Unit - 5
Earth Pressure
Q1) What is mean by active earth pressure?
A1) It is pressure exerted on retaining wall resulting from slight movement of wall away from filling.
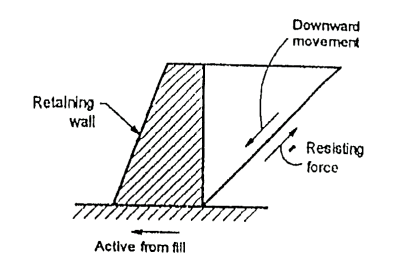
Fig.: Active earth pressure
Q2) What is mean by Passive earth pressure?
A2) When the movement of the retaining wall is such that the soil tends to horizontally.
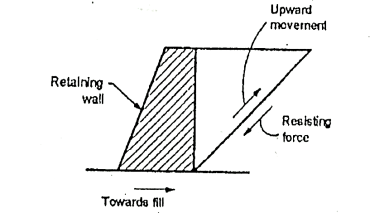
Fig.: Passive earth pressure
Q3) What are the assumptions mady by Rankine for Earth Pressure?
A3) Assumptions of the Rankine theory for active earth pressure are as follows:
Q4) Explain Rankine’s State of Plastic Equilibrium in soils?
A4)
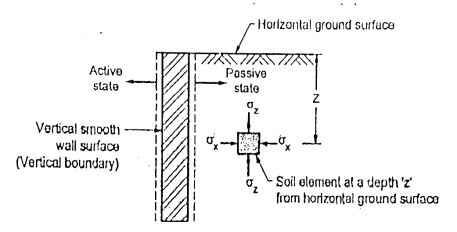
Fig.: A semi-infinite mass of soil bound by a horizontal surface and a vertical boundary
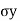
Q5) Explain Active States when Wall Moves Away from Backfill?
A5)
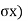
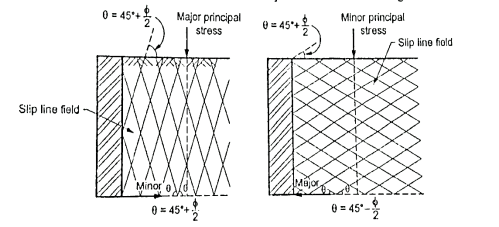
Fig.: Active and passive Rankine state due to wall movement
Active Rankine state:
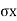
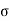
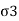
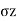
Q6) Explain Earth pressure at rest?
A6)
P0=K0  z
z
Where K0=Coefficient of earth pressure
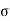 z=Effective vertical stress at depth a
z=Effective vertical stress at depth a
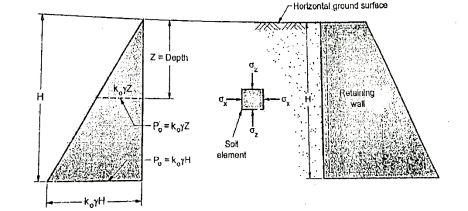
Fig.: earth pressure at rest
Q7) Explain Earth pressure on retaining wall due to submerged backfill?
A7) Fig. shows the retaining wall with backfill submerged by the natural water table saturated water. In such case, the lateral pressure is the sum of the two components.
These two components are as follows,
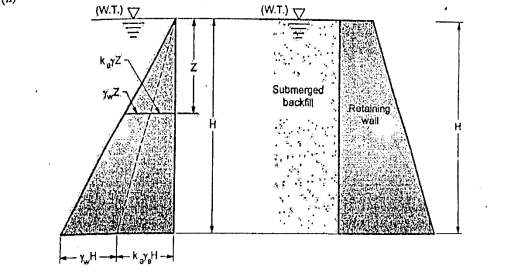
Fig.: Submerged backfill
Here at any depth 2 below the horizontal surface-active pressure is given by the following expression,
Pa=Ka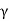 sz+
sz+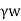 z
z
where, Pa=active pressure
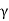 s= submerged weight of soil (y)
s= submerged weight of soil (y)
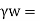 unit weight of water
unit weight of water
Fig. shows the active earth pressure distribution diagram at any depth 'z' and at the depth H.
The active pressure at the base of wall, where z H is given by the following expression,
Pa=Ka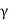 sH+
sH+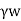 H
H
Q8) Explain Backfill with Uniform Surcharge?
A8) Fig. shows the retaining wall with horizontal backfill which is loaded by a uniformly distributed surcharge of intensity "q" by assuming the vertical pressure at any, depth is increased by "q".
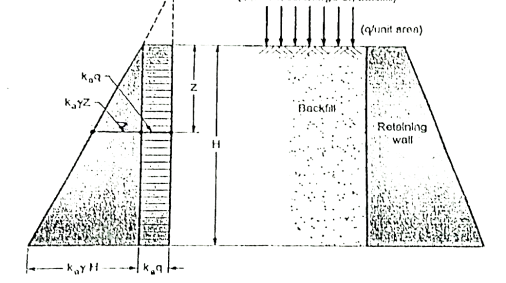
Fig.: Retaining wall with backfill carrying uniform surcharge
∴Lateral active pressure at any depth 'z' is given by the following expression
Pa=Ka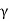 z+Kaq …. (At any depth z)
z+Kaq …. (At any depth z)
where z =H, then, active pressure at the base is given
Pa=Ka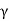 H+Kaq ......(at height H from base of wall)
H+Kaq ......(at height H from base of wall)
Q9) Explain Backfill with sloping surface?
A9)
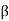
Pa= Ka γz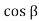 , ...For sloping surface
, ...For sloping surface
Where, Ka=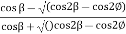
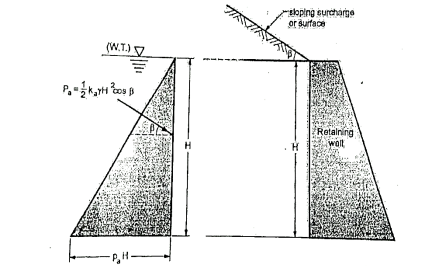
Fig.: backfill with sloping surface
For horizontal ground surface; 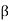 =0
=0
Ka=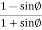
The total active pressure P, for a retaining wall having height 'II' is given by the following expression:
Pa=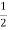 Ka
Ka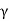 H2
H2 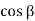
Q10) What is Basic Assumptions of Coulomb's Wedge Theory?
A10) Following are the various basic assumptions of coulomb's wedge theory
Q11) Explain Rebhann’s graphical method of determination of earth pressure?
A11)
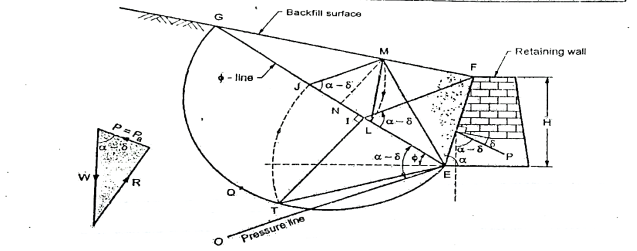
Fig.: Graphical method by poncelet construction based on Rebhann’s principles
Procedure of graphical method:
Following is the procedure of construction to find out the active earth pressure by graphical method refer Fig.
After this construction from step 1 to 10, it shows the 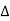 LIM. Area of
LIM. Area of 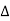 LIM in its natural unirs multiplied by the unit weight of the soil (
LIM in its natural unirs multiplied by the unit weight of the soil (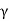 ) gives the active earth pressure (Pa) as follows:
) gives the active earth pressure (Pa) as follows:
Pa=Area of triangle LJM=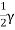 *JM*MN
*JM*MN
Where, 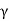 =unit wt of the soil
=unit wt of the soil
JM length of a triangle LJM
MN=height of  LJM
LJM
Pa=Active earth pressure
Q12) Explain Culmann’s graphical method of determination of earth pressure?
A12)
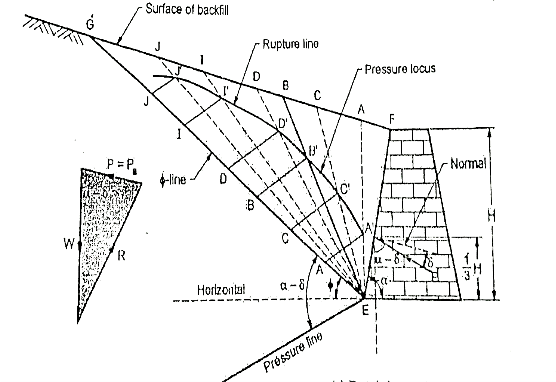
Fig.: Culmann’s graphical method for determining active earth pressure
Graphical construction procedure;