor of this concrete is about 0.85. The low working concrete has a complete concrete separation due to the lack of cement adhesive tile to adhere to the aggregates. Maintaining such a concrete surface is difficult and requires a great deal of effort. 2. Medium workable concreteMedium working concrete is useful for almost all construction work. This type of concrete allows ease of mixing, transport, placement, and assembly without losing homogeneity. This concrete does not show much variation. The density factor of such concrete is about 0.92, and the water content of cement is 0.4 to 0.55. This type of concrete is ideal for strong reinforcement construction work 3. High Workable concreteThis type of concrete provides great ease of mixing, transporting, laying, and assembling. This concrete is useful for that construction project when adequate integration is not possible. This type of concrete flows smoothly and settles down without much effort, but there is a strong possibility of separation and the loss of homosexuality in this situation. The water level of the cement in this concrete is more than 0.55. Due to the high amount of water cement, the green mixture usually settles to the ground, and then a concrete slab appears. This concrete is suitable when the density of the concrete is high, and vibration of the concrete is not possible. Joint concrete (SSC) is an example of high quality concrete. Good Workability Means Different Things to Different People There are different expectations and agendas for all construction / construction team groups when it comes to good concrete construction. A building engineer wants high strength and good bond with reinforcing steel. The architect is concerned with the attraction of cosmetics. The carrying capacity is attractive to the owner because it allows for smaller parts of the material and therefore more user-friendly space. The worker needs a blend that can be delivered, packaged, and blended well, and the finish maker is looking for something that takes a solid, high-quality finish quickly and easily. The combination of concrete and good performance brings many qualities together in balance and leads to a quality product with a long working life. FACTORS AFFECTING WORKABILITYThe dimensions and features of the building materials and structures of admixtures all contribute to the functionality and other characteristics of all concrete composite drawings, functional impacts including:Water / cement ratio:The higher the amount of cement or cement reinforcement material usually means the greater the strength, and with the right amount of water, the more glue you put in layers for easier mixing and better finishing. Not enough water for proper hydration means an increase in negative energy and non-compliant combinations that resist easy installation and elimination. Adding more water may increase performance because it makes it easier to set and mix. However, the negative impact on segregation, termination of performance, and retention potential can be so detrimental that you have to approach with extreme caution. Water to a cementitious material ratio (w / cm) of 0.45 to 0.6 is a good place for the production of active concrete. Combined Size and Shape: As the composite surface area increases, more cement paste is required to cover the entire joint area. So mixing with smaller aggregates is less effective compared to larger-size combinations. Combined, angular, and hollow joints are difficult to assemble and place and have a large cover area, reducing performance. The circular collection has a low surface area, but does not have the angularity of improving the bond strength sufficient for cement adhesion. Crushed composites in the right proportions provide better bonding with the cement matrix and adequate performance. Admixtures: Many types of admixtures change the performance of a new concrete, either by construction or as a side effect. Surfactants such as super plasticizers reduce the attraction between cement and composite particles, allowing compounds that can flow without negative energy and the effects of excess water separation. The insertion of internal admixtures of durability / dissolving solids produces internal bubbles of a controlled size that can make it easier to eliminate, although overuse produces an adhesive mix with a different effect. Grading of concreteIf the combination is well organized, that means less content will be empty and higher content will work, so as far as possible, the combination should be well organized. Surface texture of aggregate If the surface of the aggregates is smooth or glassy, it will produce less surface and will provide better performance. The contrasting resistance between the smooth particle is reduced and will produce higher performance. So this is an important factor in performance. Amount of cementThe concrete content greatly affects the performance of the concrete. If we increase the size of the cement, much will be the cement paste to cover the surface of the composite and the useless filling. It helps to reduce the friction between the composites that have led to the smooth movement of aggregates in the transport, placement, and bonding of the concrete. At a fixed amount of cement water, an increase in the amount of cement will increase the amount of water per concrete per unit, which is why it increases the efficiency of the concrete. Q6) Explain cohesion and segregation A6)COHESIONHow good it is to hold it together in a plastic state. Cohesion is affected by:1. Aggregate gradingGraded Aggregate means that there is a range of Aggregates size, from large rocks to thin sand .2. Water contentThe watery mixture will not coalesce and can separate and bleed. TREATMENT The treatment retains the moisture of the concrete for some time, allowing it to reach greater capacity. Long-term curing will provide long-lasting concrete.3. Weather Warm weather will cause the concrete to have a higher strength.4. Type of cementDifferent types of cement will affect concrete structures: which means how quickly the concrete gains.5. Water to cement ratio Too much water and too little cement means that the concrete will be weak and will not last long. The amount of water to the cement (W / C) is the amount of water divided by the weight of the cement.SEGREGATIONConcrete separation is a matter of particle separation in concrete applications, in which particle particles are usually separated due to differences in size, density, shape and other particle structures. It is defined by the American Society for Testing and Materials as follows: "Concrete separation is often thought of as the separation of other composite groups from cement mortar in isolated areas and the corresponding shortage of these materials in other areas. Separation causes parallel concrete laying different from those designed. poorly balanced and poorly blended, or highly efficient mixing, placement, or adverse weather conditions. The corresponding increase in the rate of cement adhesion in the upper areas may often expose them to increased risk of shrinkage and cracking. look up, and be in the shape of a map pattern. The result of the integrated isolation in concrete conduct and transport behavior has been the focus of birth modeling and experimental research. Q7) Explain test workability by slume cone of fresh concrete A7)ObjectiveThe word ―workable or concrete used has a broader and deeper meaning than the word alternative that is commonly used freely to make it work. Consistency is a general term that indicates the level of fluid or flow rate. Factors that help concrete to have the most effective effect of reducing internal friction that facilitates easy mixing are: (a) Water content (b) Mixing Dimensions (c) Collection Size (d) Structure Shapes (e) Spatial Design Design (f) Placement layout (g) Use of Admixtures.Slump test is the most widely used method of measuring the consistency of concrete that can be used in a laboratory or in the workplace. It is not suitable for very wet or very dry concrete. It does not measure all factors that affect performance, nor does it always represent concrete placement. Indicates the concrete feature above the drop value. When the concrete slips evenly it is called a true slump. When one part of the lump slips, it is called a shear slump. In the event of a shear bend, the slump value is measured as the height difference between the height of the mold and the average amount of shrinkage.
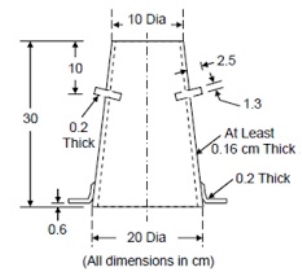
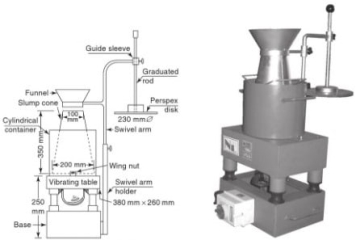
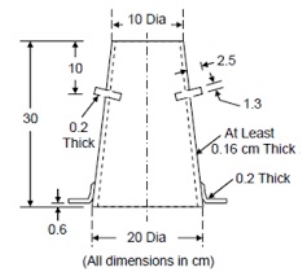
Fig no 4 Slum coneProcedureIf this test is performed in the field, a mixed concrete sample will be obtained. In the case of concrete containing a diameter of more than 38 mm, the concrete will be diluted with water by one and a half inches of screen to remove compacted particles larger than 38 mm. The inner surface of the mold will be thoroughly cleaned and freed from unwanted moisture and pre-set concrete before testing. The mold will be placed on a smooth, horizontal, strong, and non-abrasive surface, such as a carefully weighed metal table, the mold will be kept firmly in place while filling. The mold will be filled in four layers, each about a quarter of the height of the mold. Each layer will be smoothed with twenty-five lashes on the round edge of the lubricating rod. The lashes will be distributed evenly over the section at the cross section of the mold and the second and subsequent layers will fit into the lower layer. The bottom layer will be smoothed in the depth of it all. After the upper layer has been coated, the concrete will be flattened and trimmed with a trowel, so that the mold will fill directly. After the top layer has been glued, remove the concrete surface by moving and moving the lubricating rod. Any mud that may have leaked between the mold and the base plate should be cleaned. The mold will be removed from the concrete immediately by lifting it gently and carefully in a vertical direction. This allows the concrete to drop and the fall will be measured immediately by determining the difference between the height of the mold and that of the highest of the test template. The above operation will be performed in a non-vibrating or panic-free environment, and within two minutes after sampling.
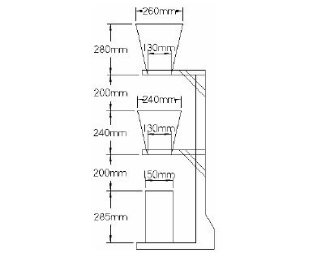
Fig no 5 Dimensions of slum coneQ8) Explain compaction factor A8)ObjectiveThe compacting factor test is mainly designed for use in the laboratory but can also be used in the field. It is more accurate and sensitive than fall testing and is especially useful for very low-performance concrete mixes and is often used when the concrete will be squeezed by vibration. This method works on bare and ventilated concrete, made of lightweight, standard weight or heavy aggregates with a maximum weight of 38 mm or less but not on open concrete or non-reinforced concrete.
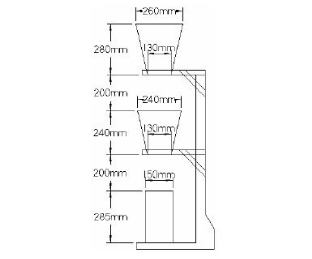
Fig no 6 Compaction factor apparatusProcedureA sample of the test concrete will be gently placed on the upper hopper, using a hand scoop. The hopper will be evenly filled with its edge and the trap door will be opened so that the concrete falls to the ground. Some mixes tend to stick to one or both hoppers. When this happens, the concrete can be helped by pushing the rod gently into the concrete from the top. During this process, the cylinder will be covered with tiles. As soon as the concrete is out, the cylinder will be exposed, the door to the bottom trap will be opened, and the concrete will be allowed to fall into the cylinder. The remaining concrete over the top of the cylinder will be removed by holding a trowel in each hand, the plane of the belts horizontally, and then moving them simultaneously to each side above the cylinder, at the same time keeping them pressed against the upper edge of the cylinder. The outside of the cylinder when it is wiped will be clean. The above work will be done in a place that will not tremble or shake. The weight of the concrete in the container will be determined by the nearest 10 g. The remaining concrete over the top of the cylinder will be removed by holding a trowel in each hand, the plane of the belts horizontally, and then moving them simultaneously to each side above the cylinder, at the same time keeping them pressed against the upper edge of the cylinder. The outside of the cylinder when it is wiped will be clean. The whole process will be done in a place where there is no vibration or shock. This weight will be known as the weight of the partially bonded concrete. The cylinder will be filled with concrete from the same sample with layers about 5 cm deep, the layers folded tightly or shaken to achieve complete integration. The surface of the fully covered concrete will be carefully beaten and weighed above the cylinder. The outside of the cylinder when it is wiped will be clean.
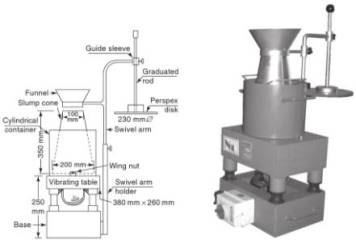
Fig no 7 Dimensions of compaction factor apparatusQ9) Explain vee bee consistometer and flow table apparatus A9)VEE BEE CONSISTOMETERObjectiveThe performance of the new concrete is a composite material, which incorporates various requirements for stability, mobility, durability, placement and finishing. There are various ways to measure performance. Each of them measures only a specific aspect of it and there is no unique test, which measures the performance of concrete completely. This test provides an indication of the flow rate of the newly mixed concrete mix. The test measures the concurrent effort required to change a pile of concrete from one concrete to another (e.g., from a circle to a cylindrical) using vibration. The amount of effort (called retrieval attempt) is taken as the time in seconds, which is required to complete the change. The results of this experiment are useful when you study the flow of concrete piles made of different amounts of water, cement and different types of composite placement. The time required for a full recovery in seconds is taken as a performance measure and is expressed as the Vee-Bee number of seconds. This method is suitable for dry concrete. With concrete drop of more than 50mm, reconstruction is so fast that time cannot be measured.
Fig no 8 Vee bee Consistometer TestProcedureSlump test as described in "IS 1199: 1959 Details of Concrete Testing Equipment (Fourth Review). Confirmed- Dis 2013". is made, inserting a collapsible lump inside a round metal pot of consist meter. The glass disk attached to the rotating arm will be moved to the top of the cone in the pot and before the cone is raised, the location of the concrete cone will be identified by fixing the glass disc attached to the arm wrist. The cone will then be lifted and the fall will be marked on the graduating rod by lowering the glass disc over the concrete cone. The electric heater will then light up and the concrete will be allowed to lay in the pot. The vibration continues until the point where the concrete shape disappears and the concrete takes on a circular shape. This can be judged by looking at the glass disc from the top disappearing visually. As soon as the concrete completely begins to form a circle, the stand clock is turned off. The time required for concrete formation to change from the formation of a collapsing lump into a circle in seconds is known as the Vee Bee Degree. This method is best suited for dry concrete with an unmeasured fall value with a Slump Test, but vibration is much stronger than concrete with a fall of more than 50 mm. FLOW TABLEFlow tests were performed to measure the performance of the concrete. As the name suggests, in this experiment concrete performance is measured by examining the flow of concrete material. Flow test Easy laboratory test. This test applies to the principal for the general weight loss of concrete and is measured by the flow of concrete. The flow of concrete indicates the performance of the new concrete.Why flow test of concrete requiredFlow tests are used to measure the performance of high or very active concrete, which ultimately indicates a fall. It gives an idea about the quality of concrete in terms of consistency and consistency. This performance test is easy to perform and is best suited for concrete with a high overall size of the joint less than 38 mm.Flow Test ApparatusMetal Cone or Mould: Mould is in the form of a frustum of a cone with a base diameter of 250 mm, upper surface diameter of 170 mm and 120 mm height. The mould comes with handles for support.Flow TableTrowelsHand scoopScaleTamping Rod
Fig no 9 Flow test apparatusProcedureClean anything toxic or dusty from the flow table and inside the mold. Place the lump on the marked area or in the middle of the flow table. Now pour the freshly mixed concrete into the mold in two layers, each layer should be moistened 25 times with a soft stick. If the concrete overflows after stamping and measure with the help of a torch, and the excess concrete should be removed from the table. After that, lift the mold upwards and allow the concrete to stand on its own without support. After that the table is raised and lowered from 12.5 mm high, 15 times in about 15 seconds. Next, measure the width of the concrete spread by about 6 points and write down the scale. Q10) Explain effect of admixture on workability of concrete and optimum dosage of admixture by marsh cone test A10)EFFECT OF ADMIXTURE ON WORKABILITY OF CONCRETEConcrete contains cement, sand, a mixture of water. Anything other than these if added to concrete before or during mixing to convert structures to our desired requirement is called admixtures. The use of admixtures provides certain beneficial effects on concrete such as improved performance, speed or delay of set time, reduction of the amount of water cement, and so on. There are two basic types of admixtures available: chemicals and minerals. Admixtures such as fly ash, silicate fume, slag come in the category of mineral admixtures. They are incorporated into concrete to increase performance, improve thermal resistance and alkaline reactions and enable us to reduce cement content. Fly ash is a good residue left over from global warming or powdered charcoal. They are all better than cement and contain mainly round glass particles as well as remnants of hematite and magnetite, char and other crystalline layers formed during cooling. The use of fly ash in concrete makes mixing more economical, and improves performance, reduces separation, bleeding and reduces hydration temperatures but also offers natural benefits. Silica fire, also known as micro silica. It is available as a product during the production of silicon and ferrosilicon alloys. The particles of silica fire particles are 100 times smaller than cement particles which mean their smoke like cigarettes. Its highly efficient pozzolanic material, which improves concrete structures such as improved durability, bond strength, abrasion resistance, dense concrete leading to reinforcement and rust protection. Chemical admixtures are applied to concrete in very small quantities especially for ventilation, reduction of water or cement content, installation of new concrete mixtures or control of concrete set time. These compounds can be widely used as super plasticizers, accelerators, retarders, water reducers and ventilation admixtures. Super plasticizers were added to reduce water demand by 15 to 20% without affecting performance leading to high durability and high concrete. Super plasticizers are liner polymers that contain sulfonic acid groups attached to the polymer from time to time. Commercial composition can dissolve melamine - formaldehyde condens- sates, sulfonated naphthalene formaldehyde condensates, and modified lingo sulfonates, derived from polycar- boxylate. The main purpose of super plasticizers is to produce a concrete slope with a very high drop of 175 to 200 mm that can be used effectively on reinforced concrete structures, a decrease in volume depending on the volume, type and timing of good plasticizers (preferably before adding concrete.), Water cement, environment and value of cement. Accelerators were added to reduce the setting time of the concrete thus facilitating pre-form removal and are also used in the combination of cold weather. Calcium chloride is the most widely used accelerator in blending. The use of calcium chloride in reinforced concrete can promote the corrosion function of the steel reinforcement. As people become aware of it there is a growing interest in using free chloride. Retarders were added to increase the setting time by delaying the hydration of the cement. They are popular in areas with high temperatures combined. Retarders contain organic & inorganic agents. Organic retarders include unrefined calcium, sodium and ammonia salt lignosulfonic acid, hydro carboxylic acid and carbohydrates. Inorganic retardants include lead oxides, zinc, phosphate and magnesium salts. Most retarders work as a water repellent. They are called retarders that reduce water. It is therefore caused by high pressure forces due to the low water content. Admixtures reduce the amount of water added to the concrete to achieve a certain effect (fall) at a lower water level. Strong concrete specified for low cement content thus saving cement. Water reducers are widely used in hot weather and assist in pumping. Water-repellent plasticizers are hygroscopic powder, which can inhale air into concrete. Ventilation admixtures bring in small concrete bubbles. These air bubbles act as rollers thus improving performance and also work more efficiently in thaw-chilling channels as they provide a stabilizing effect in expanding water where cold weather meets. Ventilation admixtures are compatible with most combinations, care should be taken to prevent them from collapsing during mixing. In general, the performance of both types of plasticizers depends on the ambient temperature and thus in the summer the amount of plasticizer that will be used to handle the same rate of plastic expansion may be more than the amount that will be used in winter. The change in the normal set time within a specific requirement also makes the product dependent on other chemicals and as plasticizers with different nomenclature available in the market. CICO Technologies Limited, a 75-year-old Indian company ISO 9001: 2000 supported producing a range of concrete installation admixtures. Many RMC companies use CICO admixtures. Further modification is required during the trial. Modification to Plasticizers can meet the needs of any particular client. OPTIMUM DOSAGE OF ADMIXTURE BY MARSH CONE TESTAdmixtures are common and important of modern concrete. Low water content, high efficient, durable and cost-effective cement Many desirable properties that can be expected from concrete made of chemical and mineral composites Admixture-Cement mixing in concrete is complex combination of chemical and physical equipment independent. All combinations in large volumes offer good results when used with cement. Cement hydration involves a series of reaction, which is highly dependent on cement composition, water / cement ratio, surface area, particle distribution of size, temperature and integration. Admixtures when added in small amounts do that the hydration process is very complex. In recent times, developments in the cement product sector are related to the use of admixtures especially organic polymeric building materials. Many species of polymeric organisms known as super plasticizers, are used construction industries to change the way it flows again concrete machinery facilities. Among the various species for chemical admixtures, PCE-based admixtures are shown to develop new flow and complex areas of low-grade concrete.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNIT – 2PRODUCTION, PROPERTIES AND TESTING OF FRESH CONCRETEQ1) Explain production and properties of fresh concrete A1)NOMINAL MIXESIn concrete mix concrete, all ingredients and their size are determined by standard definitions. This ratio is specified in the cement ratio to the specific energy gain combination. Mixing ratios such as 1: 1.5: 3, 1: 2: 4, 1: 3: 6 etc. They were adopted by mixing concrete without a scientific basis, only on the basis of previous studies of solidarity. Therefore, acceptance of ordinary concrete or not to mention, the mixing of preference is preferred for simple, insignificant and minimal concrete works. According to the 'Indian Standard- IS 456: 2000', pre-mixed concrete can be used for M20 grade concrete or lower grade such as M5, M7.5, M10, M15. Proportion of nominal mix as per Indian StandardThe volume of composite materials under M20 grade concrete will comply with IS 456: 2000 According to IS 456: 2000, in the composition of the composition can be adjusted the estimated values if the water level will be increased to overcome the difficulty of laying and density of concrete so that the water level of the cement is maintained as specified. Automatic mixing usually consists of volumetric batching. The measurement is usually determined by weight, and in combination it is converted to a volume value, i.e. in the case of one bag of cement, i.e. 50 kg of standard measuring boxes are made on site, at the rate of one bag of cement. These measuring boxes are called box gauges. Advantages of nominal Mix Concrete01. A self-proclaimed mix is a pre-determined concrete because the scale is pre-determined.02. It is easy to do in the construction site.03. It does not take much time to determine the value because the size is already provided with the standard code.04. There is no need to find people who have the skills to make concrete mixing name.Disadvantages of nominal mix concrete01. The great recurrence of the mix of claims is that, it is based on past experience and studies of art, and has no scientifically proven method.02. It can create or build well-designed energy unless all other factors such as density, w / c ratio, concrete treatment are strictly adhered to.03. The amount of water cement is considered by thought and, if left unchecked, sometimes leads to bleeding and separation of the concrete which leads to poor performance and therefore impairs the strength of the concrete.04. No consideration of composite structures such as classification and quantity of composite items etc.05. In a word mix, cement content is sometimes used in excess, which increases the total cost of construction.06. No laboratory tests are performed to ensure the quality of the new concrete.07. This combination does not consider and evaluates the specific properties of each ingredient. For example, if we take cement as part, the softness of the cement, the quality of the cement and the type of cement, the size and layout of the composite etc. It is usually not counted individually when making this fake assertion mix.Q2) Explain water cement ratioA2)The water–cement ratio is the ratio of the load of water to the load of cement utilized in a concrete blend. A decrease ratio ends in better electricity and durability, however might also additionally make the combination hard to paintings with and form. Workability may be resolved with using plasticizers or super-plasticizers. Often, the ratio refers back to the ratio of water to cement substances, w/cm. Cement substances encompass cement and supplementary cement substances which include fly ash, floor granulated blast-furnace slag, silica fume, rice husk ash and herbal pozzolans. Supplementary cement substances are delivered to reinforce concrete. However, a combination with a ratio of 0.35 might not blend very well, and might not glide nicely sufficient to be positioned. More water is consequently used than is technically important to react with cement. Water–cement ratios of 0.45 to 0.60 are greater usually used. For better-electricity concrete, decrease ratios are used, in conjunction with a plasticizer to boom flow ability. Q3) Explain process of manufacturing of fresh concrete with all processes like batching, mixing, transportation, compaction, curing of concrete, curing methods .A3)Good quality concrete is actually a compact mixture of cement, composite and good mixing with water that mixes into a hard mass due to the chemical action between cement and water. Each of the four regions has a specific function. The coarser collection serves as a filler. A good collection fills the gaps between the attachment and the green combination. Cement by contact with water acts as a bond. The flow of the mixture is aided by the adhesion of cement, fines to this day, increasingly using mixtures. Most of the reinforced concrete materials depend on the care used in all stages of concrete production. The logical separation of concrete ingredients is the core of the mixing design. However, it may not guarantee the achievement of the goal of quality workmanship. The purpose of quality control is to ensure the production of concrete of the same power from batch to batch. This requires that certain rules be followed in the various stages of concrete production and discussed below. The stages of concrete production are:1. Batching and measurement of material2. Mixing3. Transport4. Placement5. Compacting6. Curing 7. Finishing
Fig no 1 Manufacturing process of concreteBATCHING OF MATERIAL For good quality concrete should be used the correct and accurate amount of all ingredients. Combined, cement and water must be measured with an accuracy of 3 percent of batch quantity and admixtures at 5 percent of the total value. There are two most common forms of baking material, batching volume and heavy batching. Factors affecting the choice of baking method by the size of the work, the required production rate, the required batching performance standards. It is recommended for the most important tasks. a) Volume batchingb) Weight batchingMIXING1. Hand Mixing2. Mixing Machinea) Tilting mixersb) Non- tilting mixerc) Reversing Drum mixerd) Pan type or stirring mixere) Transit mixerf) Charging Mixer and mixing timeThe order for the ingredients in the mixer is as follows:About 25 percent of the water needed for mixing is initially placed in the mixing tank to prevent any cement attachment to the rings and bottom of the drum. Then the ingredients are extracted in excess. To skip over the loading sequence should be to insert the first half of the coarse cement and then the composite half to be on top of this complete cement and the aggregate to balance. After adding the ingredients to the drum equal volume was introduced. The mixing time is calculated from the total water added to the mixture. The speed of the aggregates is usually 15 to 20 per minute. With proper mixing, the number of changes per minute required by the drum is 25 to 30. The mixing time also depends on the mixing capacity
Fig no 2 Table of mixingPoor quality of concrete is obtained when mixing time is reduced. on the other hand if the mixing time is extended it is not economical. however, it is found that when the mixing time is extended to 2 minutes the compressive strength of the produced concrete is improved and beyond this time the improvement of the compressive strength is not significant. prolonged mixing can cause separation. Also, due to the long mixing times water can get in or out and lead to loss of function and energy. TRANSPORTINGThe concrete should be moved to the storage area immediately without the loss of homosexuality acquired during mixing. a maximum of 2 hours from mixing time is allowed if trucks have an agitator and 1 hour using trucks without stimulants to move the concrete. And it must be ensured that separation does not occur during travel and placement. The methods used to transport concrete depend on the quality and value of the work, the distance to the placement site, and the location. some of the concrete delivery methods are below:a. Mortar panb. wheel barrowc. Chutesd. Dumpere. Bucket and ropewayf. Belt conveyorg. skip and hoisth. PumpingPLACING Achieving quality concrete should be placed very carefully to protect the homosexuality achieved during mixing and to avoid transport segregation. studies have shown that delays in the installation of concrete results in gaining greater compressive strength as long as the concrete is not sufficiently compacted. in dry mixes in hot weather a delay of half an hour is allowed and in wet mixtures when it is cold it can be a few hours. the various conditions in which concrete is applied are discussed below. FoundationsConcrete foundations for walls and columns are provided underground. Before laying concrete on the foundation all open ground, tree roots etc., are removed. If the area is found dry it is made wet so that the soil does not absorb water from the concrete. On the other hand when the foundation bed is wet the water and mud are removed and the cement is sprinkled before laying the concrete. Beams, columns and slabsBefore laying the concrete, the forms must be inspected for proper alignment. They should be strong enough to withstand the weight of concrete and construction loads without undue damage. The forms should be light enough to avoid any mud loss that has resulted in concrete mixed with bees. the inside of the forms should be cleaned and oiled before use to avoid any adhesion to the concrete and forms and make it difficult to remove them. Concrete should not be discarded but should be placed in a place to protect against discrimination. it should be lowered as high as possible. it should be placed in one place on the formwork and allowed to flow in separate ways to take care of the bee colony. The formation of seas should be avoided. Can be tested by preventing concrete thickness by 150-300 mm with r c c function. Laitance, however, if constructed must be removed before laying the next layer of concrete. Several such layers form an elevator, as long as they follow each other fast enough to avoid cold joints. The top of the previous elevator is kept rugged and all the money spent is wiped out before setting the next elevator. Firmness should be checked for firmness and clean face. Rust or loose scales if present, are removed with a wire brush. Paint, oil or grease if found should be removed. a small tightening cover should be checked before assembly. Mass concretingWhere the concrete will be laid in bulk as a foundation for raft, dam, bridge, pier etc., the concrete is laid in sections of 350-450 mm in diameter. Several such layers arranged in quick succession form an elevator. before applying the concrete to the next lift, the front elevator area is thoroughly cleaned with water jets and scrubbing with a wire brush. in the case of dams, sand explodes. Laitance and lax matter are removed and cement mortar is applied. where the concrete is subjected to lateral thrust, binding bars or binding stones are provided to form the key between the various layers. Concreting Highways and RunwaysConcrete is placed in the areas of highway, open road, or floor slabs. First the soil on which the concrete is to be placed is prepared and all loose material and grass are removed etc. The ground is wet and compacted. The subgrades into which the concrete is to be placed should be well mixed and diamond-plated to avoid any moisture loss in the concrete. The concrete is then placed elsewhere. This allows the concrete to pass through enough and the cracks do not grow after that. Concrete is not placed in a pile in one place and then pulled out, instead it is placed in the same size. Concreting underwater2. Concrete can be placed under water with the help of dumping buckets. The concrete is soaked in water from a water-tight bucket. When you get to the floor the bucket is made open and the concrete is discarded. In this process a certain amount of cement is washed away resulting in a decrease in the strength of the concrete. Another way to make underwater concrete is to fill a bag of cement with a dry or dry mixture of cement and aggregates and lower it into the storage area. The downside to this approach is that the concrete will fill the gaps filled with the bags with the guns.3. A good way to put concrete under water is to use a termie pipe. Concrete is poured into it by a ditch. The lower edge of the pipe is covered with thick ploythene paper, below the pipe in the installation area. Concrete (150-200 mm fall) is poured into the mortar until the entire pipe is filled with cement. The pipe is slightly raised and given a jerk, the polythene metal cover falls off and the concrete is shown. It must be ensured that the end of the pipe stays inside the concrete so that water does not enter the pipe. The pipe is then filled with concrete along the border and the process is repeated to the concrete level above the water level. No reduction is required for underwater concrete as combined with hydrostatic water pressure. Concrete can also be placed under water with the help of pipes and pumps.COMPACTIONAfter the concrete has been applied to the desired location, the next step in the concrete production process is its assembly. The joint consists of new concrete inside the mold or frames and surrounding embedded parts with reinforcing steel. A lot of air is trapped in the concrete during its production and there may be partial separation. Both of these factors adversely affect the quality of the concrete. Concrete compression is the process of removing trapped air and voids, eliminating the separation and creating a uniform weight. It was found that 5 percent of the void in reinforced concrete reduced energy by more than 30 percent and 10 percent of voids reduced energy by more than 50 percent. Therefore, the density and consequence of the strength and durability of concrete depend largely on the degree of density. For maximum strength dry concrete should be mixed 100 percent. Voids increase the penetration of concrete. Impossible loss results in the easy penetration of moisture, oxygen, chlorides, and other harsh chemicals into the concrete. This causes metal corrosion and cracking (dispersion) of the concrete i.e., loss of strength. The easy penetration of sulphates from nature causes a strong reaction with tri calcium aluminate (C3A) present in the cement. This causes concrete damage and loss of strength. The infiltration of carbon dioxide causes the lightening of the concrete i.e., the loss of alkalinity of the concrete or the loss of protective energy provided by the concrete to the reinforcement or other metal embedded in it. When the depth of the carbon exceeds the size of the concrete cover of the embedded metal, the metal is exposed to moisture. This speed up the corrosion of metal as the protective concrete cover remains naturally alkaline. Voids also reduce the connection between the embedded metal and the concrete. This leads to the loss of the strength of the bond of the reinforced concrete joint and thus the member loses strength. Spaces such as honeycombs and blowholes on the exposed surface reveal a visible feature. Concrete surfaces are not good to look at in all such aspects. Concrete smoothly and perfectly, the finishing area not only looks good but is also durable and durable. The joints are obtained by providing external work over the concrete to overcome internal tensions between the particles that make up the concrete, between the concrete and the reinforcement and between the concrete and the forms and by reducing the air barrier to a minimum. Concrete congestion can be obtained in the following ways. 1. Hand compaction2. Compaction by vibrationa. Needle Vibrator:b. Formwork Vibrator3. Compaction by spinning4. Compaction by jolting5. Compaction by rollingCURING OF CONCRETECement gets stronger and harder due to the chemical action between cement and cement. This chemical reaction requires moisture, a good temperature and a period of time called treatment. Differences in compression strength and healing time. The healing of newly installed concrete is very important for its strength and durability. Most of the energy in the first phase is supplied by the clinker compound C3S and half is C2S, and is completed in about three weeks. Recent power Provided by C2S is slow and long lasting. Since enough water should be made of concrete to allow it to get full strength. The process of maintaining concrete moisture for this purpose is known as cooling. The purpose is to prevent moisture loss in concrete due to Evaporation for any other reason, provide extra moisture or heat and humidity to accelerate energy gain. Treatment should be done for at least three weeks and is not possible in less than ten days. About 14 liters of water is needed to irrigate each bag of cement. Immediately after the laying of the concrete, the increase in strength is very rapid (3 to 7 days) and then progresses slowly thereafter indefinitely. Wet concrete cured for 7 days is about 50 percent more than dry air produced all the time. If the concrete is kept wet for one month, the strength is almost twice as high as that of concrete exposed only to dry air.
Fig no 3 Development of strength with curingMETHOD OF CURING Concrete can be kept moist in many ways. The methods consist of supplying excess moisture to the concrete during the initial solidification by meditation, spraying, spraying, etc. Or by preventing moisture loss in concrete by sealing the concrete with a membrane formed by the applied treatment. The following are some of the earlier treatments. 1. Water curing2. Steam curing3. Curing by infra red radiation4. Electrical curing5. Chemical curingFinishingConcrete is used primarily because of its high compression strength. However, the end of the final product is not a good thing. In the last few decades efforts have been made to complete the construction of the land so that it can be seen better in concrete areas and is as follows.1. Formwork finishes 2. Surface treatment3. Applied finishes Q4) Explain influence of temperature and maturity of concrete A4)Temperature is something we can't control. Temperature fluctuations can affect the results of new residential or commercial concrete projects and are something to be aware of when laying it down. Concrete is originally a plastic object made of a mixture of cement, water, and composite. Water can be very hot or very cold thus affecting how the concrete appears when it hardens. This combination of precise size makes it harder for more time to provide the built-in power. Even during set-up, the concrete will emit a lot of heat and lose water, which needs to be controlled by a process known as treatment. The Effects of Heat on ConcreteTemperatures during the manufacture and installation of concrete may affect the setting time and storage capacity. When temperatures are high, this can lead to cracking, and many concrete works use cold water through the mixing process to control the concrete temperature and reduce the chances of cracking and damage. Once the concrete has been set and acquired its design strength, which is generally accepted as 28 days, the concrete will expand and operate according to the local temperature. This movement is determined by the coefficient of heat dissipation of concrete and changes in temperature when the building is exposed. The rate of development is mainly determined by the calculations used as they form 70 to 80 percent of the concrete volume. High temperatures can lead to an increase in concrete, and this can lead to cracking. The length of the concrete structure can also lead to additional stress in construction. This feature is especially important on bridges. Low temperatures, on the other hand, can lead to the reduction of concrete and this can be disrupted when water enters the cracks, leading to the formation of ice which can cause serious problems for the concrete due to the increase in volume. Impact of Temperature VariationTemperature variations can have a negative and positive impact on concrete and its strength. The temperature of the mixed area when it is first laid must be under controlled conditions so that the concrete gains the design strength it is intended to have. An increase in temperature affects the initial energy increase while reducing energy in the long run. Temperature variations can have an effect on a variety of concrete structures. The initial high temperature affects the recent strength of the concrete, as this increases the fuel and leads to uneven distribution of hydration products. This leads to product concentrations in the area of hydrating particles and this slows down hydration continuation and affects energy. High temperatures during laying can also increase voids in concrete, and this can significantly affect its durability. High temperatures also tend to reduce the performance of concrete, and this makes it very difficult for proper reinforcement. Rapid hydration leads to the concrete getting its original strength early and hard when stirred and set. This can lead to the formation of beehives in concrete, which can have a significant impact on concrete strength. Concrete is best placed at temperatures between 5 degrees Centigrade and 40 degrees Centigrade. Any temperatures above or below this require special care in the temperature of the water used in the mixing, and subsequent care while curing the concrete. This process can take years of experience to complete. If you have a big project and need experts, call us, Frederick's company with concrete. MATURITY RULEMaturityThe maturity of the concrete indicates how far the treatment has progressed. Growing the relationship between concrete temperature, time and energy gain. It is represented by a reference value that can be measured in real time in the field. How to MatureThe ripening method, often referred to as maturation, is a method of testing the strength of new local concrete by associating time measurements with temperature and actual energy values. To speed up schedules, increase safety, and improve construction methods, construction teams want to know the strength of their concrete in the workplace in real time. Since maturity is related to concrete strength, maturity method is a way of achieving this without relying solely on the standard specimens of testing and laboratory testing. Growth is calculated following the changes in the temperature of the new concrete over time. Since each concrete compound has its own solid-maturing properties, we can use maturation to measure the strength of that compound at any time after laying. Once we know the ripeness of a particular concrete, we can use special relationships of concrete with the strength of the maturity to make a reliable measure of its strength. Basic StepsMonitor internal temperatures during healing Use the internal temperature history tracked to calculate maturity Use maturity relationships to measure strength Q5) Explain workability and factors affecting workability A5)WHAT IS THE WORKABILITY OF CONCRETEConcrete performance is a broad and automated term that describes how freshly mixed concrete can be easily mixed, laid, assembled and finished with minimal loss of homosexuality. Performance is an asset that directly affects the power, quality, appearance, and even personnel costs of placement and completion. But ideas are not very important when testing and documenting concrete structures, so how are these quality factors explained in terms of measurement values. This will include everything you need to know about concrete operations, contact materials, descriptive tests, and downhill test kits to test you. The use of the word indicates the ease or difficulty with which concrete is handled, delivered and laid. The amount of water available in concrete should be at the right level. Generally, a high amount of cement water is required for it to work properly. In the real work of water is to lubricate the concrete. Easy concrete to manage and install active concrete. Types of workability1. Low workable concrete 2. Medium workable concrete3. High Workable concrete1. Low workable concrete Poor concrete can also mean rough concrete. Low-water concrete is known as underutilized concrete. It is difficult to mix the concrete by hand. Its water content of cement is less than 0.4, and the compaction factor of this concrete is about 0.85. The low working concrete has a complete concrete separation due to the lack of cement adhesive tile to adhere to the aggregates. Maintaining such a concrete surface is difficult and requires a great deal of effort. 2. Medium workable concreteMedium working concrete is useful for almost all construction work. This type of concrete allows ease of mixing, transport, placement, and assembly without losing homogeneity. This concrete does not show much variation. The density factor of such concrete is about 0.92, and the water content of cement is 0.4 to 0.55. This type of concrete is ideal for strong reinforcement construction work 3. High Workable concreteThis type of concrete provides great ease of mixing, transporting, laying, and assembling. This concrete is useful for that construction project when adequate integration is not possible. This type of concrete flows smoothly and settles down without much effort, but there is a strong possibility of separation and the loss of homosexuality in this situation. The water level of the cement in this concrete is more than 0.55. Due to the high amount of water cement, the green mixture usually settles to the ground, and then a concrete slab appears. This concrete is suitable when the density of the concrete is high, and vibration of the concrete is not possible. Joint concrete (SSC) is an example of high quality concrete. Good Workability Means Different Things to Different People There are different expectations and agendas for all construction / construction team groups when it comes to good concrete construction. A building engineer wants high strength and good bond with reinforcing steel. The architect is concerned with the attraction of cosmetics. The carrying capacity is attractive to the owner because it allows for smaller parts of the material and therefore more user-friendly space. The worker needs a blend that can be delivered, packaged, and blended well, and the finish maker is looking for something that takes a solid, high-quality finish quickly and easily. The combination of concrete and good performance brings many qualities together in balance and leads to a quality product with a long working life. FACTORS AFFECTING WORKABILITYThe dimensions and features of the building materials and structures of admixtures all contribute to the functionality and other characteristics of all concrete composite drawings, functional impacts including:Water / cement ratio:The higher the amount of cement or cement reinforcement material usually means the greater the strength, and with the right amount of water, the more glue you put in layers for easier mixing and better finishing. Not enough water for proper hydration means an increase in negative energy and non-compliant combinations that resist easy installation and elimination. Adding more water may increase performance because it makes it easier to set and mix. However, the negative impact on segregation, termination of performance, and retention potential can be so detrimental that you have to approach with extreme caution. Water to a cementitious material ratio (w / cm) of 0.45 to 0.6 is a good place for the production of active concrete. Combined Size and Shape: As the composite surface area increases, more cement paste is required to cover the entire joint area. So mixing with smaller aggregates is less effective compared to larger-size combinations. Combined, angular, and hollow joints are difficult to assemble and place and have a large cover area, reducing performance. The circular collection has a low surface area, but does not have the angularity of improving the bond strength sufficient for cement adhesion. Crushed composites in the right proportions provide better bonding with the cement matrix and adequate performance. Admixtures: Many types of admixtures change the performance of a new concrete, either by construction or as a side effect. Surfactants such as super plasticizers reduce the attraction between cement and composite particles, allowing compounds that can flow without negative energy and the effects of excess water separation. The insertion of internal admixtures of durability / dissolving solids produces internal bubbles of a controlled size that can make it easier to eliminate, although overuse produces an adhesive mix with a different effect. Grading of concreteIf the combination is well organized, that means less content will be empty and higher content will work, so as far as possible, the combination should be well organized. Surface texture of aggregate If the surface of the aggregates is smooth or glassy, it will produce less surface and will provide better performance. The contrasting resistance between the smooth particle is reduced and will produce higher performance. So this is an important factor in performance. Amount of cementThe concrete content greatly affects the performance of the concrete. If we increase the size of the cement, much will be the cement paste to cover the surface of the composite and the useless filling. It helps to reduce the friction between the composites that have led to the smooth movement of aggregates in the transport, placement, and bonding of the concrete. At a fixed amount of cement water, an increase in the amount of cement will increase the amount of water per concrete per unit, which is why it increases the efficiency of the concrete. Q6) Explain cohesion and segregation A6)COHESIONHow good it is to hold it together in a plastic state. Cohesion is affected by:1. Aggregate gradingGraded Aggregate means that there is a range of Aggregates size, from large rocks to thin sand .2. Water contentThe watery mixture will not coalesce and can separate and bleed. TREATMENT The treatment retains the moisture of the concrete for some time, allowing it to reach greater capacity. Long-term curing will provide long-lasting concrete.3. Weather Warm weather will cause the concrete to have a higher strength.4. Type of cementDifferent types of cement will affect concrete structures: which means how quickly the concrete gains.5. Water to cement ratio Too much water and too little cement means that the concrete will be weak and will not last long. The amount of water to the cement (W / C) is the amount of water divided by the weight of the cement.SEGREGATIONConcrete separation is a matter of particle separation in concrete applications, in which particle particles are usually separated due to differences in size, density, shape and other particle structures. It is defined by the American Society for Testing and Materials as follows: "Concrete separation is often thought of as the separation of other composite groups from cement mortar in isolated areas and the corresponding shortage of these materials in other areas. Separation causes parallel concrete laying different from those designed. poorly balanced and poorly blended, or highly efficient mixing, placement, or adverse weather conditions. The corresponding increase in the rate of cement adhesion in the upper areas may often expose them to increased risk of shrinkage and cracking. look up, and be in the shape of a map pattern. The result of the integrated isolation in concrete conduct and transport behavior has been the focus of birth modeling and experimental research. Q7) Explain test workability by slume cone of fresh concrete A7)ObjectiveThe word ―workable or concrete used has a broader and deeper meaning than the word alternative that is commonly used freely to make it work. Consistency is a general term that indicates the level of fluid or flow rate. Factors that help concrete to have the most effective effect of reducing internal friction that facilitates easy mixing are: (a) Water content (b) Mixing Dimensions (c) Collection Size (d) Structure Shapes (e) Spatial Design Design (f) Placement layout (g) Use of Admixtures.Slump test is the most widely used method of measuring the consistency of concrete that can be used in a laboratory or in the workplace. It is not suitable for very wet or very dry concrete. It does not measure all factors that affect performance, nor does it always represent concrete placement. Indicates the concrete feature above the drop value. When the concrete slips evenly it is called a true slump. When one part of the lump slips, it is called a shear slump. In the event of a shear bend, the slump value is measured as the height difference between the height of the mold and the average amount of shrinkage.
Fig no 4 Slum coneProcedureIf this test is performed in the field, a mixed concrete sample will be obtained. In the case of concrete containing a diameter of more than 38 mm, the concrete will be diluted with water by one and a half inches of screen to remove compacted particles larger than 38 mm. The inner surface of the mold will be thoroughly cleaned and freed from unwanted moisture and pre-set concrete before testing. The mold will be placed on a smooth, horizontal, strong, and non-abrasive surface, such as a carefully weighed metal table, the mold will be kept firmly in place while filling. The mold will be filled in four layers, each about a quarter of the height of the mold. Each layer will be smoothed with twenty-five lashes on the round edge of the lubricating rod. The lashes will be distributed evenly over the section at the cross section of the mold and the second and subsequent layers will fit into the lower layer. The bottom layer will be smoothed in the depth of it all. After the upper layer has been coated, the concrete will be flattened and trimmed with a trowel, so that the mold will fill directly. After the top layer has been glued, remove the concrete surface by moving and moving the lubricating rod. Any mud that may have leaked between the mold and the base plate should be cleaned. The mold will be removed from the concrete immediately by lifting it gently and carefully in a vertical direction. This allows the concrete to drop and the fall will be measured immediately by determining the difference between the height of the mold and that of the highest of the test template. The above operation will be performed in a non-vibrating or panic-free environment, and within two minutes after sampling.
Fig no 5 Dimensions of slum coneQ8) Explain compaction factor A8)ObjectiveThe compacting factor test is mainly designed for use in the laboratory but can also be used in the field. It is more accurate and sensitive than fall testing and is especially useful for very low-performance concrete mixes and is often used when the concrete will be squeezed by vibration. This method works on bare and ventilated concrete, made of lightweight, standard weight or heavy aggregates with a maximum weight of 38 mm or less but not on open concrete or non-reinforced concrete.
Fig no 6 Compaction factor apparatusProcedureA sample of the test concrete will be gently placed on the upper hopper, using a hand scoop. The hopper will be evenly filled with its edge and the trap door will be opened so that the concrete falls to the ground. Some mixes tend to stick to one or both hoppers. When this happens, the concrete can be helped by pushing the rod gently into the concrete from the top. During this process, the cylinder will be covered with tiles. As soon as the concrete is out, the cylinder will be exposed, the door to the bottom trap will be opened, and the concrete will be allowed to fall into the cylinder. The remaining concrete over the top of the cylinder will be removed by holding a trowel in each hand, the plane of the belts horizontally, and then moving them simultaneously to each side above the cylinder, at the same time keeping them pressed against the upper edge of the cylinder. The outside of the cylinder when it is wiped will be clean. The above work will be done in a place that will not tremble or shake. The weight of the concrete in the container will be determined by the nearest 10 g. The remaining concrete over the top of the cylinder will be removed by holding a trowel in each hand, the plane of the belts horizontally, and then moving them simultaneously to each side above the cylinder, at the same time keeping them pressed against the upper edge of the cylinder. The outside of the cylinder when it is wiped will be clean. The whole process will be done in a place where there is no vibration or shock. This weight will be known as the weight of the partially bonded concrete. The cylinder will be filled with concrete from the same sample with layers about 5 cm deep, the layers folded tightly or shaken to achieve complete integration. The surface of the fully covered concrete will be carefully beaten and weighed above the cylinder. The outside of the cylinder when it is wiped will be clean.
Fig no 7 Dimensions of compaction factor apparatusQ9) Explain vee bee consistometer and flow table apparatus A9)VEE BEE CONSISTOMETERObjectiveThe performance of the new concrete is a composite material, which incorporates various requirements for stability, mobility, durability, placement and finishing. There are various ways to measure performance. Each of them measures only a specific aspect of it and there is no unique test, which measures the performance of concrete completely. This test provides an indication of the flow rate of the newly mixed concrete mix. The test measures the concurrent effort required to change a pile of concrete from one concrete to another (e.g., from a circle to a cylindrical) using vibration. The amount of effort (called retrieval attempt) is taken as the time in seconds, which is required to complete the change. The results of this experiment are useful when you study the flow of concrete piles made of different amounts of water, cement and different types of composite placement. The time required for a full recovery in seconds is taken as a performance measure and is expressed as the Vee-Bee number of seconds. This method is suitable for dry concrete. With concrete drop of more than 50mm, reconstruction is so fast that time cannot be measured.
Fig no 8 Vee bee Consistometer TestProcedureSlump test as described in "IS 1199: 1959 Details of Concrete Testing Equipment (Fourth Review). Confirmed- Dis 2013". is made, inserting a collapsible lump inside a round metal pot of consist meter. The glass disk attached to the rotating arm will be moved to the top of the cone in the pot and before the cone is raised, the location of the concrete cone will be identified by fixing the glass disc attached to the arm wrist. The cone will then be lifted and the fall will be marked on the graduating rod by lowering the glass disc over the concrete cone. The electric heater will then light up and the concrete will be allowed to lay in the pot. The vibration continues until the point where the concrete shape disappears and the concrete takes on a circular shape. This can be judged by looking at the glass disc from the top disappearing visually. As soon as the concrete completely begins to form a circle, the stand clock is turned off. The time required for concrete formation to change from the formation of a collapsing lump into a circle in seconds is known as the Vee Bee Degree. This method is best suited for dry concrete with an unmeasured fall value with a Slump Test, but vibration is much stronger than concrete with a fall of more than 50 mm. FLOW TABLEFlow tests were performed to measure the performance of the concrete. As the name suggests, in this experiment concrete performance is measured by examining the flow of concrete material. Flow test Easy laboratory test. This test applies to the principal for the general weight loss of concrete and is measured by the flow of concrete. The flow of concrete indicates the performance of the new concrete.Why flow test of concrete requiredFlow tests are used to measure the performance of high or very active concrete, which ultimately indicates a fall. It gives an idea about the quality of concrete in terms of consistency and consistency. This performance test is easy to perform and is best suited for concrete with a high overall size of the joint less than 38 mm.Flow Test ApparatusMetal Cone or Mould: Mould is in the form of a frustum of a cone with a base diameter of 250 mm, upper surface diameter of 170 mm and 120 mm height. The mould comes with handles for support.Flow TableTrowelsHand scoopScaleTamping Rod
Fig no 9 Flow test apparatusProcedureClean anything toxic or dusty from the flow table and inside the mold. Place the lump on the marked area or in the middle of the flow table. Now pour the freshly mixed concrete into the mold in two layers, each layer should be moistened 25 times with a soft stick. If the concrete overflows after stamping and measure with the help of a torch, and the excess concrete should be removed from the table. After that, lift the mold upwards and allow the concrete to stand on its own without support. After that the table is raised and lowered from 12.5 mm high, 15 times in about 15 seconds. Next, measure the width of the concrete spread by about 6 points and write down the scale. Q10) Explain effect of admixture on workability of concrete and optimum dosage of admixture by marsh cone test A10)EFFECT OF ADMIXTURE ON WORKABILITY OF CONCRETEConcrete contains cement, sand, a mixture of water. Anything other than these if added to concrete before or during mixing to convert structures to our desired requirement is called admixtures. The use of admixtures provides certain beneficial effects on concrete such as improved performance, speed or delay of set time, reduction of the amount of water cement, and so on. There are two basic types of admixtures available: chemicals and minerals. Admixtures such as fly ash, silicate fume, slag come in the category of mineral admixtures. They are incorporated into concrete to increase performance, improve thermal resistance and alkaline reactions and enable us to reduce cement content. Fly ash is a good residue left over from global warming or powdered charcoal. They are all better than cement and contain mainly round glass particles as well as remnants of hematite and magnetite, char and other crystalline layers formed during cooling. The use of fly ash in concrete makes mixing more economical, and improves performance, reduces separation, bleeding and reduces hydration temperatures but also offers natural benefits. Silica fire, also known as micro silica. It is available as a product during the production of silicon and ferrosilicon alloys. The particles of silica fire particles are 100 times smaller than cement particles which mean their smoke like cigarettes. Its highly efficient pozzolanic material, which improves concrete structures such as improved durability, bond strength, abrasion resistance, dense concrete leading to reinforcement and rust protection. Chemical admixtures are applied to concrete in very small quantities especially for ventilation, reduction of water or cement content, installation of new concrete mixtures or control of concrete set time. These compounds can be widely used as super plasticizers, accelerators, retarders, water reducers and ventilation admixtures. Super plasticizers were added to reduce water demand by 15 to 20% without affecting performance leading to high durability and high concrete. Super plasticizers are liner polymers that contain sulfonic acid groups attached to the polymer from time to time. Commercial composition can dissolve melamine - formaldehyde condens- sates, sulfonated naphthalene formaldehyde condensates, and modified lingo sulfonates, derived from polycar- boxylate. The main purpose of super plasticizers is to produce a concrete slope with a very high drop of 175 to 200 mm that can be used effectively on reinforced concrete structures, a decrease in volume depending on the volume, type and timing of good plasticizers (preferably before adding concrete.), Water cement, environment and value of cement. Accelerators were added to reduce the setting time of the concrete thus facilitating pre-form removal and are also used in the combination of cold weather. Calcium chloride is the most widely used accelerator in blending. The use of calcium chloride in reinforced concrete can promote the corrosion function of the steel reinforcement. As people become aware of it there is a growing interest in using free chloride. Retarders were added to increase the setting time by delaying the hydration of the cement. They are popular in areas with high temperatures combined. Retarders contain organic & inorganic agents. Organic retarders include unrefined calcium, sodium and ammonia salt lignosulfonic acid, hydro carboxylic acid and carbohydrates. Inorganic retardants include lead oxides, zinc, phosphate and magnesium salts. Most retarders work as a water repellent. They are called retarders that reduce water. It is therefore caused by high pressure forces due to the low water content. Admixtures reduce the amount of water added to the concrete to achieve a certain effect (fall) at a lower water level. Strong concrete specified for low cement content thus saving cement. Water reducers are widely used in hot weather and assist in pumping. Water-repellent plasticizers are hygroscopic powder, which can inhale air into concrete. Ventilation admixtures bring in small concrete bubbles. These air bubbles act as rollers thus improving performance and also work more efficiently in thaw-chilling channels as they provide a stabilizing effect in expanding water where cold weather meets. Ventilation admixtures are compatible with most combinations, care should be taken to prevent them from collapsing during mixing. In general, the performance of both types of plasticizers depends on the ambient temperature and thus in the summer the amount of plasticizer that will be used to handle the same rate of plastic expansion may be more than the amount that will be used in winter. The change in the normal set time within a specific requirement also makes the product dependent on other chemicals and as plasticizers with different nomenclature available in the market. CICO Technologies Limited, a 75-year-old Indian company ISO 9001: 2000 supported producing a range of concrete installation admixtures. Many RMC companies use CICO admixtures. Further modification is required during the trial. Modification to Plasticizers can meet the needs of any particular client. OPTIMUM DOSAGE OF ADMIXTURE BY MARSH CONE TESTAdmixtures are common and important of modern concrete. Low water content, high efficient, durable and cost-effective cement Many desirable properties that can be expected from concrete made of chemical and mineral composites Admixture-Cement mixing in concrete is complex combination of chemical and physical equipment independent. All combinations in large volumes offer good results when used with cement. Cement hydration involves a series of reaction, which is highly dependent on cement composition, water / cement ratio, surface area, particle distribution of size, temperature and integration. Admixtures when added in small amounts do that the hydration process is very complex. In recent times, developments in the cement product sector are related to the use of admixtures especially organic polymeric building materials. Many species of polymeric organisms known as super plasticizers, are used construction industries to change the way it flows again concrete machinery facilities. Among the various species for chemical admixtures, PCE-based admixtures are shown to develop new flow and complex areas of low-grade concrete.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 matching results found