FA7
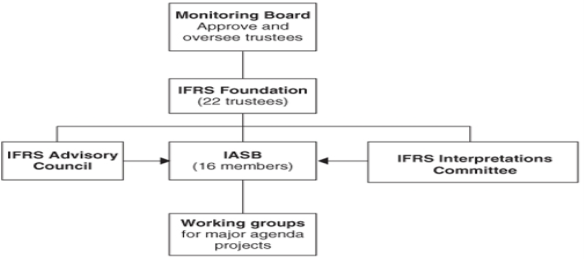
Unit 5Introduction to IFRS Q1) What is IFRS and its objectives?A1) International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are a bunch of global accounting standards expressing how specific sorts of exchanges and different occasions ought to be accounted for in budget summaries. IFRS are given by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), and they indicate precisely how bookkeepers should keep up and report their records. IFRS were set up to have a typical bookkeeping language, so business and records can be perceived from organization to organization and country to country. Objectives OF IFRS To create, in the public premium, a solitary arrangement of high caliber, justifiable and enforceable worldwide bookkeeping guidelines that require high caliber, straightforward and practically identical data in fiscal summaries and other monetary answering to help members on the planets capital business sectors and different clients settle on financial choices; To advance the utilization and thorough use of those guidelines; In satisfying the goals related with (1) and (2), to assess, as fitting, the exceptional requirements of little and medium-sized elements and arising economies. To achieve intermingling of public bookkeeping norms and International Accounting principles and IFRS to top notch arrangements. Q2) Explain Accounting standard along with its objectives.A2) Accounting standardsAccounting standards are legitimate guidelines for monetary detailing and are the essential wellspring of proper accounting rules (GAAP).Accounting principles indicate how exchanges and different occasions are to be perceived, estimated, introduced and uncovered in fiscal summaries. Their goal is to give monetary data to financial specialists, banks, loan bosses, givers, and others that is helpful in settling on choices about giving assets to the substance.Objective of Accounting Standards characterized by ICAI THE PRIMARY OBJECTIVE OF ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ARE: To give a norm to the different bookkeeping strategies and standards. To stop the non-likeness of fiscal reports. To build the unwavering quality of the fiscal reports. To give norms which are straightforward to clients. To characterize the norms which are tantamount over all periods introduced. To give a reasonable beginning stage to bookkeeping. It contains great data to produce the monetary reports. This should be possible at an expense that doesn't surpass the advantages. For the annihilation the tremendous measure of variety in the treatment of bookkeeping norms. To encourage simplicity of both between firm and intra-firm examination. The essential goal of accounting standards is to orchestrate the diverse bookkeeping strategies. The strategies are utilized in the planning of monetary reports. These reports could be set up by various undertakings. This would achieve a specific level of disarray at the hour of examination. This is the place where the accounting guidelines come in. The goal of bookkeeping guidelines is to carry a norm to the strategies. This will encourage simple correlation as for between firm and intra-firm announcing. Q3) Elaborate the advancement of Indian accounting standards.A3) Advancement of Indian Accounting Standards The ICAI perceives the requirement for a worldwide norm in these worldwide occasions. Accordingly, the Government of India alongside ICAI chose not to embrace the IFRS the manner in which they are. All things being equal, it presented the Indian AS, famously referred to as Ind AS. Allow us to investigate conclusion view at Indian AS; its set of experiences and a couple of its principle ideas. Indian AS The Institute of the Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) is the body that sets up the Accounting Standards in India. In 2006, ICAI started the way toward moving towards the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Global Accounting Standards Board (IASB) issues the IFRS. The reason for the ICAI to move towards the IFRS is to expand the agreeableness and straightforwardness of the fiscal reports of the Indian corporates on the worldwide stage. The public authority and ICAI originally investigated the prerequisites of IFRS in detail. They at that point chose to meet it. Bookkeeping Standards Board (ASB) has defined the Ind AS. It has made an honest effort to keep them in accordance with the IFRS. Just significant changes were made. The Central Government of India gave Indian Accounting Standards in counsel with the National Advisory Committee on Accounting Standards (NACAS). It did this under the oversight and control of the Accounting Standards Board (ASB) of ICAI. Indian AS (Ind AS) are IFRS merged guidelines. They are named and numbered similarly as their comparing IFRS. Public Advisory Committee on Accounting Standards (NACAS) prescribed these norms to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs. Service of Corporate Affairs (MCA) makes Ind AS pertinent on the organizations in India. So far 40 Indian AS have been given. The meaning of Indian Accounting Standards Ind AS depends on They encourage the cross-line stream of cash, worldwide posting and worldwide equivalence of the fiscal reports. This, thusly, encourages worldwide speculation and advantage to capital market partners. It improves the financial specialist's capacity to analyze the ventures on a worldwide premise. This, thusly, lessens the danger of misconceptions. It additionally dispenses with the expensive necessities of reestablishment of fiscal reports. Relevance of Indian Accounting Standards The Initial date of usage of Indian AS was 2011 yet because of specific issues, Ministry of Corporate Affairs delayed its execution date. In July 2014, the Finance Minister declared to apply Ind AS desperately. In February 2015, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs had given the Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules. It, along these lines, modified the guide of execution of Ind AS for organizations and avoided the Banking organizations, Insurance organizations, and NBFC'S from it According to the warning, from first April 2015, Ind AS will be actualized on a deliberate premise and will be required from first April 2016. Later on, it gave the guide for execution on NBFC's, Banking organizations, and Insurance organizations. Q4) Describe the International Accounting Standards.A4) International Accounting Standards (IAS) International Accounting Standards (IAS) are more established bookkeeping guidelines gave by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), an autonomous global standard-setting body situated in London. The IAS were supplanted in 2001 by International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Global bookkeeping is a subset of bookkeeping that considers worldwide bookkeeping principles when adjusting books. Understanding International Accounting Standards (IAS) Worldwide Accounting Standards (IAS) were the main global bookkeeping principles that were given by the International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC), framed in 1973. The objective at that point, as it remains today, was to make it simpler to look at organizations around the planet, increment straightforwardness and trust in monetary announcing, and encourage worldwide exchange and speculation. Worldwide tantamount bookkeeping guidelines advance straightforwardness, responsibility, and proficiency in monetary business sectors around the globe. This empowers speculators and other market members to settle on educated monetary choices about venture openings and chances and improves capital portion. Widespread guidelines additionally fundamentally diminish revealing and administrative expenses, particularly for organizations with worldwide tasks and auxiliaries in various nations. Q5) What is IASB’s role in developing IFRS?A5) Role of IASB in developing IFRSThe IASB is the free standard-setting body of the IFRS Foundation answerable for the turn of events and distribution of IFRSs and for affirming Interpretations of IFRSs as evolved by the IFRS Interpretations Committee. The Board is a free gathering of specialists with a fitting blend of ongoing down to earth insight in setting bookkeeping guidelines, in getting ready, evaluating, or utilizing monetary reports, and in bookkeeping schooling. Expansive topographical variety is likewise required. The IFRS Foundation Constitution diagrams the full rules for the structure of the Board, and the topographical portion can be seen on the individual profiles. Board individuals are answerable for the turn of events and distribution of IFRS Standards, including the IFRS for SMEs Standard. The Board is likewise liable for endorsing Interpretations of IFRS Standards as evolved by the IFRS Interpretations Committee (once IFRIC). Individuals are named by the Trustees of the IFRS Foundation through an open and thorough cycle that incorporates promoting opportunities and counseling applicable associations. The IASB initially had 13 full-time Board individuals, each with one vote. They are chosen as a gathering of specialists with a blend of involvement of standard-setting, getting ready and utilizing records, and scholarly work. At their January 2009 gathering, the Trustees of the Foundation finished up the initial segment of the subsequent Constitution Review, declaring the formation of a Monitoring Board and the extension of the IASB to 16 individuals and giving more thought to the topographical structure of the IASB. The IFRS Interpretations Committee has 15 individuals. Its brief is to give opportune direction on issues that emerge practically speaking. A consistent vote isn't essential all together for the distribution of a Standard, openness draft, or last "IFRIC" Interpretation. The Board's 2008 Due Process manual expressed that endorsement by nine of the individuals is required. IASB's Role Under the IFRS Foundation Constitution, the IASB has total obligation regarding all specialized issues of the IFRS Foundation including: Full caution in creating and seeking after its specialized plan, subject to certain conference necessities with the Trustees and people in general The readiness and giving of IFRSs (other than Interpretations) and openness drafts, following the fair treatment specified in the Constitution The endorsement and giving of Interpretations created by the IFRS Interpretations Committee. Q6) Explain the structure and framework of IASB.A6) IASB - Background and Structure The IASB was recently known as the International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC) until April 2001, when it turned into the IASB. The IASC was initially set up in 1973 and was the sole body to have both duty and position to give worldwide bookkeeping guidelines. In 2001, when the IASB took over duty regarding global monetary announcing, it took on the entirety of the IASC's principles (which were completely prefixed with 'IAS' – for example IAS 2 Inventories, IAS 10 Events After the Reporting Period). The IASB revised a significant number of the principles, yet then started to give its own guidelines, which were known as International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). This is the reason you see principles prefixed with IAS (IASC guidelines) and IFRS (IASB norms). The term 'IFRS' has become a to some degree nonexclusive term that alludes to all the guidelines (the two IAS and IFRS). The arrangement of the IASB is as per the following:
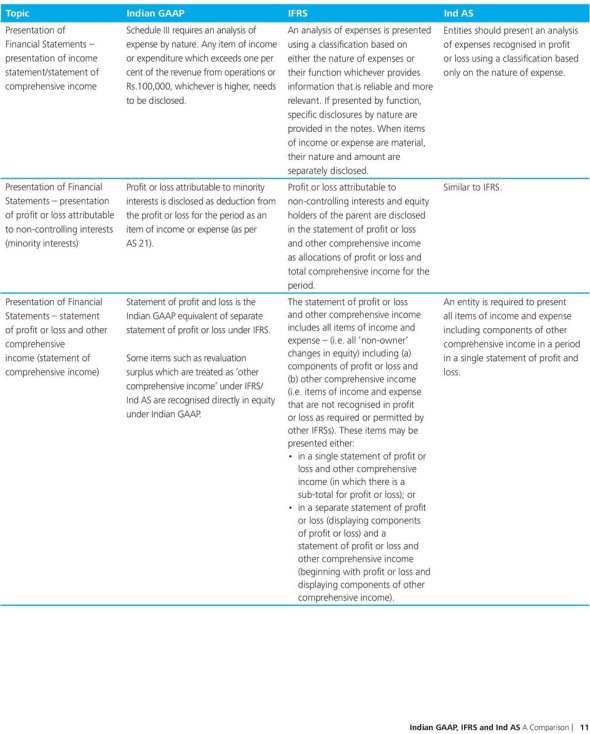
Standard Setting ProcessAccording to IASB a thorough, transparent and participatory due process is followed when issuing an IFRS Standard or an IFRIC Interpretation that helps companies better implement their Standards. Standard-setting entails:Public Board meetings broadcast live from their London office; Agenda papers that inform the Board's deliberations; Discussion and decision summaries that are made available after meetings; and Comment letters received on their consultation documents. IASB Conceptual FrameworkWhile the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) is not a country it does have a sort of constitution, in the form of the Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting (the Framework), that proves the definitive reference document for the development of accounting standards. The Framework can also be described as a theoretical base, a statement of principles, a philosophy and a map. By setting out the very basic theory of accounting the Framework points the way for the development of new accounting standards. It should be noted that the Framework is not an accounting standard, and where there is perceived to be a conflict between the Framework and the specific provisions of an accounting standard then the accounting standard prevails. The IASB Framework:Seeks to ensure that accounting standards have a consistent approach to problem solving and do not represent a series of ad hoc responses that address accounting problems on a piece meal basis Assists the IASB in the development of coherent and consistent accounting standards Is not a standard, but rather acts as a guide to the preparer of financial statements to enable them to resolve accounting issues that are not addressed directly in a standard Is an important and influential document that helps users understand the purpose of, and limitations of, financial reporting Used to be called the Framework for the Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statements Is a current issue as it is being revised as a joint project with the IASB's American counterparts the Financial Accounting Standards Board. Q7) Compare Indiad AS,IFRS and GAAP.A7)
Q8) State the difference between IND AS and IFRS.A8)
Q9) Short notes:a) Global Standardsb) Benefits of IFRSA9) Global standards for global marketsCurrent economies depend on cross-line exchanges and the free progression of global capital. In excess of 33% of all monetary exchanges happen across borders, and that number is required to develop. Financial backers look for expansion and venture openings across the world, while organizations raise capital, attempt exchanges or have worldwide tasks and auxiliaries in different nations. Previously, such cross-line exercises were muddled by various nations keeping up their own arrangements of public bookkeeping norms. This interwoven of bookkeeping prerequisites regularly added cost, multifaceted nature and eventually hazard both to organizations planning fiscal reports and financial backers and others utilizing those budget summaries to settle on monetary choices. Applying public bookkeeping guidelines implied sums detailed in fiscal summaries may be determined on an alternate premise. Unpicking this intricacy included contemplating the details of public bookkeeping norms, in light of the fact that even a little contrast in necessities could significantly affect an organization's accounted for monetary execution and monetary situation—for instance, an organization may perceive benefits under one bunch of public bookkeeping guidelines and misfortunes under another. Advantages of IFRS Standards IFRS Standards address this test by giving a high caliber, globally perceived arrangement of bookkeeping principles that bring straightforwardness, responsibility and effectiveness to monetary business sectors around the planet. IFRS Standards bring straightforwardness by upgrading the global equivalence and nature of monetary data, empowering financial backers and other market members to settle on educated monetary choices. IFRS Standards fortify responsibility by decreasing the data hole between the suppliers of capital and individuals to whom they have endowed their cash. Our Standards give data that is expected to consider the board responsible. As a wellspring of internationally tantamount data, IFRS Standards are additionally of fundamental significance to controllers around the planet. Also, IFRS Standards add to financial proficiency by assisting financial backers with recognizing openings and dangers across the world, along these lines improving capital portion. For organizations, the utilization of a solitary, believed bookkeeping language brings down the expense of capital and lessens worldwide revealing expenses. Q10) What is the need of IFRS in India?A10) International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are rule based guidelines as contrary to the standard based principles as of now in power; that sets up acknowledgment, estimation, introduction and divulgence prerequisites identifying with exchanges and occasions that are reflected in the fiscal summaries. IFRS was created in the year 2001 by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) to give a solitary arrangement of great, reasonable and uniform bookkeeping norms. IFRS in India India is one of the more than 100 nations that have or is very nearly merging with IFRS with the end goal of achieve a consistency in announcing frameworks universally, empowering organizations, funds, and assets to get to more freedoms. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) in its official statement dated 25th February 2011 had informed 35 Indian Accounting Standards united with IFRS (referred to as IND AS). The MCA will actualize the IND AS in a staged way after different issues (for instance charge related issues) are settled with the concerned divisions/specialists. However, there has been impressive deferral in the usage of these principles, endeavors are on the run. The recently modified Schedule VI which depends on IAS 1 is an away from of being hopeful on intermingling with IFRS. Need for IFRS in India Various global organizations are building up their organizations in different nations with arising economies and the other way around. The elements in arising economies are progressively getting to the worldwide business sectors to satisfy their capital requirements by getting their protections recorded on the stock trades outside their country. Capital business sectors are getting incorporated around the world. Increasingly more Indian organizations are additionally being recorded on abroad stock trades. Sound monetary detailing structure is basic for financial prosperity and powerful working of capital business sectors. Why union is needed in India? The point has consistently been to follow the IFRS, to the degree conceivable, while planning the Accounting Standards. Notwithstanding, deviations from IFRS have been made because of different unavoidable reasons as referenced beneath: 1. To keep up consistency with the Legal and Regulatory Requirements 2. Financial climate 3. Level of readiness 4. Applied contrasts Advantages of union with IFRS 1. Expansion in the development of business around the world. 2. Expansion in speculation and inflow of unfamiliar cash from abroad market 3. Data will be more dependable and equivalent as the Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Account will be readied utilizing a typical arrangement of bookkeeping guidelines (for example IFRS). Such data will assist financial backers with investigating venture openings effectively and rapidly as against the budget summaries arranged utilizing a neighborhood or distinctive arrangement of bookkeeping principles. 4. As IFRS is acknowledged around the world, union with IFRS will build financial backer's certainty. 5. Organizations will actually want to fund-raise from homegrown market as well as from abroad business sectors at lower cost if their fiscal summaries agree with worldwide acknowledged bookkeeping norms. 6. Heap of planning monetary revealing according to every nations necessity is decreased with the union of IFRS in light of the overall acknowledgment of IFRS. 7. Intermingling additionally lessens the expenses of setting up the budget summaries as just one bunch of fiscal reports should be set up rather than various arrangements of budget reports according to various nations prerequisite.
|
|
|
0 matching results found