Unit - 2
Permeability and Seepage
Q1) Explain the classification of soil water?
A1) Classification of soil water are as follows:
1. Broad classification:
2. Phenomenological basis:
3. Structural aspect:
Q2) What is the definition of permeability?
A2)
Q3) Explain Darcy’s law?
A3)
q= K.i.A
V=q/A
V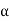 i, V=Ki
i, V=Ki
Where,
q= discharge per unit time
A= total c/s area of soil mass, perpendicular to the direction of flow
i =hydraulic gradient K Darcy's coefficient of permeability
v =velocity of flow, or average discharge velocity
we have,
q=KA (hA-hB)/L
when hydraulic gradient i = 1, then k=v
Q4) What are the factors which affects permeability?
A4) Following are the main factors that affect permeability:
Grain size:
K = C(D10)2
where, K Coefficient of permeability in cm/s and D10 is the effective grain size of the soil, C= constant (between 100 to 150)
Properties of pore fluid:
Temperature:
Void ratio:
K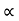 e2
e2
Stratification of soil:
Entrapped air and organic impurities:
Adsorbed water:
Degree of saturation:
Shape of particles:
Structure of soil mass:
Q5) Explain Constant Head method?
A5)
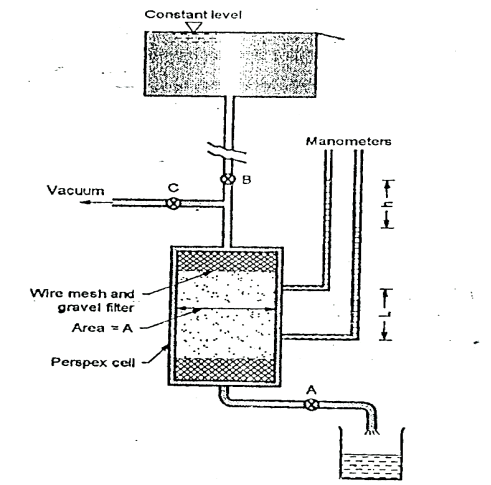
Fig.: Constant head permeability test
K=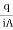 =
=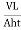
Where q=v/t=discharge in m3/s
V=volume of water collected in m3 in time t sec
A=cross sectional area of specimen in m
h =level difference between the manometer tubes in m.
L =distance between manometer points in m
Q6) Explain Falling head method?
A6)
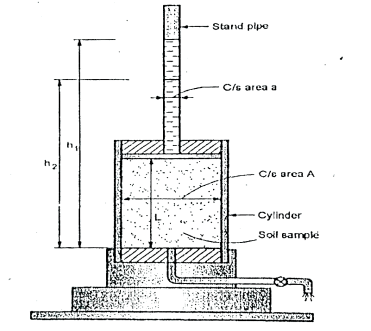
Fig.: Falling head permeability test
K = 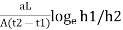
Where, a =area of c/s of stand pipe.
A =area of soil sample.
L = length of soil specimen
and h1, h2=heights of water measured in the stand pipe at time t1 and t2
If t2-t1 then
K = 2.3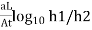
Q7) Explain Open end test?
A7)
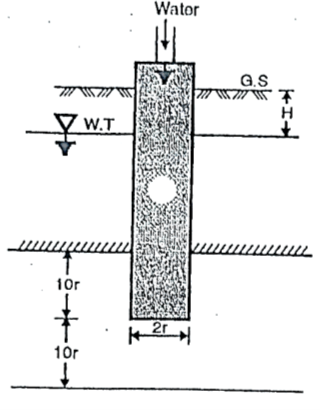
Fig.: Open end test (constant discharge)
K =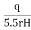
Where, K = coefficient of permeability
H = difference of level between the inlet of casing and water table
q = discharge
r= inner radius of pipe casing
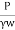
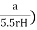
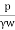
Q8) Explain Seepage pressure?
A8)
It is given by,
Ps=h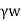
Ps =  ×L
×L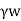
Where, h=Hydraulic head,
Z= Length over which the head (h) is lost,
i = Hydraulic gradient,
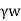 =Unit weight of water
=Unit weight of water
Seepage force (F) is given by,
Fs= Ps. A= i.Z.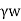 A
A
Where A= Total cross-sectional area of the soil mass
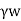 =Unit weight of water
=Unit weight of water
The seepage pressure always acts in the direction of the flow.
The effective pressure (P) in the soil mass is given by
Pe=Z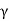 ± iz
± iz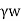
For upward flow,
Pe=Z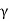 - iz
- iz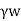
In upward direction, the effective pressure is decreased hence-ve sign.
For downward flow,
Pe=Z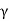 +iz
+iz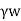
In downward direction, the effective pressure is increased hence +ve sign.
Q9) Explain Quick Sand phenomenon?
A9)
i= ic =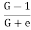
Fig.: Quick Sand Condition
Q10) What is flow net?
A10)
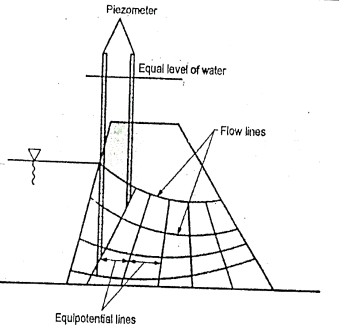
Fig.: Flow lines and equipotential line
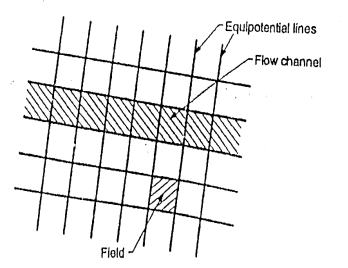
Fig.: Flow net
Q11) Explain the properties of flow net?
A11)
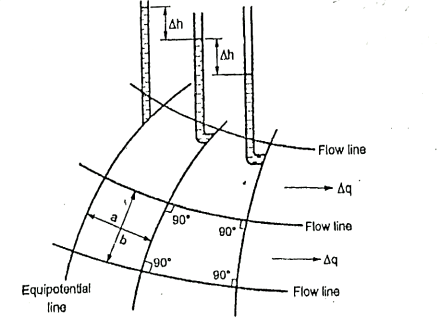
Fig.: Part of flow net illustrating characteristics
Q12) What are the applications of flow net?
A12) A flow net chart is used for following applications:
Q13) Explain flow net construction for flow under sheet pile?
A13)
Procedural steps:
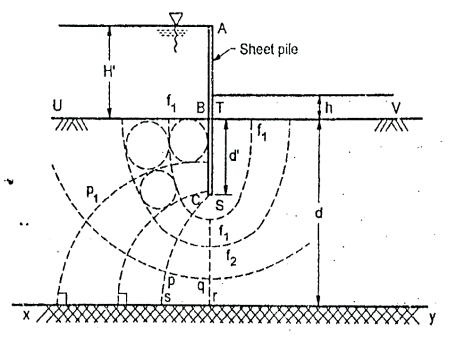
Fig.: Flow net for sheet pile