UNIT -1
Foundation of Information System
Q1) What is a system and information and their types and characteristics?
A1) System
In a system, network of components work towards a single objective, if there is lack of co-ordination among components, it leads to counterproductive results. A system may have following features:
Information
Common definition of information is data. However, data is no true information. Data gets its meaning and significance if only it is information. Information is represented with data, symbols and letters.
Information has following properties:
Representation of Information
Information is represented with help of data, numbers, letters or symbols. Information is perceived in a way it gets represented. Decimal system and binary system are two ways of representing information. The binary circuits of computers are designed to operate under two states (0,1).
Organization of Information
The way in which information is organized directly affect the way the information is managed and retrieved.
The simplest way of organizing information is through linear model. In this form, data is structured one after another, for example, in magnetic tapes, music tapes, etc.
In a binary tree model, data is arranged in an inverted tree format where it assumes two values.
The hierarchy model is derived from a binary tree model. In this model, branch can assume multi-value data, for example in the UNIX operating system this model is used for its file system.
The hypertext model is another way of organizing information; World Wide Web is an example of this model.
Random access model is another way of organizing information. This model is used for optimum utilization of available computer storage space. Here data is stored in specified location under direction of the operating system.
Networking Information
Information is networked through network topology. The layout of all the connected devices, and it provides virtual shape or structure to the network is known as network topology. The physical structure may not be representative of network topology. The basic types of topology are bus, ring, star, tree and mesh.
The above topologies are constructed and managed with help of Hubs, Switches, Bridges, Routers, Brouters and Gateways.
Securing Information
Security of information as well as an information system is critical. Data back-up is on the way through which Information can be made secured. Security management for network and information system is distinct for different setup like home, small business, medium business, large business, school and government
Information system
An information system is integrated and co-ordinate network of components, which combine together to convert data into information.
Q2) What are the different types of information systems?
A2)
Q3) What are the classifications and components of information systems?
A3) An information system is essentially made up of five components hardware, software, database, network and people. These five components integrate to perform input, process, output, feedback and control.
Hardware consists of input/output device, processor, operating system and media devices. Software consists of various programs and procedures. Database consists of data organized in the required structure. Network consists of hubs, communication media and network devices. People consist of device operators, network administrators and system specialist.
Information processing consists of input; data process, data storage, output and control. During input stage data instructions are fed to the systems which during process stage are worked upon by software programs and other queries. During output stage, data is presented in structured format and reports.
In any given organization information system can be classified based on the usage of the information. Therefore, an information system in an organization can be divided into operations support system and management support system.
In an organization, data input is done by the end user which is processed to generate information products i.e. reports, which are utilized by internal and or external users. Such a system is called operation support system.
The purpose of the operation support system is to facilitate business transaction, control production, support internal as well as external communication and update organization central database. The operation support system is further divided into a transaction-processing system, processing control system and enterprise collaboration system.
2. Transaction Processing System (TPS)
In manufacturing organization, there are several types of transaction across department. Typical organizational departments are Sales, Account, Finance, Plant, Engineering, Human Resource and Marketing. Across which following transaction may occur sales order, sales return, cash receipts, credit sales; credit slips, material accounting, inventory management, depreciation accounting, etc.
These transactions can be categorized into batch transaction processing, single transaction processing and real time transaction processing.
3. Process Control System
In a manufacturing organization, certain decisions are made by a computer system without any manual intervention. In this type of system, critical information is fed to the system on a real-time basis thereby enabling process control. This kind of systems is referred as process control systems.
4. Enterprise Collaboration System
In recent times, there is more stress on team effort or collaboration across different functional teams. A system which enables collaborative effort by improving communication and sharing of data is referred to as an enterprise collaboration system.
5. Management Support System
Managers require precise information in a specific format to undertake an organizational decision. A system which facilitates an efficient decision-making process for managers is called management support system.
Management support systems are essentially categorized as management information system, decision support system, expert system and accounting information system.
Management information system provides information to manager facilitating the routine decision-making process. Decision support system provides information to manager facilitating specific issue related solution.
Further Classification
An information system can be categorized based upon activity into strategic planning system, tactical information system and operational information system.
Q4) What are the effectiveness and efficiency criteria in information system?
A4)
Uses
Q5) What are the implications of information in business?
A5) Information processing has transformed our society in numerous ways. From a business perspective, there has been a huge shift towards increasingly automated business processes and communication. Access to information and capability of information processing has helped in achieving greater efficiency in accounting and other business processes.
A complete business information system, accomplishes the following functionalities −
The following list summarizes the five main uses of information by businesses and other organizations −
2. Recording − Business processing these days involves recording information about each transaction or event. This information collected, stored and updated regularly at the operational level.
3. Controlling − A business need to set up an information filter, so that only filtered data is presented to the middle and top management. This ensures efficiency at the operational level and effectiveness at the tactical and strategic level.
4. Measuring − A business measures its performance metrics by collecting and analyzing sales data, cost of manufacturing, and profit earned.
5. Decision-making − MIS is primarily concerned with managerial decision-making, theory of organizational behavior, and underlying human behavior in organizational context. Decision-making information includes the socio-economic impact of competition, globalization, democratization, and the effects of all these factors on an organizational structure.
In short, this multi-dimensional information evolves from the following logical foundations –
◦ Data and file structure
◦ Data theory design and implementation
◦ Computer networking
◦ Expert systems and artificial intelligence
4. Information theory
Following factors arising as an outcome of information processing help speed up of business events and achieves greater efficiency −
Q6) What is the MIS Need for Information Systems?
A6)
Managers make decisions. Decision-making generally takes a four-fold path −
MIS is an information system that provides information in the form of standardized reports and displays for the managers. MIS is a broad class of information systems designed to provide information needed for effective decision making.
Data and information created from an accounting information system and the reports generated thereon are used to provide accurate, timely and relevant information needed for effective decision making by managers.
Management information systems provide information to support management decision making, with the following goals −
MIS is of vital importance to any organization, because −
Q7 What are information and data and their collection techniques?
Data can be described as unprocessed facts and figures. Plain collected data as raw facts cannot help in decision-making. However, data is the raw material that is organized, structured, and interpreted to create useful information systems.
Data is defined as 'groups of non-random symbols in the form of text, images, voice representing quantities, action and objects'.
Information is interpreted data; created from organized, structured, and processed data in a particular context.
According to Davis and Olson −
"Information is a data that has been processed into a form that is meaningful to recipient and is of real or perceived value in the current or the prospective action or decision of recipient."
Information Processing
Information, Knowledge and Business Intelligence
Professor Ray R. Larson of the School of Information at the University of California, Berkeley, provides an Information Hierarchy, which is −
Scott Andrews' explains Information Continuum as follows −
Information/Data Collection Techniques
The most popular data collection techniques include −
Q8 How can one assess the quality of information?
A8) Information is a vital resource for the success of any organization. Future of an organization lies in using and disseminating information wisely. Good quality information placed in right context in right time tells us about opportunities and problems well in advance.
Good quality information − Quality is a value that would vary according to the users and uses of the information.
According to Wang and Strong, following are the dimensions or elements of Information Quality −
Various authors propose various lists of metrics for assessing the quality of information. Let us generate a list of the most essential characteristic features for information quality −
Q9) What is the difference between MIS and Data Processing?
A9) MIS VS. Data Processing
Data processing is term used to describe the series of actions taken to provide useful information from data. Data processing systems, whether manual, mechanical or electronic are used to produce the management information system for running the organization. Data is the term used to describe the basic fact regarding an organization’s activities which are collected and input to a system. The facts are to produce useful output or information. The process of output or information is also known as reporting system. Therefore, the data processing system processes the transactions and processes the reports. Prior to computer (before use of computers), this was done manually. In the age of computer other data processing methods continue to be used to organization where it is fell that electronic data processing (EDP) method. But it is not distracted other data processing methods, may be used in conjunction with computer data processing, for example, to produce input or deal with output.
Definition. Data Processing: The execution of a systematic sequence of operations performed upon data to transform it into information.
Data processing involves a number f transaction and file maintenance in order to provide a database for generating and providing information to various users at the management levels. A transaction is an activity like making a purchase or sales, manufacturing product or recruiting employees. It may be internal in nature and can also involve an external agency. The records to be transacted can be routed through the following ways.
1. Direct transaction to the action (automatic action).
2. Report or explain the performance (through the information report).
3. Communicate the information about the issue (ad hoc support).
The other processing activities are master file maintenance, report generation inquiry and creating support applications. The output of these processing functions provides the base to other management activities. They are routine and are in a programmed form.
A MIS is more comprehensive than data processing with only process transaction and produce reports. Before the advent of computers, data processing was performed manually or with simple machines. MIS encompasses processing in support of a wider range of organizational functions and management process. The system also includes transaction processing. Which illustrated the computer-based data processing?
It is clear from the diagram that the input data has entered into the system and formed as database, and it has again transaction in to output for the decision makers as information.
The important difference between MIS and routine data process are the capability to provide analysis, planning and decision-making support. An MIS orientation means users have access to decision models and methods for querying the data set. Information resources are utilized so as to improve decision making and achieve improved organizations effectiveness.
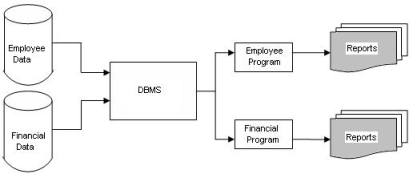
Data Processing
According to General Motors, meeting that used to last longer than two hours have been trimmed to 20 minutes due to the use of computer graphic “in charts you see the relationship vividly displayed” says another users, nothing that the interpretations of columns and rows for traditional reports are more difficult because they must be done mentally. In past, of course, managers have had in-house artists make up charts and graphs, but the time required to reduce them often make extensive use impartial. it used to take GM8 two years to manually produce maps with dots locating current and potential customers. Now Cadillac’s computer link system allows them to access vehicle registration data. Consequently, they produce 75 maps a year showing locations of their dealers, their competitors, and high income households. This information has let to the relocation of over 100Cadillac dealerships.