Unit 5
Q.1 Explain the need of PLM.
A1)
Q.2 Write a note on Collaborative Engineering
A2) “Collaborative engineering is defined for the study of interactive process of engineering collaboration wherein, in order for serving their mutual intrests, multiple interested stakeholders or partners:
i) Resolve conflicts
ii) Bargain for individual or group advantages
iii) Agree upon course of action
iv) Attempt to achieve joint outcomes
The aim of collaborative engineering is to facilitate the individuals and organizations, across the boundaries of discipline, geography and culture, to work effectively with collaborative actions for achieving joint outcomes.
It is used most effectively in product design, manufacturing, construction, etc.
Q.3 Write down the steps in Rapid Prototyping.
A3)

2. Conversion to STL Format:

3. Slice the STL File:
4. Layer by Layer Construction:
5. Clean and Finish:
Q.4 Write a note on Stereolithography
A4)
Working Principle
SLA uses a low-power, highly focused UV laser to produce a three-dimensional object in a vat of liquid photosensitive polymer.
Features
Material type: Liquid (Photopolymer)
Materials: Thermoplastics (Elastomers)
Min layer thickness: 0.02 mm
Surface finish: Smooth
Build speed: Average
Model and specification of process
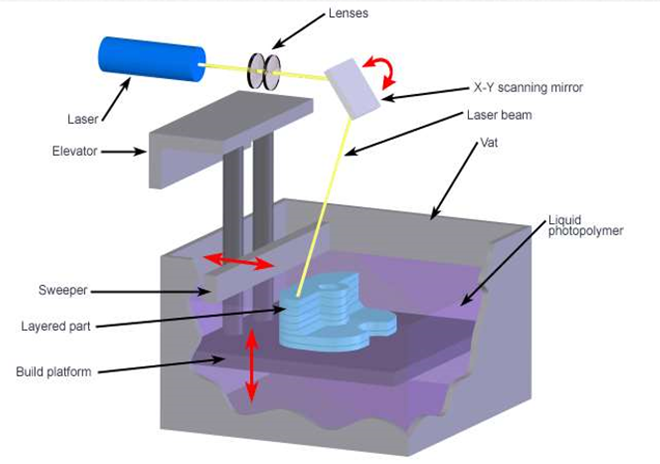
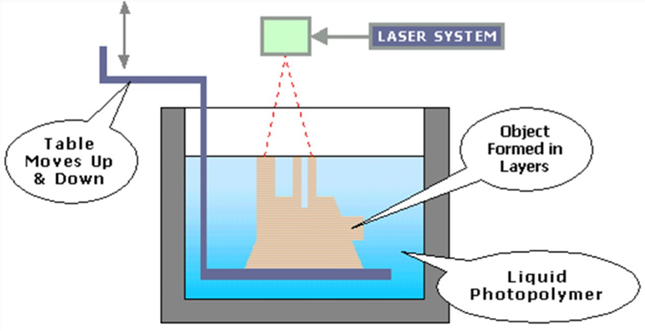
SLA Process
Working
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
Application
Q.5 Explain Principle, Process and Working of FDM
A5) Fused Deposition Modelling:
Working Principle
A plastic or wax material is extruded through a nozzle that traces the part´s cross sectional geometry layer by layer
Process
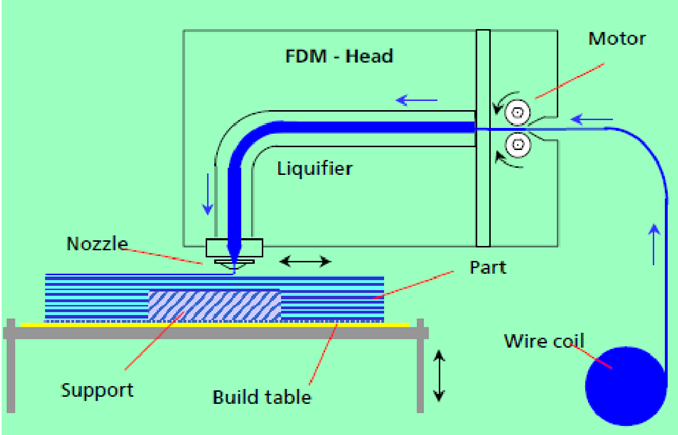
FDM Process
Working
Q.6 Explain LOM process in detail with its advantages and disadvantages.
A6) Laminated Object manufacturing:

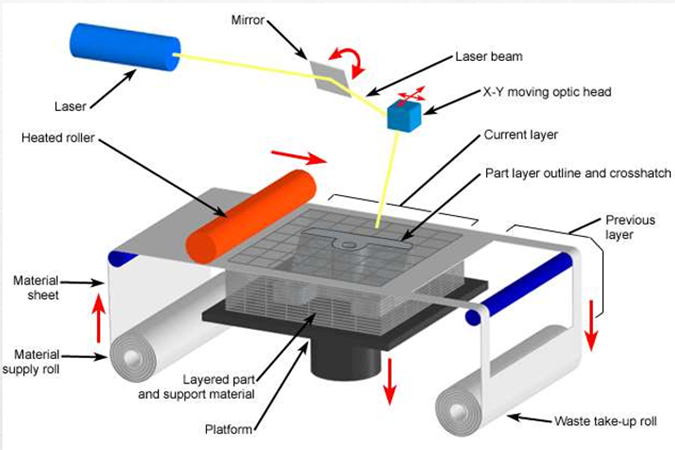
LOM Process
Working
Advantages
Disadvantages
Q.7 Write a note on SLS. State its application.
A7) Selective Laser Sintering:


SLS Process
Principle of Working
It uses a moving laser beam to trace and selectively sinter powdered polymer and/or metal composite materials.
Features
Material type: Powder (Polymer)
Materials: Thermoplastics: Nylon, Polyamide and Polystyrene; Elastomers; Composites
Min layer thickness: 0.10mm
Surface finish: Average
Build speed: Fast
Applications
Q.8 Explain the Principle and working of 3D Printing. State two advantages and two disadvantages of 3D printing.
A8)
Principle
An ink-jet printing head deposits a liquid adhesive that binds the starch powder material.

Working
Advantages
Disadvantages
Q.9 Write a note on Rapid Tooling
A9) Rapid-prototyping techniques have made possible much faster product development times, and they are having a major effect on other manufacturing processes. When appropriate materials are used, rapid-prototyping machinery can produce blanks for investment casting or similar processes, so that metallic parts can now be obtained quickly and inexpensively, even for lot sizes as small as one part.
Such technologies also can be applied to producing molds for operations (such as injection molding, sand and shell mold casting, and even forging), thereby significantly reducing the lead time between design and manufacture.
Several methods have been devised for the rapid production of tooling (RT) by means of rapid-prototyping processes.
The advantages to rapid tooling include the following:
The main shortcoming of rapid tooling is the potentially reduced tool or pattern life (compared to those obtained from machined tool and die materials, such as tool steels or tungsten carbides).
The simplest method of applying rapid-prototyping operations to other manufacturing processes is in the direct production of patterns or molds.
Q.10 What is STL file?
A10)
Q.11 Write a note on 4D printing technique.
A11) 3D printed materials can be more flexible and useful, the structures of the material can transform in a pre-programmed way in response to any external stimulus. In general, self-changing structure of 3D printed part after post process is called 4D printing process.
In 4D printing process, 1D strand or 2D surface having multi-material feature, is created using the same 3D printing techniques.
Joint and folding angle strands
Printing 4D joint includes multiple layers of material. Composition of rigid polymer, expanding material and digital material depicts the folding direction and pattern. Those materials are placed above or below of each other depending upon the type of transformation.

Custom Angle Surfaces
Similar mechanism as folding strand described previously, series of flat two-dimensional structures were generated with edge joints. The position and spacing of materials at each joint specifies the desired fold angle hence positioned accordingly.
4D printed self-folding truncated octahedron demonstrating the “transformation over time” when submerging in water.
