Unit - 6
Software Testing
Q. 1) What is static testing strategy? Explain types ?
Sol:- Static testing strategy -
A static test assesses a system's quality without ever operating the system. Although it can sound difficult to do that, it can be done in a few ways.
In order to identify issues as early as possible, the static test looks at portions or elements relevant to the device. For instance, after writing and before pushing it, developers check their code. This, a method of static testing, is called desk-checking. A review meeting held for the purpose of reviewing specifications, design, and code will be another example of a static test.
Automated static tests with the correct tools can be performed. C programmers can detect possible bugs using the lint software, while Java users can use JTest to review their scripts against a coding standard.
A decided benefit is provided by static tests: if a problem is found in the specifications before it evolves into a machine bug, it saves time and resources.
Structural Testing Strategy -
Although static tests are very helpful, they are not necessary. It is important to operate the programme on real computers, and to find all the bugs, the code must be run in its entirety. Among these tests, structural tests are among the most important.
On the basis of the software structure, structural tests are planned. As they are conducted by testers with detailed knowledge of the programme as well as the computers and systems on which it runs, they may also be called white-box tests.
In order to detect localised errors in data flows, structural tests are most commonly performed on individual components and interfaces.
Since the development of structural tests involves a detailed understanding of the software being evaluated, it is best for developers or highly qualified testers to perform them. Developers and testers work in tandem to set up test harnesses in the best-case scenario and run them at regular intervals.
Behavioral Testing Strategy -
The focus of Behavioral Research is on how a system works rather than the process behind its functions. It focuses on workflows, configurations, performance, and all user journey elements. The aim of these tests, also referred to as "black box" tests, is to assess a website or app from an end-perspective user's .
Many user profiles as well as usage scenarios must be protected by behavioural research. Most of these experiments concentrate on fully integrated systems instead of individual parts.
Instead of individual components, most of these experiments concentrate on fully integrated systems. This is because it is only possible to accurately gauge device actions through the eyes of a consumer after it has been assembled and significantly implemented.
Professional manual testers are renowned for being able to trace a bug trail and assess their effect on user experience.
Behavioral testing does require some knowledge of the technicality of the system. Tests need some measure of insight into the software's business side, particularly with regard to what target customers want. They need to know what users are likely to do in order to prepare test scenarios once they visit a website or app
Q. 2) Define software testing strategy ?
Sol ;- Software Testing is a method of assessing a software application's performance to detect any software bugs. It checks whether the developed software meets the stated specifications and, in order to produce a better product, identifies any defects in the software.
In order to find any holes, errors or incomplete specifications contrary to the real requirements, this is effectively executing a method. It is also defined as a software product verification and validation process.
To ensure that every component, as well as the entire system, works without breaking down, an effective software testing or QA strategy involves testing at all technology stack levels. Some of the Techniques for Software Testing include:
Leave time for fixing : When problems are identified, it is necessary to fix the time for the developers to solve the problems. Often, the business also needs time to retest the fixes.
Discourage passing the buck: You need to build a community that will allow them to jump on the phone or have desk-side talk to get to the bottom of stuff if you want to eliminate back and forth interactions between developers and testers. Everything about teamwork is checking and repairing.
Manual testing has to be exploratory: If any problem can be written down or scripted in specific terms, it could be automated and it belongs to the automated test suite. The software's real-world use will not be programmed, and without a guide, the testers need to break stuff.
Encourage clarity : You need to create a bug report that does not create any uncertainty but offers clarification. It is also necessary for a developer, however, to step out of the way to interact effectively as well.
Test often : This helps to avoid the build-up and crushing of morale from massive backlogs of issues. The safest method is known to be frequent checking.
Q. 3) What are strategic issues ?
Sol :-
The problems considered in implementing software testing techniques are below:
● Specify a requirement in a quantifiable manner before research begins.
● Profiles for each user category are created according to the user category.
● Create a detailed programme and it's structured to test itself.
● Formal Professional Reviews should be used for successful monitoring.
● FTR should be done in order to access the evaluation plan and test cases.
Q. 4) Describe integration testing ?
Sol:- Integration testing -
Integration testing is about integrating all the unit modules and test them for their
efficacy. After unit testing of individual modules integration testing takes place.
Types of Integration testing :
In top-down testing approach, testing of higher level modules with lower level
modules are done till successful completion of all modules. This testing yields
highdesign flaws which can be rectified early as critical modules are tested first.
The bottom to up testing approach lower level modules are tested with higher level modules until testing is successfully completed for all the modules. Top level modules are tested at the end, so it can turn into a fault.
When the software is ready to hand over to the customer it has to go through the last phase of testing where it is tested for user-interaction and response. This is important because even if the software matches all user requirements and if the user does not like the way it appears or works, it may be rejected.
The team of developers themselves perform alpha testing by using the system as if it is being used in the work environment. They try to find out how user would react to some action in software and how the system should respond to inputs.
After the software is tested internally, it is handed over to the users to use it under their production environment only for testing purposes. This is not as yet the delivered product. Developers expect that users at this stage will bring minute problems, which were skipped to attend.
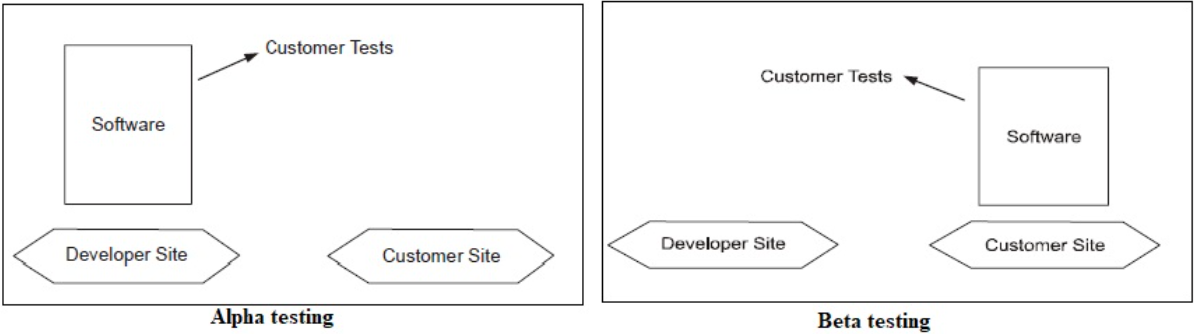
Fig : alpha and beta testing
Mutation testing is a white box approach where a mutant is inserted into the program to test whether the existing test case can detect the invader or error or not. The mutantis created by making modification or alteration in original code. This testing is done to check the ability of test cases to do testing.
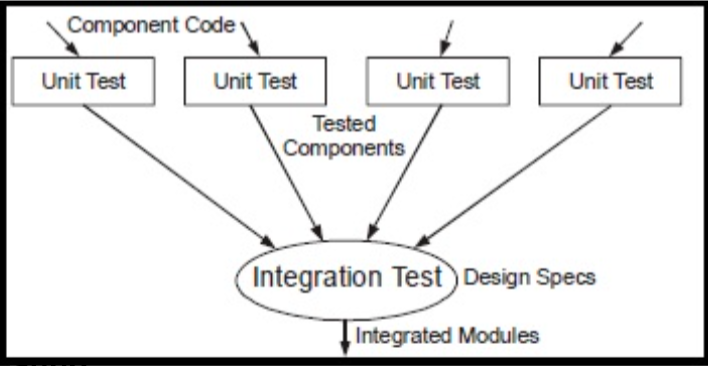
Fig : unit and integration testing
Q. 5) Describe strategies for Webapps ?
Sol :- Website testing tests for any glitches on your web application or website before it is made live and available to the general public. Web Testing tests reliability, accessibility, protection, compatibility, web application or website performance.
During this point, the functioning of the site, its access to disabled as well as regular users and its ability to manage traffic are tested for problems such as web application protection.
In Software Engineering, depending on the web testing requirements, the following test types/techniques can be carried out.
1. Functionality Testing of a Website
This is a website that contains many evaluation criteria, such as user interface, APIs, testing of databases, security testing, testing of clients and servers, and basic functionalities of the website. Functional testing is very simple and enables both manual and automated testing to be performed by users. The functionality of each feature on the website will be checked.
Check all the connections that work properly on your web pages to make sure there are no broken links. There will be connections to be reviewed like -
● Outgoing links
● Internal links
● Anchor Links
● MailTo Links
Test HTML and CSS to make sure your website can be easily monitored by search engines. This is going to include -
2. Usability Testing
Testing of usability has now become a critical part of every web-based project. It can be carried out by testers like you or a small focus group close to the web application's target audience.
3. Interface Testing
Application, Web and Database Server are three fields to be evaluated here
● Application : Test requests are sent correctly to the database, and the response is shown correctly on the client side. Errors must be identified by the programme, if any, and must be displayed only to the administrator and not to the end user.
● Web server : The Web test server manages all application requests without denial of service.
● Database server : Ensure that queries sent to the database give results that are anticipated.
4. Database Testing
One vital component of your web application is the database and stress must be put to thoroughly test it. Research operations will include—
● Test if any errors are shown when running queries
● Data Integrity is retained when data in the database is generated, modified or removed.
● Check the answer time of queries and, if appropriate, fine tune them.
● In your web application, test data obtained from your database is displayed accurately.
5. Compatibility Testing
Compatibility checks ensure the proper display of your web application across various platforms. This would include—
Browser Compatibility Test: The same website will be viewed differently in different browsers. If your web application displays correctly through browsers, JavaScript, AJAX, and authentication works great, you need to test it. You can also search for compatibility with mobile browsers.
With Operating System changes, the rendering of web elements such as buttons, text fields, etc. changes. For different combinations of operating systems such as Windows, Linux, Mac and browsers such as Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari etc., make sure your website runs fine.
6. Performance Testing
This will ensure that the network runs under all loads. Testing tasks for apps will include, but are not limited to -
● Reply times of website applications at various connection speeds
● A web server load test to assess its behaviour under regular and peak loads.
● To assess the break point when forced to above average loads at peak time, stress test your web site.
● Test how the site recovers from such an occurrence if a crash occurs due to peak load.
● Make sure optimization strategies are allowed to reduce load times, such as gzip compression, browser and server side cache.
7. Security Testing
For e-commerce websites that store sensitive customer information, such as credit cards, security testing is important. Research operations will include—
● Unauthorized access to protected pages should not be provided for research.
● Without suitable access, restricted files should not be downloadable.
● After prolonged user inactivity, check sessions are automatically killed.
● Websites should be routed to protected SSL pages when SSL certificates are used.
8. Crowd Testing
To conduct tests that would otherwise have been performed by a small group of individuals in the organisation, you will select a large number of individuals (crowd). Crowdsourced testing is a fascinating and upcoming phenomenon that allows several unnoticed vulnerabilities to be unravelled.
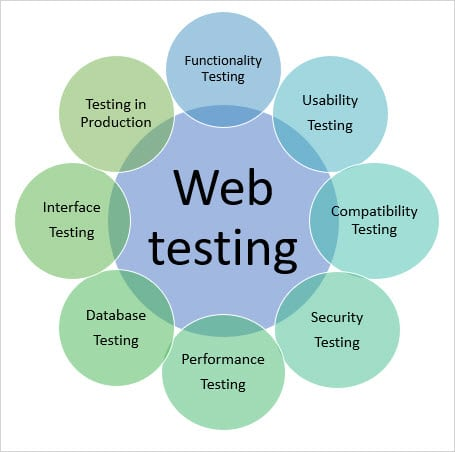
Q. 6) Describe Validation testing ?
Sol :- Validation testing -
Validation Testing, performed by QA practitioners, is to determine if the device meets the specifications and performs the functions for which it is intended and meets the objectives and user needs of the organisation. This sort of testing, as well as verification testing, is quite important. At the end of the production process, validation is performed and takes place after verification is finished.
Thus, developers apply validation testing to ensure customer satisfaction. The aim is to verify and be satisfied in the product or system and to satisfy the customer's requirements. It also requires the approval of the programme from the end user.
As software is checked, the purpose is to check the accuracy of the defects and bugs found. Developers patch them when glitches and bugs are detected. The programme is reviewed again after that to ensure that no bugs are left. The output of the software product scales up in that way.
The objective of software testing is to assess software quality in terms of the number of defects found in the software, the number of running tests and the device covered by the tests. If, with the aid of testing, bugs or defects are detected, the bugs are reported and repaired by the development team. When the bugs are patched, testing is carried out again to ensure that they are truly fixed and that the programme has not created any new defects. The consistency of the programme improves with the complete period.
Validation checking phases Process:
● Validation Planning – To coordinate all the tasks that need to be included during research.
● Define Requirements – To set targets and identify the research criteria.
● Selecting a Team – Selecting a capable and experienced leadership team
● Developing Documents – To create a document for the user specification detailing the operating conditions.
● Estimation/Evaluation – To test the programme and present a validation report as per the specifications
● Fixing bugs or Incorporating Changes - To adjust the programme so that any errors detected during assessment can be deleted.
Validation-Test Criteria
- Along with a series of checks for black boxes.
- The object of the test plan and test procedure is to check:
● Requirements are met or not met .
● Whether or not all behavioural features are accomplished.
● If all performance criteria are met or not.
● Whether or not the text is accurate .
Black-box testing
It is also known by “behavioural testing” which focuses on the functional
requirements of the software, and, is performed at later stages of testing process
unlike white box which takes place at early stage. Black-box testing aims at
functional requirements for a program to derive sets of input conditions which should
be tested. Black box is not an alternative to white-box, rather, it is a complementary
approach to find out a different class of errors other than white-box testing.
Black-box testing is emphasizing on different set of errors which falls under following
Categories:
a) Incorrect or missing functions
b) Interface errors
c) Errors in data structures or external database access
d) Behaviour or performance errors
e) Initialization and termination errors.
Configuration Review
● Check whether or not all software configuration elements have been properly created.
● This process is often referred to as a " audit"
Q. 7) Define Verification and Validation ?
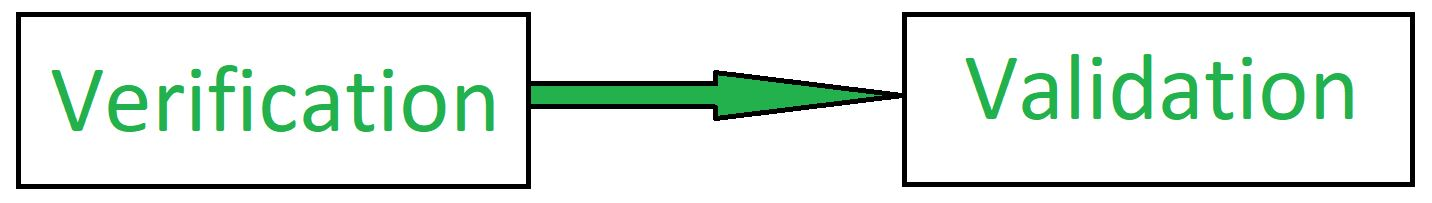
Sol :- Verification and validation is the process of investigating whether a software system meets requirements and specifications and fulfils the function necessary.
Barry Boehm defines the verification and validation -
Verification: Are we building the product right?
Validation: Are we building the right product?
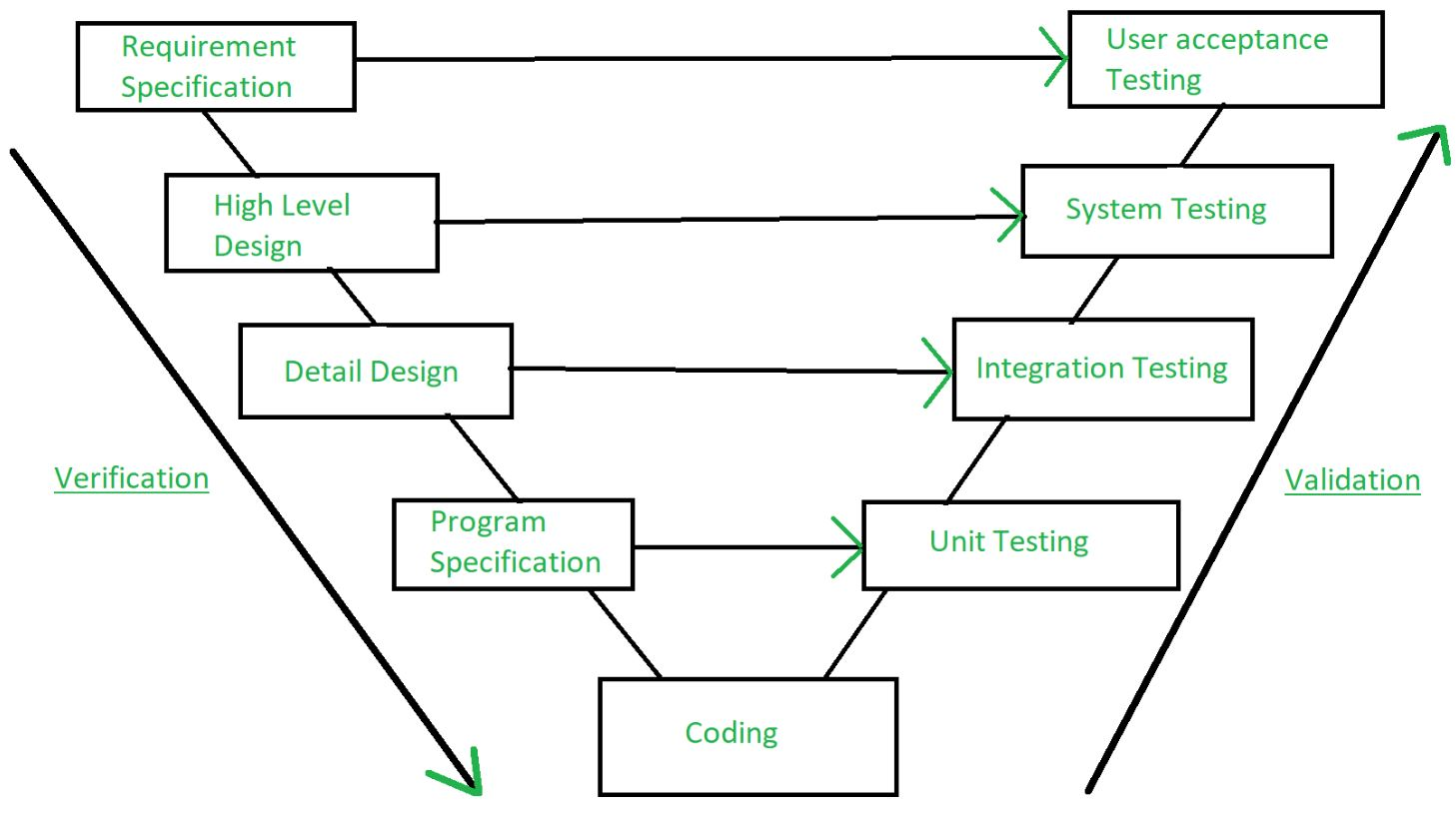
Fig : verification and validation
Verification :
Verification is the method of testing without any bugs that a programme achieves its target. It is the method of ensuring whether or not the product that is produced is right. This tests whether the established product meets the specifications we have. Verification is Static Testing.
Verification tasks involved:
Validation :
Validation is the process of testing whether the software product is up to the mark or, in other words, the specifications of the product are high. It is the method of testing product validation, i.e. it checks that the correct product is what we are producing. Validation of the real and expected product is necessary. Validation is the Dynamic Testing.
Validation tasks involved:
Note - Validation is preceded by verification.
Q. 8) Define software testing strategy ?
Sol:- Software testing strategy -
Software Testing is a method of assessing a software application's performance to detect any software bugs. It checks whether the developed software meets the stated specifications and, in order to produce a better product, identifies any defects in the software.
In order to find any holes, errors or incomplete specifications contrary to the real requirements, this is effectively executing a method. It is also defined as a software product verification and validation process.
To ensure that every component, as well as the entire system, works without breaking down, an effective software testing or QA strategy involves testing at all technology stack levels. Some of the Techniques for Software Testing include:
Leave time for fixing : When problems are identified, it is necessary to fix the time for the developers to solve the problems. Often, the business also needs time to retest the fixes.
Discourage passing the buck: You need to build a community that will allow them to jump on the phone or have desk-side talk to get to the bottom of stuff if you want to eliminate back and forth interactions between developers and testers. Everything about teamwork is checking and repairing.
Manual testing has to be exploratory: If any problem can be written down or scripted in specific terms, it could be automated and it belongs to the automated test suite. The software's real-world use will not be programmed, and without a guide, the testers need to break stuff.
Encourage clarity : You need to create a bug report that does not create any uncertainty but offers clarification. It is also necessary for a developer, however, to step out of the way to interact effectively as well.
Test often : This helps to avoid the build-up and crushing of morale from massive backlogs of issues. The safest method is known to be frequent checking.
Q. 9) Describe types of integration testing ?
Sol :- Types of Integration testing :
In top-down testing approach, testing of higher level modules with lower level
modules are done till successful completion of all modules. This testing yields
highdesign flaws which can be rectified early as critical modules are tested first.
The bottom to up testing approach lower level modules are tested with higher level modules until testing is successfully completed for all the modules. Top level modules are tested at the end, so it can turn into a fault.
When the software is ready to hand over to the customer it has to go through the last phase of testing where it is tested for user-interaction and response. This is important because even if the software matches all user requirements and if the user does not like the way it appears or works, it may be rejected.
The team of developers themselves perform alpha testing by using the system as if it is being used in the work environment. They try to find out how user would react to some action in software and how the system should respond to inputs.
After the software is tested internally, it is handed over to the users to use it under their production environment only for testing purposes. This is not as yet the delivered product. Developers expect that users at this stage will bring minute problems, which were skipped to attend.
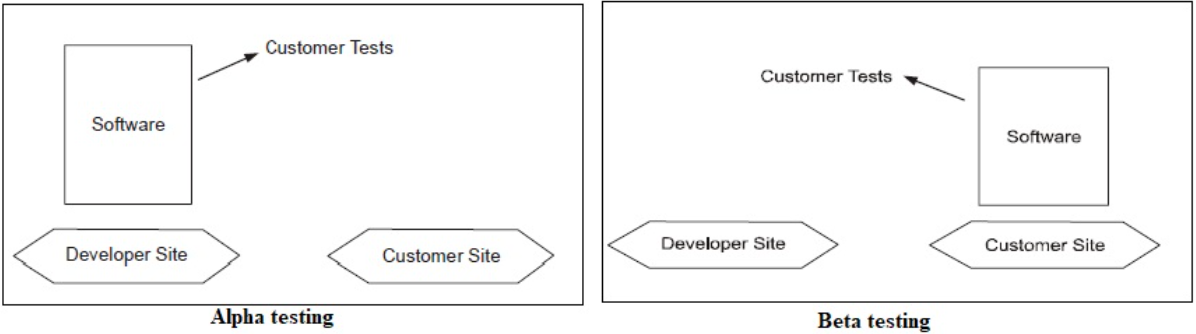
Fig : alpha and beta testing
Mutation testing is a white box approach where a mutant is inserted into the program to test whether the existing test case can detect the invader or error or not. The mutantis created by making modification or alteration in original code. This testing is done to check the ability of test cases to do testing.
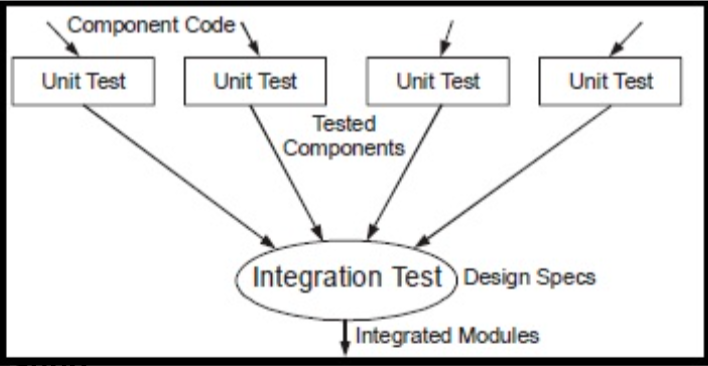
Fig : unit and integration testing
Q. 10) Describe test strategies for object-oriented software?
Sol;- The goal of research, plainly put, is to find the greatest possible number of errors over a reasonable time period with a manageable amount of effort applied.
Although for object oriented applications, this basic purpose remains unchanged.
Both testing approach and testing techniques shift the meaning of object-oriented software (Plan).
Unit Testing in the OO Context
This includes testing of the packages, attributes (i.e. data) and operations (also known as methods or services) that manipulate this data for each class and each instance of a class (object).
The smallest testable unit is the encapsulated class or object, rather than measuring an individual module. This is because a class may include a number of different operations, and as part of a number of different classes, there might be a specific operation.
Consider a hierarchy of classes in which an action X for the superclass is specified and a number of subclasses inherit it.
Operation X is used by each subclass, but it is implemented within the context of the private attributes and operations specified for the subclass.
Since the context in which operation X is used differs in subtle ways, in the context of each of the subclasses, it is important to evaluate operation X.
In comparison to unit testing class testing for OO applications, the operations encapsulated by the class and the class's state actions are powered.
Integration Testing in the OO Context
There are two distinct methods for OO system integration testing.
The first, i.e. thread-based testing, introduces the collection of classes necessary for the system to respond to one input or event. Each thread is independently integrated and checked. To ensure that no side effects occur, regression testing is applied.
The second approach to integration, i.e. use-based testing, starts the framework construction by testing certain classes (called separate classes) that use very few (if any) classes of servers. The next layer of classes, called dependent classes, which use independent classes, is evaluated after the independent classes are tested. Until the entire structure is constructed, this series of testing layers of dependent classes continues.
One phase in integration testing is cluster testing. A collaborating class cluster (determined by analysing the CRC and object-relationship model) is exercised here by developing test cases that aim to uncover collaborative errors.
Q. 11) Write the difference between verification and validation ?
Sol : Difference between the Verification and Validation -
Verification | Validation |
Verification is static testing. | Validation is the dynamic testing. |
The goal of verification is application and software architecture and specification. | The goal of validation is an actual product. |
It comes before validation | It comes after verification |
It consists of checking of documents/files and is performed by human. | It consists of execution of program and is performed by computer. |
Quality assurance team does verification. | Validation is executed on software code with the help of testing team |
It does not include the execution of the code. | It includes the execution of the code. |