Unit I
Origin of Indian Society
Question Bank
Q1) What is Indian society? (5)
A1) The question becomes difficult to answer as by the reason of Indian diversity. People of India do not have a common religion, race, language etc. The only thing that people in India share together is the identity of being Indian and the values prescribed under the constitution. India is a country of diversity and contrast. In order to know the characteristics of Indian society, it is necessary to know the multicultural and multidimensional characteristics of the people who live there. Its diversity is reflected in language, religion, caste, race, ethnicity, weather conditions, geographical features, historical heritage, clothing and eating habits
There are several other additional factors and variables that divide society into smaller pieces. There are significant differences in socio-economic and political development in rural, urban and tribal areas. India, unlike many other countries in the world, is not just a “melting pot” of diverse cultures, where people come together to switch to one uniform category. American culture envelops all inhabitants in her one unified identity. However, India's diversity is often identified as a "salad bowl" in which each of its citizens features different identities at different levels such as caste, language, religion, and region.
Indian society is a pluralistic society. Full of diversities of language, region, religion, caste and customs, Indian society is moving towards the modernization. The main values of Indian modernization model are-Socialism, Imperialism, Nationalism, Secularism, Industrialism, Democracy, Individual Freedom and Fundamental Rights.
Q2) ‘India as Multiculturalism’. Explain the statement. (7)
A2) Indian multiculturalism
According to the 1961 Indian Census, the country has 1652 indigenous languages. Indian culture has been shaped by its long history, unique geography and diverse demographics. Indian languages, religions, dances, music, architecture and customs vary from place to place in the country, but they still have something in common. Indian culture is a fusion of these diverse subcultures that span the Indian subcontinent and traditions of thousands of years ago. The Indian caste system explains the social stratification and social limitations of the Indian subcontinent. I will. Thousands of endogamy genetic groups, often referred to as Jati or caste.
Religiously, Hindus make up the majority, followed by Muslims. Statistics are Hindu (80.5%), Muslim (13.4%), Christian (2.3%), Sikh (2.1%), Buddhist, Bahai, Jain, Jewish, and Parsi populations. Linguistically, her two major linguistic families in India are Indo-Aryan (a branch of the Indo-European language family) and Dravidian. In north eastern India, people who speak Sino-Tibetan languages are common, such as Meitei (Meitei) and Austroasiatic languages, which are recognized by the Constitution of India. India follows (officially) a three-language policy. Hindi (spoken in the form of Hindustani) is the official language of the Commonwealth, English has a quasi / quasi-official federal status, and each state has its own official language (Hindi). In the linguistic sphere, this results in bilingualism). Moreover, India has no national language. The boundaries of the states of the Republic of India are drawn primarily on the basis of language groups. This decision led to the preservation and continuation of the local folk language subculture, with the exception of Hindispraum, which itself is divided into many states. As such, most states differ from each other in language, culture, cooking, clothing, style, architecture, music, and festivals.
India is religious, including the Mopra riots, the Bombay riots, the 1984 anti-seek riots, the 2002 Gujarat riots, the 2012 Assam riots, and most recently his 2013 Muzaffarnagar riots in Uttar Pradesh. I encountered motivated violence. This applies to communities that have traditionally been at a disadvantage in public employment, such as crackdowns in the same area, owners' insecurity in offering real estate for sale or rent, and social insecurity in accepting interracial marriages. It is due.
India has the largest population of some non-Indian religions, such as Baha'i Faith and Zoroastrianism.
A multidimensional society is one in which people from different origins, backgrounds, and beliefs gather to form a society and live in it. In this case, no one has any coercion or coercion to destroy the existing belief system and adapt it to the new system. Such societies are more or less based on the principle of "live and live." Even minorities are allowed to maintain their own different identities in the matter of differentiating them.
Q3) What do you mean by demography? (5)
A3) Demography is a systematic study of the population. Term is Greek .It is the origin and is composed of two words, demos (person) and graphic (describe). It means a depiction of a person. Demography studies trends and processes population-related – changes in population size, including: Pattern Birth, death, and migration. Structure and composition of population such as women, men, relative proportions of different ages group. There are different types of demographics, including formulas. Demographics, which are mostly quantitative fields, It focuses on the social, economic or political aspects of the population. All Demographic studies are based on the counting or enumeration process. As a census or survey – including systematic collection of data on people who live in the designated area.
Demography is a particularly important area for sociology. The emergence of sociology and its successful establishment as a discipline relies heavily on demographics. Two different processes happen to happen located in Europe at about the same time in the late 18th century century-Formation of the nation-state as the main form of politics the beginning of modern science of organization and statistics. Present day the state has begun to expand its role and function. For example actively interested in developing early forms of public health
Law and order management, crackdown, maintenance, economic policy Agriculture and industry, taxation and revenue generation, and Governance of the city. In this new and ever-expanding realm of national activity, systematic and regular collection of social statistics – or quantitative data on various aspects of population and economy. Collection practice national social statistics are much older in their own right,
Q4) How can you say that India is a multi- religionist .Explain different religion. (5)
A4) India is the birthplace of globalwide religions. Its ancestors have preached and practiced all of the principal religions on earth, growing secular ideals, customs, rituals, rituals, rituals and institutions. The coexistence of all religions and positive ideals is an excellent instance of non secular pluralism and tolerance. Despite a few conflicts and riots, the ideas of secularism had been again and again upheld through the public.
The Indian Constitution successfully displays the thoughts of multi-religiousists. It states that "each citizen has the proper to freely practice, preach, profess, and sell any faith or belief." A secular kingdom is described as "a kingdom wherein all religions and residents are dealt with fairly, no matter faith." Unlike its neighbors, India is a kingdom faith and consequently does now no longer assist a specific faith. Apart from the principal religions, a few tribal religions coexist in Indian society.
- Hinduism-Hinduism is one in every of her oldest religions in India. The majority of the populace continues, however its foundation isn't because of the prophets or founders. The important Hindu scriptures encompass the Vedas, so the scriptures encompass Bhagavad-Gita, Ramayan, and Prana. Idolatry, Purucharta's theory, Karma's theory, and the doctrine of rebirth are a number of the essential ideas of Hinduism.
They consider withinside the Trinity of Brahma (Creator), Vishnu (Maintainer), Mahesh or Shiva (Destroyer). It consists of 4 ideas: joy) and moksha. Hindus additionally have denominations, shaivism and vaishism, and 4 castes, Brahma and Kushatriya, defined later withinside the phase on Indian magnificence structure. , Vaisha, and Shudra.
b. Islam-Islam originated in Arabia across the seventh century AD. The Arabic time period Islam method give up to God. The Prophet Muhammad is the founding father of this faith. It is monotheistic and believes in simplest one god, Allah. The Quran is a Islamic scripture. This faith relies upon on his 5 pillars. They are Allah (believing in a single god), Ramadan (fasting withinside the auspicious moon), Hajj (pilgrimage at the least as soon as in a lifetime), catfish (praying him 5 instances a day), and zakat. (Charity). His important denominations of Islam are Shiites and Sunnis.
c. Christianity: Christianity is likewise a monotheistic faith. The Bible is a Christian scripture. They are similarly divided into Roman Catholic and Protestant. The important ideas of faith are set out withinside the Ten Commandments. The Bible consists of values of mankind, charity, mercy, repentance, and so on.
d. Sikhism: Guru Nanak is the founding father of Sikhism. Guru granth sahib is a Sikh scripture that consists of all of the hymns and songs composed through all his ten authorities of Sikhism. Sikhs consider in Satnerm, the Almighty God. A sect of Sikhs following KhalsaPanthare, known as Singh, that means lion or father or mother of faith. They are anticipated to observe his five Ks. That is, Kesh, Kara, Kanga, Kacha, Kirpan.
e. Jainism: Jainism is a faith primarily based totally entirely on moral conduct. The twenty fourth Tirthankara is Valdaman Mahavira, who's stated to be the founding father of Jainism. It is similarly divided into of his Digambara and Digambara. Jain believes in karma, however now no longer in caste inequality. Ahimsa (non-violence), non-stealing, truth, non-ownership are the various values that Jain preached. Most of the fans of this faith are in India.
f. Buddhism: Buddhism is known as a commonplace faith. Found in India, its fans are determined all around the globe. Gautama Buddha is the founding father of Buddhism. They are similarly divided into Hinayana and Mahayana. They consider in Noble Eightfold Path as a approach to the unhappiness of life.
Q5) What is caste system? (7)
A5) The caste gadget may be described as a social shape consistent with the elegance decided via way of means of beginning.
The caste gadget is a genetic class of human beings in society, distinguishing them via way of means of their relative diploma of social status or reputation. In the caste gadget, the reputation of someone is predetermined.
The social elegance that classifies human beings into one of a kind corporations known as "castes" is normally primarily based totally on a own circle of relatives tree. This gadget is called the caste gadget, wherein the social reputation is decided via way of means of beginning. No rely what sort of grownup you are, the beginning caste will now no longer change. The caste gadget commenced with a social class decided via way of means of human being’s professions. The historical caste gadget grouped human beings of the equal career beneath Neath her one elegance or "caste". This based social class is known as the caste gadget.
Being born in a selected social class in addition determines someone's manner of life, social habits, and paintings opportunities. This is the definition of the caste gadget. The starting place of the caste gadget may be primarily based totally on both spiritual ideals or positive historic influences, and is normally notion to be a aggregate of a couple of factors.
The Indian caste gadget is one of the oldest varieties of extant social stratification with inside the world. The BBC explains its complexity.
A gadget that divides Hindus into strict hierarchical corporations primarily based totally on karma (paintings) and dharma (Hindu for religion, however right here way duty) became greater than 3,000 years old. It is normally commonplace as a thing.
The concept of purity and pollution has led to some atrocities in the hierarchy against the bottom layer. Shudra and Atishdra (untouchables) faced tremendous injustice and atrocities by the hands of the top castes, especially the Brahmin. It is named after the dark ages of Indian history, where some inhumane and vicious practices were rampant in a society that denied the essential human rights of the oppressed class. Under the great leadership of Dr. Baba Saheb Ambedkar, they gained a special position as a designated caste in the Constitution of India. The term used for them was Dalit (depressed person) or Harijan (coined by Mahatma Gandhi). Baba SahebAmbedkar was a pioneer in launching the Dalit movement in India to raise the status of Dalits by converting to Buddhism, which does not believe in the caste hierarchy.
Q6) What are the features of caste system? (7)
A6) The capabilities of the caste system are as follows.
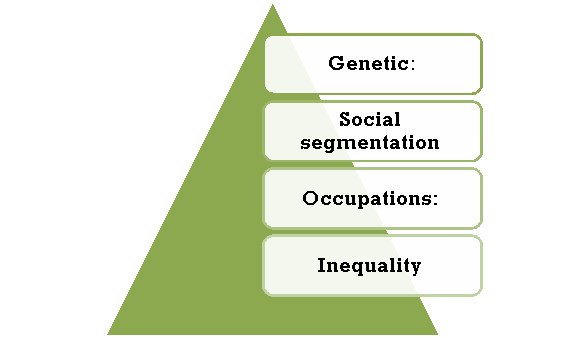
- Genetic: The caste machine is a genetic phenomenon. It might also additionally sound unfair in cutting-edge society, however the foundation of the caste machine turned into born. Because a character's caste is hereditary, it isn't always beneathneath the manipulate of the character and is pre-decided earlier than birth. In the olden days, in case you had been born right into a farmer's house, the caste machine of society required you to develop up and grow to be a farmer. Thus, this machine is taken into consideration a rigorous machine wherein human selections and dreams are limited / suppressed.
- Occupations: The caste machine turned into normally geared toward classifying societies primarily based totally on human beings's occupational specialties so that it will save you special segments of society from being combined together. The entire idea of "dignity of labor" turned into denied with inside the exercise of the caste machine. People with bad jobs had been regarded down on, and people with excessive-paying jobs had been worshiped.
- Social segmentation: The solid machine has divided society into diverse segments. This turned into supposed to organization human beings with comparable popularity. There turned into a clean difference among the wealthy and the bad, and those needed to restriction themselves best inside their caste. From marriage to socializing, interplay among castes turned into now no longer encouraged, and divergence from this norm turned into taken into consideration a punishable crime.
- Inequality: The caste machine preached inequality amongst human beings. People had been labeled as excessive caste and occasional caste and had been handled in another way in society. Caste hierarchies had been decided through their paintings and own circle of relatives history. High caste human beings loved all their freedom, whilst low caste human beings had been miserably handled through excessive caste human beings.
Q7) What can be the reason behind caste system? (8)
A7) The reasons of the caste machine are as follows.
- Discrimination through paintings capacity: The caste machine decided social popularity through the capacity to carry out paintings. Those who've a positive degree of labor capacity had been judged through their vocational capacity. For instance, locksmiths had been taken into consideration a decrease caste than commercial enterprise human beings.
- Maintaining hereditary professions: The caste machine decided human beings's profession selections. One turned into predicted to observe the direction in their ancestors and stick with hereditary professions. Children of uneducated cleaners had been now no longer loose to paintings apart from knowledgeable cleaners.
- The preference to advantage energy: The so-called "higher caste" human beings desired to advantage energy over the ones under the caste machine. The usual cause in the back of the advent of the caste machine turned into the sport of gaining energy in society. The rich and rich human beings of society desired to manipulate the susceptible elements of society.
- Feeling higher than others: The caste machine allowed human beings with better castes to have a experience of superiority over people with decrease castes. Castes belonging to the decrease ranks of the hierarchical ladder had been handled inferior through the ones better.
- Dominate Others: When there's inequality in society, the robust and the best have a tendency to dominate the susceptible. This is a regulation of nature, and the caste machine has given powers all of the freedom to make the most and rule the bad.
- To enhance social popularity: Humans are hungry for popularity and constantly need to overhaul every different in society. Thus, the caste machine has allowed human beings to keep their social popularity for generations. Born right into a better caste own circle of relatives, your complete extended family is destined to have a "better" social popularity with inside the exercise of the caste machine.
- To create worry amongst social groups: The caste machine concentrates energy amongst unique castes of society, and castes hold to create worry amongst human beings with decrease castes. The excessive caste human beings had been prepurported to dominate the low caste individuals who had been prepurported to stay in worry of the former.
- The want for finance, financial system and social safety: The monetary measurement performs a main position in instilling the caste machine in society. Once separated, the caste machine allowed better caste human beings to keep monetary and social safety for lasting generations. The complete own circle of relatives tree turned into covered from the social crisis.
- Marriage inside a closed sect and regulations for destiny generations: The caste machine seriously limited marriages among castes. The caste machine targets to keep the "purity" of caste and strongly restricts blending with different caste genes and marriage.
- Occupational Specialization: Cleaners (Shudra Castes) were categorised as low castes in step with their task description. This is a regular instance of the caste machine categorizing through occupation.
Q8) ‘Decreased sex ratios in children are a socio-economic problem’. Explain (7)
A8) Decreased sex ratios in children are a socio-economic problem, but the immediate cause is arguably the improper use of medical techniques such as pre-pregnancy and prenatal testing techniques (also known as sex-determining tests). Prenatal elimination of a female foetation, commonly referred to as a female fetal control agent. Another big reason is my son's taste. His son's tastes are deeply rooted in Indian society, strengthening patriarchal rule. This son's taste is usually justified for a variety of socio-economic or religious reasons. The financial justification is that the son inherits the father's property and is also a source of financial guarantee for old age. The religious purpose is that at least one of her sons is essential to perform the final ritual of the parents. The social benefit of having a surname in front of you and continuing your family line also plays an important role. However, the most important cause is bad dowry, which disregards girls as a parent's responsibility.
Some studies have shown that it is the wealthy and literate class of urban areas in society that is involved in sex-determination and sex-selective abortion. It is that access to small family norms and technology leads to dudu drowning of such vicious practices by this part of society. The belief-based sex ratio distribution revealed in 2001 that seeks had the most gender-biased sex ratio of 786 per 1,000 men, followed by the business community of Jaina (Jina). 870) continues. Therefore, economic prosperity has been proven to be inversely proportional to the sex ratio.
The future consequences of this issue are already beginning to appear in the rise of crime and violence against women such as trafficking, rape and sexual abuse. In states where women are scarce, such as Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Gujarat, and even Maharashtra, women in tribal areas are traded at low prices due to the lack of brides, and the value of women is worth it. It is even lower. In this proportion, India is ranked in the bottom half of the list of 134 countries in the Gender Development Index.
Some efforts have been made by civil society organizations, NGOs, scholars and some of the media, but government and legal agencies have not ended the current crisis. Welfare systems for women's empowerment should be combined with changing attitudes towards girls and strict enforcement of the law.
Q9) What are the features of rural areas? (5)
A9) The features of rural areas are:
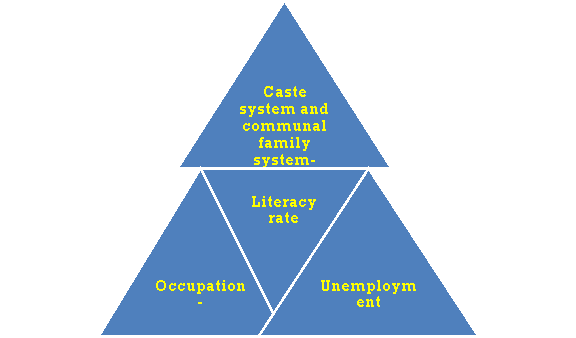
- Caste system and communal family system-The limits that underpin the rigidity, cleanliness and pollution of the caste system are essential rules of the rural social environment. An individual's status is set by birth in a particular caste and is not a situation in which an individual can climb a social status. Similarly, the joint family system strengthens patriarchy and patriarchal social organizations.
- Literacy rate-Due to traditional thinking and customs and the home of blind beliefs, local literacy rates are always less than 50% in most regions. This often leads to unemployment and poverty.
- Occupation-Agriculture is the backbone of the rural economy. However, reliance on monsoons and primitive technologies limits rural expansion and yields per hectare.
- Unemployment-There are seasonal and disguised unemployment due to the seasonal nature of agriculture and uneconomical land ownership.
- Low media exposure —— Due to poverty and high illiteracy rates, exposure to print and audio visual media is very low.
Q10) What are the features of urban areas? (5)
A10) Urban characteristics and challenges:
- Population Density-Her four metropolises in Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata and Chennai are the most densely populated, alongside some other cities.
- Literacy rate-Urban literacy rates often exceed 70%, which is usually above the national average.
- Occupation-Urban populations typically engage in secondary (industry) or service sectors such as banking, insurance, education and health.
- Unemployment — Despite the abundance of employment opportunities, high population density, computerization of the service sector and closure of the industrial sector lead to educated unemployment and layoffs.
- Pollution and lack of public health — High population densities create slum eruptions, lack of infrastructure and urban hygiene and pollution problems.
Q11) What are the features of tribal areas? (8)
A11) 1. Definite Common Topography:
Tribal humans stay in clean terrain and are a not unusual place region for all individuals of a selected tribe that occupy the region.
Without a not unusual place however clean region of lifestyles, tribes could lose different traits of tribal lifestyles, including not unusual place language, lifestyle, and network sentiment.
2. A feel of solidarity:
A institution that lives in a selected region and makes use of that region as a condo can not be known as a tribe with out a feel of solidarity. A feel of solidarity is an quintessential a part of authentic tribal lifestyles. The very life of the tribe relies upon at the feel of solidarity of the tribe at some point of peace and war.
3. Endogamy institution:
Tribal humans typically do now no longer marry outdoor the tribe, and marriage in the tribe is quite valued and admired. However, the approaching effect of extrade following mobility has additionally modified tribal attitudes, and tribal marriages are actually turning into an increasing number of not unusualplace.
4. General dialect:
Tribal individuals trade perspectives in a not unusualplace dialect. This detail similarly strengthens their feel of solidarity.
5. Blood dating:
Blood ties are the best bond and the maximum effective pressure that instills a feel of solidarity among tribes.
6. Consciousness of safety:
Tribal humans usually want invasion and safety from invasion, which establishes a unmarried political authority and offers all authority to this authority. Tribal safety is left to the talent and spirit of individuals who revel in political authority. In the occasion of an unexpected situation, the tribal leader might be assisted with the aid of using the tribal committee. The tribe is split into numerous small groups, every institution headed with the aid of using its personal leader. The institution leader will act in keeping with the commands acquired from the tribal leader.
7. Clear political employer:
Every tribe has its personal political employer that protects the pursuits of the humans of the tribe. All political authority is withinside the palms of the tribal leader. In a few tribes, tribal committees exist to assist tribal chiefs carry out their capabilities for the gain of the tribe.
8. Common lifestyle:
A not unusualplace tribe lifestyle comes from a feel of solidarity, a not unusualplace language, a not unusualplace religion, and a not unusualplace political employer. A not unusualplace lifestyle creates a homogeneous lifestyles among tribes.
9. Importance of kinship:
Relatives shape the premise of tribal social agencies. Most tribes are divided into exogamy clans and pedigrees. Marriage among tribes is primarily based totally at the guidelines of endogamy. Marriage is taken into consideration a settlement and does now no longer restrict divorce or remarriage.
10. Egalitarian values:
Tribal social agencies are primarily based totally at the precept of egalitarianism. Therefore, there may be no institutionalized inequality including caste gadget or gender-primarily based totally inequality. In this way, women and men loved identical fame and freedom. However, a few diploma of social inequality may be visible with inside the case of tribal chiefs and tribal kings who revel in better social fame, exercising political power, and own wealth.
Q12) What do you mean by diversity? (8)
A12) The concept of diversity includes acceptance and respect. It means understanding that each person is unique and recognizing our individual differences. These may be in line with race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, age, physical ability, religious beliefs, political beliefs, or other idealistic aspects. It is the quest for these differences in a safe, positive and nurturing environment. It is about understanding one another , and beyond simple tolerances, accepting and celebrating the rich dimension of diversity contained in each individual.
Diversity is a reality created by individuals and groups from a broad spectrum of demographic and philosophical differences. Support diversity to build a successful, collaborative and compassionate community that draws and creates intellectual power by valuing unbiased individuals and groups and fostering a culture of impartiality and mutual respect. And protection is very important. An innovative solution from the synergies of those people.
"Diversity" is more than just recognizing and tolerating differences. Diversity is a series of conscious practices that include:
Understand and understand the interdependence of humanity, culture and the natural environment.
Respect each other for qualities and experiences that are different from ours.
Understanding diversity involves not only how it exists, but how it knows it.
Recognize that personal, cultural and institutionalized discrimination creates and retains privileges for some while creating and sustaining disadvantages for others.
Build alliances across differences in order that we will work together to eradicate all sorts of discrimination.
Diversity therefore includes knowing how we relate to these qualities and conditions that exist in other individuals and groups, but not outside ourselves or the groups to which we belong. .. These include age, ethnicity, class, gender, physical ability / qualities, race, sexual orientation, as well as religious status, gender expression, educational background, geographical location, income, marriage history, parental status, and work. Included, but not limited to. Experience. Finally, recognizing that the categories of difference are not always fixed and can be fluid, respecting the individual's right to self-identification, one culture is inherently superior to another. I am aware that I am not.
Q13) Discuss the types of diversity. (8)
A13) Types of Diversity are :
Below is a list of the different types of diversity in the workplace.
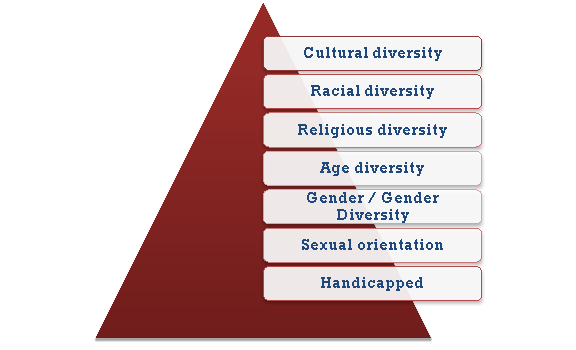
- Cultural diversity,
- Racial diversity,
- Religious diversity,
- Age diversity,
- Gender / Gender Diversity,
- Sexual orientation,
- Handicapped.
The breakdown of these forms of diversity is as follows:
- Cultural diversity
This kind of diversity is related to each person's ethnicity and is usually a set of norms derived from the values of the society and family in which we grew up. In multinational companies, it is more common to have different cultures in the workplace.
b. Racial diversity
Race is associated with grouping of people based on physical characteristics (despite the predominant scientific view that race is a social component and not biologically defined). Examples of races are Caucasian, African, Latino, and Asian.
c. Religious diversity
This kind of diversity refers to the existence of multiple religions and spiritual beliefs (including their lack) in the workplace.
d. Age diversity
Age diversity means working with people of different ages, and most importantly, generations. For example, millennials, GenZers, and GenXers can coexist in the same workplace.
e. Gender / Gender / Sexual Orientation
Gender and gender can be used in the traditional sense of male and female employees. For example, you may hear the term "gender balance" used by companies trying to achieve a balance of 50-50 between employees identified as male and employees identified as female. However, as gender is increasingly redefined, the term "gender diversity" may become more appropriate because there are multiple variations in gender and sexual orientation.
f. Handicapped
It includes a wide variety of disorders and chronic illnesses, from mental to physical. Companies often make reasonable accommodations to help people with disabilities integrate into the workplace, such as installing slopes for wheelchairs and providing mental health support. Some companies are coordinating the hiring process to ensure it is comprehensive.
Q14) Why is diversity important? (8)
A14) Diversity is important due to :
1. Increased acceptance, reduced discrimination
Promoting diversity is not only "tolerance", but the first step towards true inclusion and acceptance. By deepening contact, exposure, and communication with people different from us, we can learn how to relate to differences in ways that do not have to be problems, barriers, or threats. And by chance, you may find that people we thought were very different from us might actually have much more in common than they thought. Maybe. Familiarity with these differences (and commonalities) can shape and shift our perspective (see # 3), foster acceptance that promotes attribution, and reduce misunderstandings and prejudices that promote discrimination.
2. Become a global citizen
Experiencing diversity in our daily lives allows us to regularly come into contact with people, cultures, traditions and customs that are different from ourselves. Hopefully you will learn the skills to communicate and interact with unfamiliar communities, concepts, and belief systems, and thus gain a more mundane, balanced, and informed perspective. Not only can you promote your social development, but you can also deepen your true understanding of the world. This prepares you to be part of the global community, whether you're traveling to a new country, collaborating with people from different backgrounds, or reading about news events that have a huge impact on a different population. It will be ready.
3. Prospect
By listening to the experiences of others, you can shed light on a life different from your own and gain a new perspective. By contrasting one's struggles, needs and values with those of others, one can really begin to understand where an individual is coming from and empathize with their attitudes, behaviors and beliefs at a deeper level. (Through it allows you to gain a deeper understanding of yourself). Perhaps talking to a new person changes your mind, challenges your values that seem scary to our brain at the subconscious level, and the rewards of flexible thinking are many different for us. It's a life to see through the lens and experience the kaleidoscope of diversity. You need to provide a perspective.
4. Richer life experience
Diversity is a natural state for humankind. In fact, it depends on our survival. What if everyone around you was exactly the same as you in every respect? How easy can an illness wipe you out? And where is the fun of having a relationship with the exact same person as you? Groupthink may feel safer and more reliable, but it invites cognitive dissonance, one-dimensional ideas, and fairly limited conversation. We need new ideas, views and practices to inspire and inspire us and show us how others eat, celebrate and love! Therefore, it is important to recognize that diversity is absolutely essential to our survival, as well as to our prosperity.
5. Productivity
By bringing together people from different backgrounds and different life experiences, you can come up with ideas and perspectives that others have never thought of or noticed. Everyone has their own way of looking at problems, which is shaped by the individual experiences they have and the worldview they have. When tackling a problem, many interpretations and approaches can create creativity and innovation, rather than everyone drawing the same thoughts and conclusions. Thus, it is important to recognize the usefulness of diversity. It, after all, supports natural productivity and we can learn a lot from the natural world. But the productivity debate comes with user warnings ... Should productivity be prioritized over people's basic humanity and the way they appear as humanity? Do we want our heritage to be something that allows people to be themselves because it has helped capitalism, or does it want to accept diversity because it has helped social justice? Diversity productivity and business cases are undeniable, but they can still distract us for the real reason we have to live and breathe diversity ... Because that's right.
In summary, our differences combine to form a strong and beautiful global community. In the face of intolerance, discrimination and violence, we must not forget to spread the importance of diversity and respond to it with extreme affection that unconditionally values people.
Q15) Write about the classification of S. Guha. (5)
A15) In his book Tribal India, Nadeem Hasnain refers to the geographical distribution of Indian tribes drawn from observations by anthropologist B. S. Guha. Guha provided a theoretical system for classification based on the geographical distribution of Indian tribes. Guha categorized the geographical distribution of Indian tribes into three broad zones –
- North and northeast zones.
- Central zone. And
- Southern zone.
- According to Guha, the eastern frontier hills and sub-Himalayan region of India make up the north and northeast zones. This classification also includes tribal people from Tripla, Assam, and Manipur in the eastern part of the zone, as well as tribal communities in eastern Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, northern Uttar Pradesh, and eastern Punjab in the north. The zone is home to many tribal groups, including many subsections of the Naga people living around Nagaland, Tharu in Uttar Pradesh, and the Lepchas in Sikkim. In large areas, the population density is not as high as in other parts of India. Given the geographical characteristics of the region, most of the tribes here are engaged in terrace or slash-and-burn cultivation and face economic downturn.
- The central zone, also known as the middle zone, consists of mountainous areas and plateaus up to the Ganges Plain in the north and the Krishna River in the south. This zone is also separated from the northeastern zone by the space between Garo Hill and Rajimahar Hill. The tribal groups in this zone come primarily from Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Orissa, as well as the tribal communities of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, northern Maharashtra and southern Rajasthan. Some important tribal groups in this zone include Gondi, Bill, Kondobumuji, Biya, Santar and Munda. Most tribes in the area cultivate slash-and-burn, but some tribes such as Santar, Gondi, Munda, and Oraon employ cultivation to interact with local rural residents.
- The Southern Zone is south of the Krishna River from Winard to Cape Comorin. The tribal community is part of Andhra Pradesh, Travancoa, Kodagu, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Cochin. Tribal groups living in this zone include Toda, Elba, Centu, Panyan, Irura and Kurumba. Primitive tribes such as Kadar, Malbadan, Kanicker and Malaklavan are jungles along the travan core and Cochin range and are one of the most economically backward communities in the world. Most tribes in this zone collect food by hunting and fishing, with the exception of some tribes such as the Kota, Badagas, and Toda.
Hasnain states that Guha excluded tribes living in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in his system of classifying the geographical distribution of Indian tribes. Hasnine includes the tribes that live in these areas as the fourth zone of tribal groups such as Jarawas, Onge, Andaman, Nikobari, and Sentinel (Hasnine, 1999). Apart from tribal classification based on the geographical distribution of Indian tribes, tribal groups are classified based on the level of linguistic, racial, economic or occupational characteristics, local city groups and cultural distance from religion. Can also be based. Belief. However, with such classifications, some ambiguity can appear in some tribal categories, and in many cases clear demarcation is not always possible.