Unit - 3
Project Resources and Site Planning
Q1) What are the objectives of material management?
A1) To meet the primary objectives, the primary functions of the materials management are given as follows:
Materials Requirements Planning (MRP)
Purchasing
Inventories
The zero inventories are the ideal planning. There are three types of inventories.
Inventory at different levels is necessary to make sure about the availability of all these types of materials and goods and their proper flow from one facility to another at different levels of production centers in a manufacturing concern.
Ascertaining and Maintaining the Flow and Supply of Materials
The distribution of materials requisitioned by the various production centers and other departments must be ascertained and the materials management department must maintain its flow and continuity of supply.
The management has to maintain continuity in production to meet this uncertainty in demand and control the situation by proper flow of materials supply and distribution at various production facilities and other departments as per changes in production quantity.
Quality Control of Materials
The quality of the product manufactured by the organization depends upon the quality of the materials used to manufacture that product. It is a very important and necessary function of materials management to purchase the right quality of materials.
The inspection, quality control, simplification, specification, and standardization are the activities which are to be followed for the measurement of quality of the materials.
Departmental Efficiency
The objective of this function is to ensure the efficiency of the system adopted. Management Information System (MIS) and feedback control at every stage of working must be adopted to control and make the management and employee work as efficiently as possible to achieve the best results.
There can be number of secondary functions.
Standards define the quality, reduction in sizes and variety, interchangeability of parts and products. It ensures efficient utilization of materials and reduces wastages.
The objective of this function will be to produce standard product reducing the overall cost of the product.
2. Design and Development of the Product
The variety in product and functionality are the important factors to promote the sales of a product. The new techniques of designing a product using Computer Aided Design (CAD) has made possible to develop variety of products at faster rate.
3. Make and Buy Decisions
These types of decisions are the policy decisions of the management. The capacity of the organization and the various facility developed by the organization to manufacture various items is the main objective of every organization.
4. Coding and Classification of Materials
5. Forecasting and Planning Materials
Q2) How are stores classified?
A2) Stores are classified basically in the following broad categories.
Examples are fuels store, chemicals store, tools store, raw materials store, spare parts store, equipment store, refractory store, electric store, explosives store, and finished goods store etc.
b. Physical stores – Physically stores can be centralized stores or decentralized stores. These stores are named based on the size and location of the store. Examples are central store, sub store, department store, site store, transit stores, receipt store, intermediate store, open yard store, and covered store etc.
c. Stores are also classified by naming them after the departments to which they serve.
Examples are construction stores, operation stores, rolling mill stores, blast furnace stores, and steel melting shop stores etc.
Advantages.
Disadvantages
The variety of materials to be stored can be large and it can create complications in the systematic storage as well as in storage procedures
Q3) What are the functions of store?
A3) Functions of a store
Store personnel are responsible for carrying out the following functions.
Q4) What is record keeping?
A4) One of the main parts of accounting is recordkeeping or bookkeeping. Recordkeeping is the process of recording transactions and events in an accounting system. Since the principles of accounting rely on accurate and thorough records, record keeping is the foundation accounting.
Accounting is used to identify events that need to be recorded, recording the transactions of these events, and communicating the effects of these transactions with people inside and outside of the company. As you can see, record keeping is only a small part of the broader definition of accounting.
Q5) How to record keeping using excel?
A5) Record Keeping using excel
Step 1: Start with a bookkeeping Excel sheet template.
The template is separated into three parts:
Step 2: Customize the chart of accounts within your template.
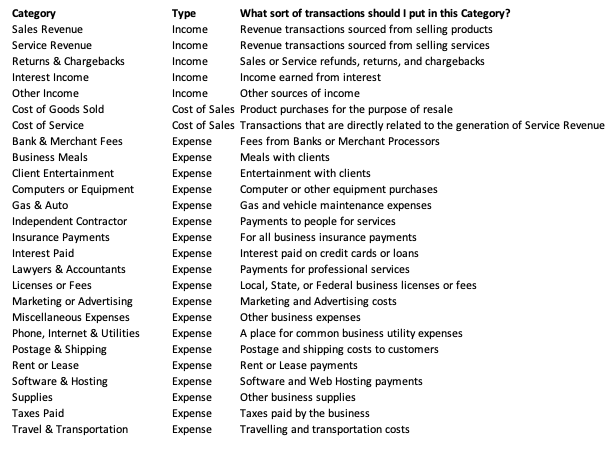
Customize the chart of accounts, the chart of accounts sheet will serve as your point of reference—reminding you how to categorize different transactions.
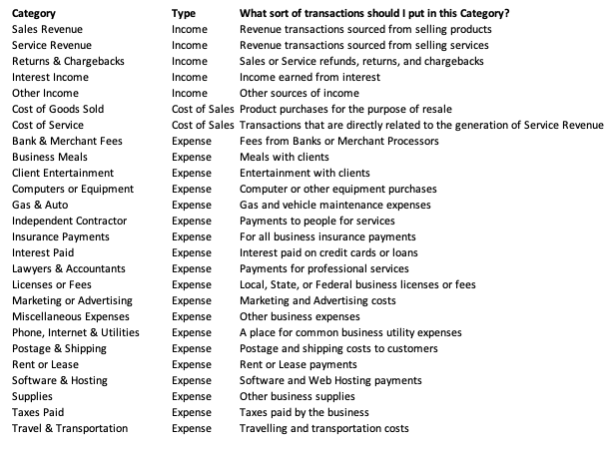
As the figure displays, make a list of every type of expense or income your business uses, and create an account type for each. However, to keep your accounts in Excel, each account should be categorized as one of the following:
Step 3: Customize the income statement sheet.
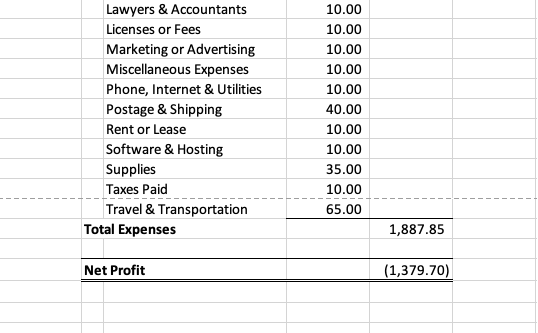
After customizing the chart of accounts, next work on customizing your income statement sheet. As shown in the figure enter the information from your chart of accounts making sure to include all accounts, but keeping them separated according to whether they’re income, expenses, or COGS.
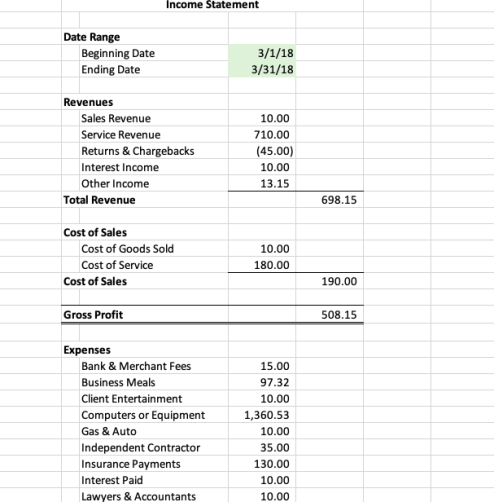
After editing the income statement Excel bookkeeping sheet, make sure to duplicate this sheet (if your template only has one). In order to generate monthly income statements, you’ll need separate sheets for each month. Make 12 copies of the original income statement, one for each month in the year—don’t forget to label each one and enter the date range in the appropriate cell.
Step 4. Add a sheet for tracking invoices.
When you enter income from paid invoices into your transactions sheet, include the invoice number. By doing this, you can cross-reference it to avoid errors like forgetting to enter invoice payments, or entering the same payments twice. It’s much easier to cross-reference if you’ve got a separate sheet to track your invoices.
You can add a tab within your bookkeeping Excel document, or, once again, download an invoice tracking Excel template. If you download a template, you can copy and paste the contents into a new sheet within your master bookkeeping Excel document.
If you want to add an invoice tracking sheet, keep this sheet next to your transactions sheet within the Excel document—this will make it easier to check for reference.
Step 5. Add a sheet for projecting cash flow.
Just like the tracking invoice sheet, you can simply create a new sheet within your master document and paste a cash flow tracking template or, of course, make your own. Download Fundera’s cash flow template here.
Step 6. Save the file to a secure location on your computer.
After you’ve edited and added all of the different sheets within your master Excel bookkeeping document, save the file in a secure location on your computer or drive. Therefore, make sure the file is secure, yet accessible when you need it to perform your day-to-day bookkeeping tasks.
Q6) What is ERP?
A6) Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a process used by companies to manage and integrate the important parts of their businesses.
Many ERP software applications are important to companies because they help them implement resource planning by integrating all of the processes needed to run their companies with a single system.
An ERP software system can also integrate planning, purchasing inventory, sales, marketing, finance, human resources, and more.
Q7) What are the features of ERP?
A7) ERP software can integrate all of the processes needed to run a company.
Q8) What is ABC Cycle?
A8) ABC analysis is a system for inventory control used throughout materials and distribution management. It is also sometimes referred to as selective inventory control, or SIC.
However, in terms of their consumption value B and C would make up on 20 per cent of the value combined, with C the least, perhaps split at 15 per cent and 5 per cent respectively. The percentages will vary based on a distributor’s unique inventory control needs.
This means that ABC analysis conforms with the Pareto principle which states that items that account for a large proportion of the overall value are small in number and that items with a low overall value are high in number.
Q9) Explain delivery process.
A9)
Q10) What are the objectives of store manager?
A10) An efficient stores management has normally the following main objectives.