Unit 03
Question Bank
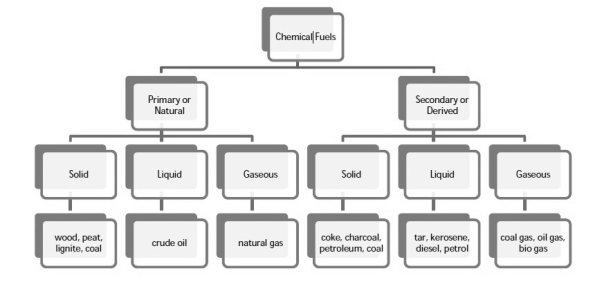
Q-1Classify fuels on the basis of occurrence.
The secondary fuels are obtained from primary fuel by processing or they are manmade. e.g.:- charcoal is obtained from wood by partial combustion of wood , ethyl alcohol is obtained by fermentation of carbohydrates .
Both the primary and secondary fuels are further classified on the basis of physical state into solid liquid and gaseous fuels.
Q-2Explain the construction and working of bomb calorimeter.
The gross calorific value of solid fuels and liquid fuels can be determined by bomb calorimeter .( if the liquid is volatile , then it is filled in a polythene capsule of negligible mass then used in experiment.
Construction :- a bomb colorimeter consists of
- Bomb pot
- Calorie meter
- Water and air jackets
- Accessories
- Pellet press
- Oxygen cylinder
Bomb pot :-
It is a cylindrical strong stainless-steel pot having a lid . The lid can be fitted air. Tight to bomb pot by screwing.
- There are two type of electrodes fitted through lid and there is an oxygen inlet valve as its center.
- One of these electrodes is provided with a ring to hold the crucible containing fuel .there is thin resistance wire tied to the electrodes in loop form and the loop touches the fuel.
- The weighed fuel is burnt in the bomb pot in the presence of high-pressure oxygen.
Calorimeter :-
- There is a stainless steel or copper calorimeter in which the bomb pot is kept .it contains a known volume of water and the water is kept circulating around the bomb pot with the help of a stirrer.
- A Beckman thermometer or digital thermometer is kept in the water of calorimeter , which can record the rise in temperature of welter due to absorb in a heat generated .
- There are insulator stands between calorimeter and water jacket.
Accessories :-
- There is a pellet press to convert the powder of solid fuel to pellet form .for a liquid fuel a capsule of negligible weight can be used.
- There is an oxygen cylinder with pressure gauge to fill oxygen in the bomb pot at the pressure of nearly 25 kg / cm².
- There is also a D.C battery of a about 6 volts to start combustion of fuel.
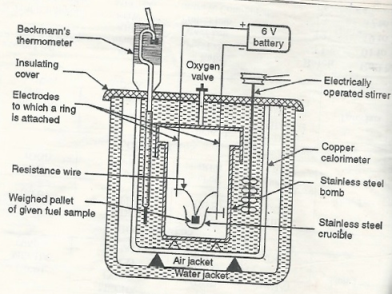
Fig: Bomb Caloriemeter
Working :-
- Weigh the pellet of solid fuel or liquid capsule and keep it in the crucible .keep the crucible in the ring of the electrode . Keep the resistance wire touching to the fuel.
- Add about 10 ml of distilled water at the bottom of bomb pot and fix the lid tightly to bomb by screwing.
- Fill the bomb with oxygen at the pressure about 25 kg / cm².
- Place the bomb in calorimeter add known volume of water in the calorimeter so that the bomb gets immersed in the water.
- Place the calorimeter in the water jacket over the plastic studs .keep the thermometer and stirrer in the water of calorimeter.
- Put the plastic cover on the and make electrical connections from battery to electrodes.
- Operate the stirrer for s minutes and note the initial temperature of water ( t1° c ).
- Pass the current for about 5 – 10 seconds to heat the wire so that the fuel catches fire. If the fuel contains S and N elements, they get converted to SO3 and N2O5 .these gases get dissolved in the distilled water in bomb to form H2SO4 and HNO3 ( along with liberation little heat ).
- Note the maximum temperature reached .after that note the rate of fall of temperature per minute and the time taken for reaching to initial temp. Are noted.
Open the bomb pot and wash the contents at its bottom into a beaker to find out the amount of H2SO4 and HNO3 formed.
Q-3Explain the Boy’s gas calorimeter with well labeled diagram.
- Start burning the gas at suitable pressure and adjust the rate of water flow such that the temperature of outgoing water remains constant.
- Burn the gas for 5 – 10 minutes to have the steady temperatures in and around the combustion chamber.
- After the steady ( temperature in and around the combustion chamber ) conditions of outgoing.
A) Volume of gas burnt at given temperature and pressure in certain time period.
B) Quantity of water passed through coil during this period.
C) Mass of water condensed from product gas during the period.
D) The steady rise in temperature of water ( t2 – t1 )
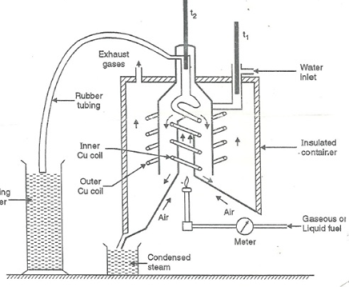
Fig: Boy’s gas calorimeter
Q-4What is the purpose of coal analysis?
The purpose for coal analysis is
- To decide price of coal
- To determine quality
- To specify use of coal for a particular purpose
- To calculate theoretical calorific values of coal
- To calculate air requirement for complete combustion of coal and design the furnace fire box suitably.
Q-5What is combustion?
Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance reacts rapidly with oxygen and generates heat. The original substance is called the fuel, and the source of oxygen is called the oxidizer. The fuel can be a solid, liquid, or gas, although for airplane propulsion the fuel is usually a liquid. The oxidizer, likewise, could be a solid, liquid, or gas, but is usually a gas for airplanes. For model rockets, a solid fuel and oxidizer is used.
Q-6Explain the construction of Orsat apparatus with well labeled diagram.
The apparatus consists of a calibrated water-jacketed gas burette connected by glass capillary tubing to two or three absorption pipettes containing chemical solutions that absorb the gases it is required to measure. For safety and portability, the apparatus is usually encased in a wooden box. The absorbents are: Potassium Hydroxide (Caustic Potash) Alkaline pyrogallol ammoniacal cuprous chloride the base of the gas burette is connected to a leveling bottle to enable readings to be taken at constant pressure and to transfer the gas to and from the absorption media. The burette contains slightly acidulated water with a trace of chemical indicator for coloration.
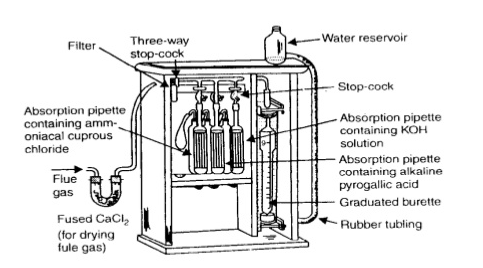
Q-7Explain the working of Orsat apparatus.
The apparatus used for flue gas (O2, CO2 & CO) analysis is called Orsat Apparatus. It consists of a water burette of 100ml.capacity and is graduated in 0.2ml divisions, it is connected to a stop cock at top with an absorption pipette connected at each position. The absorption pipette contains 30% KOH which is used to remove CO2 from flue gas. The second absorption pipette from flue gas contains 30% alkaline pyragallol solution which absorb O2 gas from flue gas. Some time a third absorption pipette is provided to measure CO in case of incomplete combustion. It contains ammonia Cal cuprous chloride solution. The bottom of the burette is connected to a movable reservoir levelling bottle containing 25% NaCl solution acidified with HCl and colored with methyl orange. By adjusting the height of levelling bottle gases in burette may be vented to atmosphere.
Q-8Calculate C , N , H , S from the following observation for a sample of coal.
2.05 gms of the coal is burnt in combustion tube. The increase in weight of any hydrous Cacl2 is 0.55 gm and increase in weight of KoH tube is 5.75gm.
0.75 of the coal is kjaldahl experiment released NH3 which is passed in 50ml 0.12 N NaoH to neutralize in back titration.
Washings of the bomb pot when 1.8 gm.
Given data :-
Increase in weight of any hydrous calcl2 = 0.55
Mass of coal = 0.75gms
Volume of 0.12 NHCL consumed by NH3 = 50 – 41
= 9 ml
Mass of coal = 1.8gms
Weight of Baso4 = 0.31 gm
- Weight of CO 2 formed = increase in wt. OfKoH
Therefore ,
C percent ) = 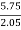 *
*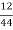 *100 = 76.5 percent .
*100 = 76.5 percent .
Increase in weight of any hydrous Cacl2
= weight of H2O formed
Mass of coal = 2.05gm
H ( percent ) = 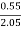 *
*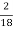 *100
*100
= 2.98 ( percent )
2. N ( percent ) = 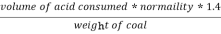
= 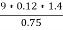
= 2.02 ( percent )
3. S ( percent ) = 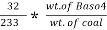 *100
*100
= 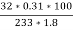
= 2.36 ( percent )