2. Pervasive Function
Directing takes place at every level of the organization. Wherever there is a superior-subordinate relationship, directing exists as every manager provides guidance and inspiration to his subordinates.3. Continuous Activity
It is a continuous function as it continues throughout the life of organization irrespective of the changes in the managers or employees. Q2) State the principles of directing.A2)2. Principle of Harmony of Objectives:
According to this principle, there must be full coordination between organisational and individual objectives. Employees work in an organisation with an objective to get better remuneration, promotion, etc. On the other hand, organisational goal can be to earn more profits and to increase market share.Sometimes it is seen that there is a conflict between the objectives of both the parties, e.g., organisation wants that it should get a major share of profit whereas employees perceives that as they work directly on the job, so more profit must be shared among them in the form of bonus.Management here must establish coordination between the objectives of both the parties/factors by adopting suitable method of direction.3. Principle of Unity of Command:
According to this principle, a subordinate should get directions from one officer at a time. If the subordinate gets directions from more than one officer, the subordinate will be unable to priorities his work.As a result, situation of confusion, conflict and disarrangement is created. By following this principle, effective direction takes place.4. Principle of Appropriateness of Direction Technique:
According to this principle, appropriate direction techniques should be used, e.g., to supervise effectively, to provide able leadership, to adopt free communication and to motivate through right medium.5. Principle of Managerial Communication:
According to this principle, it should be monitored by the management that the subordinates get the same meaning for what has been said. This simplifies the job of the subordinates and they need not go to the managers repeatedly for enquiring.6. Principle of Use of Informal Organisation:
According to this principle, there must be a free flow of information between the seniors and the subordinates. The success of direction depends upon effective exchange of information to a great extent.Information should be given both through formal and informal mediums. Special attention should be given to the informal organisation. This strengthens the formal organisation.7. Principle of Leadership:
According to this principle, while giving directions to the subordinates a good leadership must be provided by the managers. By this, subordinates get influenced by the managers. In this situation, subordinates act according to the wish of the managers.8. Principle of Follow Through:
According to this principle, it must be monitored by management as to what extent the policies framed and issued directions have been enforced. Thus, it must be seen whether the employees are following the management or not.If yes, then to what extent. As per this principle, the job of managers is not to sit idle after framing policies or issuing directions but to continuously take feedback. The advantage of this will be that if there is any problem in implementing a policy or a direction it can be removed then and there. Q3) What is leadership traits and styles.A3)1. Vision
This quality separates them from managers. Having a clear vision turns the individual into a special type of person. This quality of vision changes a “transactional manager” into a “transformational leader.”While a manager gets the job done, great leaders tap into the emotions of their employees.2. Courage
One of the more important qualities of a good leader is courage. Having the quality of courage means that you are willing to take risks in the achievement of your goals with no assurance of success. Because there is no certainty in life or business, every commitment you make and every action you take entails a risk of some kind.Among the seven leadership qualities, courage is the most identifiable outward trait.3. Integrity
In every strategic planning session that I have conducted for large and small corporations, the first value that all the gathered executives agree upon for their company is integrity. They all agree on the importance of complete honesty in everything they do, both internally and externally.The core of integrity is truthfulness.Integrity requires that you always tell the truth, to all people, in every situation. Truthfulness is the foundation quality of the trust that is necessary for the success of any business.4. Humility
Humility doesn’t mean that you’re weak or unsure of yourself. It means that you have the self-confidence and self-awareness to recognize the value of others without feeling threatened.This is one of the rarer attributes – or traits – of good leaders because it requires containment of one’s ego.It means that you are willing to admit you could be wrong, that you recognize you may not have all the answers. And it means that you give credit where credit is due –which many people struggle to do.5. Strategic Planning
Great leaders are outstanding at strategic planning. It’s another one of the more important leadership strengths. They have the ability to look ahead, to anticipate with some accuracy where the industry and the markets are going.Leaders have the ability to anticipate trends, well in advance of their competitors. They continually ask, “Based on what is happening today, where is the market going? Because of increasing competitiveness, only the leaders and organizations that can accurately anticipate future markets can possibly survive. Only leaders with foresight can gain the “first mover advantage.”6. Focus
Leaders always focus on the needs of the company and the situation. Leaders focus on results, on what must be achieved by themselves, by others, and by the company. Great leaders focus on strengths, in themselves and in others.They focus on the strengths of the organization, on the things that the company does best in satisfying demanding customers in a competitive marketplace.Your ability as a leader to call the shots and make sure that everyone is focused and concentrated on the most valuable use of their time is essential to the excellent performance of the enterprise.7. Cooperation
Your ability to get everyone working and pulling together is essential to your success. Leadership is the ability to get people to work for you because they want to. Q4) What do you understand by the term motivation and state its importance.A4) Definition- Leadership captures the essentials of being able and prepared to inspire others. Effective leadership is based upon ideas—both original and borrowed—that are effectively communicated to others in a way that engages them enough to act as the leader wants them to act.Effective managers have the ability to motivate those they work with to behave in a specific, goal-directed way. Motivation is defined as energizing, directing and sustaining employee efforts.A motivated team should be energized and excited about performing tasks. They should be focused on doing what is important for the organization. Managers want a sustained effort from their employees so that they work hard whether or not the boss is present.It is equally important that effective managers understand how to influence people to perform specific behaviors and tasks they are likely to find mundane. A manager needs to be able to persuade workers to stay with the organization. Managers want workers to complete mundane tasks at times and always perform at a high level and be a good organizational citizen.With an effective motivational scheme in place, managers are much more likely to retain the most talented workers and dissuade them from leaving and going to a competitor.There are several reasons why employee motivation is important. Mainly because it allows management to meet the company’s goals. Without a motivated workplace, companies could be placed in a very risky position.Motivated employees can lead to increased productivity and allow an organisation to achieve higher levels of output. Imagine having an employee who is not motivated at work. They will probably use the time at their desk surfing the internet for personal pleasure or even looking for another job. This is a waste of your time and resources. Benefits of Motivated EmployeesEmployee motivation is highly important for every company due to the benefits that it brings to the company. Benefits include:1. Increased employee commitment
When employees are motivated to work, they will generally put their best effort in the tasks that are assigned to them.2. Improved employee satisfaction
Employee satisfaction is important for every company because this can lead towards a positive growth for the company.3. Ongoing employee development
Motivation can facilitate a worker reaching his/her personal goals, and can facilitate the self-development of an individual. Once that worker meets some initial goals, they realise the clear link between effort and results, which will further motivate them to continue at a high level. Q5) What do you understand by the term co-ordination state its importance with its features.A5) Coordination is the function of management which ensures that different departments and groups work in sync. Therefore, there is unity of action among the employees, groups, and departments.It also brings harmony in carrying out the different tasks and activities to achieve the organization’s objectives efficiently. Coordination is an important aspect of any group effort. When an individual is working, there is no need for coordination.Therefore, we can say that the coordination function is an orderly arrangement of efforts providing unity of action in pursuance of a common goal. In an organization, all the departments must operate a part of a cohesive unit to optimize performance.Coordination implies synchronization of various efforts of different departments to reduce conflict. Multiple departments usually perform the work for which an organization exists.Therefore, synchronization between them is essential. Lacking coordination, departments might work in different directions or at different timings, creating chaos. Features of coordinationCoordination is the integration, unification, synchronization of the efforts of the departments to provide unity of action for pursuing common goals. A force that binds all the other functions of management.The management of an organization endeavours to achieve optimum coordination through its basic functions of planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling.Therefore, coordination is not a separate function of management because management is successful only if it can achieve harmony between different employees and departments. Here are some important features of coordination:2. Objectivity:
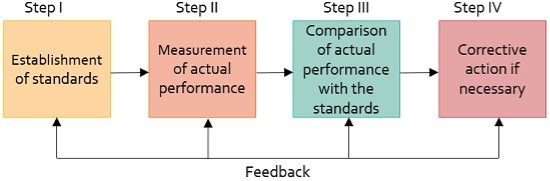
The standards of performance should be objective and specific, quantified and verifiable. They should be based on the facts so that control is acceptable and workable.3. Promptness:
The control system should provide information soon enough so that the managers can detect and report the deviations promptly and necessary corrective actions may be taken in proper time. Corrective measures are of no value if those are taken too late.4. Economy:
The control system must justify the expenses involved. In other words, anticipated earnings from it should be greater than the expected costs in its working. A small organisation cannot use the expensive control technique applied in large enterprises.5. Flexibility:
Internal goals and strategies must be responsive to the changes in the environment and the control system should be flexible enough to adapt the changing conditions or unforeseen situations. It should be adaptable to the new developments. Flexibility in control system can be introduced by making alternative plans.6. Accuracy:
The control system should encourage accurate information in order to detect deviations. The technique of control used should be appropriate to the work being controlled.7. Suitability:
Control must reflect the needs and nature of the activities of the organisation, the control system should focus on achieving the organisational goals.8. Forward-looking Nature:
The control system must be directed towards the future. It must pay attention on how the future actions can be conformed with the plans adopted.9. Focus on Strategic Points:
The control system should focus attention on strategic or critical deviations. Only exceptional deviations require the attention of the managers.10. Motivating:
A good control system should pay due attention to the human factor, It should be designed to secure positive action from the workers. Self-control tends to be motivated. Direct contact between the controller and the controlled also helps in making the control system motivational. Q8) Explain in detail what are the leadership styles.A8) Let’s now examine some of the most popular leadership styles-2. Autocratic leadership-
Autocratic or authoritarian leadership style emphasizes the role of the leader in terms of the decision-making process. The leader won’t involve or even consult the team when it comes to deciding the next course of action.The style is efficient in terms of making decisions, and can often be effective in crises or in circumstances where the leader has access to knowledge the subordinates don’t. Nonetheless, autocratic leadership style can also lead to high staff turnover.3. Democratic leadership-
Lewin’s second leadership style was the democratic model. Lewin’s style saw leaders under this framework still in charge of the final decisions, but instead of rejecting input from the subordinates, the leader seeks and encourages engagement. Therefore, the subordinates are more involved with the tasks or courses of action, even though they might not have actual power to decide.The democratic style can remove the issues of low morale and high turnover through the more participative approach. On the other hand, decisions can take a long-time to make and the subordinate’s ability to comprehend the intricacies of certain circumstances might not be equal.4. Laissez faire leadership-
The final leadership style Lewin identified was the laissez faire leadership. Under this framework, the subordinates are given the ultimate power to decide how they want to achieve the vision set forward by the leader. The leader’s role is essentially to provide the subordinates with the right resources and advice, if needed.Like the democratic leadership style, this can help increase job satisfaction, but the lack of structure can create problems within the organization. It also needs experienced and enthusiastic employees to work efficiently. Q9) Explain in detail the types of motivation.A9) There are four types of motivation that you’ll frequently see in the workplace. Each serves a different purpose and can be useful in unique ways. Here are four types of motivation you might find in the workplace:1. Affiliation motivation-
Affiliation motivation is the desire to belong to a certain group of people or an organization. If you are motivated by affiliation, you thrive when supporting or interacting with a team of other employees. You find it rewarding when you can contribute to a team effort or when you are considered a valuable member of a particular group. An employee who is affiliation motivated can be a benefit in the workplace because they strive to promote connections and relationships between people. Other positive results of affiliation motivation include:2. Competence motivation-
Competence motivation relates to an individual’s need to feel competent or capable. People who are motivated by competence work typically toward goals that involve education, training and knowledge. Competence motivation pushes students to ace classes, employees to achieve certification and professionals to master industry-specific techniques. In the workplace, you might be motivated to learn to operate a new software program not because you will be rewarded for it, but rather because you want to be able to list it as a professional skill on your resume. Companies might specifically provide opportunities for individuals who are competence motivated in order to focus on promoting highly-skilled employees. Employees who are competence motivated seek out opportunities to learn in the workplace and might take initiative when it comes to acquiring new skills. If you are competence motivated, you may be able to:3. Achievement motivation-
Achievement motivation involves the satisfaction that you gain when reaching a goal. Typically, the goal involves some sort of award or professional acknowledgment. People who are achievement motivated are not satisfied with a completed project unless it earns them some level of recognition. Achievement motivation is an extrinsic form of motivation because it requires outside sources in order to provide a sense of accomplishment. In the workplace, achievement motivation drives individuals to be goal-oriented in their work. Employees who are achievement motivated need to be able to anticipate future acknowledgment in order to remain engaged throughout a process or project. Examples of achievement motivation in the workplace include:4. Incentive motivation-
Incentive motivation involves working to earn predetermined compensation for above-average performance. Incentive motivation drives you to pursue a worthwhile reward in exchange for your time and effort. People who are incentive motivated work best when they know they will be appropriately compensated. Incentive motivation is an effective form of positive motivation that encourages success instead of punishing failure.In the workplace, incentive motivation involves managers or supervisors providing opportunities for employees to earn specific awards. This usually fosters a predominantly goal-oriented atmosphere. In some cases, each task that an employee accomplishes each day may count toward earning a certain reward. In other situations, employees might actively exceed expectations in order to qualify for compensation beyond their usual paycheck.Examples of incentive motivation in the workplace include: