BEX
UNIT - 2TRANSISTOR AND OPAMP Draw and explain BJT in detail. What are the different types of BJT? Explain each. What is emitter, collector and base of BJT? Explain transistor operation in detail. Write down the biasing conditions for different regions of operation. Explain Common Base configuration with suitable diagram. Explain Common Emitter configuration with suitable diagram. Explain Common Collector configuration with suitable diagram. Draw the input and output characteristics of a common base configuration. Draw the input and output characteristics of a common emitter configuration. Draw the input and output characteristics of a common collector configuration. Derive the expression for current gain in CB configuration. Derive the expression for voltage gain in CE configuration. Derive the relation between IC and IB. Derive the relation between  &
& .
. Calculate the  d.c and
d.c and  .c for the given transistor for which IC =5mA IB = 50mA and ICBO = 1mA.
.c for the given transistor for which IC =5mA IB = 50mA and ICBO = 1mA. For a transistor in common emitter configuration the reverse leakage current is 21 mA whereas when the same transistor connected in common base configuration it reduces to 1.1mA calculate values of 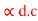 and
and 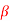 d.c of the transistor.
d.c of the transistor. Compare CC, CB and CE. Draw and explain VI characteristics of MOSFET. Given Vi = 0.25v, Ii = 1 Ma, Vo = 8 v, Io = 10 mA, Rs = 50 Ω. Find voltage gain and current gain for MOSFET. Explain MOSFET as an amplifier. What is an op-amp? Explain the characteristics of an ideal op-amp. Draw the functional block diagram of op-amp and explain each block. Explain inverting op-amp in detail. Explain non-inverting op-amp in detail.
 &
& .
. d.c and
d.c and  .c for the given transistor for which IC =5mA IB = 50mA and ICBO = 1mA.
.c for the given transistor for which IC =5mA IB = 50mA and ICBO = 1mA.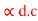 and
and 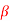 d.c of the transistor.
d.c of the transistor.0 matching results found