UNIT 4
ENERGY SOURCES AND POWER PLANTS
QUESTION BANK
Question
1) why many environmental activists are opposed to nuclear power. In other words, what are the disadvantages?
Answer 1) some of the disadvantages are listed below:
- The nuclear waste produced is dangerous as it is radioactive and needs to be stored for long periods of time as the used fuel remains radioactive for hundreds of years. There are environmental concerns about what is done with the radioactive waste as it damages plant and animal life.
- The nuclear power plants are expensive to build.
- There are many safety concerns about what happens if a plant is not maintained properly and there is a meltdown or a reactor leaks. This is dangerous to the workers and the environment. An accident or any miss happening can have devastating effects for years, decades or even longer.
Question 2) Explain the difference between renewable and non-renewable resources?
Answer 2) The main difference between renewable and non-renewable resources are given below.
Renewable Resources | Non-renewable Resources |
Depletion | |
Renewable resources cannot be depleted over time | Non-renewable resources deplete over time |
Sources | |
Renewable resources include sunlight, water, wind and also geothermal sources such as hot springs and fumaroles | Non-renewable energy includes fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum. |
Environmental Impact | |
Most renewable resources have low carbon emissions and carbon footprint | Non-renewable energy has a comparatively higher carbon footprint and carbon emissions. |
Cost | |
The upfront cost of renewable energy is high, but the “fuel” is free | Non-renewable energy has a comparatively more expensive cost – for implementation as well as for “fuel.” |
Maintenance Cost | |
Very high maintenance cost | Comparatively low maintenance cost |
Area Requirements | |
Requires a large land/ offshore area, especially for wind farms and solar farms | Comparatively lower area requirements |
Question 3Explain photovoltaic effect?
Answer 3)
Photovoltaic Effect
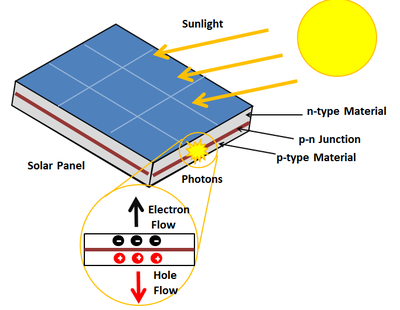
The photovoltaic effect is a process that generates voltage or electric current in a photovoltaic cell when it is exposed to sunlight. These solar cells are composed of two different types of semiconductors—a p-type and an n-type—that are joined together to create a p-n junction. By joining these two types of semiconductors, an electric field is formed in the region of the junction as electrons move to the positive p-side and holes move to the negative n-side. This field causes negatively charged particles to move in one direction and positively charged particles in the other direction.[5] Light is composed of photons, which are simply small bundles of electromagnetic radiation or energy. When light of a suitable wavelength is incident on these cells, energy from the photon is transferred to an electron of the semiconducting material, causing it to jump to a higher energy state known as the conduction band. In their excited state in the conduction band, these electrons are free to move through the material, and it is this motion of the electron that creates an electric current in the cell.
Question 4) What is wind energy?
Answer 4) Wind Energy is the most mature and developed renewable energy. It generates electricity through wind, by using the kinetic energy produced by the effect of air currents. It is a source of clean and renewable energy, which reduces the emission of greenhouse effect gases and preserves the environment.
Question 5) Explain the difference between Windmills and Wind Turbines?
Answer 5) Sometimes people use the terms “windmill” and “wind turbine” interchangeably, but there are important differences. People have been using windmills for centuries to grind grain, pump water, and do other work. Windmills generate mechanical energy, but they do not generate electricity. In contrast, modern wind turbines are highly evolved machines with more than 8,000 parts that harness wind's kinetic energy and convert it into electricity.
Wind power has been used since antiquity to move boats powered by sails or to operate the machinery of mills to move their blades. Since the early twentieth century, it produces energy through wind turbines. The wind drives a propeller and through a mechanical system, it rotates the rotor of a generator that produces electricity.
Wind turbines are often grouped together in wind farms to make better use of energy, reducing environmental impact. The machines have a lifespan of twenty years.
Question 6) what are the challenges of wind power?
Answer 6) Wind power must still compete with conventional generation sources on a cost basis. Even though the cost of wind power has decreased dramatically in the past several decades, wind projects must be able to compete economically with the lowest-cost source of electricity, and some locations may not be windy enough to be cost competitive.
Good land-based wind sites are often located in remote locations, far from cities where the electricity is needed. Transmission lines must be built to bring the electricity from the wind farm to the city. However, building just a few already-proposed transmission lines could significantly reduce the costs of expanding wind energy.
Wind resource development might not be the most profitable use of the land. Land suitable for wind-turbine installation must compete with alternative uses for the land, which might be more highly valued than electricity generation.
Turbines might cause noise and aesthetic pollution. Although wind power plants have relatively little impact on the environment compared to conventional power plants, concern exists over the noise produced by the turbine blades and visual impacts to the landscape.
Wind plants can impact local wildlife. Birds have been killed by flying into spinning turbine blades. Most of these problems have been resolved or greatly reduced through technology development or by properly siting wind plants. Bats have also been killed by turbine blades, and research is ongoing to develop and improve solutions to reduce the impact of wind turbines on these species. Like all energy sources, wind projects can alter the habitat on which they are built, which may alter the suitability of that habitat for certain species.
Question 7) Explain the different sizes of hydroelectric power plants?
Answer 7) Facilities range in size from large power plants that supply many consumers with electricity to small and micro plants that individuals operate for their own energy needs or to sell power to utilities.
1) Large Hydropower: large hydropower as facilities that have a capacity of more than 30 megawatts (MW).
2) Small Hydropower: small hydropower as projects that generate 10 MW or less of power.
3) Micro Hydropower: A micro hydropower plant has a capacity of up to 100 kilowatts. A small or micro-hydroelectric power system can produce enough electricity for a home, farm, ranch, or village.
Question 8) Explain the different type of hydraulic turbines?
Answer 8) There are two main types of hydro turbines: impulse and reaction.
The type of hydropower turbine selected for a project is based on the height of standing water referred to as "head" and the flow, or volume of water, at the site. Other deciding factors include how deep the turbine must be set, efficiency, and cost.
IMPULSE TURBINE
The impulse turbine generally uses the velocity of the water to move the runner and discharges to atmospheric pressure. The water stream hits each bucket on the runner. There is no suction on the down side of the turbine, and the water flows out the bottom of the turbine housing after hitting the runner. An impulse turbine is generally suitable for high head, low flow applications.
Pelton
A pelton wheel has one or more free jets discharging water into an aerated space and impinging on the buckets of a runner. Draft tubes are not required for impulse turbine since the runner must be located above the maximum tail water to permit operation at atmospheric pressure. The water stream is applied on one side, goes across the blades and exits on the other side.
Cross-Flow
A cross-flow turbine is drum-shaped and uses an elongated, rectangular-section nozzle directed against curved vanes on a cylindrically shaped runner. It resembles a "squirrel cage" blower. The cross-flow turbine allows the water to flow through the blades twice. The first pass is when the water flows from the outside of the blades to the inside; the second pass is from the inside back out. A guide vane at the entrance to the turbine directs the flow to a limited portion of the runner. The cross-flow was developed to accommodate larger water flows and lower heads than the Pelton.

REACTION TURBINE
A reaction turbine develops power from the combined action of pressure and moving water. The runner is placed directly in the water stream flowing over the blades rather than striking each individually. Reaction turbines are generally used for sites with lower head and higher flows than compared with the impulse turbines.
Propeller
A propeller turbine generally has a runner with three to six blades in which the water contacts all of the blades constantly. Picture a boat propeller running in a pipe. Through the pipe, the pressure is constant; if it isn't, the runner would be out of balance. The pitch of the blades may be fixed or adjustable. The major components besides the runner are a scroll case, wicket gates, and a draft tube. There are several different types of propeller turbines:

BULB TURBINE
The turbine and generator are a sealed unit placed directly in the water stream.
STRAFLO
The generator is attached directly to the perimeter of the turbine.
TUBE TURBINE
The penstock bends just before or after the runner, allowing a straight line connection to the generator.

KAPLAN
Both the blades and the wicket gates are adjustable, allowing for a wider range of operation.

Francis
A Francis turbine has a runner with fixed buckets (vanes), usually nine or more. Water is introduced just above the runner and all around it and then falls through, causing it to spin. Besides the runner, the other major components are the scroll case, wicket gates, and draft tube.

Kinetic
Kinetic energy turbines, also called free-flow turbines, generate electricity from the kinetic energy present in flowing water rather than the potential energy from the head. The systems may operate in rivers, man-made channels, tidal waters, or ocean currents. Kinetic systems utilize the water stream's natural pathway. They do not require the diversion of water through manmade channels, riverbeds, or pipes, although they might have applications in such conduits. Kinetic systems do not require large civil works; however, they can use existing structures such as bridges, tailraces and channels.
Question 9) Discuss the difference between bio gas and natural gas?
Answer 9) The following are the differences shown below:
S. No. | Bio gas | Natural gas |
1. | It is produced from organic waste such as cow dung, dead plant, agricultural waste. | It is found along with petroleum and come out before crude oil |
2. | It is an excellent fuel for cooking and lighting and also produce huge amount of organic manure. | It is produced under the earth's surface by natural process. |
3. | It is non-exhaustible and of good quality. | It is exhaustible but a good source of energy. |
4. | It is very cheap source of energy. | It is of low cost too. |
Question 10) Discuss advantages and disadvantages of bio fuel?
Answer 10) followings are the some advantages and disadvantages given below:
ADVANTAGES OF BIODIESEL FUEL
Easy to use: No vehicle modification or any fueling equipment needed.
Power, Performance and Economy: Proven power generation, performance and cost efficiency made biodiesel a useful fuel.
Effect on environment: Biodiesel is helping in reducing pollution and improve health by lowering the emission of CO2 which reduces the effect of global warming.
Biodiesel reduces the use of foreign oils.
Biodiesel is safer to handle because it is less toxic and easy to store than petroleum.
Biodiesel helps communities by keeping energy dollars at home.
DISADVANTAGES OF BIODIESEL FUEL
At present, Biodiesel fuel is about one and a half times more expensive than petroleum diesel fuel.
It requires energy to produce biodiesel fuel from soya crops, plus there is the energy of sowing, fertilizing and harvesting.
Another biodiesel fuel disadvantage is that it can harm rubber houses in some engines.
As Biodiesel cleans the dirt from the engine, this dirt can get collected in the fuel filter and clogging occurs. So, filters should be changed regularly.
Biodiesel fuel distribution infrastructure needs improvement, which is another of the biodiesel fuel disadvantages