UNIT-6
Mechanism in Automation Systems
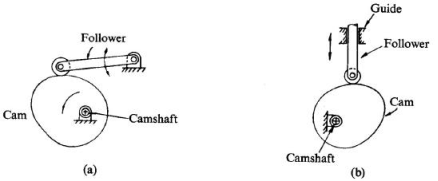
Q1) Define Cam and follower mechanism in brief?
Ans.1) A cam may be a robot want to transmit motion to a lover by direct contact. the driving force is named the cam and also the driven member is named the follower. in an exceedingly cam follower combine, the cam unremarkably rotates whereas the follower might translate or oscillate. a well-known example is that the cam shaft of associate engine, wherever the cams drive the push rods (the followers) to open and shut the valves in synchronization with the feeling of the pistons.
Cams square measure accustomed convert rotation into mutual motion. The motion created are often straightforward and regular or complicated and irregular. because the cam turns, driven by the circular motion, the cam follower traces the surface of the cam transmittal its motion to the desired mechanism. Cam follower style is very important within the approach the profile of the cam is followed. A fine pointed follower can additional accurately trace the define of the cam. This additional correct movement is at the expense of the strength of the cam follower.
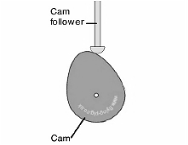
Q2) Classify the cams?
Ans 2) Cams can be classified based on their physical shape.
a) Disk or plate cam: The disk (or plate) cam has associate degree irregular contour to impart a selected motion to the follower. The follower moves in an exceedingly plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the cam shaft and is command in grips with the cam by springs or gravity.

Figure.6.2. Disk or Plate Cam
b) Cylindrical cam: The cylindrical cam contains a groove cut on its cylindrical surface. The roller follows the groove, and therefore the follower moves during a plane parallel to the axis of rotation of the cylinder.
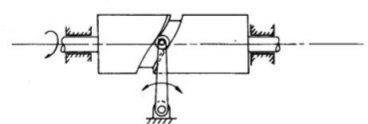
Figure.6.3. Cylindrical Cam
c) Translating cam: The translating cam may be a contoured or grooved plate slippery on a guiding surface(s). The follower could oscillate (Fig.6.4. a) or reciprocate (Fig.6.4. b). The contour or the form of the groove is decided by the desired motion of the follower.
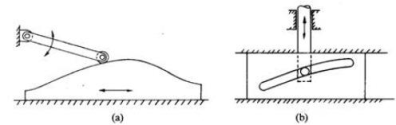
Figure.6.4 Translating Cam
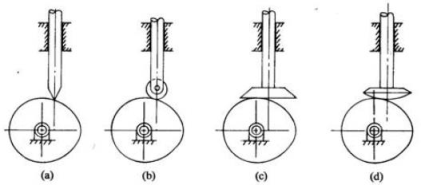
Q.3) Classify the followers?
Ans.3.) Based on surface in contact:
(a)Knife edge follower
(b)Roller follower
(c)Flat faced follower
(d)Spherical follower
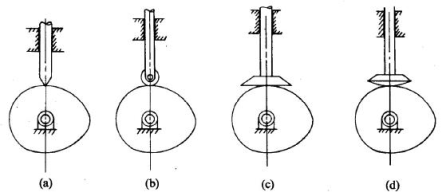
Figure.6.5: Followers
(i) Based on type of motion:
(a) Oscillating follower
(b) Translating follower
Based on line of motion:
(a) Radial follower: The lines of movement of in-line cam followers pass through the centers of the cam shafts.
(b) Off-set follower: For this type, the lines of movement are off set from the centers of the Cam shafts.
Q4) Explain with follower motion with modified velocity?
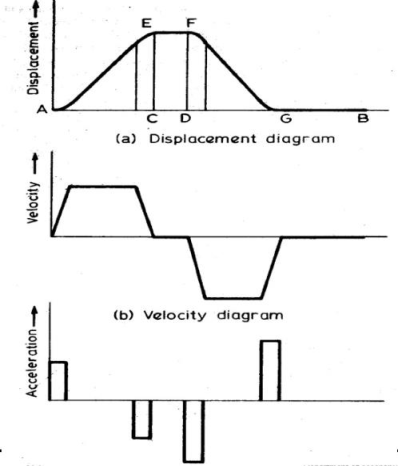
Ans.4.) It is discovered within the displacement diagrams of the follower with a regular rate that the acceleration of the follower becomes infinite at the start and finish of rising and come strokes. so as to forestall this, the displacement diagrams square measure slightly changed. within the changed kind, the speed of the follower changes uniformly throughout the start and finish of every stroke. consequently, the displacement to the follower varies parabolically throughout the periods. With this modification, the acceleration becomes constant throughout the periods, rather than being infinite a sin the uniform rate variety of motion. The displacement, rate and acceleration patterns square measure shown in fig.
Q5) Draw the cam profile for following condition?
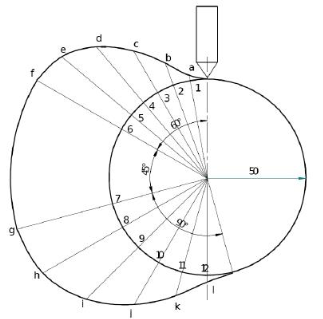
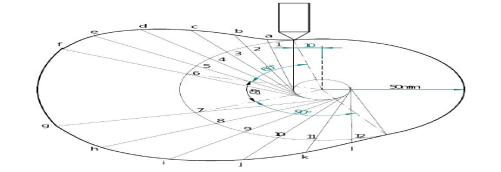
Ans 5) Follower type = Knife edged, in-line; lift = 50mm; base circle radius = 50mm; outstroke with SHM, for 60°cam rotation; dwell for 45°cam rotation; return stroke with SHM, for 90° cam rotation; dwell for the remaining period. (2) Draw the cam profile for the same operating condition with the follower offset by 10mm to the left of cam center.
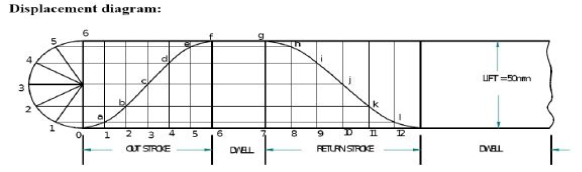
Cam profile:
Cam profile with 10 mm offset:
Q6) Define automation with examples?
Ans.6) In today’s fast-moving, extremely competitive industrial world, a corporation should be versatile, efficient and economical if it desires to survive. within the method and producing industries, this has resulted in nice demand for industrial management systems/ automation so as to contour operations in terms of speed, responsibleness and merchandise output. Automation plays Associate in Nursing progressively vital role within the world economy and in daily expertise.
Automation is that the use of management systems and knowledge technologies to cut back the requirement for human add the assembly of products and services. within the scope of manufacture, automation may be a step on the far side mechanization. Whereas mechanization provided human operators with machinery to help them with the muscular necessities of labour, automation greatly decreases the requirement for human sensory and mental necessities further.
Q7) Define types of automation system with examples?
Ans.7) Automated production systems can be classified into three basic types:
FIXED AUTOMATION
It is a system during which the sequence of process (or assembly) operations is fastened by the instrumentation configuration. The operations within the sequence ar sometimes straightforward. it's the combination and coordination of the many such operations into one piece of apparatus that creates the system advanced. the standard options of fastened automation are:
a. High initial investment for custom–Engineered equipment;
b. High production rates; and
c. comparatively inflexible in accommodating product changes.
The economic justification for fastened automation is found in product with terribly high demand rates and volumes. The high initial price of the instrumentation may be touch a awfully sizable amount of units, therefore creating the cost enticing compared to different strategies of production. samples of fastened automation embody mechanized assembly.
PROGRAMMABLE AUTOMATION
In this, the assembly instrumentality is meant with the potential to vary the sequence of operations to accommodate totally different product configurations. The operation sequence is controlled by a program, that could be a set of directions coded in order that the system will browse and interpret them. New programs are often ready and entered into the instrumentality to supply new merchandise. a number of the options that characterize programmable automation are:
a. High investment in all-purpose equipment;
b. Low production rates relative to mounted automation;
c. Flexibility to handle changes in product configuration; and
d. most fitted for batch production.
Automated production systems that square measure programmable square measure utilized in low and medium volume production. The elements or merchandise square measure usually created in batches. to supply every new batch of a distinct product, the system should be reprogrammed with the set of machine directions that correspond to the new product. The physical setup of the machine should even be modified over: Tools should be loaded; fixtures should be hooked up to the machine table even be modified machine settings should be entered. This transformation procedure takes time. Consequently, the everyday cycle for the given product includes a amount throughout that the setup and reprogramming come about, followed by a amount during which the batch is created. samples of programmed automation embody numerically controlled machine tools and industrial robots.
FLEXIBLE AUTOMATION
It is associate degree extension of programmable automation. a versatile machine-driven system is one that's capable of manufacturing a range of product (or parts) with just about no time lost for changeovers from one product to consecutive. there's no production time lost whereas reprogramming the system and fixing the physical setup (tooling, fixtures, and machine setting). Consequently, the system will turn out varied mixtures and schedules of product rather than requiring that they be created in separate batches. The options of versatile automation may be summarized as follows:
1. High investment for a custom-engineered system.
2. Continuous production of variable mixtures of product.
3. Medium production rates.
4. Flexibility to traumatize product style variations.
The essential options that distinguish versatile automation from programmable automation are:
1. the capability to alter half programs with no lost production time; and
2. the aptitude to conversion the physical setup, once more with no lost production time.
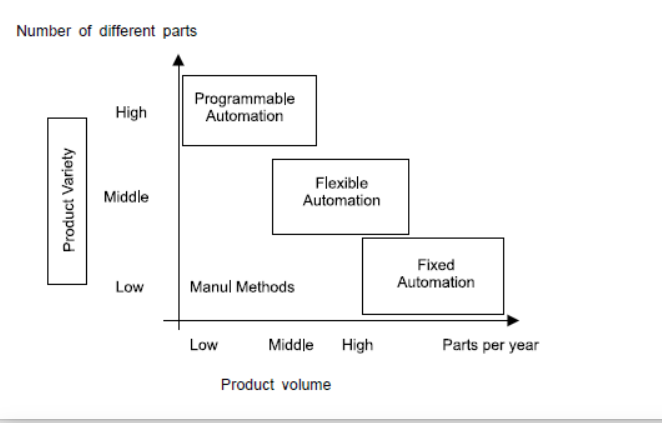
These options permit the machine-driven production system to continue production while not the period of time between batches that's characteristic of programmable automation. dynamic the half programs is usually accomplished by making ready the programs off-line on a system and electronically transmittal the programs to the machine-driven production system. Therefore, the time needed to try to the programming for consecutive job doesn't interrupt production on this job. Advances in laptop systems technology square measure mostly accountable for this programming capability in versatile automation. dynamic the physical setup between components is accomplished by creating the conversion off-line so moving it into place at the same time because the next half comes into position for process. the utilization of pallet fixtures that hold the components and transfer into position at the geographic point is a method of implementing this approach. For these approaches to be successful; the range of components which will be created on a versatile machine-driven production system is sometimes additional restricted than a system controlled by programmable automation. The relative positions of the 3 sorts of automation for various production volumes and merchandise varieties square measure pictured within the following figure.
Q8) What are the methods of work part transport?
Ans.8) The transfer mechanism of the machine-controlled flow line should not solely move the partly completed work components or assemblies between adjacent stations, it should conjointly orient and find the components within the correct position for process at every station. the final strategies of transporting work items on flow lines will be classified into the subsequent 3 categories:
1) Continuous Transfer
2) Intermittent or Synchronous Transfer
3) Asynchronous or power and Free Transfer
These 3 classes square measure distinguished by the sort of motion that's imparted to the work piece by the transfer mechanism. the foremost acceptable variety of transport system for a given application depends on such factors as:
• The kinds of operation to be performed
• The range of stations on the road
• The weight and size of the work components
• Whether manual stations square measure enclosed on the road
• Production rate needs
• Balancing the varied method times on the lines
These transfer systems square measure used for each process and assembly operations. within the case of automatic assembly machines, we have a tendency to square measure bearing on the mechanisms that transport the partly completed assemblies between stations, not the feed mechanisms that gift new parts to the assemblies at a selected station. The devices that feed associate degreed orient the parts square measure usually an integral a part of the digital computer.
Continuous transfer: With the continual methodology of transfer, the work components square measure moved incessantly at constant speed. this needs the work heads to maneuver throughout process so as to take care of continuous registration with the work half. for a few kinds of operations, this movement of the work heads throughout process isn't possible. it might be tough, as an example, to use this sort of system on a machining transfer line owing to inertia issues because of the scale and weight of the work heads. In different cases, continuous transfer would be terribly sensible. samples of its use square measure in drinkable bottling operations, packaging, manual assembly operations wherever the human operator will move with ‘the moving flow line, and comparatively easy automatic assembly tasks.
Intermittent transfer: because the name suggests, during this methodology the workpieces square measure transported with associate degree intermittent or discontinuous motion. The workstations square measure mounted in position and also the components square measure moved between stations then registered at the correct locations for process. All work components square measure transported at identical time and, for this reason, the term “synchronous transfer system” is additionally accustomed describe this methodology of labour half transport. samples of applications of the intermittent transfer of labour components will be found in machining operations, press operating operations or progressive dies.
Asynchronous transfer: this technique of transfer, conjointly cited as a power-and-free system, permits every work half to maneuver to subsequent station once process at the present station has been completed. every half moves severally of different components. Hence, some components square measure being processed on the road at identical time that others square measure being transported between stations. Asynchronous transfer systems supply the chance for larger flexibility than do the opposite 2 systems, and this flexibility will be an excellent advantage in bound circumstances. In-process storage of labor components will be incorporated into the asynchronous systems with relative ease. Power-and-free systems may also make amends for line equalisation issues wherever their square measure important variations in method times between stations.
Q9) What are the types of automated assembly systems?
Ans9) Based on the type of work transfer system that is used in the assembly system:
• Continuous transfer system
• Synchronous transfer system
• Asynchronous transfer system
• Stationary base part system
The first three types involve the same methods of work part transport described in automated flow line. In the stationary base part system, the base part to which the other components are added is placed in a fixed location, where it remains during the assembly work.
Based on physical configuration:
• Dial-type assembly machine
• In-line assembly machine
• Carousel assembly system
• Single-station assembly machine
The dial-type machine, the base part are indexed around a circular table or dial. The workstations are stationary and usually located around the outside periphery of the dial. The parts ride on the rotating table and arc registered or positioned, in turn, at each station a new component is added to base part. This type of equipment is often referred to as an indexing machine or dial index machine and the configuration is shown in Figure 1 and example of six station rotary shown in figure.
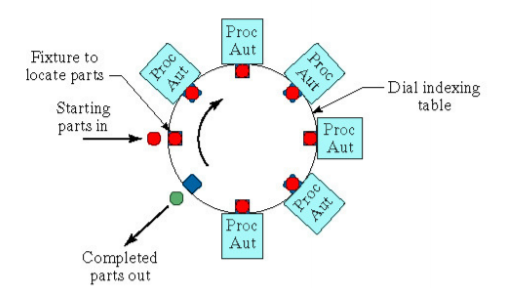
Figure.6.16. Dial Type Machine
In-line type configuration
The in-line configuration assembly system consists of a sequence of workstations in a more-or-less straight-line arrangement as shown in figure. An example of an in-line transfer machine used for metal-cutting operations is illustrated in Figure. The in-line assembly machine consists of a series of automatic workstations located along an in-line transfer system. It is the automated version of the manual assembly line. Continuous, synchronous, or asynchronous transfer systems can be used with the in-line configuration.
Assembly line balancing Buffer Storages
An automated transfer line is consisted of several workstations which are linked together by a material handling system where parts are transferred from one station to the next
Buffer Storage
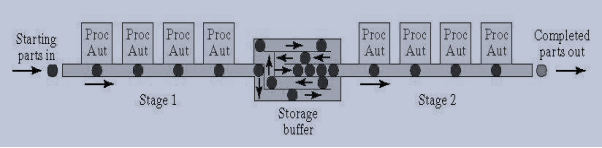
Figure.6.18. Buffer Storage
Q10) Write a short note on Artificial intelligence in automation?
Ans10) AI refers to however pc systems will use vast amounts of knowledge to imitate human intelligence and reasoning, permitting the system to be told, predict and advocate what to try to to next. Associate in Nursing AI capable of understanding selling KPIs will use numerous algorithms that act collectively realize to seek out to search out the signal within the noise of knowledge and find methods to solutions that no human would be capable of. Most AI these days works in Associate in Nursing helpful fashion, providing next best action recommendations to humans UN agency then decide whether or not to trust them or not then manually build changes.
Combining Automation and AI
When robotic method automation is combined with parts of AI like machine learning, the result's called intelligent method automation (IPA). Associate in Nursing IPA tool is powerful as a result of it permits US to reap each the advantages of automation inflated speed, efficiency, time-savings, and skill to scale with the insights, flexibility, and process power of AI. Marketers UN agency use IPA area unit ready to augment their capabilities, whereas off-loading repetitive campaign management tasks to the machine. This will be totally different from pure robotic automation therein the AI can begin, stop, or maybe alter what it's doing supported the atmosphere within which it operates. What’s a lot of, as a result of the most effective AI systems permit marketers to line guardrails, there’s no probability of unforeseen events taking outcomes too so much wide.