SURVEY2
UNIT-3Modern Surveying Equipment’s and Project Surveys Q1) What do you mean by electronic distance measurement(EDM)?A1) EDM is electronic distance measurement survey which is used to find the distance of two point or object. This technique provides precise and faster surveying than the old and conventional instruments that are used earlier. In old and conventional surveying, in linear measurement, chain and tape are used while in angular measurements compass are used, Dumpy level and a levelling staff are used in work of levelling. With this instruments, survey work become tedious Q2) What are the types of EDM instrument used in survey?A2) The following are the instrument which are used in EDM as carrier wave: -Microwave instruments Infrared wave instruments Light wave instruments. Microwave Instruments - other name is tellurometers, microwaves are used in this instrument. Infrared Wave Instruments – it Uses prism reflectors that pick up amplitude modulated infrared waves. Visible Light Wave Instruments – it Uses modulated light waves to find out the specific range. 1. Microwave Instruments:Microwaves are used in this instrument. In 1950 in South Africa by Dr. T.L. Wadley and named later as Tellurometers.. The range of these instruments is up to 100 km. 12 to 24 V batteries are required in this instrument ,That’s why light and portable. This instrument can be used in both day and night time.It consists of two identical units. 1.master unit and 2.remote unit. pressing a button in instrument, master unit can be converted into a remote unit and vice versa. It requires two skilled persons to operate. 2. Infrared Wave Instruments:These instruments is useful for the most of the civil works. In this instrument amplitude modulated infrared waves are used. The range of these instruments is up to 3 km. Prism reflectors is used at the end to find the line to be measured. accuracy up to ± 10 mm is achieved in this instrument. These instrument is economical and can be mounted on theodoliteDISTOMAT DI 1000 and DISTOMAT DI 55 are the name of instrument used as infrared wave instrument.Dustcoat DI 1000: -Distomats are latest in the field of the EDM instruments. These instruments measure distances by using amplitude as it works on the same principle of infrared wave instrument The Distomat is a very small in size and very compact and mainly use in the construction and engineering works. It measures distances up to and smaller than 500 meters by simply pointing the instrument to a reflector.3. Visible Light Wave Instruments:This was first developed in Sweden and was named as Geodimeter. in day its range is up to 3 km and in night its range is up to 2.5 km. Accuracy of these varies from 0.5 mm to 5 mm/km distance in this instrument. These instruments use the propagation of modulated light waves. These instruments are also very useful and popular in civil works Q3) What is total station?A3) A total station is an electronic/optical instrument used in modern surveying and building construction that uses electronic transit theodolite in conjunction with electronic distance meter (EDM).It is also integrated with microprocessor, electronic data collector and storage system.The instrument is used to measure sloping distance of object to the instrument, horizontal angles and vertical angles. This Microprocessor unit enables for computation of data collected to further calculate the horizontal distance, coordinates of a point and reduced level of point.Data collected from total station can be downloaded into computer/laptops for further processing of information.Total stations are mainly used by land surveyors and civil engineers, either to record features as in topographic surveying or to set osut features (such as roads, houses or boundaries). They are also used by archaeologists to record excavations and by police, crime scene investigators, private accident Reconstructionist and insurance companies to take measurements of scenes.Missing line measurement (MLM} Control Survey (Traverse). Archaeologists use total station to record excavations and its details Height measurement (Remove elevation measurement- REM). Resection are easy by total station. Remote Distance Measurement (RDM) General purpose of angle and distance measurement detailed maps Q4) Explain advantages and application of total station? A4) Advantages of Using Total Stations: -Field work is very fast as compared to conventional survey. Calculation is also fast and accurate. Accuracy is very high. Manual errors can be eliminated. Computers can have used for map making and contour and its cross-sections Applications of Total Station: -the following application of total station are as given below: -Detail survey is carried out easily by this technique. Missing Line Measurement (MLM) Plotting of contours Carrying out controlled surveys Used to fix the missing pillars and column. Area calculations Q5) What are error in total station survey?A5) 1 CALIBRATION OF TOTAL STATIONSMaintaining the high level of accuracy offered by modern total stations, there is much more emphasis on monitoring instrumental errors, and some construction sites require all instruments to be checked regularly using procedures outlined in the quality manuals. Some instrumental errors can be eliminated by observing on two faces of the total station and averaging, but because one face measurements are the preferred method on site, it is important to determine the amount of instrumental errors and correct for them.For total stations, instrumental errors are measured and corrected by electronic calibration procedures that are carried out at any time and are applied to the instrument on site. Since calibration parameters can change due to mechanical shock, temperature changes and rough handling of high-precision instrument, an electronic calibration should be carried out on a total station as follows:Before using the instrument for the first time After long storage periods After rough or long transportation After long periods of work Following big changes in temperature Regularly for precision surveys Before every calibration, it is essential to allow the total station enough to reach the ambient temperature.2 HORIZONTAL COLLIMATION (OR LINE OF SIGHT ERROR) This axial error happens when the line of sight is not perpendicular to the tilting axis. It affects all horizontal circle readings and increases parallel to steep sightings, but this is eliminated by observing on two faces. For single face measurements, an on-board calibration function is used to determine c, the deviation between the actual line of sight and a line perpendicular to the tilting axis. A correction will be applied automatically for this to all horizontal circle readings.
3. TILTING AXIS ERROR axial errors occur when the titling axis of the total station is not perpendicular to its vertical axis, this has no effect on sightings taken when the telescope is horizontal, but produces errors into horizontal circle readings when the telescope is tilted, especially for steep sightings. But with horizontal collimation error, this error is erased by two face measurements, or the tilting axis error (a) is measured in a calibration procedure and a correction applied for this to all horizontal circle readings.4 .COMPENSATOR INDEX ERRORErrors that were caused by not levelling a theodolite or total station carefully cannot be eliminated by taking face left and face right readings. If the total station is fitted with a compensator it will measure residual tilts of the instrument and will apply corrections to the horizontal and vertical angles for these.All compensators will have a longitudinal error l and traverse error t known as zero point errors which are averaged using face left and face right readings but for single face readings must be determined by the calibration function of the total station.
A vertical collimation error exists on a total station if the 0o to 180o line in the vertical circle does not coincide with its vertical axis and this zero-point error is present in all vertical circle readings and like the horizontal collimation error, it is eliminated by taking FL and FR readings or by determining i Any difference between the measured horizontal and vertical angles is then identified as an instrumental error and applied to all readings. The total station is thus calibrated and the procedure is the same for all of the error type. Q6) What is wavelength and frequency?A6) The frequency of a wave is the number of times it repeats in one second, and frequency is measured in terms of Hertz (1 Hz = 1 cycle/second). The wavelength is the distance between successive wave peaks. For electromagnetic waves, wavelength is termed in units of nanometers (nm).Q7) What are the parts and accessories of total station?Parts of a Total StationA7) There are mainly four main components which are EDM (Electronic Distance Measurement), electronic theodolite, microprocessor and electronic display Accessories of Total Station Accessories of total station are as follows: -Total Station Battery & Charger, Total Station Prism, Total Station Tripod & Bipod, Total Station Prism Pole and 5.Stand for Total Station Q8) what is the field procedure for total station?A8) Basic Steps involved in Total station surveyingStep-1: Setting up the of the instrument along with the tripodStep-2: Levelling of the instrument approximately with the help of “bull’s eye bubble” and then verifying the levelling electronicallyStep-3: Adjustment of reticle focus and image.Step-4: Recording all the measurementsStep-5: Data ProcessingStep 1: Tripod Setup Tripod legs should be equally spacedTripod head should be approximately levelHead should be directly over survey pointStep 2: Mount Instrument on TripodPlace Instrument on Tripod Secure with centering screw while bracing the instrument with the other hand Insert battery in instrument before levelingStep 3: Focus on Survey PointFocus the optical plummet on the survey pointStep 4: Leveling the InstrumentAdjust the leveling foot screws to center the survey point in the optical plummet reticle Center the bubble in the circular level by adjusting the tripod legsStep 4: Leveling ... Loosen the horizontal clamp and turn instrument until plate level is parallel to 2 of the leveling foot screws Center the bubble using the leveling screws- the bubble moves toward the screw that is turned clockwiseRotate the instrument 90 degrees and level using the 3rd leveling screwStep 4: Leveling ... Observe the survey point in the optical plummet and center the point by loosening the centering screw and sliding the entire instrumentAfter re-tightening the centering screw check to make sure the plate level bubble is level in several directionsStep 5: Turn on the instrument by pressing and holding the “on” button The opening screen will be the “MEAS” screen. Select the Tilt function and then adjust the foot level screws to exactly center the electronic “bubble Q9) What is GPS and its segment?A9) SegmentsGPS is made up of three different components, called as segments:
The three segments of GPS are:Space (Satellites) —satellites circling the Earth, transmitting signals to users on geographical position and time of day. Ground control —Control Segment is made up of Earth-based monitor stations, master control stations and ground antenna. It includes tracking and operating the satellites in space and monitoring transmissions. User equipment — GPS receivers and transmitters including items like watches, smartphones etc. Satellite and receiver clock errors Each GPS Block II and Block IIA satellite contains four atomic clocks, two cesium and two rubidium. The newer generation Block IIR satellites carry rubidium clocks only. One of the on-board clocks, a cesium for Block II and IIA, is selected to provide the frequency and the timing requirements for generating the GPS signals. OCS OperationsThe MCS is the center of the control segment operations and is found at Falcon Air Force Base, Colorado Springs, CO. The monitor stations inactively track the GPS satellites as they pass overhead by making pseudorange and delta range measurements. These measurements are made using both the L1 and L2 GPS satellite downlink frequencies. This raw data and the received navigation message with local weather is transmitted to the MCS through the Defense Satellite Communications System and other ground communications systems. Q10)What are the data of GIS?A10)Spatial data
iv.
Polygon data can be “multipart” like the islands of the state of Hawaii.B. raster or grid data (matrices of numbers describing e.g., elevation, population, herbicide use, etc.C. images or pictures such as remote sensing data or scans of maps or other photos. This is special “grid” where the number in each cell describes what color to paint or the spectral character of the image in that cell. (to be used, the “picture” must be placed on a coordinate system, or “rectified” or “georeferenced”)D. TINs – Triangular Irregular Networks – used to discretize continuous dataE. Terrain datasets built from lidar and other point clouds.Demo in ArcGIS2. Attribute data are non-spatial characteristics that are connected by tables to points, lines, “events” on lines, and polygons (and in some cases GRID cells)A point, vector or raster geologic map might describe a “rock unit” on a map with a single number, letter or name, but the associated attribute table might have most GIS programs can either plot the polygon by the identifier or by one of the attributes 3. Metadata metadata are the most forgotten data type absolutely necessary if you’re going to use data, or if someone is going to use your data later (or your derivative information) contains information about More specifically, GIS is used through:Environmental Geography – to analyse the impact people have on the environment. Physical Geography – to study the elements of atmosphere, biosphere and geosphere. Emergency Management Information System – to give real time data to emergency responders about the geographical layout. Health Geography – to use geographical information to study health related issues such as disease and illness. Economic Geography – to study economic activities across the earth. Transportation Geography – to investigate the spatial interactions of people or things.
|
|
The three segments of GPS are:
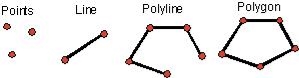
- vector data
- Point Data — layers containing by points (or “events”) described by x,y (lat,long; easting, northing)
- Line/Polyline Data — layers that are described by x,y points (nodes, events) and lines (arcs) between points (line segments and polylines)
- Polygon Data — layers of closed line segments enclosing areas that are described by attributes
|
Polygon data can be “multipart” like the islands of the state of Hawaii.B. raster or grid data (matrices of numbers describing e.g., elevation, population, herbicide use, etc.C. images or pictures such as remote sensing data or scans of maps or other photos. This is special “grid” where the number in each cell describes what color to paint or the spectral character of the image in that cell. (to be used, the “picture” must be placed on a coordinate system, or “rectified” or “georeferenced”)D. TINs – Triangular Irregular Networks – used to discretize continuous dataE. Terrain datasets built from lidar and other point clouds.Demo in ArcGIS2. Attribute data are non-spatial characteristics that are connected by tables to points, lines, “events” on lines, and polygons (and in some cases GRID cells)
- age
- lithology
- percent quartz
- etc, for each rock type on the map.
- scale
- accuracy
- projection/datum
- data source
- manipulations
- how to acquire data
0 matching results found