Unit 3
Ethics in Functional Areas
Q1) Explain ethics in functional area.
A1)
Ethical issues can arise in various functional areas of a business such as marketing, research and development, HRM, production and finance. Ethical issues in all these functional areas must be controlled or coordinated by the chief executive officer (CEO) of the enterprise. Figure below shows the main functional areas of a business that usually give rise to ethical issues.
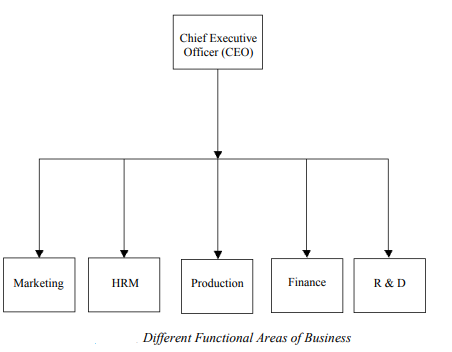
Q2) Explain ethics in finance.
A2)
Ethics in Finance
Finance is an important element of an organization and it helps in its growth and development. Finance plays an important role in making resources available in an organization, such as man, machine, material, market and money. The finance manager of the firm is responsible for arranging the finances for the firm. The finance manager can raise funds from the following two sources:
Internal Sources: Internal sources means the owner’s own funds that are invested as equity in the organization. In case of small organizations, the owner’s contribution in terms of equity is low. Therefore, large amount of money is raised from external sources. The entrepreneur can raise finance internally from various sources:
1) Deposits and loans given by owner.
2) Personal loan from provident fund and life insurance policy.
3) Funds accumulated by the retention of profits.
4) Ploughing back of profits.
External Sources: External sources means the various financial institutions from where entrepreneurs can raise funds, such as fixed capital, commercial banks and development banks. The entrepreneur can raise finance by:
1) Borrowing money from friends and relatives
2) Borrowing from financial institutions
Figure below shows the organizational chart for the finance function.
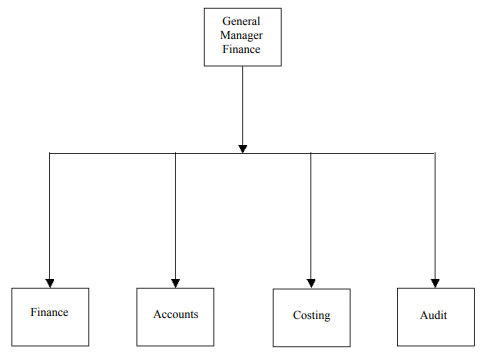
The finance department of an enterprise is prone to the following unethical practices:
1) Overestimating promoters’ capital utilization.
2) Overbudgeting project costs.
3) Using underhand tactics with the financers to gain benefits for the firm as well as for themselves.
4) Purchasing capital equipments at a time when there is no requirement for it.
5) Selling the capital equipments in order to raise additional and unaccounted funds.
6) Siphoning funds for the promoter’s personal benefit.
7) Investing unapproved funds in order to gain extra profits.
8) Claiming insurance cover for losses that never happened.
9) Overpricing the current assets in order to gain more working capital than permitted.
10) Using working capital funds for personal gains.
The accounts department of an enterprise is prone to the following types of unethical issues:
1) Showing inflated salaries and getting receipts from employees for an amount larger than what they actually get.
2) Playing inflated vendor bills in order to get discounts or commissions.
3) Paying overtime wages when there in no requirement for them.
4) Maintaining two different sets of books, one for the management and the other for income tax.
5) Refusing to reject unacceptable raw materials when the vendor bills have to be paid.
6) Delaying the clearance of the bills payable in order to get maximum interest for the amount to be paid.
7) Allotting extra travelling allowances to favourite employees.
8) Showing wrong figures in the monthly trial balances for personal benefits.
The following are the unethical practices of the costing manager:
1) Reducing manufacturing costs by manipulating work hours.
2) Ignoring cost of rejects.
3) Ignoring cost of rework.
4) Not accounting for man-hours lost due to strikes and absenteeism.
5) Not accounting for man-hours lost in maintenance work.
6) Not considering the work stoppages due to change in models.
7) Ignoring the man-hours lost due to change in the manufacturing process.
8) Ignoring time lost in failed experimentations.
9) Not taking into acccount the benefits of economies of sales and experience curve
The following points describe the unethical behaviour of the auditing manager:
1) Ignoring major deviations from the budgets.
2) Rejecting the tender having lowest cost among all due to personal reasons.
3) Helping in hiding black money in order to reduce the tax payable amount.
4) Ignoring inflated travel bills of selected employees.
5) Accepting payments made by the directors for personal purchases as official payments.
6) Enabling the directors in sending and receiving money from overseas through unofficial hawala channels.
7) Approving payments to suppliers without checking bills or deliverables.
8) Approving the substandard construction made by the constructor and approving their bills for payment.
Q3) Explain ethics in marketing.
A3)
Marketing is a technique that is used to attract and persuade customers. Marketing provides a way in which a product is sold to the target audience. Marketing is a management process that identifies, anticipates and supplies consumer requirements efficiently and effectively. The main aim of marketing is to make customers aware of the products and services. It also focuses on attracting new customers and keeping existing customers interested in the product. The marketing department consists of various subdivisions, such as sales, after-sales service and marketing and research. The different subdivisions of the marketing department are shown in Figure
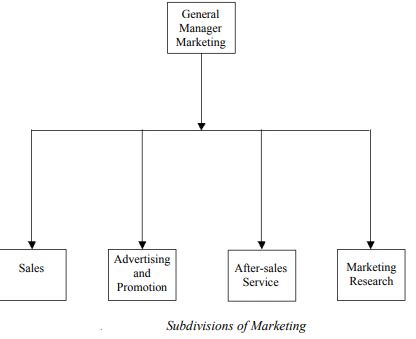
In the field of sales, the following ethical issues require safeguards against unethical behaviour:
1) Not supplying the products made by the company as per the order.
2) Not accepting responsibility for the defective product.
3) Not giving details about the hidden costs, such as transportation cost, while making the contract with the client.
4) Changing the specifications of the product without giving any prior information to the customer.
5) Changing the terms of the business without taking any approval from the client.
6) Delaying the delivery of the goods without giving any proper reason.
7) Treating two customers differently.
8) Not providing the after sales service as per the contract.
9) Selling the same product at different prices to different customers.
Advertising and promotion provide the means for communicating with the customer. In the field of advertising and promotion, the following are examples of unethical communication practices:
1) Making false commitments to the customers about the benefits of the product.
2) Supplying products that are different from those that are advertised.
3) Giving wrong prices to the customers during advertising.
4) Not giving the promised gift in the promotional campaign.
5) Hiding major flaws of the product.
6) Providing wrong testimonials about the product to prospective customers.
7) Not providing the advertised service to the customers as a part of the promotional plans.
8) Increasing the price of the product before starting its promotional campaign.
9) Making false references about the competitive products.
While selling the product to the customer, a company provides some extended features or facilities along with the product, such as after-sales service. These facilities are provided to increase the sale of the product. In the field of after-sales service, the following ethical issues require safeguards against unethical behaviour:
Using below-standard material for the service and charging for relatively better material from the customer
Marketing research is done to find out the needs of the market, its trends and competitive activities. In the field of marketing research, the following are example of unethical behaviour:
1) Research is conducted only to substantiate the viewpoint of the manager.
2) Research is focused on the areas that do not need to be covered.
3) Some old research is presented as the new one just for the purpose of financial gain.
4) A biased research report is prepared to suit the marketing manager.
5) The research report is sold to the competitor.
6) The report does not include important facts.
Q4) Explain ethics in human resource.
A4)
Ethics in Human Resources:
HRM is concerned with the management of the ‘people’ of an organization. The term HRM is used to refer to the procedures, philosophy, policies, and practices related to the management of people within an organization. HRM is an approach to bring the people and the organization together so as to achieve the desired goals. It helps in creating a relation between the management of the organization and the employees which is based on cooperation and coordination according to the designed strategy. It is the art of promoting, developing and maintaining a competent workforce to achieve the goals of an organization in an effective manner. HRM is responsible for performing various functions like planning, organizing, directing and controlling of human resources. HRM also involves activities like procurement, development, compensation and maintenance.
According to Ivancevich and Glucck, ‘Human resource management is the function performed in organizations that facilitates the most effective use of people (employees) to achieve organizational and individual goals.’
HRM is extensive in nature and it is present in all organizations and at all levels of an organization. HRM focuses on action rather than theoretical procedures and it encourages an employee to utilize his skills and potential completely to give his best to the organization. It encourages the employees through systematic procedures like recruitment, selection, training and development. An effective HRM works towards achieving its goals by providing a competent and motivated workforce. The primary aim of HRM is the promotion of effectiveness of the people employed in the organization and the performance of their allotted duties with cooperation. It seeks to develop and bring together an effective organization, enabling the women and men who make up an enterprise to give their best contribution towards its success both as members of a working group and as individuals. HRM can help organizations achieve their goals more effectively and efficiently. Effective management of human resources helps in improving the quality of work life. It seeks to provide fair conditions and terms of employment and work that satisfies all those employed. The following are the key objectives of HRM:
1) To recruit trained and spirited employees.
2) To help the organization reach its goals.
3) To train the employees for best results.
4) To communicate HR policies to the employee.
5) To ethically respond to the needs of the society.
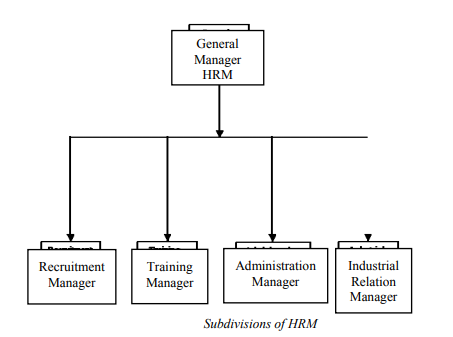
The following are examples of unethical practices during the recruitment process of a company:
1) Recruitment of known persons without assessing their abilities.
2) Recruitment on the basis of financial favours.
3) Recruitment of the relatives of other employees.
4) Recruitment based on the recommendations of friend, business associates
a) and other persons close to the leader.
b) Recruitment of underqualified persons.
c) Recruitment of overqualified persons.
d) Recruitment of less acceptable men when there are better suited women available for the job.
e) Employing children below fourteen years for the job.
f) Giving less than minimum wages fixed by the government.
The training manager of the company can also indulge in unethical practices as can be seen from the following points:
a) Arranging training only for favourite employees, whether they deserve it or not.
b) Employing outsiders for providing training to trainees even when there are several persons available inside.
c) Planning and organizing the training programme without even knowing the need for training.
d) Organizing training during peak seasons or on days when workload is very high.
e) Starting training programmes in an ill-prepared manner.
f) Extending the time of the training programme to allow the trainees to have a relaxed time.
g) Supplying outmoded and old training materials for the purpose of training.
h) Experimenting with trainees by asking them to set their own timetable for training.
In the area of administration, the following are the unethical practices the manager can indulge in:
a) Tampering leave records of the employees.
b) Giving leaves continuously to favourite employees.
c) Giving promotions to non-eligible persons merely on the recommendations of a friend or business associate.
d) Ignoring issues related to the security of the company.
e) Interference in various activities of the administration from the top management.
Giving the contract for uniforms of the employees to the wrong companies just for the sake of personal benefits.
Q5) Explain ethics in IT.
A5)
Ethics in information technology-
Information technology refers to the gathering, processing, creation, delivery and storage of information and all the processes that make all this possible. The volume of work that is handled using IT continues to increase almost everyday. Whatever be the field, one is sure to find IT at work.
Information technology is new to the world in which the clear legal environment is yet to develop, so getting benefits by using IT cannot be surely ethical or legal. Therefore, when we talk about ethics and IT, many new problems crop up.
The characteristic of IT is that it is a particular field which has no geographical boundaries but application of IT may affect culture and environment differently. The features which are acceptable in one culture may be unethical in another.
Computer ethics was founded by MIT Professor Norbert Wiener in the early 1940s when he was providing a helping hand in the development of an aircraft cannon, capable of gunning down fast-moving war planes. Wiener created a new branch of science called cybernetics—the science of information feedback. By combining cybernetics with digital computers, he foresaw revolutionary social and ethical consequences.
Technology Ethics: Technology ethics is a new subject. The profile of technology ethics is as follows:
1. Thinking ethically about human biotechnology.
2. Taking responsibility for e-wastage like environmental damage from computer and other electronic wastages.
3. Employers must check whether employees are wasting time at recreational websites or sending unprofessional e-mails.
4. Sometimes the invasions of piracy occurs through to use of the Internet services.
Ethical Issues: There are various ethical issues involved in information technology. In 1986, Masovi had classified ethical issues in the following four groups:
It involves the right of accessing the required information as well as the true payment of charges to access the information.
2. Privacy
It deals with the degree of privacy and dissemination of information about an individual.
3. Property
It talks about ownership and value of information.
4. Accuracy
The information which is viable and being accessed is now much more accurate and authentic.
The Computer Ethics Institute in Washington DC has laid down the following ten commandments of computer ethics:
a) You will not use computer to harm other people.
b) You will not interfere with the computer network of other people.
c) You will not snoop around in files of other people’s computer.
d) You will not use a computer to steal.
e) You will not use a computer to bear false witness.
f) You will not copy or use proprietary software for which you have not paid.
g) You will not use other people’s computer resources without authorization.
h) You will not use other people’s intellectual output.
i) You will think about the social consequences of the programme you are writing or the system you are designing.
j) You will always use a computer in ways that demonstrate considerations and respect for your fellow humans.
Q6) Explain ethics in marketing and finance.
A6)
Ethics in Marketing
Marketing is a technique that is used to attract and persuade customers. Marketing provides a way in which a product is sold to the target audience. Marketing is a management process that identifies, anticipates and supplies consumer requirements efficiently and effectively. The main aim of marketing is to make customers aware of the products and services. It also focuses on attracting new customers and keeping existing customers interested in the product. The marketing department consists of various subdivisions, such as sales, after-sales service and marketing and research. The different subdivisions of the marketing department are shown in Figure
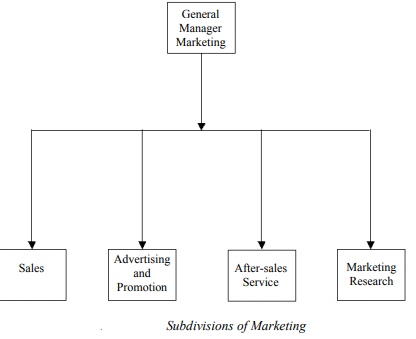
In the field of sales, the following ethical issues require safeguards against unethical behaviour:
1) Not supplying the products made by the company as per the order.
2) Not accepting responsibility for the defective product.
3) Not giving details about the hidden costs, such as transportation cost, while making the contract with the client.
4) Changing the specifications of the product without giving any prior information to the customer.
5) Changing the terms of the business without taking any approval from the client.
6) Delaying the delivery of the goods without giving any proper reason.
7) Treating two customers differently.
8) Not providing the after sales service as per the contract.
9) Selling the same product at different prices to different customers.
Advertising and promotion provide the means for communicating with the customer. In the field of advertising and promotion, the following are examples of unethical communication practices:
1) Making false commitments to the customers about the benefits of the product.
2) Supplying products that are different from those that are advertised.
3) Giving wrong prices to the customers during advertising.
4) Not giving the promised gift in the promotional campaign.
5) Hiding major flaws of the product.
6) Providing wrong testimonials about the product to prospective customers.
7) Not providing the advertised service to the customers as a part of the promotional plans.
8) Increasing the price of the product before starting its promotional campaign.
9) Making false references about the competitive products.
While selling the product to the customer, a company provides some extended features or facilities along with the product, such as after-sales service. These facilities are provided to increase the sale of the product. In the field of after-sales service, the following ethical issues require safeguards against unethical behaviour:
Using below-standard material for the service and charging for relatively better material from the customer
Marketing research is done to find out the needs of the market, its trends and competitive activities. In the field of marketing research, the following are example of unethical behaviour:
1) Research is conducted only to substantiate the viewpoint of the manager.
2) Research is focused on the areas that do not need to be covered.
3) Some old research is presented as the new one just for the purpose of financial gain.
4) A biased research report is prepared to suit the marketing manager.
5) The research report is sold to the competitor.
6) The report does not include important facts.
Ethics in Finance-
Finance is an important element of an organization and it helps in its growth and development. Finance plays an important role in making resources available in an organization, such as man, machine, material, market and money. The finance manager of the firm is responsible for arranging the finances for the firm. The finance manager can raise funds from the following two sources:
Internal Sources: Internal sources means the owner’s own funds that are invested as equity in the organization. In case of small organizations, the owner’s contribution in terms of equity is low. Therefore, large amount of money is raised from external sources. The entrepreneur can raise finance internally from various sources:
1) Deposits and loans given by owner.
2) Personal loan from provident fund and life insurance policy.
3) Funds accumulated by the retention of profits.
4) Ploughing back of profits.
External Sources: External sources means the various financial institutions from where entrepreneurs can raise funds, such as fixed capital, commercial banks and development banks. The entrepreneur can raise finance by:
1) Borrowing money from friends and relatives.
2) Borrowing from financial institutions.
Figure below shows the organizational chart for the finance function.
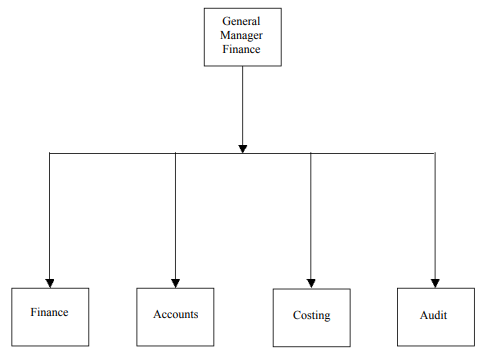
The finance department of an enterprise is prone to the following unethical practices:
1) Overestimating promoters’ capital utilization.
2) Overbudgeting project costs.
3) Using underhand tactics with the financers to gain benefits for the firm as well as for themselves.
4) Purchasing capital equipments at a time when there is no requirement for it.
5) Selling the capital equipments in order to raise additional and unaccounted funds.
6) Siphoning funds for the promoter’s personal benefit.
7) Investing unapproved funds in order to gain extra profits.
8) Claiming insurance cover for losses that never happened.
9) Overpricing the current assets in order to gain more working capital than permitted.
10) Using working capital funds for personal gains.
The accounts department of an enterprise is prone to the following types of unethical issues:
1) Showing inflated salaries and getting receipts from employees for an amount larger than what they actually get.
2) Playing inflated vendor bills in order to get discounts or commissions.
3) Paying overtime wages when there in no requirement for them.
4) Maintaining two different sets of books, one for the management and the other for income tax.
5) Refusing to reject unacceptable raw materials when the vendor bills have to be paid.
6) Delaying the clearance of the bills payable in order to get maximum interest for the amount to be paid.
7) Allotting extra travelling allowances to favourite employees.
8) Showing wrong figures in the monthly trial balances for personal benefits.
The following are the unethical practices of the costing manager:
1) Reducing manufacturing costs by manipulating work hours.
2) Ignoring cost of rejects.
3) Ignoring cost of rework.
4) Not accounting for man-hours lost due to strikes and absenteeism.
5) Not accounting for man-hours lost in maintenance work.
6) Not considering the work stoppages due to change in models.
7) Ignoring the man-hours lost due to change in the manufacturing process.
8) Ignoring time lost in failed experimentations.
9) Not taking into acccount the benefits of economies of sales and experience curve.
The following points describe the unethical behaviour of the auditing manager:
1) Ignoring major deviations from the budgets.
2) Rejecting the tender having lowest cost among all due to personal reasons.
3) Helping in hiding black money in order to reduce the tax payable amount.
4) Ignoring inflated travel bills of selected employees.
5) Accepting payments made by the directors for personal purchases as official payments.
6) Enabling the directors in sending and receiving money from overseas through unofficial hawala channels.
7) Approving payments to suppliers without checking bills or deliverables.
8) Approving the substandard construction made by the constructor and approving their bills for payment.
Q7) Explain ethics in human resource and finance.
A7)
Ethics in Human Resources
HRM is concerned with the management of the ‘people’ of an organization. The term HRM is used to refer to the procedures, philosophy, policies, and practices related to the management of people within an organization. HRM is an approach to bring the people and the organization together so as to achieve the desired goals. It helps in creating a relation between the management of the organization and the employees which is based on cooperation and coordination according to the designed strategy. It is the art of promoting, developing and maintaining a competent workforce to achieve the goals of an organization in an effective manner. HRM is responsible for performing various functions like planning, organizing, directing and controlling of human resources. HRM also involves activities like procurement, development, compensation and maintenance.
According to Ivancevich and Glucck, ‘Human resource management is the function performed in organizations that facilitates the most effective use of people (employees) to achieve organizational and individual goals.’
HRM is extensive in nature and it is present in all organizations and at all levels of an organization. HRM focuses on action rather than theoretical procedures and it encourages an employee to utilize his skills and potential completely to give his best to the organization. It encourages the employees through systematic procedures like recruitment, selection, training and development. An effective HRM works towards achieving its goals by providing a competent and motivated workforce. The primary aim of HRM is the promotion of effectiveness of the people employed in the organization and the performance of their allotted duties with cooperation. It seeks to develop and bring together an effective organization, enabling the women and men who make up an enterprise to give their best contribution towards its success both as members of a working group and as individuals . HRM can help organizations achieve their goals more effectively and efficiently. Effective management of human resources helps in improving the quality of work life. It seeks to provide fair conditions and terms of employment and work that satisfies all those employed. The following are the key objectives of HRM:
1) To recruit trained and spirited employees.
2) To help the organization reach its goals.
3) To train the employees for best results.
4) To communicate HR policies to the employee.
5) To ethically respond to the needs of the society.
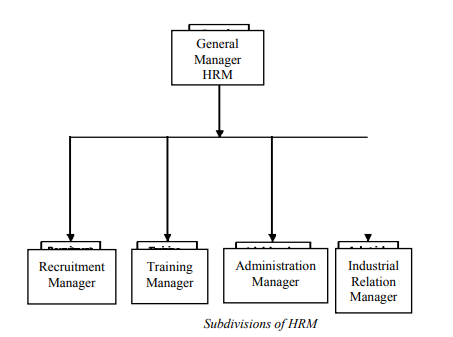
The following are examples of unethical practices during the recruitment process of a company:
1) Recruitment of known persons without assessing their abilities.
2) Recruitment on the basis of financial favours.
3) Recruitment of the relatives of other employees.
4) Recruitment based on the recommendations of friend, business associates.
a) and other persons close to the leader.
b) Recruitment of underqualified persons.
c) Recruitment of overqualified persons.
d) Recruitment of less acceptable men when there are better suited women available for the job.
e) Employing children below fourteen years for the job.
f) Giving less than minimum wages fixed by the government.
The training manager of the company can also indulge in unethical practices as can be seen from the following points:
a) Arranging training only for favourite employees, whether they deserve it or not.
b) Employing outsiders for providing training to trainees even when there are several persons available inside.
c) Planning and organizing the training programme without even knowing the need for training.
d) Organizing training during peak seasons or on days when workload is very high.
e) Starting training programmes in an ill-prepared manner.
f) Extending the time of the training programme to allow the trainees to have a relaxed time.
g) Supplying outmoded and old training materials for the purpose of training.
h) Experimenting with trainees by asking them to set their own timetable for training.
In the area of administration, the following are the unethical practices the manager can indulge in:
a) Tampering leave records of the employees.
b) Giving leaves continuously to favourite employees.
c) Giving promotions to non-eligible persons merely on the recommendations of a friend or business associate.
d) Ignoring issues related to the security of the company.
e) Interference in various activities of the administration from the top management
Giving the contract for uniforms of the employees to the wrong companies just for the sake of personal benefits.
Ethics in Finance
Finance is an important element of an organization and it helps in its growth and development. Finance plays an important role in making resources available in an organization, such as man, machine, material, market and money. The finance manager of the firm is responsible for arranging the finances for the firm. The finance manager can raise funds from the following two sources:
Internal Sources: Internal sources means the owner’s own funds that are invested as equity in the organization. In case of small organizations, the owner’s contribution in terms of equity is low. Therefore, large amount of money is raised from external sources. The entrepreneur can raise finance internally from various sources:
1) Deposits and loans given by owner.
2) Personal loan from provident fund and life insurance policy.
3) Funds accumulated by the retention of profits.
4) Ploughing back of profits.
External Sources: External sources means the various financial institutions from where entrepreneurs can raise funds, such as fixed capital, commercial banks and development banks. The entrepreneur can raise finance by:
1) Borrowing money from friends and relatives.
2) Borrowing from financial institutions.
Figure below shows the organizational chart for the finance function.
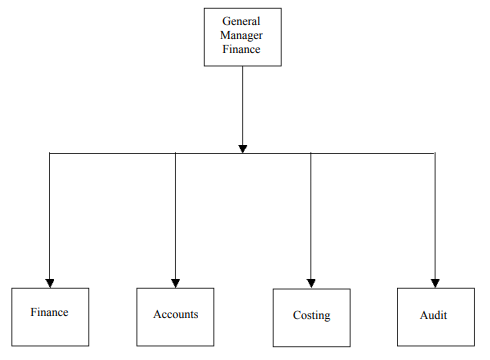
The finance department of an enterprise is prone to the following unethical practices:
1) Overestimating promoters’ capital utilization.
2) Overbudgeting project costs.
3) Using underhand tactics with the financers to gain benefits for the firm as well as for themselves.
4) Purchasing capital equipments at a time when there is no requirement for it.
5) Selling the capital equipments in order to raise additional and unaccounted funds.
6) Siphoning funds for the promoter’s personal benefit.
7) Investing unapproved funds in order to gain extra profits.
8) Claiming insurance cover for losses that never happened.
9) Overpricing the current assets in order to gain more working capital than permitted.
10) Using working capital funds for personal gains.
The accounts department of an enterprise is prone to the following types of unethical issues:
1) Showing inflated salaries and getting receipts from employees for an amount larger than what they actually get.
2) Playing inflated vendor bills in order to get discounts or commissions.
3) Paying overtime wages when there in no requirement for them.
4) Maintaining two different sets of books, one for the management and the other for income tax.
5) Refusing to reject unacceptable raw materials when the vendor bills have to be paid.
6) Delaying the clearance of the bills payable in order to get maximum interest for the amount to be paid.
7) Allotting extra travelling allowances to favourite employees.
8) Showing wrong figures in the monthly trial balances for personal benefits.
The following are the unethical practices of the costing manager:
1) Reducing manufacturing costs by manipulating work hours.
2) Ignoring cost of rejects.
3) Ignoring cost of rework.
4) Not accounting for man-hours lost due to strikes and absenteeism.
5) Not accounting for man-hours lost in maintenance work.
6) Not considering the work stoppages due to change in models.
7) Ignoring the man-hours lost due to change in the manufacturing process.
8) Ignoring time lost in failed experimentations.
9) Not taking into acccount the benefits of economies of sales and experience curve.
The following points describe the unethical behaviour of the auditing manager:
1) Ignoring major deviations from the budgets.
2) Rejecting the tender having lowest cost among all due to personal reasons.
3) Helping in hiding black money in order to reduce the tax payable amount.
4) Ignoring inflated travel bills of selected employees
5) Accepting payments made by the directors for personal purchases as official payments.
6) Enabling the directors in sending and receiving money from overseas through unofficial hawala channels.
7) Approving payments to suppliers without checking bills or deliverables.
8) Approving the substandard construction made by the constructor and approving their bills for payment.
Q8) Explain ethics in finance And IT.
A8)
Ethics in information technology
Information technology refers to the gathering, processing, creation, delivery and storage of information and all the processes that make all this possible. The volume of work that is handled using IT continues to increase almost everyday. Whatever be the field, one is sure to find IT at work.
Information technology is new to the world in which the clear legal environment is yet to develop, so getting benefits by using IT cannot be surely ethical or legal. Therefore, when we talk about ethics and IT, many new problems crop up.
The characteristic of IT is that it is a particular field which has no geographical boundaries but application of IT may affect culture and environment differently. The features which are acceptable in one culture may be unethical in another.
Computer ethics was founded by MIT Professor Norbert Wiener in the early 1940s when he was providing a helping hand in the development of an aircraft cannon, capable of gunning down fast-moving war planes. Wiener created a new branch of science called cybernetics—the science of information feedback. By combining cybernetics with digital computers, he foresaw revolutionary social and ethical consequences.
Technology Ethics: Technology ethics is a new subject. The profile of technology ethics is as follows:
1. Thinking ethically about human biotechnology.
2. Taking responsibility for e-wastage like environmental damage from computer and other electronic wastages.
3. Employers must check whether employees are wasting time at recreational websites or sending unprofessional e-mails.
4. Sometimes the invasions of piracy occurs through to use of the Internet services.
Ethical Issues: There are various ethical issues involved in information technology. In 1986, Masovi had classified ethical issues in the following four groups:
It involves the right of accessing the required information as well as the true payment of charges to access the information.
2. Privacy
It deals with the degree of privacy and dissemination of information about an individual.
3. Property
It talks about ownership and value of information.
4. Accuracy
The information which is viable and being accessed is now much more accurate and authentic.
The Computer Ethics Institute in Washington DC has laid down the following ten commandments of computer ethics:
a) You will not use computer to harm other people.
b) You will not interfere with the computer network of other people.
c) You will not snoop around in files of other people’s computer.
d) You will not use a computer to steal.
e) You will not use a computer to bear false witness.
f) You will not copy or use proprietary software for which you have not paid.
g) You will not use other people’s computer resources without authorization.
h) You will not use other people’s intellectual output.
i) You will think about the social consequences of the programme you are writing or the system you are designing.
j) You will always use a computer in ways that demonstrate considerations and respect for your fellow humans.
Ethics in Finance
Finance is an important element of an organization and it helps in its growth and development. Finance plays an important role in making resources available in an organization, such as man, machine, material, market and money. The finance manager of the firm is responsible for arranging the finances for the firm. The finance manager can raise funds from the following two sources:
Internal Sources: Internal sources means the owner’s own funds that are invested as equity in the organization. In case of small organizations, the owner’s contribution in terms of equity is low. Therefore, large amount of money is raised from external sources. The entrepreneur can raise finance internally from various sources:
1) Deposits and loans given by owner.
2) Personal loan from provident fund and life insurance policy.
3) Funds accumulated by the retention of profits.
4) Ploughing back of profits
External Sources: External sources means the various financial institutions from where entrepreneurs can raise funds, such as fixed capital, commercial banks and development banks. The entrepreneur can raise finance by:
1) Borrowing money from friends and relatives.
2) Borrowing from financial institutions.
Figure below shows the organizational chart for the finance function.
The finance department of an enterprise is prone to the following unethical practices:
1) Overestimating promoters’ capital utilization.
2) Overbudgeting project costs.
3) Using underhand tactics with the financers to gain benefits for the firm as well as for themselves.
4) Purchasing capital equipments at a time when there is no requirement for it.
5) Selling the capital equipments in order to raise additional and unaccounted funds.
6) Siphoning funds for the promoter’s personal benefit.
7) Investing unapproved funds in order to gain extra profits.
8) Claiming insurance cover for losses that never happened.
9) Overpricing the current assets in order to gain more working capital than permitted.
10) Using working capital funds for personal gains.
The accounts department of an enterprise is prone to the following types of unethical issues:
1) Showing inflated salaries and getting receipts from employees for an amount larger than what they actually get.
2) Playing inflated vendor bills in order to get discounts or commissions.
3) Paying overtime wages when there in no requirement for them.
4) Maintaining two different sets of books, one for the management and the other for income tax.
5) Refusing to reject unacceptable raw materials when the vendor bills have to be paid.
6) Delaying the clearance of the bills payable in order to get maximum interest for the amount to be paid.
7) Allotting extra travelling allowances to favourite employees.
8) Showing wrong figures in the monthly trial balances for personal benefits.
The following are the unethical practices of the costing manager:
1) Reducing manufacturing costs by manipulating work hours.
2) Ignoring cost of rejects.
3) Ignoring cost of rework.
4) Not accounting for man-hours lost due to strikes and absenteeism.
5) Not accounting for man-hours lost in maintenance work.
6) Not considering the work stoppages due to change in models.
7) Ignoring the man-hours lost due to change in the manufacturing process.
8) Ignoring time lost in failed experimentations.
9) Not taking into acccount the benefits of economies of sales and experience curve.
The following points describe the unethical behaviour of the auditing manager:
1) Ignoring major deviations from the budgets.
2) Rejecting the tender having lowest cost among all due to personal reasons.
3) Helping in hiding black money in order to reduce the tax payable amount.
4) Ignoring inflated travel bills of selected employees.
5) Accepting payments made by the directors for personal purchases as official payments.
6) Enabling the directors in sending and receiving money from overseas through unofficial hawala channels.
7) Approving payments to suppliers without checking bills or deliverables.
8) Approving the substandard construction made by the constructor and approving their bills for payment.
Q9) Explain ethics in marketing and human resource.
A9)
Ethics in Human Resources
HRM is concerned with the management of the ‘people’ of an organization. The term HRM is used to refer to the procedures, philosophy, policies, and practices related to the management of people within an organization. HRM is an approach to bring the people and the organization together so as to achieve the desired goals. It helps in creating a relation between the management of the organization and the employees which is based on cooperation and coordination according to the designed strategy. It is the art of promoting, developing and maintaining a competent workforce to achieve the goals of an organization in an effective manner. HRM is responsible for performing various functions like planning, organizing, directing and controlling of human resources. HRM also involves activities like procurement, development, compensation and maintenance.
According to Ivancevich and Glucck, ‘Human resource management is the function performed in organizations that facilitates the most effective use of people (employees) to achieve organizational and individual goals.’
HRM is extensive in nature and it is present in all organizations and at all levels of an organization. HRM focuses on action rather than theoretical procedures and it encourages an employee to utilize his skills and potential completely to give his best to the organization. It encourages the employees through systematic procedures like recruitment, selection, training and development. An effective HRM works towards achieving its goals by providing a competent and motivated workforce. The primary aim of HRM is the promotion of effectiveness of the people employed in the organization and the performance of their allotted duties with cooperation. It seeks to develop and bring together an effective organization, enabling the women and men who make up an enterprise to give their best contribution towards its success both as members of a working group and as individuals . HRM can help organizations achieve their goals more effectively and efficiently. Effective management of human resources helps in improving the quality of work life. It seeks to provide fair conditions and terms of employment and work that satisfies all those employed. The following are the key objectives of HRM:
1) To recruit trained and spirited employees.
2) To help the organization reach its goals.
3) To train the employees for best results.
4) To communicate HR policies to the employee.
5) To ethically respond to the needs of the society.
The following are examples of unethical practices during the recruitment process of a company:
1) Recruitment of known persons without assessing their abilities.
2) Recruitment on the basis of financial favours.
3) Recruitment of the relatives of other employees.
4) Recruitment based on the recommendations of friend, business associates.
a) and other persons close to the leader.
b) Recruitment of underqualified persons.
c) Recruitment of overqualified persons.
d) Recruitment of less acceptable men when there are better suited women available for the job.
e) Employing children below fourteen years for the job.
f) Giving less than minimum wages fixed by the government.
The training manager of the company can also indulge in unethical practices as can be seen from the following points:
a) Arranging training only for favourite employees, whether they deserve it or not.
b) Employing outsiders for providing training to trainees even when there are several persons available inside.
c) Planning and organizing the training programme without even knowing the need for training.
d) Organizing training during peak seasons or on days when workload is very high.
e) Starting training programmes in an ill-prepared manner.
f) Extending the time of the training programme to allow the trainees to have a relaxed time.
g) Supplying outmoded and old training materials for the purpose of training.
h) Experimenting with trainees by asking them to set their own timetable for training.
In the area of administration, the following are the unethical practices the manager can indulge in:
a) Tampering leave records of the employees.
b) Giving leaves continuously to favourite employees.
c) Giving promotions to non-eligible persons merely on the recommendations of a friend or business associate.
d) Ignoring issues related to the security of the company.
e) Interference in various activities of the administration from the top management.
f) Giving the contract for uniforms of the employees to the wrong companies just for the sake of personal benefits.
Ethics in Marketing
Marketing is a technique that is used to attract and persuade customers. Marketing provides a way in which a product is sold to the target audience. Marketing is a management process that identifies, anticipates and supplies consumer requirements efficiently and effectively. The main aim of marketing is to make customers aware of the products and services. It also focuses on attracting new customers and keeping existing customers interested in the product. The marketing department consists of various subdivisions, such as sales, after-sales service and marketing and research. The different subdivisions of the marketing department are shown in Figure
In the field of sales, the following ethical issues require safeguards against unethical behaviour:
1) Not supplying the products made by the company as per the order.
2) Not accepting responsibility for the defective product.
3) Not giving details about the hidden costs, such as transportation cost, while making the contract with the client.
4) Changing the specifications of the product without giving any prior information to the customer.
5) Changing the terms of the business without taking any approval from the client.
6) Delaying the delivery of the goods without giving any proper reason.
7) Treating two customers differently.
8) Not providing the after sales service as per the contract.
9) Selling the same product at different prices to different customers.
Advertising and promotion provide the means for communicating with the customer. In the field of advertising and promotion, the following are examples of unethical communication practices:
1) Making false commitments to the customers about the benefits of the product.
2) Supplying products that are different from those that are advertised.
3) Giving wrong prices to the customers during advertising.
4) Not giving the promised gift in the promotional campaign.
5) Hiding major flaws of the product.
6) Providing wrong testimonials about the product to prospective customers.
7) Not providing the advertised service to the customers as a part of the promotional plans.
8) Increasing the price of the product before starting its promotional campaign.
9) Making false references about the competitive products.
While selling the product to the customer, a company provides some extended features or facilities along with the product, such as after-sales service. These facilities are provided to increase the sale of the product. In the field of after-sales service, the following ethical issues require safeguards against unethical behaviour:
Using below-standard material for the service and charging for relatively better material from the customer
Marketing research is done to find out the needs of the market, its trends and competitive activities. In the field of marketing research, the following are example of unethical behaviour:
1) Research is conducted only to substantiate the viewpoint of the manager.
2) Research is focused on the areas that do not need to be covered.
3) Some old research is presented as the new one just for the purpose of financial gain.
4) A biased research report is prepared to suit the marketing manager.
5) The research report is sold to the competitor.
6) The report does not include important facts.
Q10) Explain ethics in IT and marketing.
A10)
Ethics in Marketing
Marketing is a technique that is used to attract and persuade customers. Marketing provides a way in which a product is sold to the target audience. Marketing is a management process that identifies, anticipates and supplies consumer requirements efficiently and effectively. The main aim of marketing is to make customers aware of the products and services. It also focuses on attracting new customers and keeping existing customers interested in the product. The marketing department consists of various subdivisions, such as sales, after-sales service and marketing and research. The different subdivisions of the marketing department are shown in Figure
In the field of sales, the following ethical issues require safeguards against unethical behaviour:
1) Not supplying the products made by the company as per the order.
2) Not accepting responsibility for the defective product.
3) Not giving details about the hidden costs, such as transportation cost, while making the contract with the client.
4) Changing the specifications of the product without giving any prior information to the customer.
5) Changing the terms of the business without taking any approval from the client.
6) Delaying the delivery of the goods without giving any proper reason.
7) Treating two customers differently.
8) Not providing the after sales service as per the contract.
9) Selling the same product at different prices to different customers.
Advertising and promotion provide the means for communicating with the customer. In the field of advertising and promotion, the following are examples of unethical communication practices:
1) Making false commitments to the customers about the benefits of the product.
2) Supplying products that are different from those that are advertised.
3) Giving wrong prices to the customers during advertising.
4) Not giving the promised gift in the promotional campaign.
5) Hiding major flaws of the product.
6) Providing wrong testimonials about the product to prospective customers.
7) Not providing the advertised service to the customers as a part of the promotional plans.
8) Increasing the price of the product before starting its promotional campaign.
9) Making false references about the competitive products.
While selling the product to the customer, a company provides some extended features or facilities along with the product, such as after-sales service. These facilities are provided to increase the sale of the product. In the field of after-sales service, the following ethical issues require safeguards against unethical behaviour:
Using below-standard material for the service and charging for relatively better material from the customer
Marketing research is done to find out the needs of the market, its trends and competitive activities. In the field of marketing research, the following are example of unethical behaviour:
1) Research is conducted only to substantiate the viewpoint of the manager.
2) Research is focused on the areas that do not need to be covered.
3) Some old research is presented as the new one just for the purpose of financial gain.
4) A biased research report is prepared to suit the marketing manager.
5) The research report is sold to the competitor.
6) The report does not include important facts.
Ethics in information technology
Information technology refers to the gathering, processing, creation, delivery and storage of information and all the processes that make all this possible. The volume of work that is handled using IT continues to increase almost everyday. Whatever be the field, one is sure to find IT at work.
Information technology is new to the world in which the clear legal environment is yet to develop, so getting benefits by using IT cannot be surely ethical or legal. Therefore, when we talk about ethics and IT, many new problems crop up.
The characteristic of IT is that it is a particular field which has no geographical boundaries but application of IT may affect culture and environment differently. The features which are acceptable in one culture may be unethical in another.
Computer ethics was founded by MIT Professor Norbert Wiener in the early 1940s when he was providing a helping hand in the development of an aircraft cannon, capable of gunning down fast-moving war planes. Wiener created a new branch of science called cybernetics—the science of information feedback. By combining cybernetics with digital computers, he foresaw revolutionary social and ethical consequences.
Technology Ethics: Technology ethics is a new subject. The profile of technology ethics is as follows:
1. Thinking ethically about human biotechnology.
2. Taking responsibility for e-wastage like environmental damage from computer and other electronic wastages.
3. Employers must check whether employees are wasting time at recreational websites or sending unprofessional e-mails.
4. Sometimes the invasions of piracy occurs through to use of the Internet services.
Ethical Issues: There are various ethical issues involved in information technology. In 1986, Masovi had classified ethical issues in the following four groups:
It involves the right of accessing the required information as well as the true payment of charges to access the information.
2. Privacy
It deals with the degree of privacy and dissemination of information about an individual.
3. Property
It talks about ownership and value of information.
4. Accuracy
The information which is viable and being accessed is now much more accurate and authentic.
The Computer Ethics Institute in Washington DC has laid down the following ten commandments of computer ethics:
a) You will not use computer to harm other people.
b) You will not interfere with the computer network of other people.
c) You will not snoop around in files of other people’s computer.
d) You will not use a computer to steal.
e) You will not use a computer to bear false witness.
f) You will not copy or use proprietary software for which you have not paid.
g) You will not use other people’s computer resources without authorization.
h) You will not use other people’s intellectual output.
i) You will think about the social consequences of the programme you are writing or the system you are designing.
j) You will always use a computer in ways that demonstrate considerations and respect for your fellow humans.
Q11) Explain ethics in human resource and IT.
A11)
Ethics in Human Resources
HRM is concerned with the management of the ‘people’ of an organization. The term HRM is used to refer to the procedures, philosophy, policies, and practices related to the management of people within an organization. HRM is an approach to bring the people and the organization together so as to achieve the desired goals. It helps in creating a relation between the management of the organization and the employees which is based on cooperation and coordination according to the designed strategy. It is the art of promoting, developing and maintaining a competent workforce to achieve the goals of an organization in an effective manner. HRM is responsible for performing various functions like planning, organizing, directing and controlling of human resources. HRM also involves activities like procurement, development, compensation and maintenance.
According to Ivancevich and Glucck, ‘Human resource management is the function performed in organizations that facilitates the most effective use of people (employees) to achieve organizational and individual goals.’
HRM is extensive in nature and it is present in all organizations and at all levels of an organization. HRM focuses on action rather than theoretical procedures and it encourages an employee to utilize his skills and potential completely to give his best to the organization. It encourages the employees through systematic procedures like recruitment, selection, training and development. An effective HRM works towards achieving its goals by providing a competent and motivated workforce. The primary aim of HRM is the promotion of effectiveness of the people employed in the organization and the performance of their allotted duties with cooperation. It seeks to develop and bring together an effective organization, enabling the women and men who make up an enterprise to give their best contribution towards its success both as members of a working group and as individuals . HRM can help organizations achieve their goals more effectively and efficiently. Effective management of human resources helps in improving the quality of work life. It seeks to provide fair conditions and terms of employment and work that satisfies all those employed. The following are the key objectives of HRM:
1) To recruit trained and spirited employees.
2) To help the organization reach its goals.
3) To train the employees for best results.
4) To communicate HR policies to the employee.
5) To ethically respond to the needs of the society.
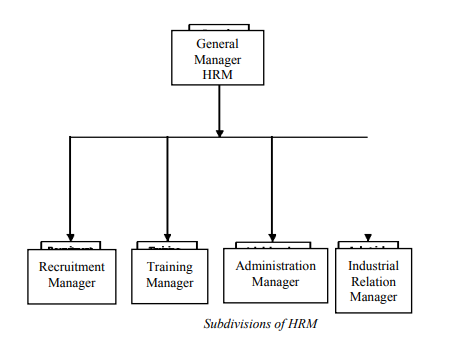
The following are examples of unethical practices during the recruitment process of a company:
1) Recruitment of known persons without assessing their abilities.
2) Recruitment on the basis of financial favours.
3) Recruitment of the relatives of other employees.
4) Recruitment based on the recommendations of friend, business associates.
a) and other persons close to the leader.
b) Recruitment of underqualified persons.
c) Recruitment of overqualified persons.
d) Recruitment of less acceptable men when there are better suited women available for the job.
e) Employing children below fourteen years for the job.
f) Giving less than minimum wages fixed by the government.
The training manager of the company can also indulge in unethical practices as can be seen from the following points:
a) Arranging training only for favourite employees, whether they deserve it or not.
b) Employing outsiders for providing training to trainees even when there are several persons available inside.
c) Planning and organizing the training programme without even knowing the need for training.
d) Organizing training during peak seasons or on days when workload is very high.
e) Starting training programmes in an ill-prepared manner.
f) Extending the time of the training programme to allow the trainees to have a relaxed time.
g) Supplying outmoded and old training materials for the purpose of training.
h) Experimenting with trainees by asking them to set their own timetable for training.
In the area of administration, the following are the unethical practices the manager can indulge in:
a) Tampering leave records of the employees.
b) Giving leaves continuously to favourite employees.
c) Giving promotions to non-eligible persons merely on the recommendations of a friend or business associate.
d) Ignoring issues related to the security of the company.
e) Interference in various activities of the administration from the top management.
Giving the contract for uniforms of the employees to the wrong companies just for the sake of personal benefits
Ethics in information technology
Information technology refers to the gathering, processing, creation, delivery and storage of information and all the processes that make all this possible. The volume of work that is handled using IT continues to increase almost everyday. Whatever be the field, one is sure to find IT at work.
Information technology is new to the world in which the clear legal environment is yet to develop, so getting benefits by using IT cannot be surely ethical or legal. Therefore, when we talk about ethics and IT, many new problems crop up.
The characteristic of IT is that it is a particular field which has no geographical boundaries but application of IT may affect culture and environment differently. The features which are acceptable in one culture may be unethical in another.
Computer ethics was founded by MIT Professor Norbert Wiener in the early 1940s when he was providing a helping hand in the development of an aircraft cannon, capable of gunning down fast-moving war planes. Wiener created a new branch of science called cybernetics—the science of information feedback. By combining cybernetics with digital computers, he foresaw revolutionary social and ethical consequences.
Technology Ethics: Technology ethics is a new subject. The profile of technology ethics is as follows:
1. Thinking ethically about human biotechnology.
2. Taking responsibility for e-wastage like environmental damage from computer and other electronic wastages.
3. Employers must check whether employees are wasting time at recreational websites or sending unprofessional e-mails.
4. Sometimes the invasions of piracy occurs through to use of the Internet services.
Ethical Issues: There are various ethical issues involved in information technology. In 1986, Masovi had classified ethical issues in the following four groups:
It involves the right of accessing the required information as well as the true payment of charges to access the information.
2. Privacy
It deals with the degree of privacy and dissemination of information about an individual.
3. Property
It talks about ownership and value of information.
4. Accuracy
The information which is viable and being accessed is now much more accurate and authentic.
The Computer Ethics Institute in Washington DC has laid down the following ten commandments of computer ethics:
a) You will not use computer to harm other people.
b) You will not interfere with the computer network of other people.
c) You will not snoop around in files of other people’s computer.
d) You will not use a computer to steal.
e) You will not use a computer to bear false witness.
f) You will not copy or use proprietary software for which you have not paid.
g) You will not use other people’s computer resources without authorization.
h) You will not use other people’s intellectual output.
i) You will think about the social consequences of the programme you are writing or the system you are designing.
j) You will always use a computer in ways that demonstrate considerations and respect for your fellow humans.
Q12) Give examples of unethical practices during the recruitment process of a company.
A12)
The following are examples of unethical practices during the recruitment process of a company:
1) Recruitment of known persons without assessing their abilities.
2) Recruitment on the basis of financial favours.
3) Recruitment of the relatives of other employees.
4) Recruitment based on the recommendations of friend, business associates.
a) and other persons close to the leader.
b) Recruitment of underqualified persons.
c) Recruitment of overqualified persons.
d) Recruitment of less acceptable men when there are better suited women available for the job.
e) Employing children below fourteen years for the job.
Giving less than minimum wages fixed by the government.
Q13) Explain ethical issue in technology.
A13)
Ethical Issues: There are various ethical issues involved in information technology. In 1986, Masovi had classified ethical issues in the following four groups:
It involves the right of accessing the required information as well as the true payment of charges to access the information.
2. Privacy
It deals with the degree of privacy and dissemination of information about an individual.
3. Property
It talks about ownership and value of information.
4. Accuracy
The information which is viable and being accessed is now much more accurate and authentic.
The Computer Ethics Institute in Washington DC has laid down the following ten commandments of computer ethics:
a) You will not use computer to harm other people.
b) You will not interfere with the computer network of other people.
c) You will not snoop around in files of other people’s computer.
d) You will not use a computer to steal.
e) You will not use a computer to bear false witness.
f) You will not copy or use proprietary software for which you have not paid.
g) You will not use other people’s computer resources without authorization.
h) You will not use other people’s intellectual output.
i) You will think about the social consequences of the programme you are writing or the system you are designing.
j) You will always use a computer in ways that demonstrate considerations and respect for your fellow humans.