Unit - 1
Introduction and Index Properties
Q1) What are the applications of Geotechnical Engineering to Civil Engineering?
A1)
1. Foundation design:
2. Pavement Design:
3. Design of Earth Dam
4. Earth Retaining Structure:
5. Design of Embankments:
6. Design of Underground Structures:
Q2) What are the types of Soil structure?
A2) The following types of soil structure are generally recognized
1. Single grained structure:
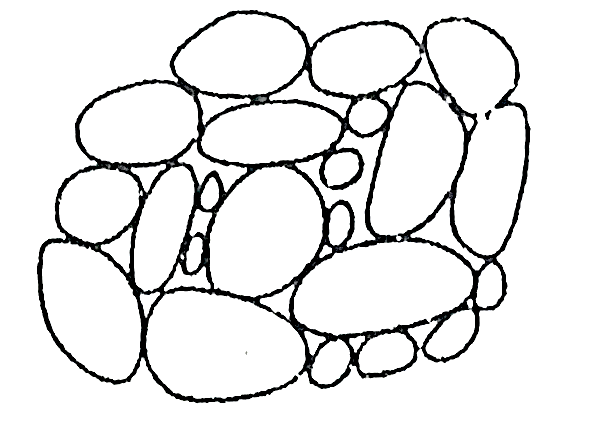
Fig. Single grained structure
2. Honeycomb structure:
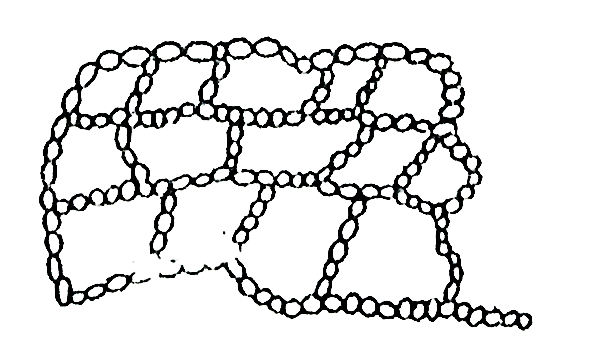
Fig. Honeycomb structure
3. Flocculent structure:
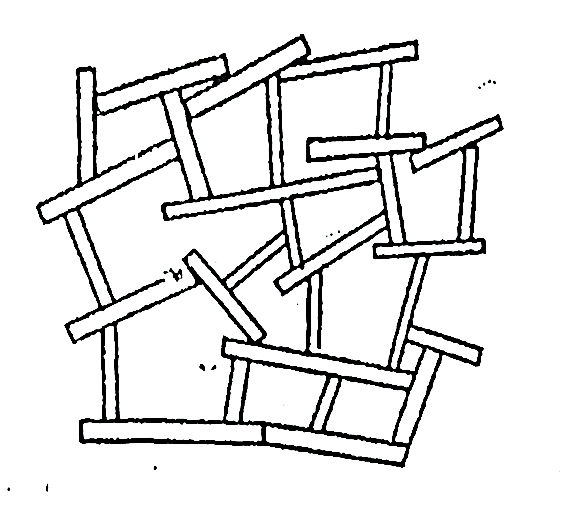
Fig. Flocculent structure
4. Dispersed structure:
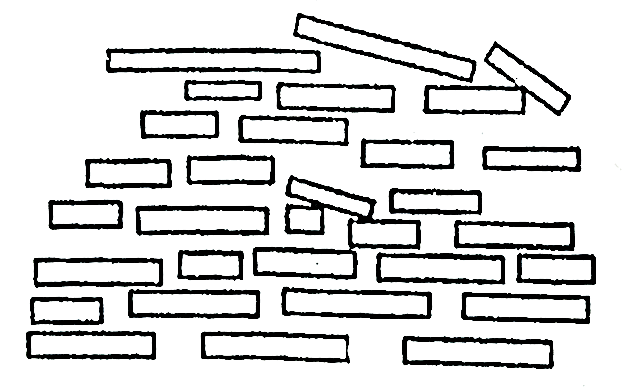
Fig. Dispersed structure
Q3) Which are the major soil deposits in India?
A3) The major soil deposits in India are as follows:
1.Marine deposits:
2. Black cotton soil:
3. Laterites and lateritic soil
4. Alluvial deposits
5. Desert soils
6. Boulder deposits
Q4) What are the identification methods of coarse-grained soil?
A4) Grading:
Grain shape:
Colour:
Strength and structure:
Presence of fines:
Q5) What is the purpose of soil exploration?
A5) 1. For finding Index properties:
2. To determine bearing capacity for foundation design:
3. To know stratification:
4. For seepage control:
5. For treating problem soils:
(a) The quick sand condition
(b) The black cotton soil
6. For enhancing properties by compaction and stabilization:
Q6) What is three phase soil system?
A6)
Q7) What are the index properties of soil?
A7) The index properties are sometimes divided into two:
1) Properties of soil mass
2) The properties of individual particle size.
1) Properties of soil mass:
2) The properties of individual particle size:
Q8) Explain Over drying method?
A8)
Q9) Explain plastic limit?
A9)
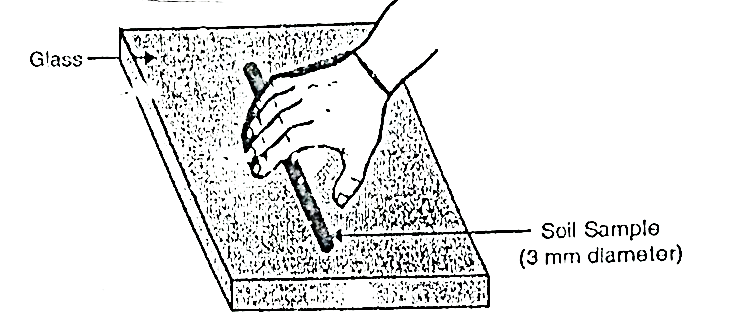
Fig.: Plastic limit determination
Q10) Explain Core cutter method?
A10)
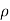
ρ=  (g/cm3)
(g/cm3)
Bulk unit weight, r= 9.81 ρ kN/m
Where w=water content
The core-cutter is shown in Fig.
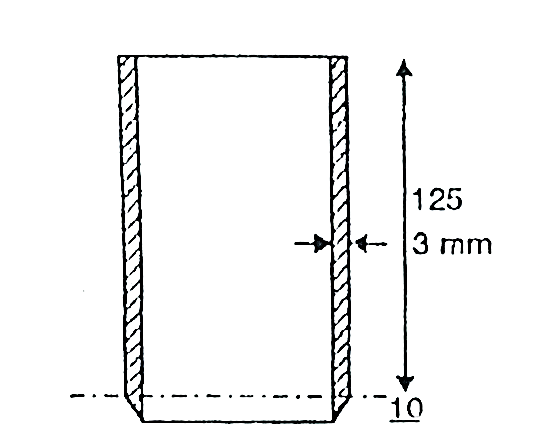
Fig. Core cutter
Q11) Explain Shrinkage limit?
A11)
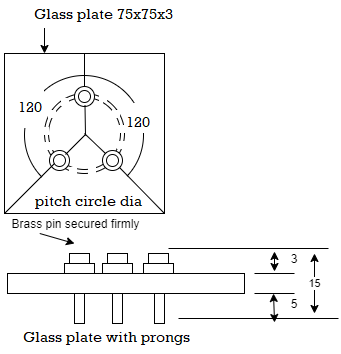
Fig. Shrinkage limit apparatus
Q12) Explain Calcium Carbide method?
A12)
W = 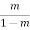
W= 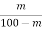 x 100 %
x 100 %
Q13) Explain dry strength test?
A13)