TID | ITEAMs |
1 | Bread, Milk |
2 | Bread, Diaper, Beer, Eggs |
3 | Milk, Diaper, Beer, Coke |
4 | Bread, Milk, Diaper, Beer |
5 | Bread, Milk, Diaper, Coke |
Alpha | beta | gamma |
Alpha | beta | theta |
Alpha | beta | epsilon |
Alpha | beta | theta |
2. Association rules are usually required to satisfy a user-specified minimum support and a user-specified minimum confidence at the same time. Association rule generation is usually split up into two separate steps
3. A minimum support threshold is applied to find all frequent itemsets in a database.
4. A minimum confidence constraint is applied to these frequent itemsets in order to form rules.
5. While the second step is straightforward, the first step needs more attention.
6. Finding all frequent itemsets in a database is difficult since it involves searching all possible itemsets (item combinations).
7. The set of possible itemsets is the powerset over and has size (excluding the empty set which is not a valid itemset).
8. Although the size of the power-set grows exponentially in the number of items in , efficient search is possible using the downward-closure property of support (also called anti-monotonicity) which guarantees that for a frequent itemset, all its subsets are also frequent and thus no infrequent itemset can be a subset of a frequent itemset.
9. Exploiting this property, efficient algorithms (e.g., Apriori\and Eclat) can find all frequent itemsets.
Q.4.What is Clustering?Answer: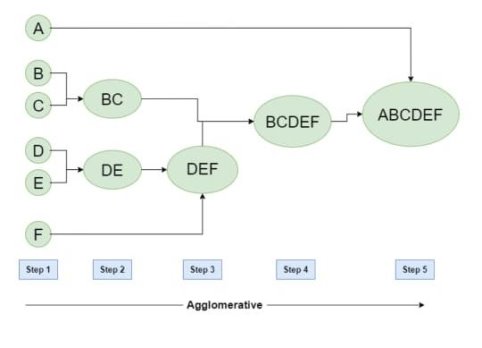 Fig 1: Example of Agglomerative • Step-1: -Consider each alphabet as a single cluster and calculate the distance of one cluster from all the other clusters. • Step-2: -In the second step comparable clusters are merged together to form a single cluster. Let’s say cluster (B) and cluster (C) are very similar to each other therefore we merge them in the second step similarly with cluster (D) and (E) and at last, we get the clusters[(A), (BC), (DE), (F)] • Step-3: -We recalculate the proximity according to the algorithm and merge the two nearest clusters ([(DE), (F)]) together to form new clusters as [(A), (BC), (DEF)] • Step-4: -Repeating the same process; the clusters DEF and BC are comparable and merged together to form a new cluster. We’re now left with clusters [(A), (BCDEF)]. • Step-5: -At last, the two remaining clusters are merged together to form a single cluster [(ABCDEF)]. Q.10. Explain Rule Evaluation Metrics and its Example.Answer:
Fig 1: Example of Agglomerative • Step-1: -Consider each alphabet as a single cluster and calculate the distance of one cluster from all the other clusters. • Step-2: -In the second step comparable clusters are merged together to form a single cluster. Let’s say cluster (B) and cluster (C) are very similar to each other therefore we merge them in the second step similarly with cluster (D) and (E) and at last, we get the clusters[(A), (BC), (DE), (F)] • Step-3: -We recalculate the proximity according to the algorithm and merge the two nearest clusters ([(DE), (F)]) together to form new clusters as [(A), (BC), (DEF)] • Step-4: -Repeating the same process; the clusters DEF and BC are comparable and merged together to form a new cluster. We’re now left with clusters [(A), (BCDEF)]. • Step-5: -At last, the two remaining clusters are merged together to form a single cluster [(ABCDEF)]. Q.10. Explain Rule Evaluation Metrics and its Example.Answer: