Unit 05
Conducting materials
Q1) What is conductor materials and what property they have?
A1) Conductor materials permits the electron freely from the particles to the particles. When an object is made conducting materials will be allow charge to be transferred over the complete surface of object. If electron is transferred to object at the given location, which charge is quickly transferred over the complete object. When electrons are doing movement distribution charge is taking place. Conductors materials are permit to electrons to transported from the particle to particle.
Conductor materials have property.
In the condition of equilibrium conductor exhibits following properties.
Resistance
Inductance
Electric field inside the conductor is 0
Density of charge inside the conductor is 0
On the conductor surface free charge exists only.
At the conductor surface, electric field is normal to surface.
Resistance
Generally conductors electricity possessed too low resistance for electricity flow. A perfect conductor contain resistance zero ideally. But, in practical conductors resistivity varies from low to high. Conductor containing low resistivity or high conductivity are utilized as the conductor winding of the electrical machines, for electrical contact, for transmission lines and earth wires etc. the conducting materials keeping high resistivity or low conductivity are utilized for building heating elements and filaments incandescent lamp for the electric heaters, furnaces and ovens.
Inductance
In AC supply when a conductor is utilized, a magnetic flux is developed. This flux has two parts. Internal and external flux. Internal flux has the very low value as comparison of the external flux. Cause of this flux linkage to the conductor itself and inductance is come into the picture. This occurred inductance give results in extra voltage drop in the conductor. Besides, this inductance effect distribution of the current over the cross section area of the conductor. Because of, current is always prefer to flow by outer part of the cross sectional area. And this effect named skin effect. This distribution of the current over the cross sectional area is effected through flux linkage to the conductor besides to the current by the nearby conductor. This is the proximity effect and both effect proximity and skin effect exist only the for AC supply. Not for the DC supply.
Electric field inside the conductor zero
A perfect conductor has electric field zero. In a conductor, if electric field is exists, it will lead a force on the electron and accelerate them. But, when the equilibrium condition is occurred net force on the electron is zero. Thus, electric field is not exist in conductor. This show electric field must be outside the conductor. This property is used for the electrostatic shielding for the electrical equipment.
Charge density inside the conductor is zero
Inside the conductor electric charge does not exist. The reciprocal electrostatic repulsion force, between charges that is electrons, requests which the electrons should be as far as possible. This force pushes the electrons to surface on the conductor. Besides there is no electric charges exists in conductor outcomes in the zero charge density into the conductor.
Free charges exists only on conductor surface
As we know that the charge particles does not exist inside conductor. Besides of the electrostatic repulsion force, electrons are move to the outer surface of the conductor. This is happen only by the electric charges which exists in side the conductor. Therefore, free electrons exists only on surface of conductor.
Conductor surface, electric field is normal to surface
When we discuss about the boundary condition of the dielectric to the conductor, electric field is normal to the conductor surface and electric field tangent part to surface is zero. This give the information about the electric field intensity is normal for the conductor surface and electric field tangential part intensity is zero.
Q2) Describe electrical conductor materials and their applications?
A2) Materials which are provide conduction of electricity due to the free electron and an electric potential is difference is applied over them are called as the conducting materials. These materials are good conductor of the electricity and heat. Current and heat is flow due to the free electron in the materials.
Aluminum
Aluminum is electrically conductive material. Which is discovered by Hans Oersted in 1825. The name aluminum is derived from the Latin language for alum, alumen meaning bitter salt. Its atomic number is 13. Electron configuration is [Ne]3s23p1. Aluminum is the silvery white and light weight metal. It is the malleable and soft. Properties of the aluminum are
Strength to weight ratio
Corrosion resistance of aluminum
Thermal and electrical conductivity of the aluminum
Heat and light reflectivity of aluminum
Aluminum toxicity
Recyclability of aluminum
Production of aluminum
Aluminum smelting
Environmental considerations
Applications
Different type of aluminum alloys have provided outcome in being aluminum utilized in the industries as the food preparation, diverse as the transport, packaging, energy generation, electrical transmission and architecture applications. Aluminum material is ralpced naothe materials like steel, zinc, tin plate, stainless steel, copper, wood , paper, composites and concrete. These all applications takes approximately 85% of aluminum hold annually. 15% which are left is utilized in the applications including- high pressure gas, cylinders, ladders, sporting goods, road barriers and signs, furniture, lithographic printing and plates.
Copper
The term copper is derived from the latin word ‘cuprum’, that means ‘ore of the cyprus’. So the symbol of the copper is Cu. The material copper is tough, malleable and ductile materials. Having these properties make the copper extremely suitable for the wire drawing, deep drawing, tube forming and spinning. The other properties are
Excellent heat conductivity
Electrical conductivity
Excellent carrion resistance
Better biofouling resistance
Better machinability
Mechanical and electrical properties retention at the cryogenic temperatures.
Non magnetic
Copper has the melting point is 1083 degree C.
Applications are
Copper material permits heat to transfer through it fast. It is so utilized in more applications where fast heat transfer is essential. In this include-
Copper plate-Sauce pan bottom
Copper pipes- In hot water tanks heat exchangers, all weather football pitches, under floor heating system and car radiators.
Heat sinks- Disk drives, TV sets and computers.
Q3) Define copper alloys characteristics.
A3) Copper characteristics
Copper materials are ductile, tough and malleable. These qualities make copper suitable for wire drawing, tube forming, deep drawing and spinning. There are other key properties by copper and copper alloys include:
Heat conductivity exllency
Best electrical conductivity
Better corrosion resistance
Good biofouling resistance
Better machinability
Mechanical and electrical retention qualities at the cryogenic temperature
Non- magnetic
There are many copper alloys are so we represent through a copper tree. Approximate 400 various types of copper and copper alloy constitutions loosely categorized such as high copper alloy, copper, brasses, copper nickels, bronzes, copper-nickel- zinc, special alloys and leaded copper.
Characteristics of bronzes
Copper alloy bronze generally is a golden hard and brittle metal. Due to specific composition of the copper alloy properties depends on. There are some typical characteristics discussed below.
Highly ductile
Bronze shows low friction against the other metals.
Many of the bronze alloys are showing the unusual property of expansion a small amount while solidifying from the liquid into the solid. Like sculpture casting, and helps to fill mold.
Less than brittle from cast iron.
Upon the exposure to the air, bronze oxidizes, however on their outer layer. This patina keeps of the copper oxide, that eventually becomes copper carbonate. The layer of oxides saves interior metal from the further corrosion. But, if the chlorides are presents copper chlorides form, that can be cause bronze disease, a situation in which the corrosion works by metal and damage it.
Far from steel, striking against bronze a hard surface won’t be produce sparks. This develops bronzes useful for metal utilized around explosive materials.
Characteristics of the brass
Copper alloy brass, and zinc of the enduring and historical essential because of their workability and hardness. The premature brass, named calamine brass, dates to the Neolithic times, it was likely build through the reduction of the mixtures of the zinc ores and the copper ores.
The ductility of the brass relies on zinc content, brasses which contain more than 45 % zinc are not performed, either cold or hot. Like brasses, which is known brasses are of the little important on the behalf industry use. This are utilized in soldering, they also make the basis for determine alloys utilized in the die-casting. The soft brasses further subdivided into those which can be performed cold and those with the good zinc content, that need hot working.
Q4) Give explanation of the thermal bimetal’s alloys.
A4) Bimetal or thermocouple metal is a strip of 2 or more composite materials keeping various coefficient of the linear thermal expansion bond through riveting, welding or brazing. Bimetal consists the alloys iron, manganese or chrome and nickel in different type of chemical compositions.
Thermocouple is electrical device which consisting of the two dissimilar electrical conductors which making an electrical junction. It produces a voltage which dependent on temperature as the results of thermoelectric effect and voltage can be exaplined of measurement of the tempareture. Alloys of the thermocouple alumel utilized in the conjuction with the chromel in the type K thermocouple, alumel 1 is made from the manganese, aluminum, nickel and silicon, rhenium-tungsten, constantan, and chromel utilized with alumel in the type of k thermocouples and with the constantan type E thermocouples, chromel 2 is made of the chromium and nickel.
Q5) What materials are used in lamp filaments?
A5) Filament is an essential part of the incandescent lamp. Duration of the incandescent lamp, relies on the filament. Various kind of materials are utilized for making the filament of incandescent lamp. There are some materials are used in filament given below-
Carbon
Tantalum
Tungsten
Solders
Solders are melted when give them to heat from an iron connected to the temperature controller. Solders are heated up to the temperatures exceeds its melting points at the around of 600 degree F that then caused it to melt, that cools making the joints. Materials are used for making solders are- filler metals utilized in the soldering were once lead solder, because of regulations, lead based solders are replaced by the lead free solders, that may have antimony, brass, copper, bismuth, tin, indium or the silver.
Q6) Describes types of conductor?
A6) Metals
Many conductive materials are metals utilized in the practical applications. For example, the wire around house is likely to utilize copper wires as materials conducting, as materials conducting or their alloys. The electric plugs have the metal in them, and metals are often used as their conducting materials by the internal mechanism of their electric irons. This is because there are lots of free electrons in the metals and they promote mobility.
Non-metals
There are certain non-metals that are a very good electricity conductor. For example, the graphite shaped carbon is a very good electricity conductor. Just three of four carbon atoms are utilized for the bonding, if they see the graphite structure. This leaves 1 electron at the bonding free. But most non-metals are not effective electricity conductors.
Ionic conductors
Conductors are called ionic conductors in their solution form. Saltwater, for example is an ionic solution and is a good electricity conductor.
Semiconductors
Semiconductors are not as good as conductors when conducting electricity, they still gave their uses. Semiconductor examples include germanium (Ge) and silicon (Si).
Q7) What are the limitations of the classical theory of the free electron? Or state any four demerits of classical free theory of the electrons?
A7) It is the theory of a microscopic sort. According to the classical theory of free electron all free electrons will be absorb energy, but theory of quantum free electron states which only a few electrons will be absorb. This theory is unable to describe of Compton, photoelectric effect, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism etc. this theory can’t describe semiconductor and isolator electron conductivity. One not describe the dual existence of the light radiation. Not matching the theoretical and experimental values of natural heat and complex electronic heat.
By the classical theory
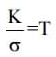 is constant for all temperature, but by the quantum theory
is constant for all temperature, but by the quantum theory 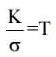 is not constant for all temperature.
is not constant for all temperature.
Q8) Describe factors which affect the electrical conductor.
A8) The way a substance conducts electricity may be influenced by certain factors.
Temperature
Adjusting the silver or any other conductive temperature affects its conductivity. In general, that temperature allows the atoms to thermally excite and decrease conductivity while increasing resistivity. The connection is linear but at low temperature it breaks down.
Impurities
Impurity applied to a conductor reduces its conductivity. Sterling silver, for example is not as strong as pure silver on a conductor. Oxidized silver is not a conductor as strong as untarnished silver. Impurities are impeding the migration of the electrons.
Crystal structure and phases
If a substance has different phases, the conductivity at the interface will slow down slightly and may be different from one structure to another. The manner in which a material is treated will influence how well it conducts electricity.
Electromagnetic fields
When electricity runs through them, conductors generates their own electromagnetic fields, with the magnetic field perpendicular to the electric field. External electromagnetic fields can generate magnetoresistance which can slow current flow.
Frequency
Frequency in hertz is the number of the oscillation cycles that an alternating electric completes per second. A high frequency above a certain amount will cause current to flow more around a conductor than through it. Since there is no oscillation and thus no frequency, the effect on the skin is not present with direct current.
Q9) What factors affected the resistivity of the conductor?
A9) Temperature and the materials utilized in the conductor making process. So, the characteristics and properties of the conductors and insulators are almost opposite. The key differences between these two are, conductors make the energy flow by them, while insulators regulate the energy flow. Driver conductivity is high while insulators have poor conductivity.
Q10) Describe the nickel chromium alloy?
A10) Typically, nichrome alloys consist of the 80% nickel and 20% chromium (nichrome 80/20), although other formulation can be found in different ratios. Nichrome has a silver gray colour and high electrical flow and heat resistance. It is also very carrion and wear resistant, is very durable and has a very high melting point at the about 1400 degree C.
Its oxidation resistance makes nichrome a common material for use in heating elements. The heating elements in a home toaster, for example are most commonly made of thick nichrome wire. When used in this manner the nichrome is usually wound to a certain electrical resistance in coils before passing trough a current to generate the heat emitted. When nichrome gets heated to high temperature. Another common use of nichrome as an electric ignition is in fireworks and explosives. The nichrome glows red hot as the current passes by it, and heats up incurability fast even with a tiny voltage. This makes it an excellent choice for igniting fireworks and other pyrotechnics because it can be triggered at the push of a button a safe distance.