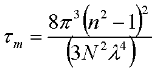SURVEY2
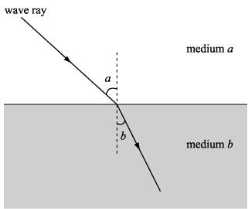
Unit-6Modern methods of surveying Q1) What is remote sensing?A1) Remote Sensing is defined as the collecting information of an object without making physical contact with object specially in the earth. It works on the principle of radiation when waves i.e. electromagnetic radiation from sun after meeting or interaction with atmosphere and surface of earth is detected by sensor and it makes or stored as image data. Q2) Explain electromagnetic spectrum?A2) The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of following waves such asradio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet light, and even X-rays and gamma rays all electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space. Unlike sound waves or water waves, EM waves do not require medium to travel through them. This is important, because EM waves could not travel through empty space, then the light and heat from the Sun would not be able to reach in ground surface.Q3) Explain element of visual interpretation?A3) Element of Remote sensing for visual interpretation and GISThe various visual elements are as follows:1) Tone2) Shape3) Size4) Pattern5) Texture6) Shadow7) Association 1) Tone- Tone is the brightness or colour of object in an image. It is the fundamental element to find out different target. Human eye can differentiate 20 to 30 shades of Grey tones and more than million colours.Tone can easily distinguishable variation from white to black. Images from satellite are transmitted in digital form to station and each image pixel is expressed in 256 grey-level 2) Texture-It represents arrangement of and frequency of total variation in a certain area of image.Coarse texture abrupt tonal variation. Smooth texture very little tonal variation. It is also important for distinguishing features in radar imagery. Smooth texture example such as fields, grassland. Rough surface example such as forest. 3) Shapes-It represent outline of an object.Many components in image or environment can be identified with their shape or forms. Shape is the very distinctive clue for interpretation. Example- a) Forest edges- irregular shape b) Straight edges- agricultural field.c) Circular shape- rotating sprinkles in land.4) Size-It is the function of scale.Example- a) small building represent residential use. b) last building represents warehouse and factory.It is an important element to detect the size of target relative to other object in image and also for interpretation of image of target. 5) Shadow - Shadow element helps in or give an idea of relative height of target.To distinguish show and cloud unfortunately deep shadow observe significant features. Shadow also help in identifying topography and landforms. 6)Pattern-It represents spatial arrangement of visibly discernible objects.A repetition of similar tones and texture will produce a distinctive and recognisable pattern. Urban Street with regular spaced house is an example of pattern. 7)Association / site-It is the feature in proximity to the target of interest. It takes into account the relationship between recognisable objects Examples such as residential areas would be associated with school, playground, etc. Similarly, lake is associated with boats, Marina etc. Q4) Difference between platforms and sensor?A4) Remote sensing platforms can be defined as the structures on which remote sensing instruments that is sensor are placedRemote sensing systems which measure energy that is naturally available are called passive sensors. Passive sensors are only used to find energy when the naturally occurring energy is presentl over there.Active sensors rely on their own sources of radiation for illuminating objects. The sensor emits radiation towards the target to be investigated. Then the reflected energy from that target is find out and measured by sensor. Q5) What are the types of platforms?A5) Types of platforms: - 1.Ground-borneplatforms: It is used to record detailed information about the ground surface which is compared with information collected from aircraft or satellite sensors. Ground observation includes both the laboratory and field study, used for both in designing sensors and identification and types of land features.Ground observation platforms include –handheld platform, cherry picker, towers, portable masts and vehicles etc. spectroradiometers and Portable handheld photographic cameras are largely used in laboratory 2.Air-borne platforms: Is is used to collect detailed images and to facilitate the collection of data over virtually any portion of the ground surface at any time. Airborne platforms was the main non-ground-based platforms for early remote sensing work application. Balloon: - Balloons are used for remote sensing observation generally for the aerial photography and. The first aerial images captured aloft by a balloon in 1859. Balloon floats at a constant height of about 30 km. The balloon is control by the wind at the floating height. This technique is rarely used today because they are not very stable Drone: - Drone is a miniature remotely piloted aircraft. It is designed for a low cost vehicles or platform.Drone includes equipment of photography, infrared findion, radar observation and TV surveillance. Drone uses satellite communication link. An onboard computer controls the payload and stores data from different sensors and instruments. it was developed in Britain during World War-II, now it plays important role in remote sensing. The different advantage is that it could be easily located above the area and it is capable to provide both night and day data. Aircraft aircraft with cameras and sensors used to capture the aerial photographs and images of ground surface features. While low altitude aerial photography results in large scale images providing detailed information on the terrain, the high altitude smaller scale images offer advantage to cover a larger area with low spatial resolution.Multi spectral, hyperspectral and microwave imaging is also done by aircraft.Aircraft platforms offer an economical method of remote sensing data collection for small to large areas with different tools such as cameras, electronic imagers, across-track and along-track scanners, and scanners. The AVIRIS hyperspectral imaging is famous and widely used aircraft aerial photographic operation. High Altitude Sounding Rockets Balloons have a maximum altitude of approx 37 km, while satellites cannot orbit below 120 km. High altitude sounding rockets is used to moderate altitude above terrain. Imageries with moderate synoptic view can be obtained from such rockets for areas of some 500,000 square kilometers per frame.high altitude sounding rocket is controlled from a mobile launcher. During the flight its scanning work is done from a stable altitude. 3.Space-borne platforms: In this platforms, sensors are placed on-board a spacecraft orbiting the earth. Space-borne which is also called as satellite platform are onetime cost investment but relatively lower cost per unit area of coverage, can cover imager of entire earth. the imaging ranges for space borne platforms are from altitude 250 km to 36000 km. Spaceborne remote sensing provides the following advantages: it coverage Large area;Frequent and repetitive coverage of an area processing and analysis is done by Semi-automated computerizedcost is low for unit area of coverage. There are two types of well recognized satellite platforms-manned satellite platform and unmanned satellite platform. Q6) Explain the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with the atmosphere and earth surface?A6) All wave used for remote sensing passes through the atmosphere before and after it has interacted with the Earth's surface. atmosphere changes the wave or radiation's frequency, intensity, and direction. Radiance measured by an air- or space-borne sensor is affected by various factors, not solely diffuse sky irradiance between the sensor and the target on the ground surface. The atmosphere generally affects the visible and infra-red wavelengths and has more minor effects on microwave wavelength. There are three physical processes involved: scattering, - it changes the direction and intensity of wave absorption, - in which incident wave is retained by constituent parts of the atmosphere, reducing its intensity. refraction, - it changes the direction of wave as it passes through the atmosphere
Atmospheric Refraction.
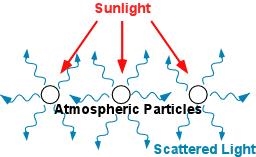
Scattering Scattering is the changing or redirection of EM radiation by particles present in the atmosphere. The amount of scattering depends upon the size of the particles present over the atmosphere.the abundance of particles, the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation, and the depth of the atmosphere all are the factor which governs the scattering.There are four main types of scattering: -Rayleigh scattering (Rayleigh scattering was discovered by Lord Rayleigh in 1890s, for which he gets the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1904.) This type of scattering is caused by gases in the upper atmosphere, or by particles that are smaller than the wavelength of the wave. As shown by the equation below, the degree of scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of wavelength (λ )
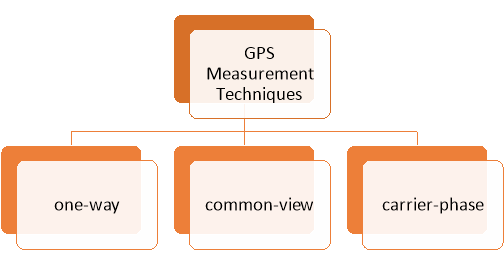
Mie Scattering Non-selective scattering Raman scattering Q7) Explain surveying with GPS in modern system?A7)Now a days GPS is part of everyday life. The following things were the GPS is used are as follows mobile phones, navigation in car rescue and search equipment. GPS was rapidly using for surveying, as it can give direct position of Latitude, Longitude and Height, without measureing angles and distances between 2 points or intermediate points. clear view of the sky is required so the signal from the GPS satellites could received clearly. Trilateration and EDM are similar as of GPS except that the known positions are now the GPS satellites. equipment and calculations are extremely difficult and complex, but for the user it is very simple. GPS receiver almost instantly works out its position with refrence of Latitude, Longitude and Height, from the data broadcast by the satellites which are is space. These data include a description of the satellites changing position or its orbit and the time at which data was transmitted. Q8) Explain GPS measurement?A8) there are many different types of GPS measurements used in time and frequency metrology. These measurements can be divided into three generalcategories: one-way, common-view, and carrier-phase. normally GPS measurements made in calibration and testing laboratories are one-way measurements.
In GPS measurement techniques -One-way measurements are easy to make and their uncertainties are small enough to meet the requirements calibration and testing laboratory. Common-view and carrier-phase measurements require more effort in processing of the measurement data. For this reason, they are usually used for small as possible. 1-Way GPS Measurements: -one-way GPS technique measurement use the signals obtained from receiver of GPS as the reference for calibration. GPS signals are used in real time, and no post processing of the measurement results is required. The purpose of the measurement is usually either to synchronize a non-time pulse, or to calibrate frequency source. Before receiver is used for measurements, it must complete its signal process. Part of the acquisition process involves surveying the antenna position. time and frequency receivers generally collect single position fix, and use that same position. Many receivers automatically start survey when they are turned on. When the process is completed, a front panel indicator shows the operator that the receiver is ready for use. Once the signal acquisition is completed, an output signal from the receiver is connected to measurement system. For time synchronization measurements, 1 pps signal from the receiver is used as input to time interval counter. For frequency measurements, frequency output from GPSDO is used as input to a phase comparator, or used as the external time base for counting of freqQ9) Explain the GPS segment or its part?A9)GPS is made up of three different components, called as segments:
The three segments of GPS are:Space (Satellites) —satellites circling the Earth, transmitting signals to users on geographical position and time of day. Ground control —Control Segment is made up of Earth-based monitor stations, master control stations and ground antenna.It include tracking and operating the satellites in space and monitoring transmissions. User equipment — GPS receivers and transmitters including items like watches, smartphones etc Q10) What is GPS?A10) GPS is a navigation system using satellites, a receiver and algorithms to synchronize location, velocity and time data for air, sea and land travel.
|
|
|
|
The three segments of GPS are:
0 matching results found