Unit II
Management Information Systems
Q1 Explain the concept of MIS.
A1) The concept of the Management Information System (MIS) has evolved over a perick-: of time comprising many different facets of the organizational function. MIS is a necessity of all the organizations. The initial concept of MIS was to process data from the organization and present it in the form of reports at regular intervals. The system was largely capable of handling the data from collection to processing. It was more impersonal, requiring each individual to pick and choose the processed data and use for his requirements. This concept was further modified when a distinction was made between data and information.
The information is a product of an analysis of data. This concept is similar to a raw material and the finished product. What are needed are information and not a mass of data. However, the data can be analyzed in a number of ways, producing different shades and specifications of the information as a product. It was, therefore, demanded that the system concept be an individual- oriented, as each individual may have a different orientation. Towards the information this concept was further modified, that the system should present information in such a form and format that it creates an impact on its user, provoking a decision or an investigation.
The MIS is a dynamic concept subject to change, time and again, with a change in the business management process. It continuously interacts with the internal and the external environment of the business and provides a corrective mechanism in the system so that the change needs of information are met effectively. The M1S, therefore, is a dynamic design the primary objective of which is to provide the information for decision making and it is developed considering the organizational fabric, giving due regard to the people in the organizational the management functions and the managerial control.
Q2) What is the structure of MIS?
A2) MIS STRUCTURE
A classical system is recommended to assure the development of a management information system that is fully responsive to a client's performance objectives and resource constraints. Like most complex systems, management information system can be described in number of ways. Multiple approaches are used in this section to explain structure of an organization information system or management information system.
This approach includes the following major components:
Operational elements
System support includes all of the resources required to operate, maintain, and rove the system. A crucial aspect of the system operation phase is the fact that the design team will, at some point, be ending its involvement in the MIS. At that point, important that the client have the personnel know-how and resources to continue ration of the system, maintain it, and improve it. It is necessary to develop a system is easy to use and improve. To accomplish this goal, training materials and cedures can be developed that can be used to assure the continued operation of them in the future. There are certain kinds of operational elements which play an important role in eloping an effective MIS like:
Element | Description |
Hardware | Multiple computer systems: mainframes, minicomputers, personal computers. Computer system components are: central processor(s), memory hierarchy, input and output devices. Communications: local area networks, metropolitan area networks, and wide area networks. |
Software | Systems software and applications software |
Database | Organised collections of data used by applications software. |
Personnel | Professional cadre of computer specialists; and users in certain aspects of their work. |
Procedures | Specifications for the use and operation of computerized information systems collected in user manuals, operator manuals, and similar documents. |
Q3) What are the differences between MIS and Data processing?
A3) Data processing is term used to describe the series of actions taken to provide useful information from data. Data processing systems, whether manual, mechanical or electronic are used to produce the management information system for running the organization. Data is the term used to describe the basic fact regarding an organization's activities which are collected and input to a system. The facts are to produce useful output or information. The process of output or information is also known as reporting system. Therefore, the data processing system processes the transactions and processes the reports. Prior to computer (before use of computers), this was done manually. In the age of computer other data processing methods continue to be used to organization where it is fell that electronic data processing (EDP) method. But it is not distracted other data processing methods, may be used in conjunction with computer data processing, for example, to produce input or deal with output. Data processing involves a number of transaction and file maintenance in order to provide a database for generating and providing information to various users at the management levels. A transaction is an activity like making a purchase or sales, manufacturing product or recruiting employees. It may be internal in nature and can also involve an external agency.
The records to be transacted can be routed through the following ways.
1. Direct transaction to the action (automatic action).
2. Report or explain the performance (through the information report).
3. Communicate the information about the issue (ad hoc support).
The other processing activities are master file maintenance, report generation inquiry and creating support applications. The output of these processing functions provides right information to other management activities. They are routine and are in a programmed form.
A MIS is more comprehensive than data processing which only processes transaction and produces reports. Before the advent of computers, data processing was performed manually or with simple machines. MIS encompasses processing in support of a wider range of organizational functions and management process. The system also includes inaction processing.
Q4) What are the characteristics of Decision Support System?
A4) While developing the DSS therefore, care must be taken to ensure that the DSS assesses the following desirable characteristics:-
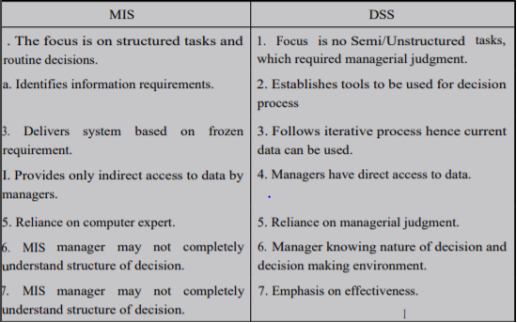
Q5) What are the differences between MIS and DSS?
A5) The Decision Support System (DSS) is a special class of system which is used as a support in decision making. Many of the decision making situations, at all levels of management, are such that its occurrence is infrequent but the methodology of decision making is known. Some of the methods are proven and are widely used. Such applications are separated and are packed in the DSS. These systems use data from general MIS and they are used by a manager or a decision maker for decision sups The basic characteristic of the decision support system is that it is based on some technique or model. These systems are used sometimes for resting new alternat training and learning. They are also used for sensitizing the various parameters of model. The DSS could be an internal part of the MIS.
When the decision making need in real time dynamic mode, all such systems are designed to read, measure, moni evaluate, analyze and act as per the decision guidance embedded in the system. example, in a simple case of order processing, the embedded DSS will accept or reject order based on the CRISIL, credit rating, availability of stock and so on. If the order accepted, the order acceptance is generated and the dispatch is scheduled for the ord quantity. The DSS, in all such cases, uses the data already present in the system and g it activated for action as per the guidelines. The MIS designer has to look for all situations and design the DSS for integration in the system. The MIS would become more useful if the decision making is made person-independent and executed with w designed DSS.
All such embedded systems cover the normal variety of decision situations. If anything outside the considered variety crops up, DSS will bring to notice of the decision makers that action is called for in the situation. When the decision situation requires multidimensional analysis using the internal and external data, the such decision support systems are kept out of the main MIS design scope. Most of this situation calls for the use of models and the nature of decision is strategic, calling for planned activity. Decisions like a new product launch, price revision, appointing new dealers, change of product design or change in the manufacturing process are strategic decisions which require critical analysis of data, careful evaluation of various alternatives and selecting one of them for implementation on the given criteria. The decision support system plays a dominant role in the management information system, as a support to decision making.
MIS is basically a kind of link to facilitate communication between managers across different areas in a business organization. MIS plays a pivotal role in enabling communications across the floor of an organization, between various entities therein. DSS, many consider, is an advancement from the original MIS. However, this is not the sole difference between the two. While there may not be too much separating the two, the difference is still there, as is apparent when we say DSS is an advancement over MIS. The essential difference between the two is in focus. DSS, as the term indicates, is about leadership and senior management in an organization providing good, reliable judgement as well as vision. MIS, on the other hand, is about focusing on the actual flow information itself.
Q6) Explain Data Processing?
A6) Data processing is term used to describe the series of actions taken to provide useful information from data. Data processing systems, whether manual, mechanical or electronic are used to produce the management information system for running the organization. Data is the term used to describe the basic fact regarding an organization's activities which are collected and input to a system. The facts are to produce useful output or information. The process of output or information is also known as reporting system. Therefore, the data processing system processes the transactions and processes the reports.
Prior to computer (before use of computers), this was done manually. In the age of computer other data processing methods continue to be used to organization where it is fell that electronic data processing (EDP) method. But it is not distracted other data processing methods, may be used in conjunction with computer data processing, for example, to produce input or deal with output. Data processing involves a number of transaction and file maintenance in order to provide a database for generating and providing information to various users at the management levels. A transaction is an activity like making a purchase or sales, manufacturing product or recruiting employees. It may be internal in nature and can also involve an external agency.
The records to be transacted can be routed through the following ways. 1. Direct transaction to the action (automatic action). 2. Report or explain the performance (through the information report). 3. Communicate the information about the issue (ad hoc support). The other processing activities are master file maintenance, report generation inquiry d creating support applications. The output of these processing functions provides the necessary information to other management activities. They are routine and are in a programmed form.
Q7) What are MIS subsystems?
A7) MIS provides managers with information and support for effective decision and provides feedback on daily operations. Outputs, or reports, are usually erated through accumulation of transaction processing data. Each MIS is a grated collection of subsystems, which are typically organized along functional line an organization.
There are two approaches to define a subsystem:
2. Activity Subsystem: Another approach to understand the structure of an information system is in terms of the subsystem which performs various activities. Some of activities subsystem will be useful for one organizational function subsystem others will be useful for only one function. It supports the activity for which they are used. E.g., Transactions, Operations etc.
Q8) What are the advantages of MIS?
A8) There are several advantages:
2. Ability to link and enable employees: Electronic communication increases the overall amount of communication within a firm. The most important aspect is that people from the various units of a corporation can interact with each other and thus horizontal communication is promoted. All the obvious advantages of quicker information availability is the outcome of this function of I'?' but it must also be remembered that too much electronic communication leads to increased alienation of employees due to increased impersonality.
3. Increases boundary spanning: An individual can access any information in any part of the organization with the aid of the appropriate technology. This eliminates the need for the repetition of information and thus promotes non-redundancy. If information provided is adequate, one can deal with factors like business risk and uncertainties effectively.
4. Ability to store and retrieve information at any instance: It means that the organization does not have to rely solely on the fallibility of human error, which is subject to error and erosion. Information can be stored, retrieved and communicated far more easily and effectively. The information support improves the lack of knowledge, enriches experience and improves analytical ability leading to better business judgment. It helps managers to act decisively.
5. Helps in forecasting and long term planning: A disciplined information system creates a structured database and knowledge base for all people in the organization. The information available in such a form that it can be used either straight away or using blending and analysis thereby saving manager's valuable time.
Q9) What is Information Resource Management?
A9) Information Resource Management (IRM) is a program of activities directed at king effective use of information technology within an organization. These activities go from global corporate information planning to application system development, ration, and maintenance and support of end-user computing. Information resource management has become a popular way to emphasize a major change in the management and mission of the information systems function in many organizations.
IRM may be viewed as having five major dimensions:
Strategic Management
Information technology must be managed to contribute to a firm's strategic objectives and competitive advantages, not just for operational efficiency or decision making.
Operational Management
Information technology and information systems can be managed by functional organizational structures and managerial techniques commonly used throughout other business units.
Resource Management
data and information, hardware and software, telecommunications networks, and IS personnel are vital organizational resources that must be managed like other business assets.
Technology Management
All technologies that process, store, and communicate data and information throughout the enterprise should be managed as integrated systems of organizational resources.
Distributed Management
Managing the use of information technology and information system resources in business units or workgroups is a key responsibility of their managers, - matter what their function or level in the organization.
Q10) What are Technology Management and Operations Management?
A10) Operational Management - The IRM concept stresses that managerial functions and techniques and organizational structures common to most businesses can be used to manage information technology. Business and Information Systems managers can use managerial techniques (such as planning models, financial budgets, and project management), and a mix of functional and process-based work groups and business units, just as they do in other major areas of business. The information systems' function is treated like other functions and expected to use the managerial techniques employed by other business units to manage its resources and activities.
All technologies that process, store, and deliver data and information throughout the emprise must be managed as integrated systems of organizational resources. Such technologies include the Internet, intranets, and electronic commerce and collaboration terns, as well as traditional computer-based information processing. These "islands of technology" are bridged by IRM and become a primary responsibility of the CIO, since is in charge of all information technology services. The rapid growth of the Internet, intranets, extranets, and client/server networks has de network management a major technology management function. This function is responsible for managing a company's Internet access, intranets and extranets, and the i.e. area networks and interconnected local area networks of client/server computing.
These networks require:
1. The major commitment of hardware and software resources.
2. The creation of managerial and staff positions to manage their use.
Network management is responsible for overseeing the quality of all the communications services that most businesses rely on today.