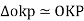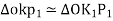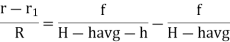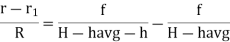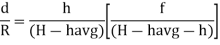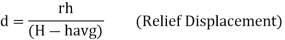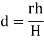SURVEY2
Unit-5Photogrammetry Q1) What do you mean by photogrammetry survey?A1) Photogrammetric is a mapping and surveying procedure or technique which has many applications in Transportation Department Q2) What is relief and tilt displacement in aerial photography?A2)
Tilted aerial photographf -focal lengthn -nadir points –swingp -principal pointt -angle of tilti –isocentertan (t/2) = (pi)/f ; (pi) = f tan (t/2)tan (t) = (pn)/f ; (pn) = f tan (t) Q3) Explain stereoscopy?A3)A combination of stereoscopic photographs or images can be viewed stereoscopically by viewing at the left image with the left eye and the right image with the right eye. It is known stereoscopy. Stereoscopy is based on Porro-Koppe's Principle that the same light path will be generated through an optical system if a light source is gauge onto the image taken by an optical system. The principle will be realized in a stereo model if a combination of stereoscopic images is reconstructed using the relative location or tilt at the time the photography was taken. Such an adjustment is known relative orientation in photogrammetric terms. Q4)Explain scale?A4) The scale of an aerial photograph is the ratio of the distance on the photo to the corresponding distance on the ground, i.e. 1 unit on the photo equals "x" units on the ground. Aerial photograph scale is usually expressed one of two ways:
Unit Equivalent - For example 1cm= 1km Representative Fraction- Expressed as a unit-less ratio, 1: 25,000 or 1/25,000. This is the most common way scale is expressed in aerial photographs. Q5) What is terrestrial photography?A5)Photographs are taken from a stable, usually known as, position on or near the ground and with the camera axis horizontal or nearly so. The position and orientation of the camera are frequently measured directly at the time of exposure. Instrument used for exposing such photograph is known photo theodolite. Q6) What do you mean by flight planning?A6) Confirm project outline conforms to customer’s project requirements. Confirm project specifications or requirements for the flight plan. (scale, GSD, camera or sensor type) based on customer dialog or scope of work) Make the flight plan in accordance with client provided specifications. QC flight plan to confirms the plan adheres to project specifications/requirements. Export flight plan in the required format, and send to the customer for review and approval (kml, shape file) After final customer approval, forward the flight plan to Flight Operations for project setup. Flight Ops will make a sensor specific flight plan, disseminate to the crews. Q7) Write short note on ground controls extension for photography mapping?A7) Ground control can be categorized as targeted and photo-identifiable (picked) control points, and can also be known as horizontal control, vertical only control, or as 3-D control. Horizontal and vertical controls need different configurations to make them serve their intended purposes. The use of only ground control is now restricted to small projects, such as bridge sites, borrow areas and where only one or two models are needed. Photo identifiable control points are needed. The surveyor must know what type of control is known for when he or she attempts to pick or photo-identify the point. Accessibility for surveying should also be considered while selecting the position for control points.Ground Control Research project region for existing control. Existing control that can be choose to save time and money by avoiding unnecessary field surveys. it is more cost efficient to expand the aerial photography slightly beyond the project area to include existing control than to make a new control. Selecting operations is an essential part of photogrammetric mapping to be considered prior to establishing a control survey. Pre-flight targeting is done to make ground locations of control points to clear on the photographs. Easy identification and clear image of the control points on the photograph increases the accuracy and efficiency of the photogrammetric procedure Highway design mapping usually requires careful pre-flight planning for optimal target placement. To reduce the possibility of pre-marked points being moved or lost prior to the aerial mission, it is important to either paint them on a hard surface or schedule the field panelling operation as near as possible to the anticipated flight. Targets should be located where shadows will not affect the visibility of the panel. Field surveys for photogrammetric control should be seen as ordinary surveys. The procedures that are described in the manual should be applied to photogrammetric control field work. The issue here is to choose suitable survey procedures that address the project requirements. Photogrammetric control points are spaced widely around the project area. For large projects, distancing could be extensive enough to require a significant surveying effort. Therefore, GPS is the better suited surveying method for largest photogrammetric projects. Ground control that is used in successive photogrammetric projects or field surveys should be monumental. Compute, adjust the field data and make a coordinate values for the control points. Make a report on the surveys and on the results. An accuracy analysis of the results should be included in the report. The analysis must indicate the methodology used to find that the results are in agreement with the project statement. Q8) Explain aerial triangulation?A8) The term applied to the process of finding out x, y, and z ground coordinate of each separate points by measuring from the photograph.The principle behind this application is extending ground control through strip for use in subsequent photogrammetric operation. Method of Aerial triangulation: - Analogue Aerial triangulation Semi Analytical Aerial triangulation Analytical Aerial triangulation Procedure of Aerial triangulation: -
Benefits of aerial triangulation: - It minimize delays and hardships due to worst weather condition Field surveying in difficult area, such as Marshes, slope, hazardous rock formation, etc; from aerial triangulation it can be minimized. Q9) What is application of aerial photography?A9) Application of aerial photography:
Mapping: Itis a valuable tool for soil mapping. It is found to fast, precise, indispensable in inaccessible areas and it is cost effective in the long run.
Interpretation: Photointerpretation has revolutionised the method of data collection in many disciplines. It decreases the field work and thereby the cost. The information is reliable and acceptance for most studies for example as in the fields of geology, water resources, geomorphology, hydrogeology, forestry and ecology, and urban and regional planning Q10) Explain types of photogrammetry?A10) Types of photogrammetryAerial Photogrammetry The camera is mounted in an aircraft, usually pointed perpendicular towards the ground with the camera axis vertical or nearly so. Many photographs are taken with the clincher – built concept. Later the processing of these photographs done using stereo-plotter. Photos are also being used in for Digital Elevation Model (DEM) creation. Terrestrial Photogrammetry Photographs are taken from a stable, usually known as, position on or near the ground and with the camera axis horizontal or nearly so. The position and orientation of the camera are frequently measured directly at the time of exposure. Instrument used for exposing such photograph is known photo theodolite. Space Photogrammetry In this type of photogrammetry, satellites are used. Global coverage of satellite image is taken in lesser time with a high-resolution data. Interpretative Photogrammetry Images are studied and identification is done for judging their significance with standard and careful analysis.
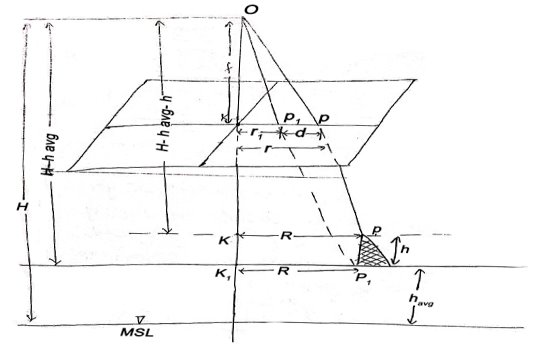
From (1) and (2)
If the point is taken to datum, (havg – 0)
Shift of Image of a point on photograph, if the point is taken to detum is called relief displacement. |
|
|
Mapping: Itis a valuable tool for soil mapping. It is found to fast, precise, indispensable in inaccessible areas and it is cost effective in the long run.
Interpretation: Photointerpretation has revolutionised the method of data collection in many disciplines. It decreases the field work and thereby the cost. The information is reliable and acceptance for most studies for example as in the fields of geology, water resources, geomorphology, hydrogeology, forestry and ecology, and urban and regional planning Q10) Explain types of photogrammetry?A10) Types of photogrammetry
0 matching results found