Unit 2
Interfacing of PLC with I/O devices
Q1) What is Push button?
A1) Push Button
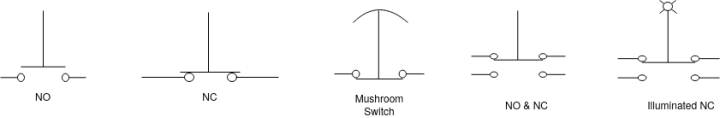
It is electromechanical switch. It consists two points. A push button consists switch body which contains electrical contact to energize and de-energized the circuit. In case of mushroom type push button the operating surface may be a type of mushroom head.
Advantages:-
1) Low cost
2) High current carrying capacity
3) Available in variety of sizes and shapes
Disadvantages:-
1) Requires physical contacts.
2) Damaging
3) Contact may bounce
Applications:-
Push buttons are placed in control circuitry to turn ON/OFF the control circuits of machines.
Q2) Describe Limit and Selector switch?
A2) Limit switch:-

It is electromechanical switch. It consists of switch body and operating head. In switching body there are electrical contact to energize and de-energized the circuit.
Advantages:-
1) Low cost
2) High current capability
3) Available in variety of shapes and sizes.
Disadvantages:-
1) Requires physical contact for operations.
2) Very slow response.
3) Easily damageable
Applications:-
They are used to sense the position of objects and materials.
Selector switch:-
Selector switch consists of switch body which includes electrical contacts to energize and the energy is the circuit and the operating head is some type of knob.
Advantages:-
1) Low cost
2) High current carrying capacity
3) Available for different contacts
Disadvantages:-
1) Required physical contact
2) Easily damageable
Applications:-
Selector switch is placed in control circuit to turn on and off the control circuit of machines.
Q3) Explain proximity switch and its types.
A3) Proximity switch:- (inductive proximity switch):-
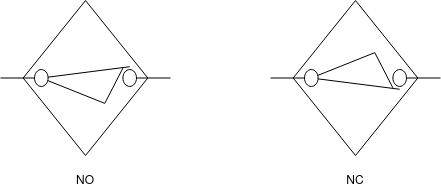
Inductive proximity sensors consists of switch body and sensing surface. It consists of
1) Coil
2) Oscillator (LC)
3) Trigger circuit
4) Output (driver circuit)
Advantages:-
1) Actuated without physical contact with object.
2) Solid state construction.
3) No wear and tear
4) Small size
5) High switching frequency
6) Reliable operation under extreme conditions such as dusty, oily and corrosive environment.
7) Maintenance free.
Disadvantages:-
1) Device or object should be near to switch.
2) Proper fitting is required.
3) Excitation is required for operation.
Applications:-
They are used to detect the presence or absence of object without making a contact with it.
Proximity switch:- (capacitive proximity switch]:-
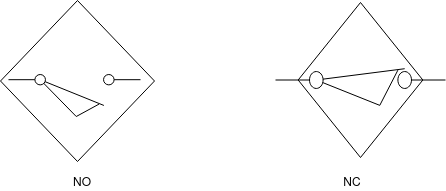
Capacitive proximity switch consists of switch body. The sensing surface is formed by two concentrically shaped metal electrode of an unwound capacitor.
It consists of
1) Dielectric plate
2) Oscillator
3) Trigger circuit
4) Output [driver circuit]
Disadvantages:-
1) The range of detection of capacitive sensor depends upon dielectric constant of materials, the larger the dielectric constant of material of target, it is easier to detect by capacitive proximity sensor.
2) The sensors must be operated in dry environment.
Applications:-
These switches are used to detect non conductive materials:- glass, plastic, paper.
Proximity switch[ultrasonic proximity switch]:-
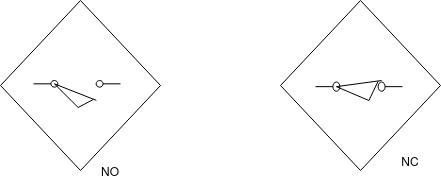
Ultrasonic proximity switch consists of switch body and sensing element or surface. It uses transducer to send and receive high frequency sound signal.
These sensor use piezoelectric ceramic disk mounted on sensor surface.
Applications:-
It is used in process industry to count object drum and bottles.
Proximity switch [photoelectric proximity switch]:-
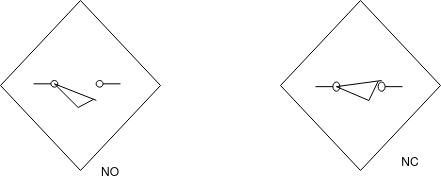
Photoelectric proximity sensors are position sensing device. These sensor senses or detects modulated light beam return from target.
It consists switch body and sensing surface. The sensing surface consists of emmiter (light source) and receiver to detect the emitted light.
The switch body is associated with electronic circuit to amplify and detect the signal and to change the state or output from No to NC.
Advantages:-
Actuated without physical contact with object.
Disadvantages:-
1) Direction sensitive
2) Specific light wavelength required for operation.
3) Source and detector should be near.
Applications:-
They are used to since the presence of object e.g. Process industries.
Q4) Explain Flow, Level & Pressure switch.
A4) Flow switch:-

It consists of slow body and sensing element. Sensing element is valve that extends into the fluid stream.
Flow switch is inserted into pipe or duct, to sense the movement of fluid. It may be air, water, oil.
Advantages:-
1) Suitable for different pipe size.
2) No moving part.
3) Flow range adjustment facility.
Disadvantages:-
1) Installation and mounting is difficult.
2) Not suitable for viscous fluids.
Applications:-
1) Flow switches are used to detect level, flow and provide digital feedback to PLC, if the floor level exceeds the specific limit.
2) Flow switches are widely used in process applications.
 Level switch:-
Level switch:-
Pressure switch:-
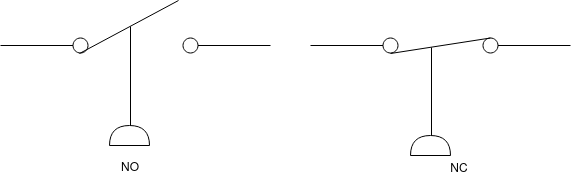
This switch turn on or off at present pressure. This pressure is called 'safe point of switch'. The pressure switch is used in some form of control. E.g. to operate a solenoid valve at a given pressure or startup pump.
Advantages:-
1) Certain applications requires dual functions.
2) Mostly used for controlling the start and stop centrifugal pump.
Disadvantages:-
1) Requires constant recalibration.
2) Limited life cycle.
3) Over pressure sensitive.
4) It has certain dead band.
Applications:-
Pressure switch is used in steam power plants.
Q5) Describe Analog input devices.
A5)
1) Potentiometer:-
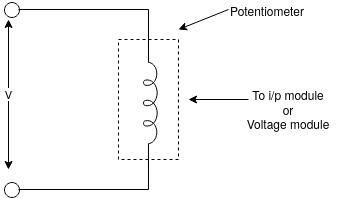
a sliding contact is moved around the carbon element by rotating shaft. As the sliding contact is rotated, the resistance to the end connections varies.
If the PLC input voltage does not match with output voltage of potentiometer then voltage converter for amplifier is required between potentiometer output and PLC input module.
2) LVDT [linear variable differential transformer]
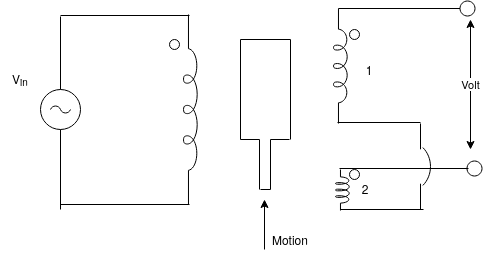
The AC output of LVDT where is as the movable magnet coil is moved linearly. As the coil moves linearly then output voltage volt varies. The voltage variation of LVDT output is used to indicate position of device.
3) Temperature transducer:-
i) RTD:- (RESISTANCE TEMPERATURE DETECTOR]
Resistance vary as well as temperature vary.
- They possess high degree of accuracy.
- They are fast in response.
- They have temperature range (from -200°c to 650°c)
Ii) Thermistor:-
It measures the temperature as the resistance of semiconductor material hanger and in thermistor the resistance varies inversely as temperature varies.
Advantages:-
- Fast response
- Greater sensitivity
- Small size
Disadvantages:-
- Temperature versus resistance curve is non linear.
- They are unstable for wide temperature span.
Iii) Thermocouple:-
Advantages:-
- They have extremely wide temperature range (from -270°c to 2800°c)
- They have high speed of response
- Accuracy is high.
Disadvantages:-
- They have limited used in temperature span of less than about 33°c.
- They need to hold reference junction temperature constant.
Applications of temperature transducer:-
1) Measurement of temperature
2) Measurement of thermal conductivity
3) Heat exchanger
4) Boiler
Flow measurement:-
1) Ventary tube:-
It is widely used for measurement of discharge thermal pipe.
Advantages:-
- They have been extensively used for a long period.
- Low head loss
- They have high coefficient off discharge.
2) Nozzle:-
- Low initial cost
- Measures flow of high viscous liquid.
Disadvantages:-
- Higher maintenance
- Have poor pressure recovery
3) Orifice:-
It is the most common type of head flow.
Disadvantages:-
- Its sensitivity is much slower.
- The loss of head is much as much 60-70%
Advantages:-
- Initial cost, easy to install.
Applications:-
1) Used for measurement of water, fluids, gases and dirty liquid in industrial process.
Pressure transducer:-
1) Diaphragm:-
Used to convert pressure into displacement and such a displacement is proportional to electrical signal.
2) Bellows:-
This is used to convert 'pressure into displacement', in this LVDT is used to convert displacement into electrical signal i.e. voltage.
3) Bourdon tube:-
It will convert pressure into displacement, and such displacement is proportional to electrical signals.
Applications:-
- Home applications
- Industrial applications
Level transducer:-
1) Capacitance type
2) Ultrasonic type
3) Photoelectric types
Applications:-
- Level transducers are used in process industries, to measure the level of different. Fluids like water, oil, chemical and petrol.
Q6) Define Temperature switch.
A6)
Bimetallic and bulb/ capillary type temperature switch is typically used switching contacts while thermocouple switches use solid-state output.
Advantages:-
1) Temperature range adjustment facility
2) Digital indications available.
3) Easy installation
Disadvantages:-
1) Limited life cycle
2) Periodically recalibration is needed.
Applications:-
1) They are used to detect over temperature conditions.
2) They are often used for thermal protection purpose
Q7) Explain Output on - off devices.
A7) Output devices receive voltage or current from PLC output module. These devices are lamp, heater, actuator, relay, contactor, solenoids etc.
These devices actually control the process.
1) Solenoids:-
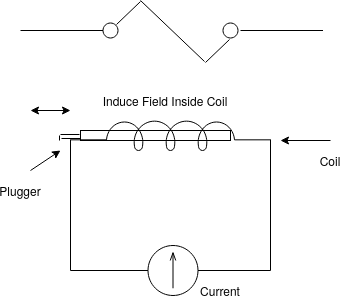
Solenoid convert electrical signal into mechanical signal.
Electromagnetic coil attracts the plunger
Advantages:-
1) Easy installation
2) Small output
Disadvantages:-
1) Slow response
2) Back pressure of lewd effect on a operation.
Applications:-
1) They are used in process industries.
2) They are used to change gears of two position transmitter.
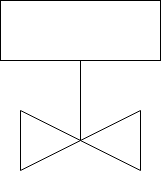 Electrically operated solenoid valve:-
Electrically operated solenoid valve:-
Operating principle:-
These devices convert electrical signal into initiating force or movement. An electric solenoid coil is basically simple electromechanical unit, used to control opening and closing of valve.
Advantages:-
1) Low cost
2) Lower maintenance
3) High current capability
Disadvantages:-
1) Requires physical contacts
2) Easily damageable
Applications:-
1) In chemical and petroleum industries.
Relay:-
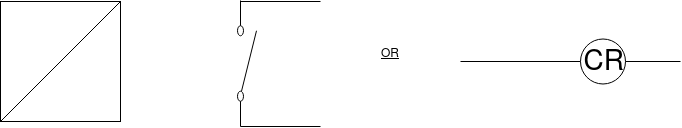
Relay is electromagnetic switch. Industrial control relay can be classified as,
1) Electrically held relay.
2) Mechanically held relay.
3) Timing relay
4) Solid state relay
5) Reed relay
Advantages:-
1) Available in different ratings
2) Release is small contactors that are designed for use only in control circuit.
Disadvantages:-
1) Limited life.
2) switching time is more
Applications:-
1) They are used for switching valve, motor and heaters.
Contactor:-
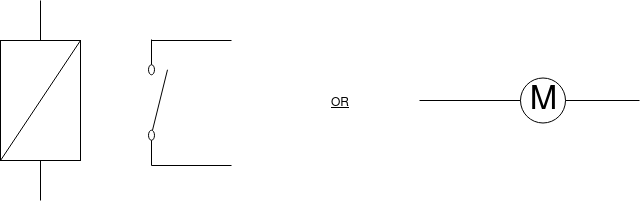
Contactors are used only for high ratings. They are used for high voltage control, for large motors above 250 Hp.
Stepper motor:-
Stepper motor is a device that rotates through some angle for which digital pulse is supplied to its input.
Stepping angle=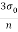
Advantages:-
1) Available with various stepping angles.
Disadvantages:-
1) Output in step form.
2) Driver circuit is required for operation.
3) Torque requirement is less.
Q8) Explain Analog output devices.
A8) Analogue output devices communicate with PLC by receiving standard 4-20 mA current or 0-10 V DC voltage.
The analog output devices are:-
1) Control valve.
2) Digital panel meter
3) Analog meters.
4) Dampers
These devices actually, controls the process. These devices receives voltage or current signal from terminal of output module of PLC.
Digital panel meter[DPM]:-
It is connected to output of PLC through the module for measurement of process for other variables.
It consists
1) Signal conditioning circuit
2) Analog to digital converter circuitry
3) Data outputs
4) Power supply
Advantages:-
1) It will measure voltage.
2) It provide numeric read out
3) Small size lightweight.
Disadvantages:-
1) Unable to represent fluctuations.
2) Module circuit is required for interfacing to PLC.
Applications:-
1) Medical, scientific, analog instruments.
2) Data acquisition system.
3) Measurement of process variables.
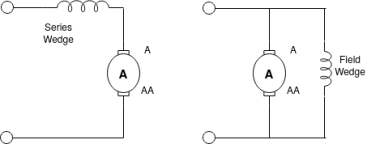
DC motor:-