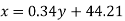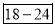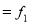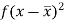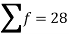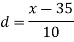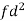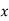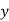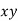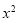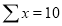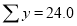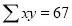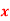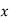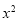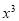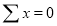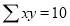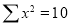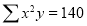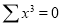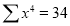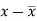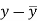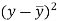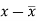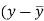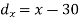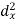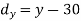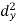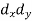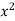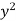Unit-3
Statistics
Question-1: Find the mean of the following dataset.
x | 20 | 30 | 40 |
f | 5 | 6 | 4 |
Sol.
We have the following table-
X | F | Fx |
20 | 5 | 100 |
30 | 6 | 180 |
40 | 7 | 160 |
| Sum = 15 | Sum = 440 |
Then Mean will be-
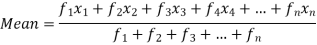

Question-2: Find the median of the following dataset-

Sol.
Class interval | Frequency | Cumulative frequency |
0 - 10 | 3 | 3 |
10 – 20 | 5 | 8 |
20 – 30 | 7 | 15 |
30 – 40 | 9 | 24 |
40 – 50 | 4 | 28 |
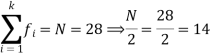
So that median class is 20-30.
Now putting the values in the formula-
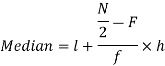
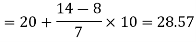
So that the median is 28.57
Question-3: Find the mode from the following data:
Age | 0-6 | 6-12 | 12-18 | 18-24 | 24-30 | 30-36 | 36-42 |
Frequency | 6 | 11 | 25 | 35 | 18 | 12 | 6 |
Solution.
Age | Frequency | Cumulative frequency |
0-6 6-12 12-18
24-30 30-36 36-42 | 6 11 25 35
12 6 | 6 17 42 77 95 107 113 |
Mode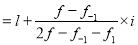
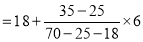

Question-4: Find the quartile deviation of the following data-
Class interval | 0-10 | 10-20 | 20-30 | 30-40 | 40-50 |
Frequency | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 4 |
Sol.
Here N/4 = 28/4 = 7 so that the 7’th observation falls in class 10 – 20.
And
3N/4 = 21, and 21’st observation falls in the interval 30 – 40 which is the third quartile.
The quartiles can be calculated as below-
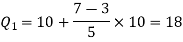
And
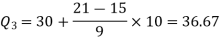
Hence the quartile deviation is-

Question-5: Find the mean deviation from the mean of the following data-
Class interval | 0-6 | 6-12 | 12-18 | 18-24 | 24-30 |
Frequency | 8 | 10 | 12 | 9 | 5 |
Sol.
Class interval | Mid-value | Frequency | d = x - a | f.d | |x - 14| | f |x - 14| |
0-6 | 3 | 8 | -12 | -96 | 11 | 88 |
6-12 | 9 | 10 | -6 | -60 | 5 | 50 |
12-18 | 15 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 12 |
18-24 | 21 | 9 | 6 | 54 | 7 | 63 |
24-30 | 27 | 5 | 12 | 60 | 13 | 65 |
Total |
| 44 |
| -42 |
| 278 |
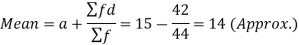
Then mean deviation from mean-
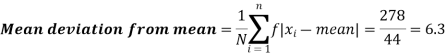
Question-6: Compute the variance and standard deviation.
Class | Frequency |
0-10 | 3 |
10-20 | 5 |
20-30 | 7 |
30-40 | 9 |
40-50 | 4 |
Sol.
Class | Mid-value (x) | Frequency (f) |
|
0-10 | 5 | 3 | 1470.924 |
10-20 | 15 | 5 | 737.250 |
20-30 | 25 | 7 | 32.1441 |
30-40 | 35 | 9 | 555.606 |
40-50 | 45 | 4 | 1275.504 |
Sum |
|
| 4071.428 |
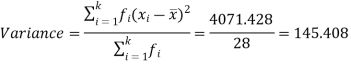
Then standard deviation,

Question-7: If the coefficient of skewness is 0.64. The standard deviation is 13 and mean is 59.2, then find the mode and median.
Sol.
We know that-
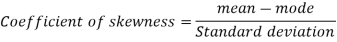
So that-
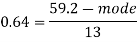

And we also know that-

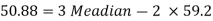
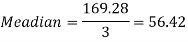
Question-8: Calculate Karl Pearson’s coefficient of skewness of marks obtained by 150 students.
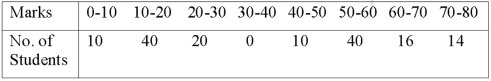
Sol. The mode is not well defined so that first we calculate mean and median-
Class | f | x | CF |
| fd |
|
0-10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | -3 | -30 | 90 |
10-20 | 40 | 15 | 50 | -2 | -80 | 160 |
20-30 | 20 | 25 | 70 | -1 | -20 | 20 |
30-40 | 0 | 35 | 70 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
40-50 | 10 | 45 | 80 | 1 | 10 | 10 |
50-60 | 40 | 55 | 120 | 2 | 80 | 160 |
60-70 | 16 | 65 | 136 | 3 | 48 | 144 |
70-80 | 14 | 75 | 150 | 4 | 56 | 244 |
Now,
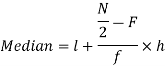
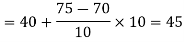
And
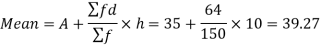
Standard deviation-
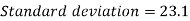
Then-
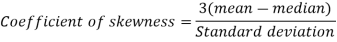
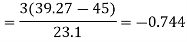
Question-9: Find the best values of a and b so that 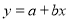 fit the data given in the table.
fit the data given in the table.
X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
Y | 1 | 2.9 | 4.8 | 6.7 | 8.6 |
Solution: 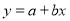
|
|
|
|
0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 1 |
2 | 4.8 | 9.6 | 4 |
3 | 6.7 | 20.1 | 9 |
4 | 8.6 | 13.4 | 16 |
| |
|
|
Normal equations 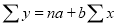 …. (2)
…. (2)
 …. (3)
…. (3)
On putting the values of 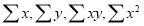 in (2) and (3), we have
in (2) and (3), we have
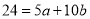 …. (4)
…. (4)
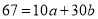 …. (5)
…. (5)
On solving (4) and (5), we get
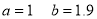
On Substituting the values of a and b in (1), we get
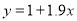
Question-10: Find the least-squares approximation of the second degree for the discrete data.
| -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| 15 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 19 |
Solution:
Let the equation of second-degree polynomial be 
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-2 | 15 | -30 | 4 | 60 | -8 | 16 |
-1 | 1 | -1 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
2 | 19 | 38 | 4 | 76 | 8 | 16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Normal equations are

On putting the values of 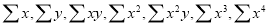 in equations (2), (3), (4), we have
in equations (2), (3), (4), we have
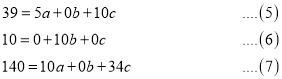
On solving (5), (6), (7), we get 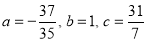
The required polynomial of the second degree is 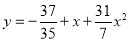
Question-11: Fit a second-degree parabola to the following data:
x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
y | 1 | 1.8 | 1.3 | 2.5 | 6.3 |
Solution: Let 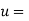 and
and  so that the parabola of fit
so that the parabola of fit 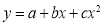 becomes
becomes
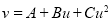 …. (i)
…. (i)
The normal equations are


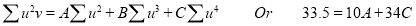
Saving these as simultaneous equations we get
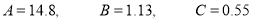
(i) becomes

Or 
Hence 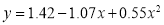
Question-12: Find the correlation coefficient between age and weight of the following data-
Age | 30 | 44 | 45 | 43 | 34 | 44 |
Weight | 56 | 55 | 60 | 64 | 62 | 63 |
Sol.
x | y |
|
|
|
| ( |
30 | 56 | -10 | 100 | -4 | 16 | 40 |
44 | 55 | 4 | 16 | -5 | 25 | -20 |
45 | 60 | 5 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
43 | 64 | 3 | 9 | 4 | 16 | 12 |
34 | 62 | -6 | 36 | 2 | 4 | -12 |
44 | 63 | 4 | 16 | 3 | 9 | 12 |
Sum= 240 |
360 |
0 |
202 |
0 |
70
|
32 |
Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation-
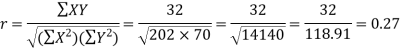
Here the correlation coefficient is 0.27.which is the positive correlation (weak positive correlation), this indicates that as age increases, the weight also increases.
Question-13: Find the correlation coefficient between the values X and Y of the dataset given below by using the short-cut method-
X | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
Y | 90 | 85 | 80 | 60 | 45 |
Sol.
X | Y |
|
|
|
|
|
10 | 90 | -20 | 400 | 20 | 400 | -400 |
20 | 85 | -10 | 100 | 15 | 225 | -150 |
30 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 100 | 0 |
40 | 60 | 10 | 100 | -10 | 100 | -100 |
50 | 45 | 20 | 400 | -25 | 625 | -500 |
Sum = 150 |
360 |
0 |
1000 |
10 |
1450 |
-1150 |
Short-cut method to calculate correlation coefficient-

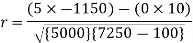
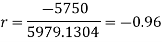
Question-14: Two variables X and Y are given in the dataset below, find the two lines of regression.
x | 65 | 66 | 67 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 | 71 |
y | 66 | 68 | 65 | 69 | 74 | 73 | 72 | 70 |
Sol.
The two lines of regression can be expressed as-
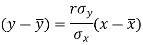
And

x | y |
|
| xy |
65 | 66 | 4225 | 4356 | 4290 |
66 | 68 | 4356 | 4624 | 4488 |
67 | 65 | 4489 | 4225 | 4355 |
67 | 69 | 4489 | 4761 | 4623 |
68 | 74 | 4624 | 5476 | 5032 |
69 | 73 | 4761 | 5329 | 5037 |
70 | 72 | 4900 | 5184 | 5040 |
71 | 70 | 5041 | 4900 | 4970 |
Sum = 543 | 557 | 36885 | 38855 | 37835 |
Now-
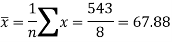
And
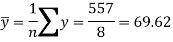
The standard deviation of x-
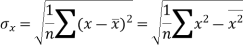

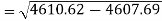
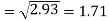
Similarly-
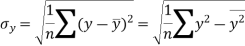
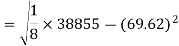
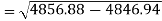
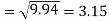
Correlation coefficient-
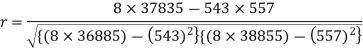
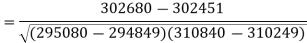
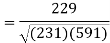
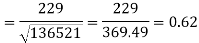
Put these values in the regression line equation, we get
Regression line y on x-
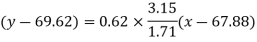
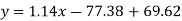
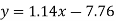
Regression line x on y-