Unit 2
Nuclear, Diesel, Gas Power Plant
Q1) With the help of diagram describe the layout of nuclear power plant.
Answer:
A1) Plant layout of nuclear power plant
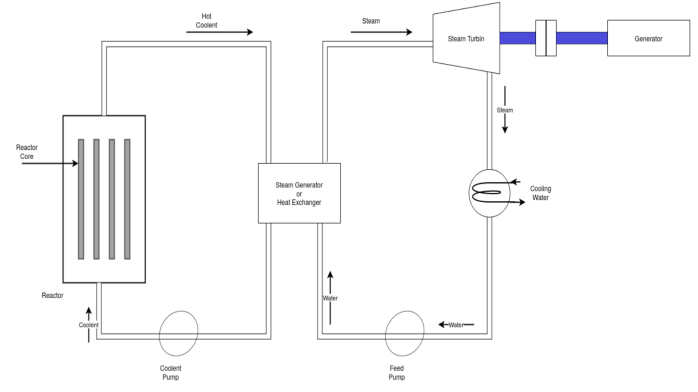
- The concept of nuclear power generation is much similar to that of conventional steam power generation, only difference lies in the steam generation part.
- The burning finance and boiler are replaced by nuclear reactor and heat exchanger the schematic arrangement is shown in above figure.
- Nuclear power plant consists of nuclear reactor for heat generation, heat exchanger for converting water into steam, steam turbine, alternator, condenser etc.
- The reactor and the cooling circuit have to be heavily shielded to eliminate radiation hazards.
- The tremendous amount of heat energy produced in breaking uranium or other similar metals of large atomic weight into lower atomic weight by fission process in an atomic reactor is extracted by pumping fluid or molten metal like liquid sodium or gas.
- The heated metal or gas is then allowed to exchange the heat to the heat exchanger by circulation. Here steam is generated which utilized to drive the gas turbine coupled to alternator thereby generating electricity.
Q2) Explain the nuclear reactor in nuclear power plant.
A2)
Definition: - nuclear reactor is an apparatus in which nuclear fission is produced in the form of a controlled self-sustaining chain reaction. In other words, it is controlled chain reaction system.
Mechanism of heat production: -
Most of the energy is imported to the two-fusion fragment into which the nucleus divides causing them to move at high speed. However, because they have taken birth in a dance mass of metal, they are rapidly slowed down and brought to rest by colliding with other atoms of the metal. In so doing, their energy is converted into heat in much the same way as energy given up by slowing motor can be converted into heat in the brake lining. In this way, the mass of uranium metal gets heated up.
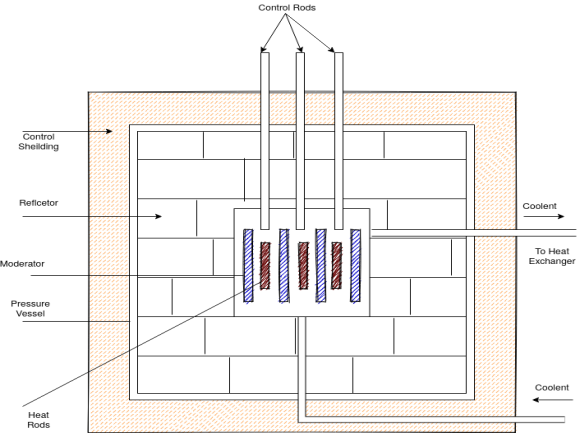
1) Reactor core: - the reactor core is that part of a nuclear power plant where fission chain reaction is made to occur and where fission energy is liberated in the form of heat for operating power conversion equipment.
Diameter -0.5 to 15m.
2) Reflector: - a reflector is usually placed round the core to reflect back some of the neutrons that leak out from the surface of the core. It is generally made of the same material as the moderator.
3) Control mechanism: - it is an essential part of a reactor and serve the following purpose.
a) For starting the reactor
b) For maintaining operating level at steady state.
c) For shutting the reactor down under normal or emergency condition.
The control system is necessary to prevent the chain reaction from becoming violent and damaging the reactor. The number of neutrons keep on increasing and temperature also increase rapidly.
4) Moderator: -
Function
a) To slow down the neutron from the high velocities.
b) To slow down the neutrons but not absorb them:
Materials:- 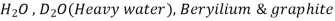
5) Coolants: - the function of a coolant is to remove the intense heat produced in the reactor and to bring out for being utilised.
Q3) Discuss the merits and demerits of nuclear power plant.
A3)
Merits:
- The amount of fuel required is very small.
- The demand for coal, oil and gas is reduced.
- These plants need less area as compared to thermal power plant.
- Plant can be located near to load centre.
- These plants are most economical in large capacity (100 MVA or more),
- The output control is extremely flexible.
- The operating cost is quite low and once installation is completed, the loading of the power plant will have no effect on generation cost.
Demerits:
- The initial capital cost is very high.
- The erection and commissioning of the plant requires greater technical knowledge.
- The fission byproducts are generally radioactive and may cause radioactive pollution.
- Maintenance charges high.
- The disposal of radioactive products is big problem.
- The cooling water requirement are more as compared to thermal plant.
Q4) Explain the site selection criteria for nuclear power plant.
A4)
Following factors should be considered for the location of nuclear power plant
- Availability of water supply
- Distance from populated area
- Transportation facilities
- Nearness to the load centre
- Availability of space for disposal of waste.
- Type of land
Q5) Enlist main components of diesel engine power plant and state application of diesel power plant
A5)
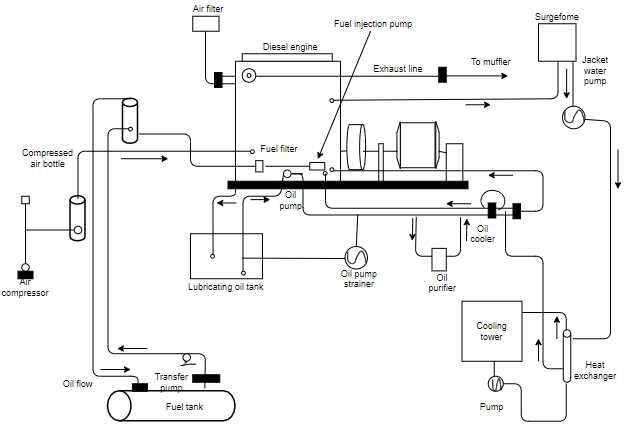
Main Components Diesel power plant
1) Engine
2) Air intake system
3) Exhaust system
4) Fuel system
a) Fuel injection system
b) Fuel pump
5) Cooling system
a) Air cooling
b) Liquid cooling
6) Lubrication system
7) Engine starting system
a) Auxiliary engine
b) Used electric motor
c) Compressed air system
Q6) Discuss the merits and demerits of diesel power plant
A6)
Merits:
- The design and installation is easy
- Can be located at any place
- Requires less space
- Can response to varying loads
- The quantity of water requirement is less.
- High operational efficiency.
- Less fire hazards
- Such plants can be started and loaded quickly.
Demerits:
- Operating cost is very high.
- Maintenance and lubrication cost are also high
- Diesel unit capacity is limited.
- Noise and pollution are produced
Q7) Explain the site selection criteria for nuclear power plant
A7)
- Distance from the load centre
- Availability of land
- Availability of fuel
- Availability of transportation facility
- Distance from the populated area
- Type of land
- Availability of water
Q8) Discuss the merits and demerits of a gas turbine power Plant.
A8)
Merits:
- Simplicity of design
- High reliability
- Simple lubrication system
- Low initial cost
- Compactness
- Requires less space
- Requiring little cooling water
Demerits:
- Low net output
- Low overall less efficiency
- Noisy operations
- Limited unit capacity
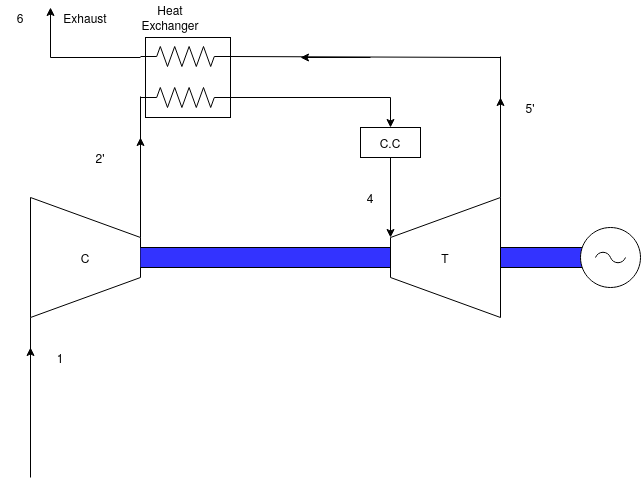
Q9) Explain closed cycle gas turbine power plant with neat sketch.
A9)
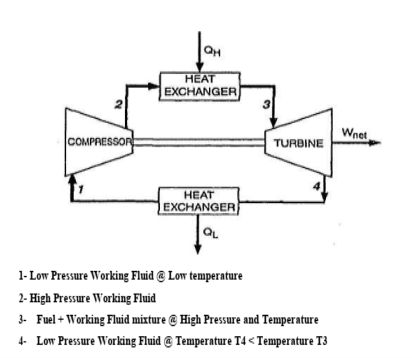
- In closed cycle gas turbine plant, the working fluid (air or any other suitable gas) coming
out from compressor is heated in a heater by an external source at constant pressure. - The high temperature and high-pressure air coming out from the external heater is passed
through the gas turbine. - The fluid coming out from the turbine is cooled to its original temperature in the cooler using external cooling source before passing to the compressor.
- The working fluid is continuously used in the system without its change of phase and the
required heat is given to the working fluid in the heat exchanger
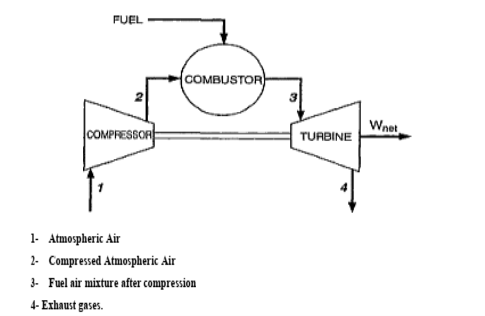
Q10) Explain open cycle gas turbine power plant with neat sketch.
A10)
The heated gases coming out of combustion chamber are then passed to the turbine where
it expands doing mechanical work. Part of the power developed by the turbine is utilized in
driving the compressor and other accessories and remaining is used for power generation.
Since ambient air enters into the compressor and gases coming out of turbine are exhausted
into the atmosphere, the working medium must be replaced continuously. This type of cycle is
known as open cycle gas turbine plant and is mainly used in majority of gas turbine power
plants as it has many inherent advantages.
Q11) Explain the classification of nuclear reactor in detail.
A11)
Classification of nuclear reactor-
Nuclear reactors may be classified in several ways i.e on basis of their applications, type of fission, fuel used, state of fuel, fuel cycle, arrangement of fissile and fertile materials, are arrangement of fuel and moderator, moderator material, cooling system employed, coolant used etc.
- According to the application the reactors are classified as
- Research and development reactors- The reactors are used for testing new reactor designs and research
- Production- These reactors are used for converting fertile materials into fissile materials
- Power- These reactors are used for generation of electrical energy
2. According to the type of fission the reactors are classified as fast reactors, slow reactors and intermediate reactors.
3. According to the type of fuel use the reactors may be classified as.
- Natural Uranium
- Enriched Uranium
- Plutonium
4. According to the state of fuel the reactors may be classified as
- Solid
- Liquid
5. According to the fuel cycle the reactors may be classified as
- Burner thermal reactor- Such reactors a design for generating heat only without any recovery of converted fertile material
- Converter reactor- Such a reactor convert fertile materials into fissile material different from the one initially fed into the reactor core.
- Breeder reactor- Such reactors convert fertile material into fissile material which is similar to one initially supplied to the reactor core.
6. As per arrangement of fissile and fertile material the reactors may be classified as
- One reason ( fissile and fertile material mixed)
- Two reason ( fissile and fertile material separate)
7. According to the arrangement of fuel and moderator the reactors may be classified as
- Homogeneous
- Heterogeneous
8. On the basis of moderator material used the reactors may be classified as
- Heavy water
- Graphite
- Ordinary water
- Beryllium
- Organic reactors
9. On the basis of coolant used the directors may be classified as
- Gas
- Water
- Heavy water
- Liquid metal reactor
10. On the basis of cooling system employed the reactors may be classified as
- Direct
- Indirect reactors
Q12) Write a short note on Nuclear waste disposal.
A12)
Nuclear waste disposal-
- Solid radioactive wastes arise from use filters, sludge from the cooling ponds, pieces of discarded fuel element cans, splitters etc.
- This along with discarded items of plant such as control rods have to be stored on site in shielded concrete vaults.
- There are many ways for disposing of the solid fission products. The storing in shielded storage vaults consists in fixing the solid waste in boro-silicate glass and then storage of this class in leak tight capsules.
- These capsules can then be stored in deep salt mines or in deep wells drilled in the stable ocean floor.
- Deep salt mines are suggested because the presence of the salt rockets indicates that there has been no ground water in the vicinity for thousands of years. Sometimes, suitable containers are filled with radioactive waste and sunk to the bottom of Seas and oceans. However, this method does not completely prevent the radioactivity from leading into the water.
- Another way of disposal is the separation and transmutation of the long lived isotopes to short lived or stable products following neutron absorption in a breeder of fusion reactor.
- The past of firing these long live products into the sun or into a long-term stable orbit is also being considered.
- It is safe enough to store radioactive waste underground in liquid form in suitable tanks or in reduction to clinker.
- Gaseous effluents are filtered for discharging into atmosphere.
Q13) Explain the site selection of diesel power plant.
A13)
The following factors should be considered while selecting a site for diesel electric power plant
- Distance from the load centre- The site should be as near to the load centre as possible in order to avoid transmission cost and losses.
- Availability of land- The land should be available at cheap rate to keep the capital cost of the plant to the reasonable one.
- Availability of fuel-The fuel should be easily available and at reasonable rate.
- Availability of transportation facilities- The transportation facilities should be available.
- Availability of water- the water should be available in sufficient quantity for cooling purposes
- Distance from populated area- the site should be away from thickly populated area because of noise and nuisance caused from exhaust.
- Type of land- the land should be of high bearing capacity to withstand the load of the plant and also vibration transmitted to the foundations from compressor and diesel engines.
Q14) Explain the methods to improve the thermal efficiency.
A14)
Method to improve thermal efficiency:-
1) Intercooling
Intercooling means the removal of the heat from compress the ear between the stages of compression. This necessitates the use of compressors with two stages viz low pressure and high pressure compressor. The intercooler is heat exchanger which is the partly compressed air in order to reduce volume and increased density. the inter cooling results in improvement of thermal efficiency, air rate and work ratio. By use of intercooling the size of turbine and compressor for the same output is reduced.
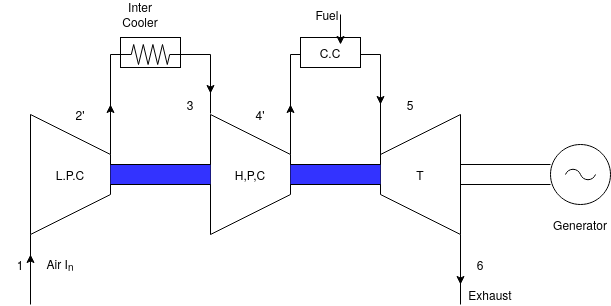
2) Reheating
In reheating the combustion gases are not expanded in one turbine only but in two turbines. The Exhaust of the high pressure turbines is reheated in a reheater and then expanded in a low pressure turbine. Reheating improves the output from the turbine due to multiple heating in the same way a as intercooling improves the performance of the compressor. However the cost of additional fuel may be heavy e unless a heat exchanger is also employed.
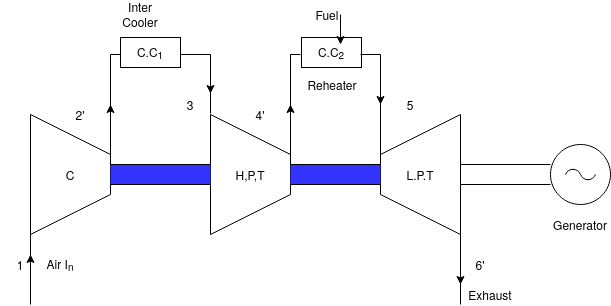
3) Regeneration
Regenerator is usually capsule and tube construction. The exhaust gases are made to flow inside the nest of tubes while air flows outside the tubes in the shell in the counter flow and heated up by the heat given out by the exhaust gases.
Thus the Regenerator utilizes the heat of exhaust gases to heat the compressed air before it is sent to the combustion chamber, reduces the fuel consumption of the plant and improves the cycle thermal efficiency.
Q15) Explain the materials used in nuclear power plant.
A15)
Materials
I) Structural
1) Aluminium
2) Stainless steel
3) Nickle alloy
4) Zirconium
5) Magnesium
II) Fuel
1) Uranium
2) Uranium ceramics
3) Thorium
4) Thorium oxide
III) Coolent
1) Water
2) Liquid metals
3) Sodium, potassium
4) Mercury
5) Helium
6) Nitrogen
IV) Control
1) Boron steel
2) Cadmium
3) Somorium oxide
V) Moderator reflector
1) Water
2) Heavy water
3) Beryllium
4) Graphite
VI) Shielding
1) Water
2) Cement and concrete
3) Iron
4) Lead
5) Boron
6) Bismuth