Unit 6
Q.1 Write the need for Automation
A1) NEED OR REASONS FOR AUTOMATION
1. To increase labor productivity
2. To reduce labor cost
3. To mitigate the effects of labor shortages
4. To reduce or eliminate routine manual and clerical tasks
5. To improve worker safety
6. To improve product quality
7. To reduce manufacturing lead lime
8. To accomplish. processes that cannot be done manually
9. To avoid the high cast of not automating
Q.2 What are the basic Automation Strategies?
A2)
First strategy in automation is to look for simple solutions and avoid complex solutions. Simple solutions are cost effective, easy for operations, and easy for maintenance.
2. Specialization of operations
Special purpose machine should be developed for performing one operation with maximum possible efficiency.
3. Multiple operations
Multiple operation should be done at one machine or workstation. This reduces the number of machines required.
4. Simultaneous operation
Multiple operations should be carried out simultaneously. This reduces machining time.
5. Integration of Workstations
Many workstations should be integrated into a single integrated mechanism using automated work handling devices. This reduces work handling time.
6. Increased flexibility
A workstation should have flexibility to machine different products. This helps in maximum utilization of machine.
7. Automated material handling and storage systems
Non-production time can be reduced using automated material handling and storage systems.
8. On-line Inspection
In-process correction is achieved due to on-line inspection. This reduces scrap and improves quality of product.
9. On-line monitoring, Process Control and Optimization
On-line monitoring and process control helps in taking the corrective actions in case of deviation.
10. Control of Plant Operations
All the plants are networked using computers so that all the plant can be controlled and monitored at one place.
11. Computer Integrated manufacturing (CIM)
CIM integrates manufacturing operations and manufacturing support systems. CIM is complete integration of factory using computer network.
Q.3 Classify Automation.
A3) Three main classification are:
1. Fixed (hard) automation – involve hardware only
2. Programmable automation – involve software only
3. Flexible (soft) automation – involve hardware and software
“Fixed automation is an automation system in which the sequence of operation is fixed by the layout of production equipment.”
2. Programmable Automation:
“Programmable automation is the automation system in which the production equipments are designed with a capability to change the sequence of operations so as to accommodate the different product configuration.”
3. Flexible (soft) Automation:
“Flexible Automation is an automation system capable of producing products of design variation, continuously with little or no time loss for changeovers of one product to another.”
Q.4 What is FMS? Explain its need and give its application.
A4) FMS may be defined as “a highly automated GT machine cell, consisting of a group of processing workstations (usually CNC machine tools), interconnected by an automated material handling and storage system, and controlled by a distributed computer system.”
FMS employs a fully integrated handling system with automated processing stations.
Need of FMS
Application of FMS
Q.5 Write a note on AGVS
A5)
Types of AGVs
The Guided driverless trains, also known as towing vehicles or automated guided tractors, are most commonly used for transporting large amount of bulky and heavy materials from the ware house to various locations in the manufacturing plant.
2. Guided Pallet Trucks
The guided pallet trucks are designed to lift and transport palletized loads. It is used for picking up or dropping off loads from and on to floor level. Thus, it eliminates the need for fixed load stands.
3. Guided unit load carriers
Guided unit load carriers have a deck that permits unit-load transport operation. They are used in settings with short/medium guide paths, high volume, and need for independent and versatility. They can operate in an environment where there is not much room and movement is restricted.
Application of AGV
Automated Guided Vehicles are used in a variety of areas to support processing and handling throughout a manufacturing facility.
Q.6 Write a note on Group Technology
A6)
Q.7 Explain CIM
A7) CIM is the integration of the total manufacturing enterprise through the use of integrated systems and data communications coupled with new managerial philosophies that improve organizational and personnel efficiency.
The term CIM comprises three words – computer, integrated and manufacturing. CIM is the application of computers in manufacturing in an integrated way. CIM is an attempt to combine computer technologies in order to manage and control the entire business and manufacturing.
CIM is the computerization of design, manufacturing, distribution and financial/business function into one coherent system
There are four Islands of Automation in CIM:
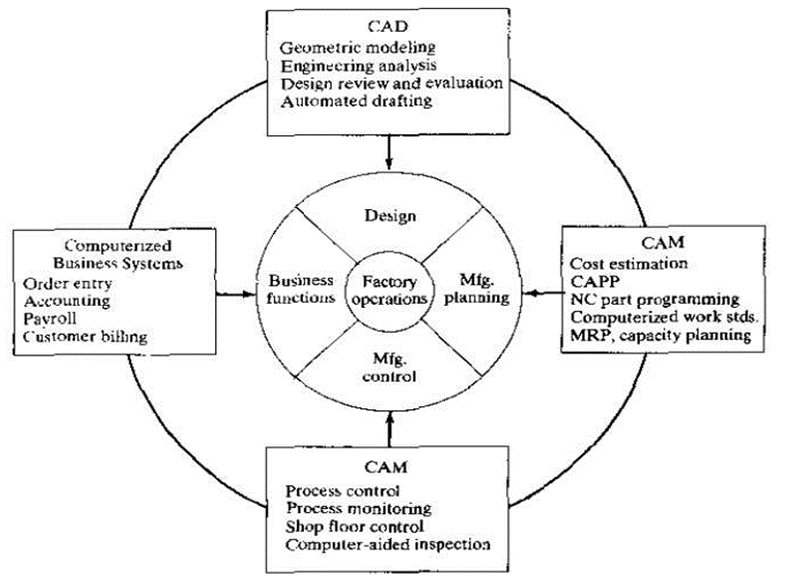
Objectives of CIM:
Q. 8 Define Robot. What are the basic laws of Robotics?
A8) Robot is defined as, “A reprogrammable and multifunction machine designed to move materials, tools or specialized instruments, by programmed movements to carry out a variety of tasks.”
There are three basic laws of robotics as follows:
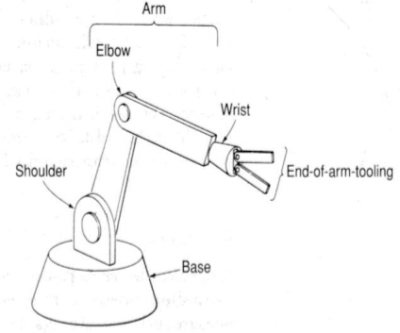
Q.9 Explain Robot Anatomy
A9) Robot anatomy consists of seven components:
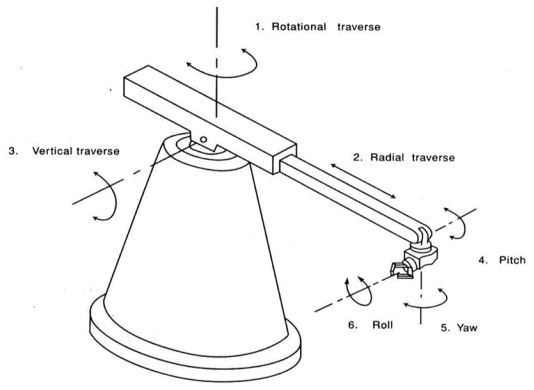
Q.10 Give all the degree of freedom of a robot
A10) A total of six degrees of freedom is needed to locate a robot’s hand at any point in its work space.
The three degrees of freedom located in the arm of a robotic system are:
The three degrees of freedom located in the wrist, which bear the names of aeronautical terms, are