Unit - 6
Stability of Slopes
Q1) Explain stability of slopes?
A1)
Q2) What is Actuating force and slip surface?
A2) Actuating force:
Slip surface:
Q3) What is Infinite slope?
A3)
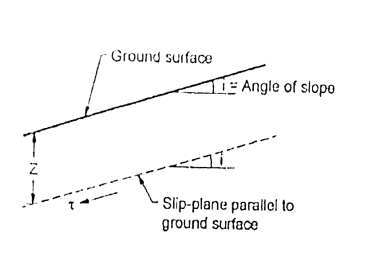
Fig.: An infinite slope
Q4) What is finite slope?
A4)
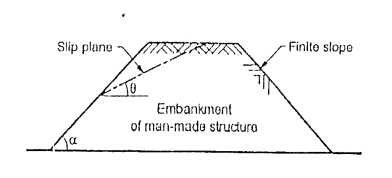
Fig.: Embankment
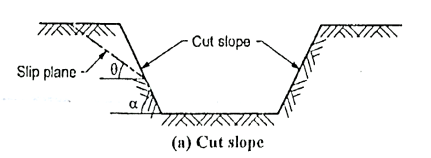
Fig.: Cut slope
Q5) What is homogenous and non-homogenous slopes?
A5) Homogeneous slopes:
Non-Homogenous slopes:
Q6) Explain modes of failure in infinite slope?
A6) For an infinite slope in a homogeneous soil, failure of slope take place due to sliding of the soil mass along a plane parallel to the ground surface at a certain depth. In short, for long steep slope, failure of slope will be along a surface parallel to the ground surface and in such case sliding surface is plane as shown in Fig.
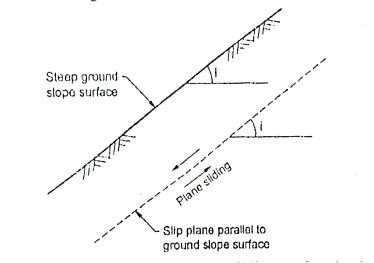
Fig.: failure in infinite slope
Q7) What is face failure?
A7)
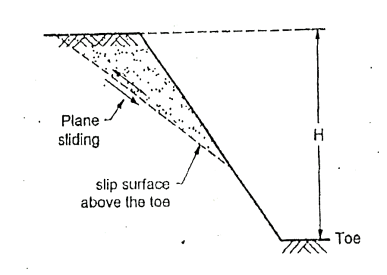
Fig.: Plane side of Face failure
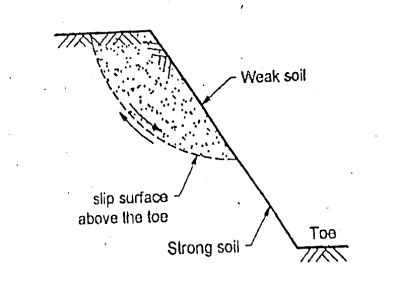
Fig.: Rotational side of face failure
Q8) What is Toe Failure?
A8) When the failure surface passes through the toe of slope, then it is termed as toe failure. Toe failure is most common mode of failure and occurs in steep slope consisting of the homogeneous solid mass above and below the base.
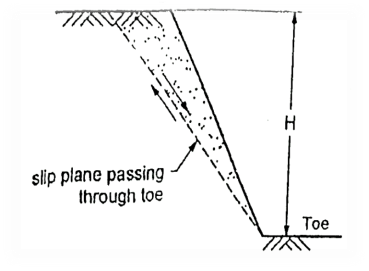
Fig.: Plane side of Toe failure
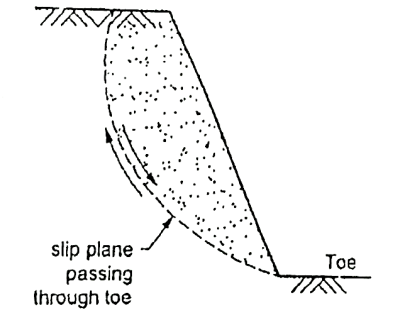
Fig.: Rotational side of toe failure
Q9) What is Base failure?
A9) When the failure surface passes below the toe of slope, then it is termed as base failure. This type of failure occurs due to the weaker material or relatively weak and soft soil at the base than that of slope. Fig. shows the base failure.
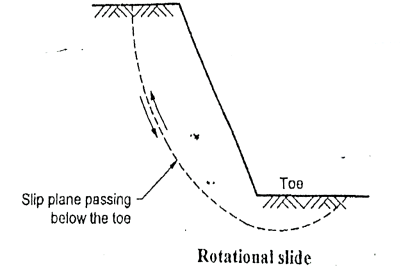
Fig.: Modes of base failure
Q10) Explain Taylor’s stability number?
A10)
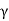
∴Weight of the wedge 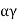 H2
H2
We know,
=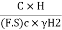
=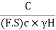 =Sn …. (1)
=Sn …. (1)
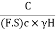
Cm=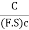 … (2)
… (2)
Where C= Cohesion:
(F.S) c= Factor of safety with respect to cohesion
Hence the Equation (1) can be written as follows:
Sn =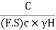 =
=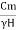 …. (3)
…. (3)
∴ (F.C) c =Hc/H… (4)
Where (F.C) c = Factor of safety with respect to cohesion
There Equation (3) becomes as
Sn =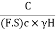 =
=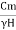 … (5)
… (5)
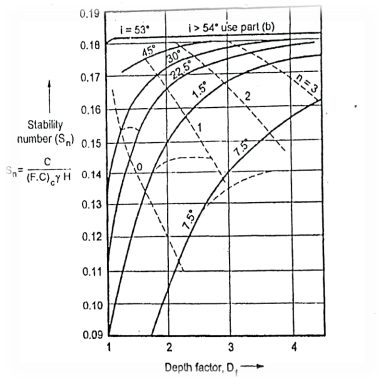
Fig.: Taylor’s stability number charts,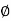 =0 with respect to depth factor
=0 with respect to depth factor
Q11) Explain Swedish slip circle method?
A11)
Q12) Explain Friction Circle method?
A12)
Q13) What are the types of landslides?
A13) Slides:
Falls:
Q14) What are the causes of landslides?
A14)
11. Morphological Causes
12. Human Causes
Q15) What are the remedial of landslides?
A15)