Unit - 1
Basics of Water Supply Engineering
Q1) Give importance of water infrastructure in India.
A1)
- Various authorities’ packages at national, state, and network degree have introduced speedy upgrades in sanitation and the consuming water deliver. Some of those packages are ongoing.
- Water is an ignored and marginalized sector of infrastructure, in contrast with others.
- Water infrastructure is capital-significant and its development consists of an extended planning and implementation cycle.
- Water infrastructure is costly, and its heavy funding desires are hard to fulfill from national financial reasserts.
- A growing chorus of influential voices are arguing in favor of government borrowing for infrastructure development
- Treatment procedures normally feature both via the bodily elimination of contaminants via filtration, settling (frequently aided via way of means of a few shapes of chemical addition) or organic elimination of microorganisms.
Q2) Why data collection is required for implementing water supply scheme?
A2)
- A water deliver gadget generally consists of the following:
- A drainage basin (see water purification – reasserts of consuming water)
- An uncooked water series point (above or underneath ground) wherein the water accumulates, inclusive of a lake, a river, or groundwater from an underground aquifer.
- Raw water can be transferred the usage of exposed ground-degree aqueducts, protected tunnels, or underground water pipes to water purification centers.
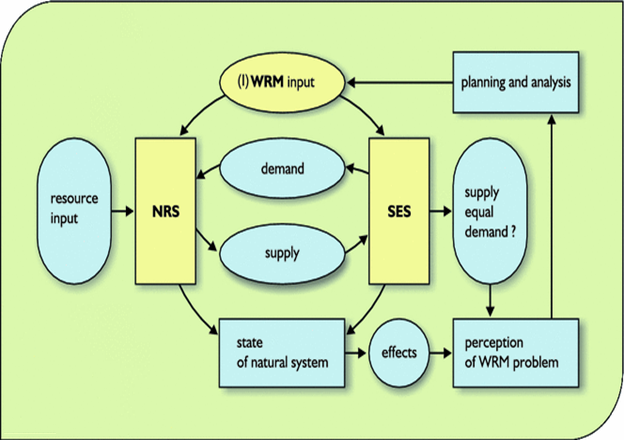
Fig. 1: Data collection
- Water purification centers.
- Treated water is transferred the usage of water pipes (normally underground). Water garage centers inclusive of reservoirs, water tanks, or water towers. Smaller water structures can also additionally shop the water in cisterns or stress vessels.
- Tall homes might also want to shop water domestically in stress vessels so as for the water to attain the top floors.
- Additional water pressurizing additives inclusive of pumping stations can also additionally want to be located at the hole of underground or aboveground reservoirs or cisterns (if gravity float is impractical).
- A pipe community for distribution of water to consumers (which can be non-public homes or industrial, commercial, or group establishments) and different utilization points.
Q3) Enlist components of water supply scheme.
A3)
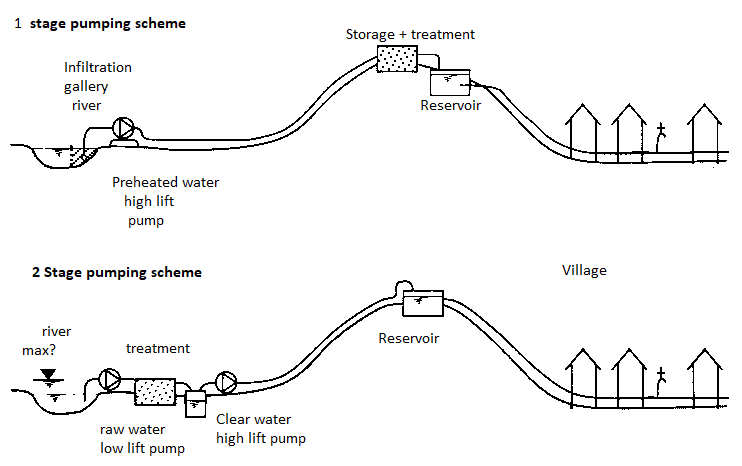
Fig. 2: Components of water supply scheme
The following are the components of water supply scheme:
- The complexity of and needs on those structures lead them to the maximum pricey unmarried detail with inside the water deliver device.
- In addition to a community of interconnecting mains or pipes, water distribution structures commonly consist of garage centers, valves, hearth place hydrants, provider connections to person centers, and possibly pumping centers.
- In all however the most important structures. The waft this is vital to fight a first-rate hearth place is typically the principal component figuring out necessities for the quantity of water to be saved, the scale of mains with inside the device, and the stress to be maintained. Fire waft requirements require a minimal residual water stress of 20 kilos consistent with rectangular inch gauge (psig) for the duration of waft.
- The waft of water distribution structures can be managed both with the aid of using gravity or with the aid of using stress (pumping). Often, public water delivers structures use a few aggregates of both.
- In those stress structures, the pumps are commonly positioned on the remedy plant and possibly with inside the distribution device. In blended structures, centers for water garage are frequently supplied together with provision for pumping.
- This kind of device offers for the garage of water for the duration of instances of least call for even as assuring that an enough amount is to be had to fulfill the height call for.
Q4) What are the steps in the layouts of water supply scheme?
A4)
The Layout is the mandatory factor in the water supply scheme.
- From the technical factor of view, the subsequent 3 fundamental questions must be replied for the duration of the making plans segment of a water deliver scheme:
- Which uncooked water supply need to be used for the water deliver scheme?
- If remedy is necessary, what form of remedy scheme need to be favored?
- How plenty water need to be disbursed to the consumers, and at what carrier level?
- Source choice is a completely primary selection entailing several results for the destiny water deliver scheme. The exceptional nearby water reassess must be evaluated with recognize to their quantity, exceptional and accessibility. The destiny water call for ought to be included with the aid of using the chosen supply with the high-satisfactory viable water exceptional, and placed as near as viable to the deliver area.
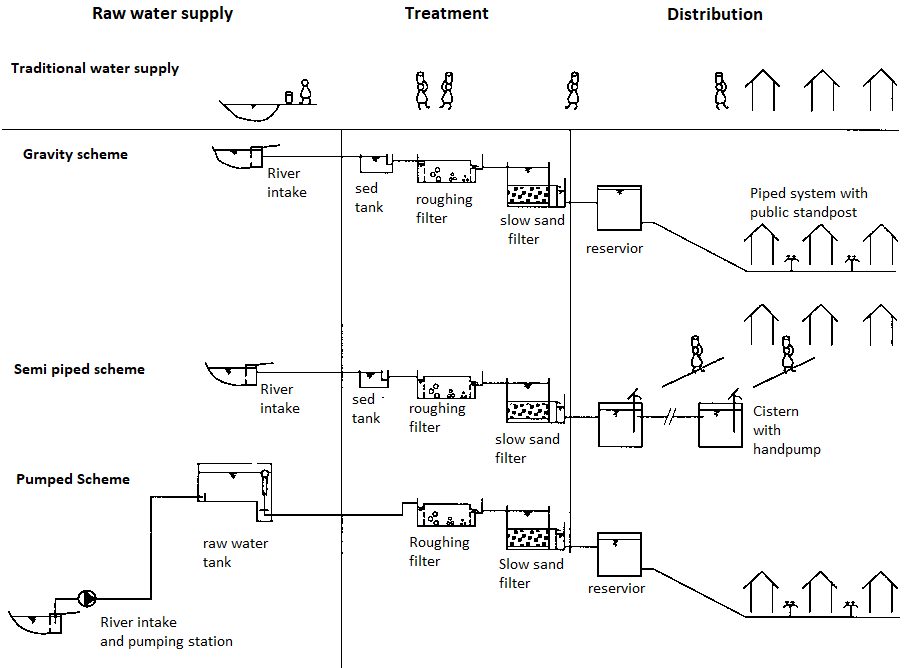
Fig. 3: Layout required for water supply scheme
- If no different opportunity is available, rural water remedy should focus on enhancing the bacteriological water pleasant through regionally sustainable remedy processes.
- Water distribution structures rely upon the kind of water supply used, at the topography, and at the furnished deliver provider stage. Individual water supplies, e.g., rainwater harvesting and shallow groundwater wells geared up with hand pumps normally do now no longer want piped deliver structures.
Q5) Explain Design Period.
A5)
- Design duration might be described because the range of years with inside the close to destiny wherein the deliver will surpass the demand. The water supply of any settlement covers huge dams to develop a reservoir.
- The water treatment plant is constructed with huge network of pipelines to search the consumers. As the population goes on increasing the demand of water is also increasing but it is not easy change existing water supply scheme or to increase its capacity.
The major motives at the back of presenting Design Periods are:
- It is prodigiously strenuous or unfeasible to provide frequent.
- It is inexpensive to deliver one immense unit in lieu of building plenty of bijou ingredients.
Q6) What are the factors affecting design period?
A6)
(i) Useful existence of aspect systems and the possibilities in their turning into vintage and obsolete. Design intervals must now no longer exceed the ones respective values.
(ii) Ease and problem this is probable to be confronted in expansions, if undertaken at destiny dates. For example, extra hard expansions imply selecting a better fee of the layout length.
(iii) Amount and availability of extra funding probable to be incurred for extra provisions. For example, if the budget isn’t available, one has to maintain a smaller layout length.
(iv) Anticipated fee of populace growth, which include viable shifts in communities, industries and business establishments. For example, if the fee of boom of populace is less, a better discern for the layout length can be chosen.
(v) The fee of hobby at the borrowings and the extra cash invested. For example, if the hobby fee is small, a better fee of the layout length can be economically justified and, therefore, adopted.
Q7) Explain Quantity and estimation of Quantity?
A7)
Quantity:
- Water amount is the timing and overall yield of water from a watershed, and is measured via way of means of overall yield and height glide over a certain duration of time. Water pleasant is the suitability of water for drinking, leisure uses, and as habitat for aquatic organisms and different wildlife.
Estimation of quantity:
- The quantity of water required for municipal uses for which the water supply scheme has to be designed requires following data:
- Water consumption rate (Per Capita Demand in liters per day per head)
- Population to be served.
Quantity= Per capita demand x Population
Q8) What are the factors that affect per capita demand?
A8)
a. Size of the city: Per capita call for huge towns is typically massive compared to that for smaller cities as huge towns have skewered houses.
b. Presence of industries.
c. Climatic conditions.
d. Habits of human beings and their financial status.
e. Quality of water: If water is aesthetically as human beings will now no longer motel to non-public wells, etc.
f. Pressure with inside the distribution system.
Q9) Explain Fire Demand and formulas necessary for calculating fire demand.
A9)
Fire demand:
- The water required for unexpected fire accidents and undesirable situation with fire is already designed during the water demand planning system.
- The demand is calculated based on empirical formulas. For all the formulas given below, Q is the discharge calculated in liters per minute and P is the population measured in thousands.
- Kuichling's Formula
Q = 3182P1/2
2. Buston's Formula
Q = 5663P1/2
3. Freeman's Formula
Q = 1136[0.2P + 10]
4. National Board of Underwater Formula
Q = 4637P1/2[1 - 0.01P1/2]
Q10) Explain in detail factors affecting ate of demand.
A10)
- Climatic Conditions:
- The requirement of water is extra at locations having warm and dry weather than at locations having bloodless and humid weather. This is so due to the fact at locations having warm and dry weather extra water is needed for bathing, washing of clothes, air coolers, air conditioning, garden watering, gardening, etc. Similarly, the requirement of water is extra in summer time season than in winter.
- Further in extraordinarily bloodless climates water can be wasted because of faucets being usually stored open to keep away from freezing of pipes, which can also additionally bring about improved charge of consumption.
2. Cost of Water:
- The fee at which water is furnished to the clients may additionally have an effect on the fee of call for of water. If the charges at which water is furnished are high, lesser amount of water can be ate up through the people, and vice versa. However, the overall commentary is that the intake of water reduces best barely because the fee is increased.
3. Pressure with inside the Distribution System:
- The intake of water will increase with the boom with inside the distribution stress. This is because of boom in loss and waste of water at excessive stress. For example, a boom of stress from 196 kN/m2 (2 kg/cm2) to 294 kN/m2 (three kg/cm2) can also additionally result in a boom in intake of water through approximately 25 to 30 in step with cent.
4. Economic Status of Consumers:
- The consumption charge of water is without delay based upon the economic recognition of the consumers. Rich and better beauty people normally consume more water due to their better well known of living. On the other hand, middle beauty people have not unusual place charge of consumption of water on the equal time because the horrific slum dwellers have a mile’s lower charge of water consumption.
Q11) Explain population forecasting and enlist methods of it.
A11)
Population Forecasting:
- Population forecasting is described because the approach of figuring out the anticipated populace for a specific layout duration of a water deliver machine with the assist of the examine and evaluation of destiny activities and to be had records. The populace is a critical parameter this is decided for the layout of the water machine of a specific area.
- Water deliver structures are designed for a populace anticipated for a sure layout duration in preference to thinking of the prevailing populace of the area. There are numerous mathematical techniques that may be used to decide the populace for a layout duration.
Population Forecasting Methods
- The populace forecasting strategies require the values of gift and beyond populace data to go through the calculation. The nearby census data of a specific place offer the cost of gift and beyond populations. The classes of strategies used for populace forecasting are:
- Short Term Methods
- Long Term Methods
The short-term methods include:
- Arithmetic Progression
- Geometric Progression
- IllerBankasi Method
- Decreasing Rate of Growth method
- Graphical Extension Method
The long-term methods include:
- Comparative Method
- Ratio and Correlation Method
- Component Method
- Logistic Method
Q12) Explain Quality of water and state chemical and physical impurities in water.
A12)
Quality:
- Man cannot survival without water but this water may be causes by bacteria if it is polluted by harmful agencies and used for drinking purpose. Pure water cannot be expected when the rain water flows as runoff if passes through the ground surface and gets collected in river lake and ponds on its way the water gets collected in river lake and ponds on its way the water get polluted by harmful salts, acids, minerals, pathogenic bacteria etc. hence odour test and disease causing microorganism.
- In early days, this types of surface water was consumed by human being for drinking, bathing, washing, etc. in these days man did not have a technical knowledge for purifying pollutant water as a result man had to suffer water borne diseases like typhoid, cholera, etc.
There are several types of impurities they are as follows:
- Physical Impurities:
- Turbidity
- Colour
- Test and odour
- Floating matters
2. Chemical impurities:
- Acids
- Organic and inorganic compounds
Therefore, for removal of such type of bacterial impurities some tests are to be conducted, and then we able to decide it is usable water or no
Q13) Explain Coastal and Inland Salinity.
A13)
Salinity
Salinity in ground water can be appreciably categorized into types, i.e., Inland Salinity and Coastal salinity.
Inland Salinity
- Inland salinity in floor water is universal particularly withinside the arid and semi-arid areas of Rajasthan, Haryana, Punjab and Gujarat and to a lesser quantity in Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh Maharashtra, Karnataka, Bihar and Tamil Nadu. About 2 lakhs sq.km location has been expected to be tormented by saline water of Electrical Conductivity in extra of 4000 μS/cm. There are numerous locations in Rajasthan and southern Haryana wherein EC values of floor water is extra than ten thousand μS /cm making water nonportable.
- Inland salinity is likewise brought on because of exercise of floor water irrigation without attention of floor water status. The sluggish upward thrust of floor water tiers with time has ended in water logging and heavy evaporation in semi-arid areas cause salinity trouble in command regions. As consistent with current evaluation approximately 2. Forty-six m ha of the location below floor water irrigation initiatives is water logged or threatened with the aid of using water logging.
Coastal Salinity
- Coastal regions constitute zones wherein land and sea meet and incorporates range of complicated environments together with deltas, estuaries, bays, marshes, dunes and beaches. Coastal aquifers have barriers in touch with seawater and are continually below dynamic equilibrium with it. Withdrawal of sparkling floor water from those aquifers may also end result in in equilibrium ensuing in intrusion of saline water in coastal aquifers.
- The Indian subcontinent has a dynamic coast line of approximately 7500 km length. It stretches from Rann of Kutch in Gujarat to Konkan and Malabar coast to Kanyakumari with inside the south to northwards alongside the Coromandal coast to Sunder bans in West Bengal.
Q14) Give drinking quality standards.
A14)
Water quality parameters and bis standards for various chemical and biological constituents
S. No. | Parameters | Drinking water | |
Permissible Limit | Maximum Limit | ||
1 | Odor | Agreeable | Agreeable |
2 | Taste | Agreeable | Agreeable |
3 | PH | 6.5 to 8.5 | No relaxation |
4 | TDS (mg/l) | 500 | 2000 |
5 | Hardness (as CaCO3) (mg/l) | 200 | 600 |
6 | Alkalinity (as CaCO3) (mg/l) | 200 | 600 |
7 | Nitrate (mg/l) | 45 | No relaxation |
8 | Sulfate (mg/l) | 200 | 400 |
9 | Fluoride (mg/l) | 1 | 1.5 |
10 | Chloride (mg/l) | 250 | 1000 |
11 | Turbidity (NTU) | 5 | 10 |
12 | Arsenic (mg/l) | 0.01 | 0.05 |
13 | Copper (mg/l) | 0.05 | 1.5 |
14 | Cadmium (mg/l) | 0.003 | No relaxation |
15 | Chromium (mg/l) | 0.05 | No relaxation |
16 | Lead (mg/l) | 0.01 | No relaxation |
17 | Iron (mg/l) | 0.3 | No relaxation |
18 | Zinc (mg/l) | 5 | 15 |
19 | Fecal Coliform (cfu) | 0 | 0 |
20 | E. Coli (cfu) | 0 | 0 |