UNIT 5
ADVANCEMENTS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Qu 1: - Explain various features of Smart City?
Ans: - Some typical features of comprehensive development in Smart Cities are described below:
- Promoting mixed land use in area based developments–planning for ‘unplanned areas’ containing a range of compatible activities and land uses close to one another in order to make land use more efficient. The States will enable some flexibility in land use and building bye-laws to adapt to change;
- Housing and inclusiveness - expand housing opportunities for all;
- Creating walkable localities –reduce congestion, air pollution and resource depletion, Preserving and developing open spaces - parks, playgrounds, and recreational spaces in order to enhance the quality of life of citizens, reduce the urban heat effects in Areas and generally promote eco-balance;
- Promoting a variety of transport options - Transit Oriented Development (TOD),
- Making governance citizen-friendly and cost effective.
- Giving an identity to the city - based on its main economic activity, such as local cuisine, health, education, arts and craft, culture, sports goods, furniture, hosiery, textile, dairy, etc;
- Applying Smart Solutions to infrastructure and services in area
- Making Areas less vulnerable to disasters, using fewer resources, and providing cheaper services.
- The road network is created or refurbished not only for vehicles and public transport, but also for pedestrians and cyclists, and necessary administrative services are offered within walking or cycling distance;
- Public transport and last mile para-transport connectivity;
Q 2:- Draw the hierarchy of solid waste management ?
Ans:-
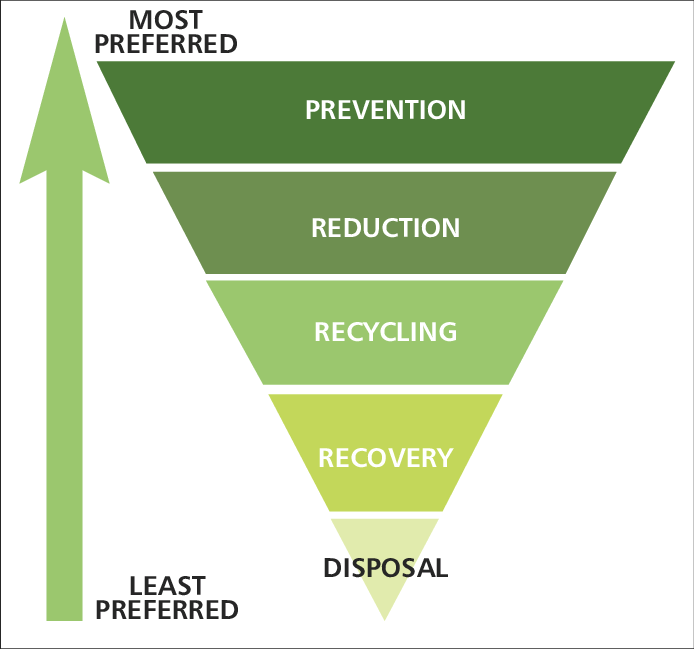
Q 3: -Enlist the various methods of Water Harvesting system in India?
Ans: - Traditional methods of water harvesting:
Paar system: Paar is a common water harvesting practice in the western Rajasthan region.
Talab / Bandhis: Talabs are reservoirs. They may be natural, such as the ponds (pokhariyan) at Tikamgarh in the Bundelkhand region. They can be human-made, such the lakes in Udaipur. A reservoir area of less than five bighas is called a talai; a medium sized lake is called a bandhi or talab; bigger lakes are called sagar or samand. The pokhariyan serve irrigation and drinking purposes. When the water in these reserviors dries up just a few days after the monsoon, the pond beds are cultivated with rice.
Johad: Johads are small earthen check dams that capture and conserve rainwater, improving percolation and groundwater recharge. Starting 1984, the last sixteen years have seen the revival of some 3000 johads spread across more than 650 villages in Alwar district, Rajasthan.
Q 4: - Draw the urban Rain Water Harvesting System?

Q 5: - Explain Waste Management system with schematic diagram?
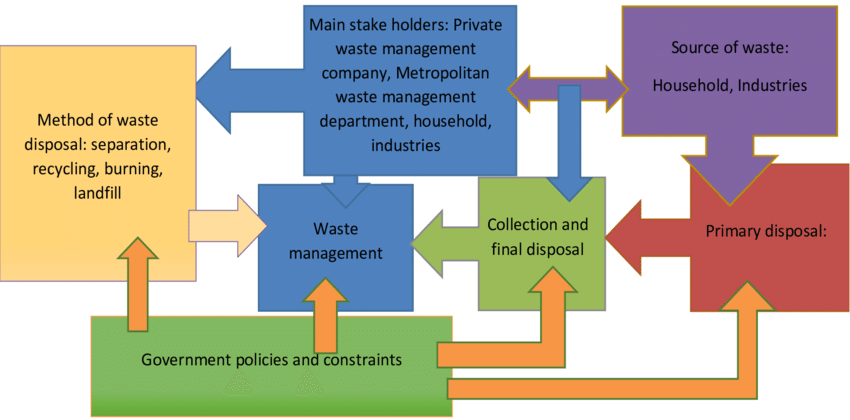
Q 6: - Explain the features of Green Building?
There are a number of features which can make a building ‘green’. These include:
- Efficient use of energy, water and other resources
- Use of renewable energy, such as solar energy
- Pollution and waste reduction measures, and the enabling of re-use and recycling
- Good indoor environmental air quality
- Use of materials that are non-toxic, ethical and sustainable
- Consideration of the environment in design, construction and operation
- Consideration of the quality of life of occupants in design, construction and operation
- A design that enables adaptation to a changing environment
Q 7: - Categorised the watershed management system through diagram?
Ans:-
- Integrated watershed management
- Adaptive watershed management

Q 8: - Define the BRTS in India?
Ans:-
Bus Rapid Transit System (BRTS) is a city-based, high-speed bus transit system in India. In BRTS, the buses travel on dedicated routes.
In India, it has become operational so far in cities like Delhi, Ahmedabad, Jaipur, Indore, Pune, Bhopal Vijayawada and Rajkot, covering a total network of over 120 km. The investment involved till now in the development of BRTS in these cities would come up to more than Rs.13.6 billion. Expansion of the BRTS network in these six cities are either already in progress or are being planned. Moreover, six new BRTS projects are already underway in cities like Kolkata, Hubli-Dharwad, Surat, Visakhapatnam, Naya Raipur and Pimpri-Chinchwad.
Q 9:-What are the main advantages of Gren Building?
Ans: - Advantages of Green Building are:
- Low Maintenance and Operation Cost. Green buildings incorporate unique construction features that ensure efficient use of resources such water and energy. ...
- Energy Efficiency. ...
- Enhances Indoor Environment Quality. ...
- Water Efficiency. ...
- Better Health. ...
- Material Efficiency. ...
- Better Environment. ...
- Reduces Strain on Local Resources.
Q 10:-Give the names of various Mass Transportation System in India ?
Metro : Metro rail is fast becoming the most popular means of mass rapid transit in India with an operational network of over 660 km across 12 cities. But did you know that the first metro in the country started operations all the way back in 1984 in Kolkata. It is also the only metro rail network that is controlled by the Indian Railways; all others are operated by autonomous local authorities.
List of Indian cities that currently have metro connectivity:
- Delhi – Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC)
- Mumbai – Mumbai Metro Rail Corporation Limited (MMRC)
- Bengaluru – Namma Metro
- Hyderabad – Hyderabad Metro Rail
- Chennai – Chennai Metro Rail (CMRL)
- Kochi – Kochi Metro Rail Limited
- Jaipur – Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (JMRC)
- Kolkata – Kolkata Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (KMRC)
- Lucknow – Lucknow Metro Rail Corporation (LMRC)
- Noida – Noida Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (NMRC)
- Gurgaon – Rapid Metro Gurgaon
- Nagpur – Nagpur Metro Rail
UNIT 5
ADVANCEMENTS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Qu 1: - Explain various features of Smart City?
Ans: - Some typical features of comprehensive development in Smart Cities are described below:
- Promoting mixed land use in area based developments–planning for ‘unplanned areas’ containing a range of compatible activities and land uses close to one another in order to make land use more efficient. The States will enable some flexibility in land use and building bye-laws to adapt to change;
- Housing and inclusiveness - expand housing opportunities for all;
- Creating walkable localities –reduce congestion, air pollution and resource depletion, Preserving and developing open spaces - parks, playgrounds, and recreational spaces in order to enhance the quality of life of citizens, reduce the urban heat effects in Areas and generally promote eco-balance;
- Promoting a variety of transport options - Transit Oriented Development (TOD),
- Making governance citizen-friendly and cost effective.
- Giving an identity to the city - based on its main economic activity, such as local cuisine, health, education, arts and craft, culture, sports goods, furniture, hosiery, textile, dairy, etc;
- Applying Smart Solutions to infrastructure and services in area
- Making Areas less vulnerable to disasters, using fewer resources, and providing cheaper services.
- The road network is created or refurbished not only for vehicles and public transport, but also for pedestrians and cyclists, and necessary administrative services are offered within walking or cycling distance;
- Public transport and last mile para-transport connectivity;
Q 2:- Draw the hierarchy of solid waste management ?
Ans:-
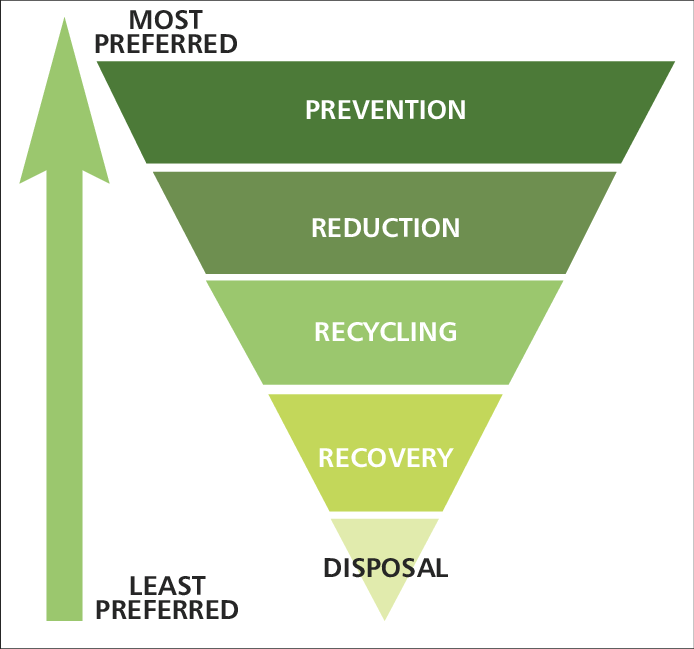
Q 3: -Enlist the various methods of Water Harvesting system in India?
Ans: - Traditional methods of water harvesting:
Paar system: Paar is a common water harvesting practice in the western Rajasthan region.
Talab / Bandhis: Talabs are reservoirs. They may be natural, such as the ponds (pokhariyan) at Tikamgarh in the Bundelkhand region. They can be human-made, such the lakes in Udaipur. A reservoir area of less than five bighas is called a talai; a medium sized lake is called a bandhi or talab; bigger lakes are called sagar or samand. The pokhariyan serve irrigation and drinking purposes. When the water in these reserviors dries up just a few days after the monsoon, the pond beds are cultivated with rice.
Johad: Johads are small earthen check dams that capture and conserve rainwater, improving percolation and groundwater recharge. Starting 1984, the last sixteen years have seen the revival of some 3000 johads spread across more than 650 villages in Alwar district, Rajasthan.
Q 4: - Draw the urban Rain Water Harvesting System?
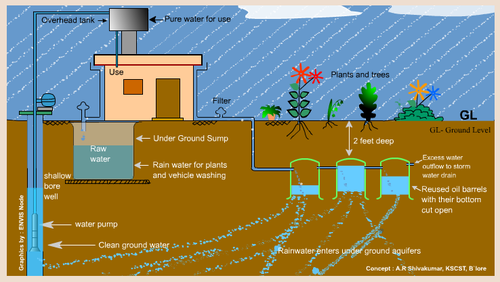
Q 5: - Explain Waste Management system with schematic diagram?
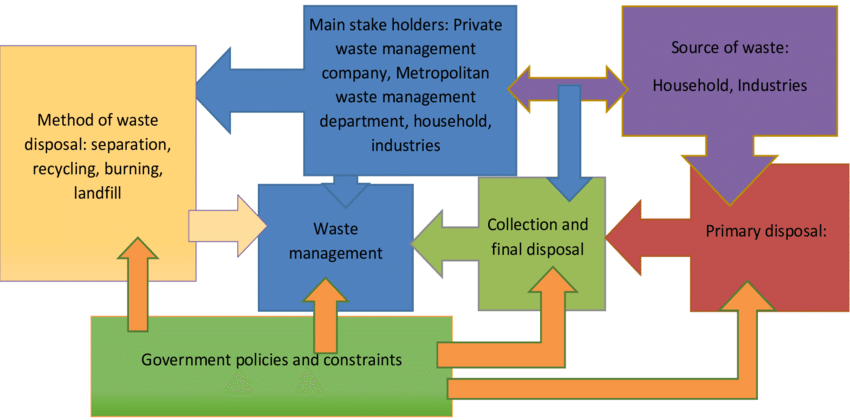
Q 6: - Explain the features of Green Building?
There are a number of features which can make a building ‘green’. These include:
- Efficient use of energy, water and other resources
- Use of renewable energy, such as solar energy
- Pollution and waste reduction measures, and the enabling of re-use and recycling
- Good indoor environmental air quality
- Use of materials that are non-toxic, ethical and sustainable
- Consideration of the environment in design, construction and operation
- Consideration of the quality of life of occupants in design, construction and operation
- A design that enables adaptation to a changing environment
Q 7: - Categorised the watershed management system through diagram?
Ans:-
- Integrated watershed management
- Adaptive watershed management

Q 8: - Define the BRTS in India?
Ans:-
Bus Rapid Transit System (BRTS) is a city-based, high-speed bus transit system in India. In BRTS, the buses travel on dedicated routes.
In India, it has become operational so far in cities like Delhi, Ahmedabad, Jaipur, Indore, Pune, Bhopal Vijayawada and Rajkot, covering a total network of over 120 km. The investment involved till now in the development of BRTS in these cities would come up to more than Rs.13.6 billion. Expansion of the BRTS network in these six cities are either already in progress or are being planned. Moreover, six new BRTS projects are already underway in cities like Kolkata, Hubli-Dharwad, Surat, Visakhapatnam, Naya Raipur and Pimpri-Chinchwad.
Q 9:-What are the main advantages of Gren Building?
Ans: - Advantages of Green Building are:
- Low Maintenance and Operation Cost. Green buildings incorporate unique construction features that ensure efficient use of resources such water and energy. ...
- Energy Efficiency. ...
- Enhances Indoor Environment Quality. ...
- Water Efficiency. ...
- Better Health. ...
- Material Efficiency. ...
- Better Environment. ...
- Reduces Strain on Local Resources.
Q 10:-Give the names of various Mass Transportation System in India ?
Metro : Metro rail is fast becoming the most popular means of mass rapid transit in India with an operational network of over 660 km across 12 cities. But did you know that the first metro in the country started operations all the way back in 1984 in Kolkata. It is also the only metro rail network that is controlled by the Indian Railways; all others are operated by autonomous local authorities.
List of Indian cities that currently have metro connectivity:
- Delhi – Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC)
- Mumbai – Mumbai Metro Rail Corporation Limited (MMRC)
- Bengaluru – Namma Metro
- Hyderabad – Hyderabad Metro Rail
- Chennai – Chennai Metro Rail (CMRL)
- Kochi – Kochi Metro Rail Limited
- Jaipur – Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (JMRC)
- Kolkata – Kolkata Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (KMRC)
- Lucknow – Lucknow Metro Rail Corporation (LMRC)
- Noida – Noida Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (NMRC)
- Gurgaon – Rapid Metro Gurgaon
- Nagpur – Nagpur Metro Rail