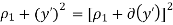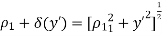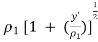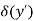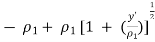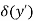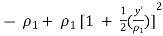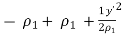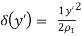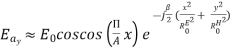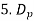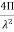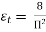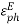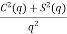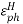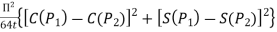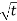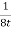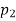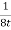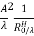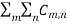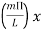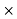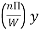|
|
● When δ(y’) is multiplied by the phase constant k, the result is a quadratic phase variation between the constant phase surface and the aperture plane.
● So the aperture fields becomes…..
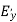 (
(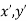 ) =
) = 
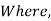
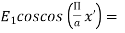 Amplitude distribution
Amplitude distribution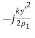 = Phase distribution
= Phase distribution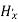 (
(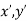 ) =
) = 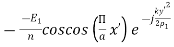 3. Directivity The directivity of the E-plane sectoral horn is found in a manner analogous to the H-plane sectoral horn:
3. Directivity The directivity of the E-plane sectoral horn is found in a manner analogous to the H-plane sectoral horn: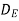 =
= 
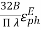 =
= 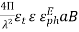 Where,
Where, =
= 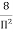 ,
, 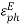 =
= 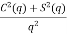 , q =
, q =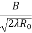
|
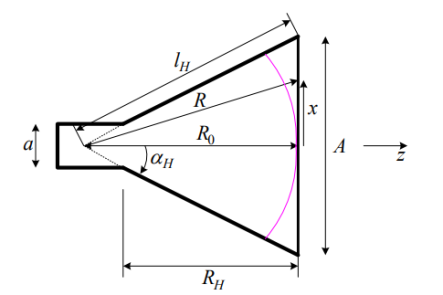
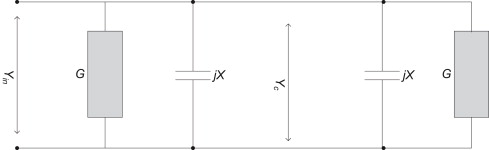
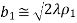 Q.3 Explain in detail H-plane sectoral horn.Ans- 1. The geometry and the respective parameters shown in the figure below are used in the subsequent analysis. The two required dimensions for the construction of the horn are A and
Q.3 Explain in detail H-plane sectoral horn.Ans- 1. The geometry and the respective parameters shown in the figure below are used in the subsequent analysis. The two required dimensions for the construction of the horn are A and 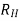 .
.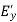 = -
= -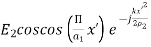
|
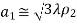
|
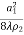 Which gives‘t’ approximately equal to:
Which gives‘t’ approximately equal to: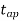 =
= 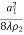 at
at 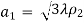 =
=  Q.3 Write a note on Pyramidal horn Ans – 1. The pyramidal horn is probably the most popular antenna in the microwave frequency ranges (from ≈1 GHz up to ≈18 GHz). The feeding waveguide is flared in both directions, the E-plane and the H-plane. 2. The field distribution at the aperture is approximated as
Q.3 Write a note on Pyramidal horn Ans – 1. The pyramidal horn is probably the most popular antenna in the microwave frequency ranges (from ≈1 GHz up to ≈18 GHz). The feeding waveguide is flared in both directions, the E-plane and the H-plane. 2. The field distribution at the aperture is approximated as
|
Where, q =
t = |
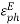 =0.8 The optimal directivity of an H-plane horn is achieved at t = 3 / 8)],
=0.8 The optimal directivity of an H-plane horn is achieved at t = 3 / 8)], 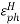 =0.79 . Thus, the optimal horn has a phase aperture efficiency of
=0.79 . Thus, the optimal horn has a phase aperture efficiency of
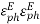 =0.632The total aperture efficiency includes the taper factor, too:
=0.632The total aperture efficiency includes the taper factor, too: 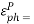
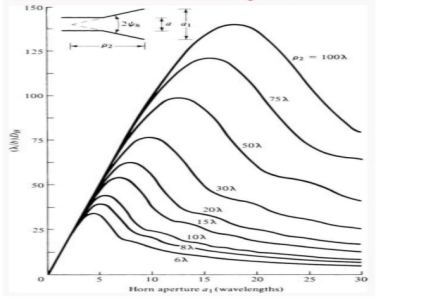
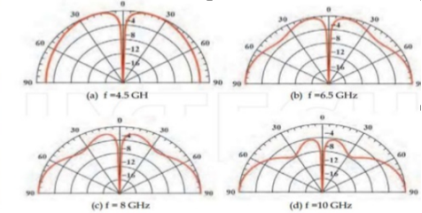
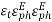 =0.81 *0.632 =0.519. Therefore, the best achievable directivity for a rectangular waveguide horn is about half that of a uniform rectangular aperture. 10. Radiation pattern of Pyramidal horn
=0.81 *0.632 =0.519. Therefore, the best achievable directivity for a rectangular waveguide horn is about half that of a uniform rectangular aperture. 10. Radiation pattern of Pyramidal horn
|
● The gain of antenna ranges to 25 dBi, with 10 to 20 dBi being typical.
● The usable BW of antenna is in the order of 10:1 and can be upto 20:1 that is upto 1GHz to 20 GHz.
● Horns of widely used as antennas
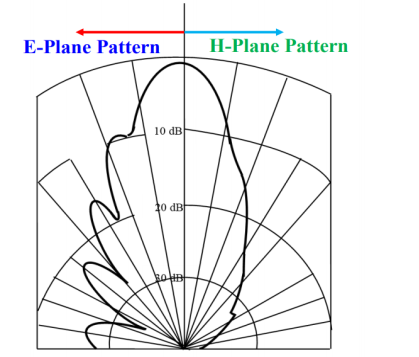
5. Radiation Pattern
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
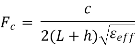 Where, c is the speed of light, and
Where, c is the speed of light, and  is the effective dielectric constant
is the effective dielectric constant 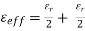
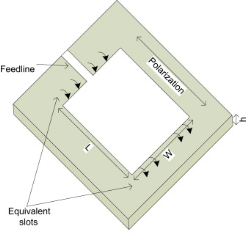
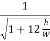 , where h/W > 110. Note that for a very small h, the relationship for the resonant frequency becomes,
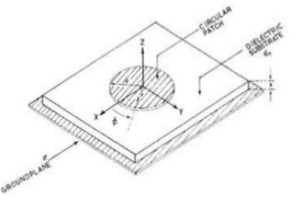
, where h/W > 110. Note that for a very small h, the relationship for the resonant frequency becomes,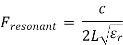 Q.11 Write a note on Circular Patch.Ans- 1. The mode supported by the circular patch antenna can be found by treating the patch, ground plane and the material between the two as a circular cavity. The radius of the patch is the only degree of freedom to control the modes of the antenna.2. The antenna can be conveniently analyzed using the cavity model. The cavity is composed of two electric conductors at the top and the bottom to represent the patch and the ground plane and by a cylindrical perfect magnetic conductor around the circular periphery of the cavity.
Q.11 Write a note on Circular Patch.Ans- 1. The mode supported by the circular patch antenna can be found by treating the patch, ground plane and the material between the two as a circular cavity. The radius of the patch is the only degree of freedom to control the modes of the antenna.2. The antenna can be conveniently analyzed using the cavity model. The cavity is composed of two electric conductors at the top and the bottom to represent the patch and the ground plane and by a cylindrical perfect magnetic conductor around the circular periphery of the cavity.
|
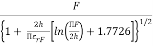 F =
F = 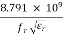
5. Above equation does not take into consideration the fringing effect. Since fringing makes the patch electrically larger, the effective radius of patch is used and is given by,
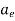 = a
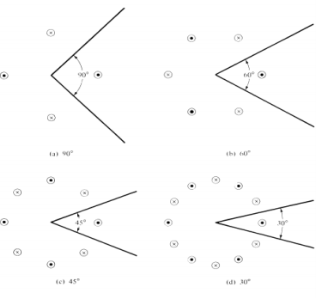
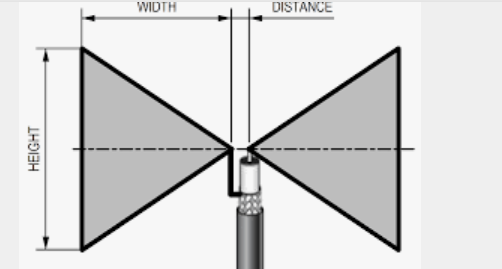
= a  Q.12 Explain in brief Bow Tie antenna.Ans- 1.A bowtie antenna uses triangular elements instead of straight rods as the antenna elements. The triangular elements sticking out on both sides of the antenna resemble a bow tie, hence the name.2. The “wings” of the antenna flare out symmetrically on both sides of the supporting beam. The two antennas nearly touch at the centre.
Q.12 Explain in brief Bow Tie antenna.Ans- 1.A bowtie antenna uses triangular elements instead of straight rods as the antenna elements. The triangular elements sticking out on both sides of the antenna resemble a bow tie, hence the name.2. The “wings” of the antenna flare out symmetrically on both sides of the supporting beam. The two antennas nearly touch at the centre.
|