Unit V
Significant Aspects of Political Processes
Question bank
Q1) What is party system in Indian politics? (5)
A1) The party system is the basis of democracy. It's a link between people, and thus the government. Political parties are a platform for people with a common idealism. All political parties aim to compete in elections to become part of the government's legislative and executive bodies. By representing the parliament, party members act as individual agents and express social dissatisfaction and challenges.
Q2) What are the features of political parties in India? (5)
A2) Characteristics of the party system in India
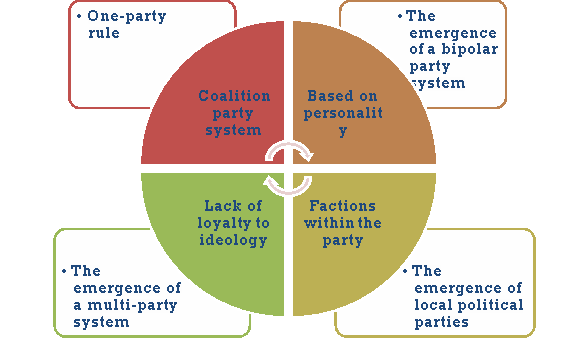
- One-party rule:
The party system was introduced in India as an influence of Western education. Indian leaders recognized the importance of united efforts to achieve independence. Therefore, political parties were established to demand reforms from the British government and eventually full autonomy. Various political parties emerged before independence, but one of the most popular and dominant political parties remained the Indian National Congress (INC). After independence, Congress dominated the political scene until her late 1980s, except for a short period in the late 1970s. Parliamentary leaders such as J. Nehru, Indira Gandhi, and Rajiv Gandhi have dominated Indian politics for many years. Many other parties were born during this period, but Parliament was considered the country's largest representative party.
b. The emergence of a multi-party system:
Internal factions caused divisions within parliament, and by the 1970s many new political parties were born. In 1977, the Janata Party, a coalition of at least five parties, was formed. This new party formed the first non-parliamentary government after independence. The increase in the BJP and many regional political parties in the state has significantly reduced Parliament's dominance over Indian politics.
c. Coalition party system
The era of coalition began in the 1990s. A large number of small parties were at the forefront as large national parties such as Congress and his BJP failed to win a majority of seats in the elections. Larger parties have become dependent on smaller parties in the formation of government. The 1996 elections formed the United Front, a coalition of up to 13 political parties. Similarly, in 1999, the National Democratic Alliance (NDA) coalition government was formed, with BJP becoming the largest member of the coalition.
d. Based on personality:
Instead of emphasizing a strong organizational structure, more emphasis is placed on party leaders and strong personalities. Many of us attend parties because of the charisma of the former leader. Balasaheb Thackery, Mamata Banerjee, Mayawati, Jayalalitha, Lalu Prasad Yadav and more.
e. Lack of loyalty to ideology:
All political parties depend on some ideology, and when people join the party, they commit to that ideology. But things are changing rapidly. Most parties are interested in gaining power. Many candidates ignore the idealistic commitments of political parties and switch between political parties to gain position within the government.
f. The emergence of local political parties:
One of the reasons for the declining power of national political parties is the emergence of political parties at various regional levels. Did the selfish motivation and desire to seize power encourage many politicians to form independent political parties? Each state has nearly a few powerful regional parties. Tamil Nadu became the home of his DMK and AIAD MK. Punjab is dominated by Shiromani Akali Dal. Shiv sena may be a powerful party in Maharashtra. National competitions are popular with Jammu and Kashmir.
g. Factions within the party:
Clashes of personalities, competition for power, and conspiracies with each other have weakened the party. Frequent party changes have increased the number of factions within the party. Caste and regional loyalty also contributed to the further division of the party.
h. The emergence of a bipolar party system:
By the 1990s, one-party rule was over and a coalition government was born. The politics of the alliance led to the polarization of political parties. It reflects a variety of political interests. Local parties play an important role in the formation of government in the center. People outside the parliament also became popular as a local political party and became a viable option. The rise of the BJP and the United Front, led by the BJP, created a second "pole" in Indian politics and dominated the center. However, Sonia Gandhi's aggressive political entry has returned Congress to the right option. The formation of the United Progressive Alliance (UPA), and thus the recent rule of the central government by a parliamentary coalition government, has transformed India's politics into a polarized party system.
Q3) What is Municipal Corporation? What are its functions? (7)
A3) Municipal Corporation:
This became first delivered with the aid of using the British in Madras in 1688, now no longer with the aid of using Bombay and Calcutta with the aid of using 1762.
The 1992 regulation introduced cohesion to neighborhood governments. Local governments had been installed in fantastically urbanized regions, neighborhood authorities councils in smaller city regions, and Nagar Panchayat in regions withinside the transition from rural to city regions. The kingdom legislature is empowered to enact law referring to the capabilities and powers of neighborhood governments.
The municipality is made of councils, the representatives of every ward are elected with the aid of using human beings known as councilors, and the time period of workplace is 5 years.
The mayor and deputy mayor are elected with the aid of using the councilors for a time period of and a 1/2 of years. They revel in outstanding honor withinside the metropolis. The mayor is taken into consideration the primary citizen of the metropolis.
MPs and MLAs are ex officio individuals of the agency.
The Chief Executive Officer is appointed thru the Indian Administrative Service (IAS), known as the Secretary of State for Local Administration. The whole govt department is moreover appointed with the aid of using the kingdom.
The agency additionally nominates a number of the residents decided on as its individuals.
Municipal function
This consists of numerous responsibilities that groups perform to make certain the general improvement of the metropolis, along with economics, society, fitness and hygiene, and infrastructure. Some of them are indexed as follows:
Mandatory function:
1. Hospitals, street sanitation, protection of city drainage,
2. Water deliver for public and private purposes,
3. Provision of scientific facilities, public vaccination and ailment prevention,
4. Establishment of hospitals and toddler welfare centers,
5. Providing avenue lights, cleansing rubbish on city roads,
6. Birth registration, loss of life registration,
7. Maintenance of bridges and public facilities,
8. To enhance the college and offer number one education,
9. Street naming and avenue and residence numbering,
10. Maintenance of energy deliver,
11. Providing transportation to the city.
Q4) What are the salient features of 73rd amendment ? (5)
A4) The 73rd amendment passed in 1992 and gave the Panchayati Large Organization a constitutional status. Its salient features are:
- A unified three-layer structure for Panchayat Raj has been created. That is, ZillaParishad at the district level, PanchayatSamiti at the intermediate level, and Gram Panchayat at the village level.
- All Panchayati level seats are elected for a five-year term.
- Scheduled seats for scheduled castes and tribes.
- Her 33% reservation for women's seats in these municipalities.
- State election committees must be established in all states to conduct and manage smooth elections for Panchayati.
- Appointment of the National Finance Commission to develop recommendations on Panchayati's financial authority.
- Establish a district planning committee to plan the development of the district.
- Formation of "gram mackerel" that will bring about the necessary changes in the village.
Q5) Mention the main rules organised in 74th amendment act. (5)
A5) The main rules are as follows.
- Formation of three types of municipalities. Municipal Corporation, Municipal Council and Nagar Panchayat.
- Appropriate representatives for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Lower Classes and Women.
- In addition, Article 12 of the Ordinance lists 18 subjects under the jurisdiction of the municipality.
- Greater financial and functional responsibility to local governments.
- Composition of the National Finance Committee, which reviews the financial condition of local governments and proposes measures to improve the financial condition.
- Regular and fair elections.
- Establishment of a ward committee, district planning committee, and metropolitan planning committee to prepare for development plans.
All of the above provisions aim to make local governments an efficient means of local administration. Several state governments have amended the law to bring unity with the constitutional provisions, in line with Amendment 74.
However, the state government is delegated final decision authority.
Q6) What are the obstacles faced by women participation in politics? (8)
A6) Obstacles Women Face in Participation in Politics:
- Male domination:
The idea of male domination is one of the main obstacles for women, as politics is considered an area of male interest and ability. Participation in politics takes time, so lacks family support and cooperation Attend party meetings, organize workers, and carry out various activities to support the party to support the party's masses Women who need to be gathered are required to stay away from home for extended periods of time. In such scenarios, women face opposition from their families.
b. Political party role:
Many political parties have not been able to provide enough representatives for women. They are less likely to get them involved in the party's organization. Party to run for election Men are prioritized when handing over her tickets. If the party has a low chance of winning, those tickets may be offered. Even after the election, political parties do not want to provide women with parliamentarians with an important portfolio. Thus, political parties also serve as a hurdle in the active participation of women in politics.
c. Political corruption and criminalization:
Political and election competition has become a costly issue these days. Election corruption and obstruction of election booths are the methods many use. Many criminals are entering politics because they need huge amounts of money. Women are not considered suitable for this changing political climate.
d. Approach of government officials:
The elected members need to meet government officials so as to fulfil the promises to the electorate. However women representatives often face non-cooperation from the govt. Officers because of their biased approaches towards women which causes hurdle in their work and reduces their efficiency.
e. Poverty, Unemployment and Illiteracy:
Poverty is the major problem faced by India and women’s condition is even worse because the unemployment rate is high among women. Many women work in unorganized sector and hence are paid low wages. Literacy rate is also low just in case of women as compared to men. Such issues are the main obstacles in her political growth.
f. Psychological Barrier:
In general it's been observed that because of all above factors they need low self-esteem and lack confidence in themselves. Many women accept that politics is man’s world and they haven't any role to play in it. The traditional approach of members of the family as well as their own beliefs stops them from participating in active politics.
Q7) What is the role of women in the municipality? (5)
A7) The role of the girl in the municipality:
After the passage of the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Bill in 1992, the number of female representatives at the grassroots level has increased by nearly 50%. A pioneering effort in this direction was made in 1983 by the state of Karnataka by offering reservations for Panchayati-level women. In some states, such as Madhya Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Bihar and Jharkhand, women's participation in Panchayati has increased to 50% of hers. The female members of Panchayati have made remarkable achievements in improving the situation of villagers in terms of medical care, education and hygiene.
Q8) Write a short note on Local Self Government. (8)
A8) Local autonomy, unlike imperial autonomy, which is the administration of the whole country, means that the people themselves manage the administration of villages, towns, districts, and prefectures through elected representatives. Elected central government.
For example, in England, parish purely local issues are managed by the elected Parish Council, towns are managed by the Town Council or businesses, and counties are managed by the Country Council.
All of these different councils are elected from time to time by the people of the parish, town and county and manage all local issues unrelated to the central government.
British history shows that local autonomy historically precedes national autonomy and is a school where national autonomy is learned. It dates back to the ancient Anglo-Saxon era.
When the Saxons, Angles and Jutes conquered Britain, they brought their own political system. Although each tribe recognized the authority of wartime leaders, all Saxons were free and accustomed to autonomy in all local affairs.
They had a town mood (mout means a meeting or rally), a hundred mute, and a general rally of a tribe called folk mood.
These local governments were established in the United Kingdom. As a result, the British have been accustomed to governing themselves on local issues for 2,000 years. In the Middle Ages, the town was mostly self-governing, had a privileged charter, and recognized its own privileges and powers.
The country's autonomy was a much slower growth. The British Parliament was formed only after the reign of Edward I at the end of the 13th century.
Parliament came to true control in 1688. And it wasn't until 1832 that Congress actually began to represent the people.
English became such an expert in national autonomy, as they were first trained in local autonomy for centuries.
India has undoubtedly benefited from the victory of British democracy. I know that autonomy is an art, an art that can only be learned by experience.
Those who are unable to manage village, town, district, or local issues cannot wish to manage kingdom or empire issues. They must learn the art of autonomy through experience before they can expect to succeed in national autonomy.
With the advent of Gandhi in politics, the idea of autonomy became deeply rooted in the country. Municipal enterprises gradually developed and by the time independence was finally achieved, India was ready to face her new obligations and responsibilities on the issue of autonomy.
Q9) Explain the salient features of 74th Amendment Act. (12)
A9) The salient features of this law are:
1. Three types of municipalities:
The law provides for three types of municipal constitutions in all states:
(A) Nagar Panchayat (whatever the name is) in the transition area, that is, the area in transition from the rural area to the urban area.
(B) Smaller urban municipalities.
(C) Municipal corporations in metropolitan areas.
A transitional area, a smaller urban area, or a larger urban area means an area that the Governor may publicly specify for this purpose with respect to the following factors:
(A) Population in the area.
(B) Population density.
(C) Income generated for local administration.
(D) Percentage of employment in non-agricultural activities.
(E) Economic significance or other factors that the Governor deems appropriate.
2. Configuration:
All members of the municipality shall be directly elected by the people of the municipality. For this purpose, each municipality shall be divided into territorial components, known as wards.
The state legislature may provide an electoral system for the chairman of a local government. We may also provide on behalf of the following persons within the municipality:
I. A person who does not have the right to vote for a local government meeting and has special knowledge or experience in local government administration.
II. Members of Lok Sabha and the state legislative assembly represent members of the municipality, in whole or in part.
III. Rajya Sabha and members of the State Legislative Council have been registered as electors in the local government.
IV. Chairman of the committee (excluding ward committees).
3. Ward Committee:
Within the territory of a municipality with a population of 30,000 rupees or more, a ward committee consisting of one or more wards will be established.
The Legislature can make provisions regarding the composition and territory of the Ward Commission and how to fill the seats of the Ward Commission. In addition to the ward committee, you can also specify the composition of the committee.
4. Seat reservation:
The law provides for reserved castes and seats for designated tribes in all municipalities, depending on the proportion of the total population of the municipality.
In addition, it is possible to make reservations for more than one-third of the total number of women's seats (including the number of women's seats belonging to SC and ST).
The state legislature may stipulate how to reserve a municipal chairman's office for SC, ST, and women.
It may also require reservations for seats in any municipality or the office of the chairman of the municipality in support of the younger class.
5. Municipal period:
The law provides for a five-year term for all municipalities. However, it can be disbanded before the end of the period.
In addition, new elections to form a municipality shall be completed (i) five years before the expiration of that period. Or (ii) In the case of dissolution, before the expiration of the period of 6 months from the date of dissolution.
6. Disqualification:
If you are elected to a municipality or disqualified because you are a member of a municipality
(I) Under the law in force for the time being for the purpose of electing the legislature of the country concerned. Or (ii) based on legislation enacted by the state legislature.
However, if you reach the age of 21, you will not be disqualified for being under the age of 25. In addition, all disqualification questions shall be referred to the authorities determined by the state legislature.
7. State Election Commission:
The preparation of the electoral list and the supervision, direction and management of all local elections shall belong to the State Election Commission.
8. Privileges and functions:
The legislature can give local governments the authority and authority they need to enable them to function as autonomous bodies.
Such plans may include provisions for delegation of authority and responsibility to local governments at an appropriate level with respect to: (I) Preparing plans for economic development and social justice. (Ii) Implementation of schemes for economic development and social justice, including those related to the 18 items listed in Schedule 12.
9. Finances:
The Legislature may (i) allow local governments to collect, collect, and make appropriate taxes, tariffs, tolls, and fees. (Ii) Allocate taxes, tariffs, tolls and tolls collected and collected by the state government to local governments. (Iii) Provide subsidies from the State Consolidated Found to local governments. (Iv) Prescribe the composition of funds for crediting all local government money.
10. Finance Commission:
The Finance Commission (composed for Panchayati) shall also review the financial position of the local government every five years and recommend to the Governor that:
(I) Principles that need to be managed:
(A) Net income from distributions between states and municipalities, state taxes, tariffs, tolls and fees.
(B) Determination of taxes, tariffs, tolls and charges that may be assigned to local governments.
(C) Subsidies from the state integrated fund to local governments.
(Ii) Measures necessary to improve the financial condition of municipalities.
(Iii) Other matters referred to the Finance Commission by the Governor for the sound finances of local governments.
The Governor shall submit the Commission's recommendations along with a report of the measures taken before the Legislature.
The Central Finance Commission shall also propose the necessary steps to increase the state's integrated fund to supplement the financial resources of the state's local government (based on recommendations from the state's Finance Commission).
11. Account audit:
The Legislature may make provisions regarding the maintenance of accounts and audits of such accounts by local governments.
Applicable to Union Territory:
The President of India may direct that the provisions of this law apply to all Union Territory subject to exceptions and amendments that he may specify.
12. Excluded areas:
This law does not apply to the planned and tribal areas mentioned in Article 244 of the Constitution of India. It shall not affect the functioning and authority of the Darjeeling Luca Hill Council in West Bengal.
Q10) Write a critical note on political party in India. (5)
A10) Political parties are one of the earliest available and visible institutions in democracy.
A political party is a group of people who gather on a common platform to oppose elections.
Political parties have three components: leaders, active members, and followers.
The main functions of political parties are to challenge elections, propose policies and programs, enact laws, form governments, act as opposition parties, share public opinion, and engage in welfare activities.
Political parties are needed to lay the foundation for a strong representative democracy. There are many political parties in the country so that people can choose.
There are two types of political parties. There are nationwide representatives and regions that are limited to only one region. INC, BJP, BSP, CPI (M), CPI, NCP are recognized as the Nationalist Party of India.
Since the birth of the coalition government in India, the number of local political parties has increased rapidly in India.
Political parties face many challenges, including a lack of internal democracy, inheritance of the dynasty, money and strength, and a lack of meaningful choices in front of people.
States parties need to promote internal democracy, increase the number of women represented, and reform through funding the state's o1 elections. Only then can democracy thrive in multiple democracy like India.
Q11) Write a short note on significance of Panchayati Raj. (5)
A11) The Panchayati system has achieved many important achievements in its achievements. No other developed country has given locals more responsibility to implement development programs than India.
Politically, the Panchayati system has made the average citizen more aware of his rights than before.
This system has greatly helped remove the element of fear from the hearts of the local people. Now they approach the BDO and talk freely about the issue with confidence. Competitive elections politicized the village and the system strengthened the institutional capacity of local governments for economic development and democratic participation in rural areas. Rajni Kothari said: Parliamentary politicians, and gradually politicians from other parties, are beginning to realize the potential of the new system. They often prefer positions in Panchayati Samitis and Zillaparishad to being elected to the state legislature. "
As far as the administrative implications of the Panchayati system are concerned, it has closed the gap between the bureaucratic elite and the people. Socially, the Panchayati system has created new leadership with a modern and pro-social perspective. Finally, from a developmental point of view, the Panchayati system has allowed rural people to foster a progressive outlook.
Q12) Explain Indian Political Structure. (5)
A12) The Constitution of Independent India got here into impact on 26 January, 1950. With its adoption India formally have become a Sovereign Socialist Secular Democratic Republic. The Indian Constitution has installed a parliamentary form of authorities each on the Centre and consequently the State.
Though the President is the top of the government, the actual powers are vested with the cupboard and consequently the Prime Minister who're accountable to the Loksabha. Similarly Governor is that the government head of the States, however the actual powers are exercised via Chief Minister and his Council of Ministers, who're accountable to the legislative meeting. The contributors of Loksabha and State legislative assemblies are elected via elections via way of means of residents of the country. Hence elections are the bottom for the formation of governments. Therefore the political events who contest the elections emerge as element and parcel of political device of the country. In India we have got multi-birthday birthday celebration device to ensure the illustration of numerous types of folks that live in it. We shall now extensively talk the birthday birthday celebration device in India.
Q13) Discuss types of Political Parties in India. (8)
A13) Political parties or party systems fall into three main categories.
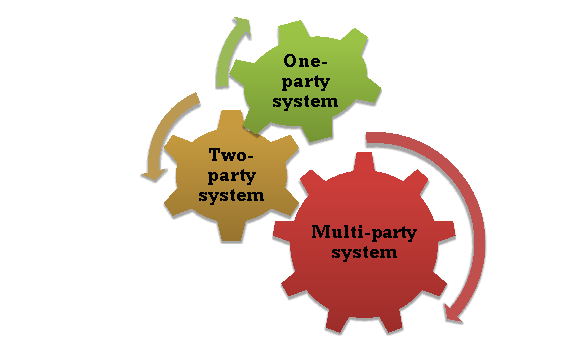
One-party, two-party or two-party, and multi-party.
I. One-party system:
The one-party system is also called the one-party system. It exists in a society where there is only one omnipotent and popular political party.
In such a system, political power is continuously used by one political party. During the election, the party will have several unique candidates, one of whom will be represented by the public. No other party can exist without the consent of this party.
Opposition parties are considered useless and harmful. Single ruling party policies and programs are considered to be the best national policies and programs. In such a system, there is no opposition. According to Curtis, "one-party is characterized by a powerful party that controls all other groups or oppresses all opposition groups. A single, all-powerful party is another party. When you do not allow yourself to live or act against you …it is called a holistic one-party system.
The Italian Fascist Party and the interwar German Nazi Party were totalitarian single parties that dominated the political life of their respective states. Military rulers and coup leaders who seize power through the revolution often organize a single party of carefully selected men and domination. In a communist country, there is only one party, the Communist Party. No other party can exist without its consent. China has a one-party system.
II. Two-party system or two-party system:
A two-party system exists with only two very popular parties, or with two major parties and some other minor or less influential parties. Each of the two major political parties sometimes has the opportunity to rule.
In some political systems, where there are only two political parties, the power is used to swing the pendulum from one party to the other at regular intervals. In some other parties that have adopted a two-party system, the two major parties occasionally share power, but other minor parties also have the opportunity to partner and govern one of the two major parties. There is.
In other words, in a two-party state, two parties dominate the political life of the people. There are bi-party systems in the United Kingdom, the United States, Belgium, Luxembourg and Ireland. In Britain, the Labor Party is currently in power and the Conservative Party is against it.
Prior to this, the latter was in power and the former was against it. Both of these are the two major political parties in the United Kingdom. As a result, Britain has a true two-party system. The two-party system is also functioning in the United States. The two major US political parties are Democrats and Republicans.
III. Multi-party system:
In a multi-party system, there are several parties that are just as popular in the party system. Several political parties are actively involved in politics. In such a system, few one-party systems are clearly in a position to win an election majority. Several political parties run the government together.
In other words, a multi-party system means that there are some popular and active parties (three or more, three parties) in the political process. People are members of several political India, Switzerland, Japan, Italy and France, and show four typical examples of a multi-party system. Parliament, BJP, CPI, CPM, BSP, NCP, BJD and several other political parties were active actors in Indian politics. Various political parties are exercising power in India. In India, the multi-party system is primarily responsible for the emergence of coalition politics.
Political instability continues to be a chronic feature of the Italian and French political systems. In Italy, coalition partners such as communists, socialists, democratic socialists, and Christian democrats continue to be involved in conflict, and their actions maintain an environment of ongoing political instability. Therefore, the establishment of a government was a very problematic issue.
In France, socialists, communists, Gaullist, liberals, and republicans are the main multi-party parties. "For years, the French coalition has been a source of political instability. The Fifth Republic's Constitution seeks to overcome this problem by creating a mixture of parliamentary and presidential systems. The latter is to ensure political stability through the directly elected and powerful head of state, the President of France. "
Switzerland also has a multi-party system with the Social Democratic Party, the Social Democratic Party, the Liberal Democratic Party, and the Communist Party as the main and equally influential parties. However, in a Swiss known businessman-like approach, the multi-party system did not result in political instability. Because these parties maintain a struggle for power and are managed to keep the political system from becoming unstable. All four major Swiss political parties share political power together.
The two-party system is considered the best and the one-party system the worst.
A two-party system that is considered to be the best. The one-party system is considered undemocratic because of its limitations and hindering people from enjoying freedom of association and freedom of action. It contains bacteria of centralization and dictatorship.
Q14) Write the functions of Municipal Council. (12)
A14) After the enactment of the 12th Schedule by the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act, the city council was assigned the following 18 subjects:
1. Plan: Creation and implementation of urban development plans.
2. Land use regulation and building construction:
We will prepare the articles of association regarding the proper use of land and undertake the construction of the building.
3. Economic and social development plans:
The city council is also tasked with implementing and implementing plans for the economic and social development of the city's inhabitants.
4. Road and bridge construction and maintenance:
The city council builds roads and bridges in the area for repair and maintenance work.
5. Household, industrial and commercial water supply:
It has the power to provide a clean drinking water supply for the area. It is to prepare for the supply of water for industrial and commercial purposes.
6. Public health and hygiene:
The city's public health and hygiene is the responsibility of the city council, and health officers and hygiene inspectors are responsible for performing this key function.
In this context, it performs some functions.
(I) Prepare public toilets and urinals.
(Ii) Provide proper drainage pipes for disposing of dirty water and urination.
(Iii) Prohibit the sale of rotten and edible foods.
(Iv) Make appropriate preparations to check for food fraud.
(V) Establish hospitals and clinics
(Vi) We will arrange vaccinations to contain epidemics such as smallpox and cholera.
7. Provision of fire fighting services:
The city council will set up a fire brigade and make all the necessary arrangements for fire fighting activities.
8. Urban forestry, environmental protection and ecological balance:
The city council makes the necessary preparations to protect the city's environment, maintain the balance of the ecosystem, and take the necessary steps to check for pollution. It makes a special drive for tree planting.
9. To protect the interests of the weak in society:
The city council has made appropriate arrangements to protect the interests of the vulnerable parts of society, including people with disabilities and mental illness. For this purpose, it can undertake the construction and operation of homes and persons with disabilities.
10. Slum improvement:
Keeping the city clean and beautiful is a basic duty of the city council. For this purpose, it makes the necessary preparations for the development and improvement of urban slums.
11. Urban poverty alleviation:
The city council provides employment and self-employment for people and takes steps to alleviate poverty in the city.
12. Maintenance and establishment of parks, gardens and playgrounds:
To keep the city clean and beautify the town, the city council has developed parks in the town, gardens in the squares and playgrounds.
13. Promotion of cultural and educational welfare:
For the cultural, educational and aesthetic development of the townspeople, the city council has established cultural centers, museums, educational institutions and items in the town.
14. Crematorium maintenance:
The city council will make the necessary arrangements for the cremation and burial of the corpse. Keep displaying that resource. The city council can also provide an electric crematorium.
15. Prevention of atrocities against animals:
The city council makes the necessary preparations to bury dead animals and prevent cruelty to animals.
16. Birth and death registration:
The city council registers for birth and death and issues a certificate of birth and death.
17. Public facilities such as street lights, parking lots, bus stops, public convenience:
The city council will make appropriate arrangements for streetlights in the town, set up parking lots in the town for parking vehicles, tanga and rickshaws, and provide facilities such as toilets and urinals.
18. Regulations for slaughterhouses and tanning factories:
The city council will open a slaughterhouse in the town and create rules for its use. It also regulates the work of the tanning plant and makes the necessary arrangements to address the problems that arise from the tanning plant.
Q15) Discuss the role of women in politics. (12)
A15) In recent years, a new dimension of women in politics has emerged around the world. More and more women are entering politics. Women were particularly absent from politics, as traditional politics reflected men's concerns.
Welfare policies have been established to strengthen the traditional position of women as wives and mothers. Women have struggled with issues that affect them, especially property and voting rights in the 19th century, and abortion, equal pay for equal work, and daycare in the 20th century.
In India, the pre- and post-independence reform movements have allowed women to gain some political power. After independence, they achieved an unprecedented political breakthrough by reserving seats in Panchayati and other public bodies.
It is encouraging to point out that Indian women, like the United States and many Western countries, were the earliest to acquire political rights (voting rights) without political movements. They were one of the leading figures in active participation in politics, even in the pre-independence era.
There is a distinction between Indian women being UNO Secretary-General (Vijay laxmi Pandit), Prime Minister (Indira Gandhi), Prime Minister (Sucheta Kriplani, Jayalalitha, Uma Bharati, Mayawati, Vasundhara Raje) and even President (Pratibha Patil).
Being a ward member of Pradan, Gram Panchayat and other citizenships, or a member of the state legislature or parliament will increase respect, self-esteem, confidence and determination not only within the family but throughout the community. -Ability to make.
Taking women's participation in politics as one of the measures of liberation shows that the number of women is now very small compared to the state legislature and men in the legislature. That's only about 11% (26 women in the Senate-Rajya Sabha with 245 members and 59 women in the House-Lok Sabha with 543 members. 8 out of a total of 75 members of Dr. Mammohan's government. There is only one female minister. Shin).
In Sweden, women occupy 45% of the parliamentary seats. As far as administration is concerned, there are only 592 female IAS officers out of 4,671 officers. In addition to booking posts in parliament, parliament (the bill has been pending for more than a decade) and other civil institutions, special concessions and demands for privileges are several steps towards empowering Indian women.
The woman wrote and began to read what other women wrote. For the past two decades, the writings of many female writers (such as Arundhati Roy) have been highly regarded by internationally reputed institutions. There are many women in the field of journalism that was previously dominated by men. Now she uses blogs and networks to express her anxiety, anger and disapproval, and meet the need for acceptance and approval for the freedoms that have been denied so far.
Despite the many benefits, there is still much work to be done to improve the status of women in India. Women's labor force participation in India is only 26%, while in China it is 46%. About 34 out of 100 women (2011) are illiterate, compared to only 13 in China.
Women's pesticides lose an estimated 500,000 women's births each year in India, reducing the sex ratio of women to a disastrous 914: 1000 (2011). The worst since independence. India is ranked 115 out of 162 countries on gender development issues, according to UNICEF reports.
The above changes mean positive benefits from the perspective of women's equality, but in reality there are many problems and tensions. Observations on improving equality apply only to a small number of Indian educated women living in urban areas.
Many studies conducted in India and elsewhere (so-called developed countries) have shown that equal sharing of household chores remains a nightmare for women. Working wives find that housework and caring for their children are still primarily their job. On average, working wives / mothers are forced to work at least 14 hours a day, so wives shared with her husband are highly unequal. Weekends aren't time to rest, but time to catch up with unfinished and pending work in your household
Women's status in society, as is generally believed, cannot be secured by economic power alone. It depends on the culture. Micro studies show that women's participation in the employment market is more concentrated when they come from poor or very poor families.
Women's income, in particular, is a means of survival for the poor. Does this important income of poor women enhance their status? The study reports further. They are empowered as far as income is concerned, but not when it comes to spending income.
The very attitude of considering women’s income supplementary and something not preferred … raises problems for women’s empowerment. Furthermore, ‘the limited empowerment that we have seen has been nurtured within the socio-economic-political empowerment process of people, including women, through the Panchayat system’ (Bagchi, 2000).