Unit - 3
Complex Numbers
- Evaluate ( 1 + i )1000.
Solution:
Let z = 1 + i
We have to represent z in the form of r(cos θ + i sin θ).
Here,
Argument = θ = arc(tan (1/1) = arc tan(1) = π/4
Absolute value = r = (1)2+(1)2=2\sqrt{(1)^2 + (1)^2}= \sqrt{2}(1)2+(1)2=2
Applying DeMoivre’s theorem, we get
z1000 = [√2{cos(π/4) + i sin(π/4)}]1000
= 21000 {cos(1000π/4) + i sin(1000π/4)}
= 21000 {1 + i (0)}
= 21000
2. Express five fifth‐roots of (√3 + i) in trigonometric form.
Solution:
We know, z = a + ib = r(cos x + i sin x)
Where r = a2+b2\sqrt{a^2+b^2}a2+b2 and tan x = (b/a)
So,
Here r = 2 and θ = 30 degrees
Therefore, z = 2[cos(300 + 3600 k) + i sin cos(300 + 3600 k)]
Applying nth root theorem:
z1/5 = {2[cos(300 + 3600 k) + i sin cos(300 + 3600 k)]}1/5
= 21/5 [cos((300 + 3600 k)/5) + i sin cos((300 + 3600 k)/5)] …(1)
Where k = 0,1,2,3,4
At k = 0; (1)=> z1 = 21/5 [cos 60 + i sin 60]
At k = 1; (1)=> z1 = 21/5 [cos 780 + i sin 780]
At k = 2; (1)=> z1 = 21/5 [cos 1500 + i sin 1500]
At k = 3; (1)=> z1 = 21/5 [cos 2220 + i sin 2220]
At k = 4; (1)=> z1 = 21/5 [cos 2940 + i sin 2940]
3. Write 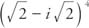 in the form a + bi.
in the form a + bi.
First determine the radius:
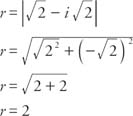
Since cos 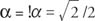 and sin
and sin 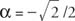 , α must be in the fourth quadrant and α = 315°. Therefore,
, α must be in the fourth quadrant and α = 315°. Therefore,
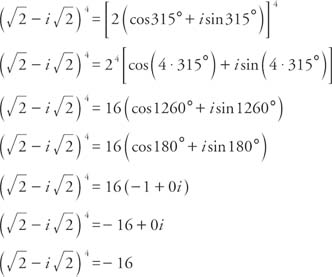
4. Solve cosh2 x – sinh2 x
Solution:
Given: cosh2 x – sinh2 x
We know that
Sinh x = [ex– e-x]/2
Cosh x = [ex + e-x]/2
Cosh2 x – sinh2 x = [ [ex + e-x]/2 ]2 – [ [ex – e-x]/2 ]2
Cosh2 x – sinh2 x = (4ex-x) /4
Cosh2 x – sinh2 x = (4e0) /4
Cosh2 x – sinh2 x = 4(1) /4 = 1
Therefore, cosh2 x – sinh2 x = 1
5. Find the inverse of the function f(x) = ln(x – 2)
Solution:
First, replace f(x) with y
So, y = ln(x – 2)
Replace the equation in exponential way , x – 2 = ey
Now, solving for x,
x = 2 + ey
Now, replace x with y and thus, f-1(x) = y = 2 + ey
6. To solve an equation: f(x) = 2x + 3, at x = 4
Solution:
We have,
f(4) = 2 × 4 + 3
f(4) = 11
Now, let’s apply for reverse on 11.
f-1(11) = (11 – 3) / 2
f-1(11) = 4
Magically we get 4 again.
Therefore, f(f(4)) = f(4)
So, when we apply function f and its reverse f-1 gives the original value back again, i.e, f-1(f(x)) = x.