UNIT 1
Introduction to Civil Engineering And Civil Engineering Materials
Theory Questions and Answers-
Qu 1 -Describe the manufacturing process of Brick ?
Ans- Manufacture of bricks involves preparation of clay, moulding, drying and burning processes.
1. Preparation of clay: It involves unsling, digging, cleaning, weathering, blending and
Tempering; pug mills are used for tempering.
2. Moulding: It may be by hand moulding or by machine moulding.
3. Drying: It may be by natural drying or by artificial drying.
4. Burning: It may be in clamps or in kilns. Intermittent and continuous kilns are used depending
Qu 2- Describe the Fine and Coarse Aggregates
Ans - Sand, gravel, crushed stones which are the products of weathering or crushing of rocks are known as aggregates. Sources of fine aggregates on the basis of which sand is classified are: sea sand, river sand, stream sand, pit sand and manufactured sand.
On the basis of grains size sand is classified as fine sand, coarse sand and gravelly sand. IS code classifies sand as grading zone - 1, Grading zone - 2, Grading zone - 3 and Grading zone - 4 on the basis of percentage of sand passing.
Coarse aggregate gives mass to concrete. For structures like abutment, retaining walls and bed concrete 40 mm down size aggregates are used. For normal R.C.C. Works like flooring roofing and columns 20 mm down size aggregates are preferred. For thin members 12.5 mm sized aggregates are used.
Qu 3- Mention the various characteristics of Good Building Stones?
Ans -Characteristics of Good Building Stones-:
1. It should possess fine grained structure, uniform and pleasing colour. It should be free from soft patches, flaws and cracks.
2. The minimum strength of 3.5 N/mm2
Is required for stone to be used for load bearing walls.
3. It should not absorb more than 5% water.
4. The specific gravity should not be less than 2.5.
5. In attrition test, it should not show wear of more than 2%.
6. Toughness index should be more than 10.
7. It should have good resistance to shocks and it should be durable.
Qu 4- What is the seasoning of Timber?
Ans - Seasoning of timber Seasoning is the process of reducing moisture content in a freshly cut tree to the desired level. Seasoning makes timber more durable and stable. The various methods of seasoning used are:
- Natural seasoning: Air seasoning or water seasoning.
- Artificial seasoning: Boiling, kiln seasoning.
- Chemical seasoning or electrical seasoning.
Qu 5- Classify the brick?
Ans- Brick is obtained by moulding good clay into a block, which is dried and then burnt. This is the oldest building block to replace stone. The size of the bricks are 190mm × 90mm × 90mm.
- First Class Bricks: These bricks are of standard shape and size. They are burnt in kilns.
They fulfill all desirable properties of bricks.
- Second Class Bricks: These bricks are ground moulded and burnt in kilns. The edges may not be sharp and uniform. The surface may be somewhat rough. Such bricks are commonly used for the construction of walls which are going to be plastered.
- Third Class Bricks: These bricks are ground moulded and burnt in clamps. Their edges are somewhat distorted. They produce dull sound when struck together. They are used for temporary and unimportant structures.
- Fourth Class Bricks: These are the over burnt bricks. They are dark in
color. The shape is irregular. They are used as aggregates for
concrete in foundations, floors and roads.
Qu 6- Define the setting time of Cement ?
Ans : Initial setting time and final setting time are the two important physical properties of cement. Initial setting time (30 minutes) is the time taken by the cement from adding of water to the starting of losing its plasticity. Final setting time (10 hrs) is the time lapsed from adding of the water to complete loss of plasticity. Vicat apparatus is used for finding the setting times.
Qu 7- Sketch the cross section of timber and also explain the defects in Timber?
Ans :

Various defects which are likely to occur in timber may be grouped into the following three:
- Due to natural forces
- Due to defective seasoning and conversions.
- Due to attack by fungi and insects.
(i) Defects due to Natural Forces: The following defects are caused by natural forces:
(a) Knots (b) Shakes (c) Wind cracks (d) Upsets
(ii) Defects due to Defective Seasoning and Conversion: If seasoning is not uniform, the
Converted timber may warp and twist in various directions.
(iii) Defects due to Fungi and Insects Attack: Fungi are minute microscopic plant organism. They grow in wood if moisture content is more than 20°C and exposed to air. Due to fungi attack rotting of wood, takes place. Wood becomes weak and stains appear on it.
Qu 8:- Define Road traffic and Intersections ?
Ans - Traffic engineering deals with the measures to be taken for safe, rapid and efficient flow of the traffic. For all this traffic survey should be carried out.
Traffic Survey-This is required to study the type and volume of present traffic and estimate future traffic. It helps in planning expansion or improving the road.
Two types of intersections:
1. Intersection at grades
2. Grade separated intersections
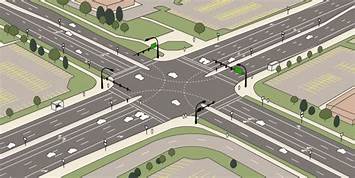
1. Intersections at grades:
• A basic requirement of it is the area of conflict should be small.
• Crossing angles should be preferably at 90° but not less than 60°.
• No blind corners. Any vehicle should safely travel for at least 8 seconds after sighting other
Vehicle.
• Adequate lighting is provided.
• Proper sign, guard rails and traffic islands should be provided.
• Speed should be reduced.
2. Grade separated intersections:
For important roads crossing, flyovers or over crossing may be provided. If major road is above the minor road, it is called over crossing. If minor road is above major road it is called flyover. For entry and exit from major road diamond junction, clover leaf junctions or rotary junctions are provided.
Qu 9:- What are the measures taken in Traffic Control-
Ans:- To regulate traffic the following measures are required:
1. Traffic signs
2. Traffic signals
3. Markings.
1. Traffic Signs-Traffic signs are provided in the form of symbols or inscriptions mounted on fixed or portable supports.
(i) Regulatory signs- These signs are shown on a 600 mm disc installed at a height of 2.8 m above ground level. They may indicate:
• No turn
• No entry
• No parking
• Overtaking prohibited
• Sound horn prohibited, etc.
(ii) Warning signs- These signs are shown on a rectangular board of size 450 × 400 mm mounted at a height of 2.8 m. They may indicate:
• Curve ahead
- Cross road ahead
• Level crossing
• School zones
• U-turns
• Narrow bridge ahead, etc.
(iii) Informatory signs- These are the signs provided to guide drivers to their destination. They may indicate speed limit and name of road also.
2. Traffic signals- These are provided at intersections of roads. They consist of three lights—red to indicate stop, amber to indicate clear and green to indicate ‘go’ signal. In some places the signal indicates how long the red signal will be there. To guide pedestrian, the signals are provided at all
These signal points.
3. Road Markings-Road markings are necessary to guide road users.
Qu 10:- Name the various Tests on Concrete and describe any one?
Ans-The following are some of the important tests conducted on concrete:
1. Slump test.
2. Compaction factor test.
3. Crushing strength test.
1. Slump Test: This test is conducted to determine the workability of concrete. It needs a slump cone for test (Fig. 3.3). Slump cone is a vessel in the shape of a frustum of a cone with diameter at bottom 200 mm and 50 mm at top and 300 mm high. This cone is kept over a impervious platform and
Is filled with concrete in four layers. Each layer is tamped with a 16 mm pointed rod for 25 times. After filling completely the cone is gently pulled up. The decrease in the height of the concrete is called slump. Higher the slump, more workable is the concrete
UNIT 1
Introduction to Civil Engineering And Civil Engineering Materials
Theory Questions and Answers-
Qu 1 -Describe the manufacturing process of Brick ?
Ans- Manufacture of bricks involves preparation of clay, moulding, drying and burning processes.
1. Preparation of clay: It involves unsling, digging, cleaning, weathering, blending and
Tempering; pug mills are used for tempering.
2. Moulding: It may be by hand moulding or by machine moulding.
3. Drying: It may be by natural drying or by artificial drying.
4. Burning: It may be in clamps or in kilns. Intermittent and continuous kilns are used depending
Qu 2- Describe the Fine and Coarse Aggregates
Ans - Sand, gravel, crushed stones which are the products of weathering or crushing of rocks are known as aggregates. Sources of fine aggregates on the basis of which sand is classified are: sea sand, river sand, stream sand, pit sand and manufactured sand.
On the basis of grains size sand is classified as fine sand, coarse sand and gravelly sand. IS code classifies sand as grading zone - 1, Grading zone - 2, Grading zone - 3 and Grading zone - 4 on the basis of percentage of sand passing.
Coarse aggregate gives mass to concrete. For structures like abutment, retaining walls and bed concrete 40 mm down size aggregates are used. For normal R.C.C. Works like flooring roofing and columns 20 mm down size aggregates are preferred. For thin members 12.5 mm sized aggregates are used.
Qu 3- Mention the various characteristics of Good Building Stones?
Ans -Characteristics of Good Building Stones-:
1. It should possess fine grained structure, uniform and pleasing colour. It should be free from soft patches, flaws and cracks.
2. The minimum strength of 3.5 N/mm2
Is required for stone to be used for load bearing walls.
3. It should not absorb more than 5% water.
4. The specific gravity should not be less than 2.5.
5. In attrition test, it should not show wear of more than 2%.
6. Toughness index should be more than 10.
7. It should have good resistance to shocks and it should be durable.
Qu 4- What is the seasoning of Timber?
Ans - Seasoning of timber Seasoning is the process of reducing moisture content in a freshly cut tree to the desired level. Seasoning makes timber more durable and stable. The various methods of seasoning used are:
- Natural seasoning: Air seasoning or water seasoning.
- Artificial seasoning: Boiling, kiln seasoning.
- Chemical seasoning or electrical seasoning.
Qu 5- Classify the brick?
Ans- Brick is obtained by moulding good clay into a block, which is dried and then burnt. This is the oldest building block to replace stone. The size of the bricks are 190mm × 90mm × 90mm.
- First Class Bricks: These bricks are of standard shape and size. They are burnt in kilns.
They fulfill all desirable properties of bricks.
- Second Class Bricks: These bricks are ground moulded and burnt in kilns. The edges may not be sharp and uniform. The surface may be somewhat rough. Such bricks are commonly used for the construction of walls which are going to be plastered.
- Third Class Bricks: These bricks are ground moulded and burnt in clamps. Their edges are somewhat distorted. They produce dull sound when struck together. They are used for temporary and unimportant structures.
- Fourth Class Bricks: These are the over burnt bricks. They are dark in
color. The shape is irregular. They are used as aggregates for
concrete in foundations, floors and roads.
Qu 6- Define the setting time of Cement ?
Ans : Initial setting time and final setting time are the two important physical properties of cement. Initial setting time (30 minutes) is the time taken by the cement from adding of water to the starting of losing its plasticity. Final setting time (10 hrs) is the time lapsed from adding of the water to complete loss of plasticity. Vicat apparatus is used for finding the setting times.
Qu 7- Sketch the cross section of timber and also explain the defects in Timber?
Ans :

Various defects which are likely to occur in timber may be grouped into the following three:
- Due to natural forces
- Due to defective seasoning and conversions.
- Due to attack by fungi and insects.
(i) Defects due to Natural Forces: The following defects are caused by natural forces:
(a) Knots (b) Shakes (c) Wind cracks (d) Upsets
(ii) Defects due to Defective Seasoning and Conversion: If seasoning is not uniform, the
Converted timber may warp and twist in various directions.
(iii) Defects due to Fungi and Insects Attack: Fungi are minute microscopic plant organism. They grow in wood if moisture content is more than 20°C and exposed to air. Due to fungi attack rotting of wood, takes place. Wood becomes weak and stains appear on it.
Qu 8:- Define Road traffic and Intersections ?
Ans - Traffic engineering deals with the measures to be taken for safe, rapid and efficient flow of the traffic. For all this traffic survey should be carried out.
Traffic Survey-This is required to study the type and volume of present traffic and estimate future traffic. It helps in planning expansion or improving the road.
Two types of intersections:
1. Intersection at grades
2. Grade separated intersections
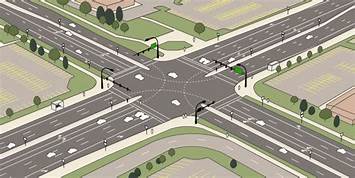
1. Intersections at grades:
• A basic requirement of it is the area of conflict should be small.
• Crossing angles should be preferably at 90° but not less than 60°.
• No blind corners. Any vehicle should safely travel for at least 8 seconds after sighting other
Vehicle.
• Adequate lighting is provided.
• Proper sign, guard rails and traffic islands should be provided.
• Speed should be reduced.
2. Grade separated intersections:
For important roads crossing, flyovers or over crossing may be provided. If major road is above the minor road, it is called over crossing. If minor road is above major road it is called flyover. For entry and exit from major road diamond junction, clover leaf junctions or rotary junctions are provided.
Qu 9:- What are the measures taken in Traffic Control-
Ans:- To regulate traffic the following measures are required:
1. Traffic signs
2. Traffic signals
3. Markings.
1. Traffic Signs-Traffic signs are provided in the form of symbols or inscriptions mounted on fixed or portable supports.
(i) Regulatory signs- These signs are shown on a 600 mm disc installed at a height of 2.8 m above ground level. They may indicate:
• No turn
• No entry
• No parking
• Overtaking prohibited
• Sound horn prohibited, etc.
(ii) Warning signs- These signs are shown on a rectangular board of size 450 × 400 mm mounted at a height of 2.8 m. They may indicate:
• Curve ahead
- Cross road ahead
• Level crossing
• School zones
• U-turns
• Narrow bridge ahead, etc.
(iii) Informatory signs- These are the signs provided to guide drivers to their destination. They may indicate speed limit and name of road also.
2. Traffic signals- These are provided at intersections of roads. They consist of three lights—red to indicate stop, amber to indicate clear and green to indicate ‘go’ signal. In some places the signal indicates how long the red signal will be there. To guide pedestrian, the signals are provided at all
These signal points.
3. Road Markings-Road markings are necessary to guide road users.
Qu 10:- Name the various Tests on Concrete and describe any one?
Ans-The following are some of the important tests conducted on concrete:
1. Slump test.
2. Compaction factor test.
3. Crushing strength test.
1. Slump Test: This test is conducted to determine the workability of concrete. It needs a slump cone for test (Fig. 3.3). Slump cone is a vessel in the shape of a frustum of a cone with diameter at bottom 200 mm and 50 mm at top and 300 mm high. This cone is kept over a impervious platform and
Is filled with concrete in four layers. Each layer is tamped with a 16 mm pointed rod for 25 times. After filling completely the cone is gently pulled up. The decrease in the height of the concrete is called slump. Higher the slump, more workable is the concrete