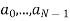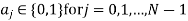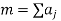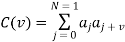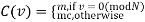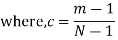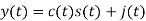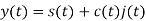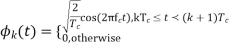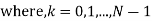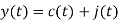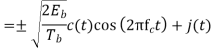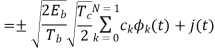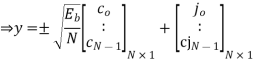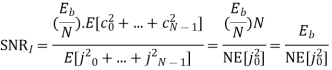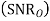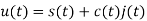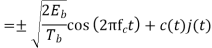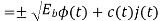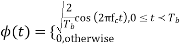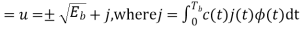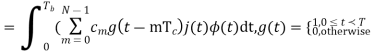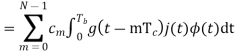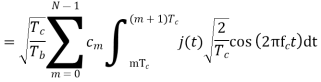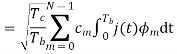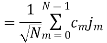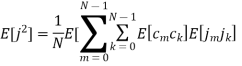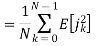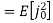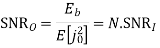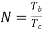A binary sequence (BS) is a sequence
ABS consist of ABS is a pseudorandom binary sequence (PRBS) if its autocorrelation given by
Has only two values
|
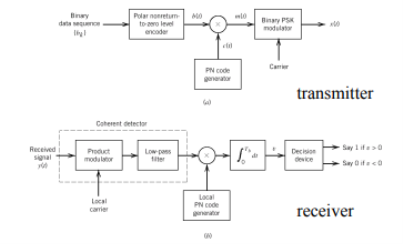
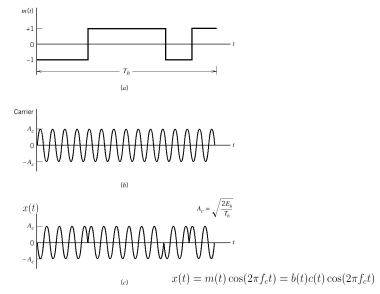
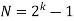 , the duty cycle is ½. Q2) What is Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) using BPSK modulation?A2) DSSS is a spread spectrum modulation technique used for digital signal transmission over airwaves. It was originally developed for military use, and employed difficult-to-detect wideband signals to resist jamming attempts. It is also being developed for commercial purposes in local and wireless networks.
, the duty cycle is ½. Q2) What is Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) using BPSK modulation?A2) DSSS is a spread spectrum modulation technique used for digital signal transmission over airwaves. It was originally developed for military use, and employed difficult-to-detect wideband signals to resist jamming attempts. It is also being developed for commercial purposes in local and wireless networks.The stream of information in DSSS is divided into small pieces, each associated with a frequency channel across spectrums. Data signals at transmission points are combined with a higher data rate bit sequence, which divides data based on a spreading ratio. The chipping code in a DSSS is a redundant bit pattern associated with each bit transmitted. This helps to increase the signal's resistance to interference. If any bits are damaged during transmission, the original data can be recovered due to the redundancy of transmission.
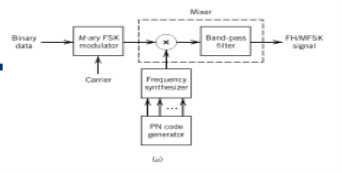
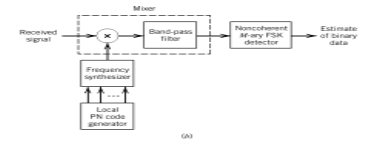
The entire process is performed by multiplying a radio frequency carrier and a pseudo-noise (PN) digital signal. The PN code is modulated onto an information signal using several modulation techniques such as quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK), binary phase-shift keying (BPSK), etc. A doubly-balanced mixer then multiplies the PN modulated information signal and the RF carrier. Thus, the TF signal is replaced with a bandwidth signal that has a spectral equivalent of the noise signal. The demodulation process mixes or multiplies the PN modulated carrier wave with the incoming RF signal. The result produced is a signal with a maximum value when two signals are correlated. Such a signal is then sent to a BPSK demodulator. Although these signals appear to be noisy in the frequency domain, bandwidth provided by the PN code permits the signal power to drop below the noise threshold without any loss of information.
|
SNR before spreading
SNR after spreading
Orthonormal basis vused at the receiver end
SNR before spreading (SNR)
SNR afterv spreading
|
|
FHSS | DSSS |
Multiple frequencies are used | Single frequency is used |
Hard to find the user’s frequency at any instant of time | User frequency, once allotted is always the same |
Frequency reuse is allowed | Frequency reuse is not allowed |
Sender need not wait | Sender has to wait if the spectrum is busy |
Power strength of the signal is high | Power strength of the signal is low |
Stronger and penetrates through the obstacles | It is weaker compared to FHSS |
It is never affected by interference | It can be affected by interference |
It is cheaper | It is expensive |
This is the commonly used technique | This technique is not frequently used |
|