Unit - 4
Shear Strength of Soil
Q1) Explain Shear strength as an Engineering property?
A1)
Q2) What are the principal stresses in Mohr’s circle?
A2)
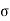
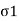
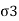
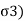
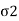
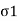
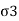
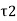 +
+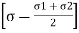 2 =
2 =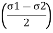 2
2
Where, 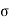 = Normal stress
= Normal stress
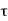 = Shear stress
= Shear stress
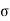 1= Major principal stress
1= Major principal stress
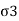 = Minor principal stress
= Minor principal stress
The co-ordinates of centre of circle are 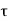 =0 and
=0 and
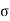 =
=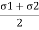 and its radius is
and its radius is 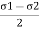
Q3) Explain Effective Stress principle?
A3) The principle of effective stress can be stated as
a) Effective stress governs volume changes in soils.
b) Effective stress (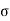 l) Total stress (
l) Total stress (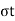 )-pore pressure(uw)
)-pore pressure(uw)
c) Effective stress controls shearing strength of soils.
:. Total stress = component of stress carried by solid particles + pressure in the fluid in the void space.
Q4) What is Peak shear strength?
A4)
Q5) What is Residual shear strength?
A5) When the shearing resistance comes at a constant level after a continued large strain then corresponding shear resistance at a constant level is termed residual shear strength.
Q6) What are the factors which affects shear strength?
A6) For Cohesionless soil:
For Cohesive Soil:
Q7) Explain stress-strain behavior of sand?
A7)
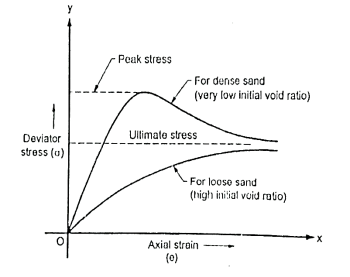
Fig.: Typical stress-strain behavior of sands from CD test
In both the specimen, the cell pressure is kept constant and axial stress is increased the sample specimen fails in shear.
Q8) Explain stress-strain behavior of clay?
A8)
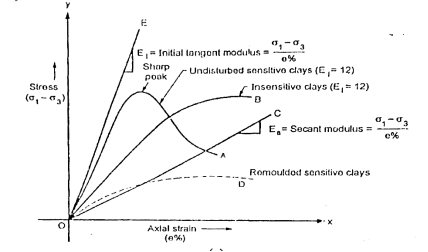
Fig.: Typical stress-strain behavior of clays from UU test
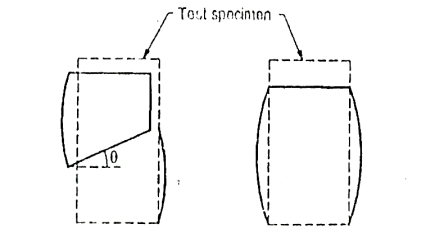
Fig.: Brittle and plastic failure resp.
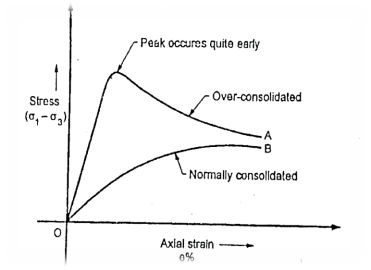
Fig.: Stress-strain behavior of clay obtained from CD test
Q9) Write advantages and disadvantages of direct shear strength?
A9) Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Q10) Write advantages and disadvantages of triaxial test?
A10) Following are the various advantage of triaxial test:
Disadvantages of Triaxial Test:
Q11) Write advantages and disadvantages of unconfined compression test?
A11) Advantages of Unconfined Compression Test:
Disadvantages of Unconfined Compression Test:
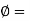
Q12) What are the drainage condition for shear test?
A12) There are three types of drainage conditions for shear tests as explained follows:
1. Consolidated-undrained conditions (CU condition)
2. Consolidated drained conditions (CD condition)
3. Unconsolidated-undrained condition (UU condition)
Q13) What is Sensitivity?
A13)
St =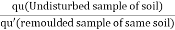
Where, qu= unconfined compressive strength of an undisturbed sample of soil or clay
qu’=unconfined compressive strength of remoulded sample of soil or clay at the same water content as in the undisturbed soil
Sr.no. | Sensitivity | Classification |
1 | 1-14 | Normal |
2 | 4-8 | Sensitive |
3 | 8-16 | Very sensitive |
4 | 16-32 | Slightly quick |
5 | 32-64 | Medium quick |
6 | Greater than 64 | Quick |
7 | Less than 1 | Stiff clay |
Q14) What is thixotropy?
A14)