Unit IV
Soft Skills for Effective Interpersonal Communication
Question bank
Q1) Define Soft skills with its importance. (8)
A1) Soft skills are often defined as "personal attributes that allow someone to interact effectively and harmoniously with others." This skill is certainly one of the rare intangible abilities that makes the difference between success and failure. This article discusses the importance of soft skills and how they can help you succeed.
We are well aware that we need to hone our technical skills to encourage employment. Professional and technical skills may give you a job and open up opportunities, but if you really want to achieve this competitive world, soft skills provide the icing you need for cakes. I will. Your work ethic, your attitude, your emotional intelligence, your communication skills and other personal attributes are many soft skills that are essential to the success of your career.
Having soft skills increases your chances of becoming a leader. Motivating, solving problems, delegating, and building teams is easy in the corporate world. You need to know that how to get along and be positive with people is important to success.
Importance of soft skills
Most interactions with people require some soft skill. Companies may negotiate to win new contracts, present new ideas to colleagues, or network for new jobs. We use soft skills every day at work, and developing these soft skills can help us win more businesses and accelerate our career progress.
On the contrary, lack of soft skills can limit your potential and lead to business failure. Develop strong leadership, delegation, teamwork, and communication skills to run projects more smoothly, deliver pleasing results to everyone, and improve interaction with others to improve your personal life. You can influence.
Outside the office, use soft skills such as communication to build friendship groups and meet potential partners. You may be negotiating the value of a new home remodelling, or you may be teaching your neighbour’s children over the weekend. Soft skills are useful both at work and in private.
Importance of soft skills
1. Career advancement and promotion
CIMS Hiring Insights (2017) said, "94% of hiring professionals believe that employees with strong soft skills are more likely to be promoted to leadership positions than employees with more years of experience but weaker soft skills. I am. "
You are trying to separate you from others in interviews and jobs, so developing these skills is essential if you want to advance your career.
2. Modern workplaces are interpersonal
Skills such as active listening, collaboration, idea presentation, and communication with colleagues are all highly valued in the modern workplace. Strong soft skills ensure a productive, collaborative and healthy working environment. This is an important attribute for organizations in an increasingly competitive world.
3. Customers and clients demand soft skills
Consumers these days have many choices about where to buy from the internet or smartphones. For these consumers, convenience and low prices are easy to return, so it is usually customer service that influences the choice to use a particular business.
Therefore, the ability to speak with customers at the individual level is an important idea for an organization's success.
4. Long-term workplace believes in soft skills
Automation and artificial intelligence will increase the proportion of work that relies on soft skills. Advances in technology have made tasks that require hard skills say no, and soft skills have become an important differentiator in the workplace. According to a Deloitte Access Economics survey, "soft-skilled occupations will account for two-thirds of all jobs by 2030."
As robot costs go down and AI performance improves, tasks such as production line workers are automated. Traditional skills such as teamwork, communication and important thinking are more important than ever.
5. Soft skills are difficult to automate
Continuing from the previous point, soft skills like emotional intelligence are difficult to automate and are unlikely to be automated soon. This suggests that they are expected to become more desirable in the near future.
However, soft skills are often difficult to show and track for improvement. Companies like Virtual Speech are working on this by using VR as a way to enhance their soft skills.
6. Soft skills are in high demand from recruiters
Soft skills are in high demand for the workforce. Consistent with a 2017 paper by Harvard students on the importance of social skills in the labor market, jobs that require a high level of social interaction have increased by almost 12 percent in the U.S. Workforce share. Did. Most Demanded Soft Skills
a) Communication,
b) Organization,
c) Teamwork,
d) Critical thinking,
e) Social skills,
f) Creativity,
g) Interpersonal communication,
h) Adaptability.
In the conclusion of this paper, social skills are still considered important, as computers are very poor at simulating human interactions. Therefore, individuals need to look to improve their social and soft skills through activities such as volunteering, team leadership, or conducting open source projects with people.
Q2) State the importance of sentimental skills to businesses. (7)
A2) Importance of sentimental skills for businesses
For example, nurses, beauticians, mechanics, etc. need soft skills in every industry. The development of each soft skill has its own advantages, such as improved communication. Employees can interact more effectively and be more productive by improving time management.
There are also general benefits for employees with soft skills.
1. Increase productivity-Improve the efficiency of employee tasks and responsibilities, and help your company reach its goals.
2. Improving teamwork-In order for a business to function effectively, people need to work together to achieve common goals. By using your personal strengths and skills together, you can improve the quality of your work.
3. Improving Retention Rate-People want to think of a company that is investing in employee career development. In fact, 63% of UK employees change employers when offered a job at a company with a lot of training opportunities. Also, as employee retention increases, so does the cost of hiring the company.
4. Improving Employee Satisfaction-Investing in employees shows that they are valued. Being grateful and having a positive outlook for the company increases job satisfaction.
5. Improved Leadership-Soft skills require specific skills such as active listening and empathy to help employees prepare for leadership positions. This is often important because 50% of employees quit their jobs because of poor managers.
6. Attract new clients-If clients are proud of your company's services, they are more likely to recommend you.
Q3) What do you mean by listening? What are effective listening skills? (8)
A3) Listening is receiving language through the ear. Listening involves identifying the sounds of spoken words and processing them into words and sentences. When we hear, we use our ears to receive individual sounds (letters, stress, rhythms, poses) and our brains to translate them into messages that are meaningful to us.
Listening in any language requires concentration and attention. This is a skill that some people need to work harder than others. People who have difficulty concentrating are generally not good at listening. To listen in a second language, you need to focus more.
Like babies, we learn this skill by listening to people who already know how to speak a language. This may or may not include native speakers. For practice, you can hear live or recorded voices. The important thing is to listen to as many different voices as possible.
Listening is the first of four language skills:
Listening
Busy
Reading
Writing
In our native language, listening is usually the first language skill to learn.
To be able to speak English fluently, you need to acquire strong listening skills. Listening doesn't just help you understand what people are saying to you. It also helps you speak clearly to others. It helps you learn how to pronounce words correctly, how to use intonation, and where to put stress in words and sentences. This makes it easier for others listening to your speech to understand.
Effective listening skills
1. Discover your area of interest.
2. Understand and understand the matter / content.
3. Keep calm. Don't lose your temper. Anger interferes with and hinders communication. An angry person is troubled by the words of others.
4. Being hospitable accept new ideas and knowledge.
5. Make a note of it and note the details.
6. Listen and work. Analyze and evaluate your speech in your spare time.
7. Paraphrase and summarize the speaker's thoughts.
8. Please continue the question. This shows how well you understand and hear the speaker's ideas.
Q4) What are the characteristics of good listener? Explain the different types of listening skills depending on the speaker. (8)
A4) Excellent and effective listener characteristics
1. Good audience : good and effective listener tries to offer maximum thought to the speaker's ideas being conveyed and minimizes the quantity of your time that mental movements get off the bottom .
2. Attentive-A good listener must concentrate to big points. He must be vigilant. He should avoid any quite distraction.
3. Don't assume-a good listener doesn't ignore information he considers unnecessary. You ought to always summarize the speaker's thoughts so as to not misunderstand the speaker's thoughts. He avoids premature judgment about the speaker's message.
4. Hear Emotions and Facts-A good listener deliberately listens to the speaker's emotions. He's completely focused on the facts. He evaluates the facts objectively. His listening is sympathetic, lively and attentive. He sharply observes the speaker's gestures, facial expressions, and visual communication . In short, an honest listener may be a projection (i.e., someone who tries to know the speaker's perspective) and an empathy (that is, someone who seeks the speaker's emotions and feelings, not just the superficial meaning of the message)
5. Focus kindly and generously on other speakers-Good listeners strive carefully to offer other speakers the chance to precise their thoughts and views. He tries to find out from all the speakers. He evaluates the speaker's thoughts in his spare time. He focuses on the content of the speaker's message, not on the speaker's personality or appearance.
6. Give Opportunity-Good listeners seek to profit from the opportunities that arise. He asks, "What's in it for me?"
There are differing types of listening counting on the speaker
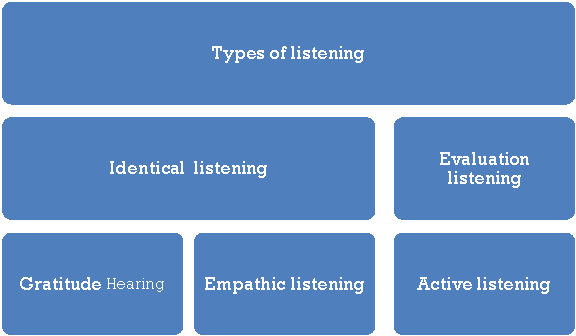
1. Identical listening: When the listener distinguishes between different parts of the speaker message.
2. Evaluation listening: Listening is claimed to be evaluation when the listener evaluates the evidence and reaches a conclusion.
3. Gratitude Hearing: Here, the listener is in words or visual communication , indicating that he likes a part of the speech and agrees with the speaker.
4. Empathic Listening: When the listener puts himself in situ of the speaker's position, it's called empathic listening.
5. Active Listening: Active listening is when the listener is seriously curious about understanding the opposite person's thoughts, feelings, desires, and therefore the meaning of the message, and actively checks our understanding.
Q5) Explain the four steps of listening process. (5)
A5) The four steps of listening process are:
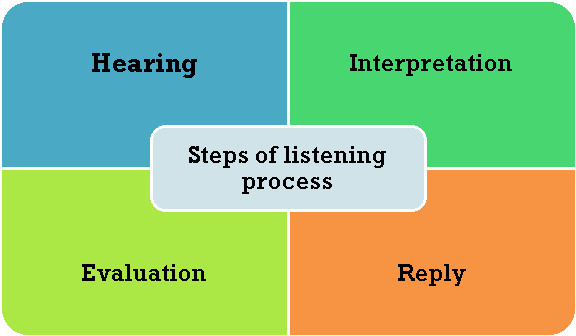
1. Hearing is that the initiative within the process. At this stage, listeners got to take care to make sure that they hear the message.
2. The second step is interpretation. Misinterpretation of the speaker's words is usually misleading. Words could also be interpreted differently thanks to different experiences, knowledge, vocabulary, culture, background, and attitudes.
3. An honest speaker uses voice tones, facial expressions and manners to clarify the message to the listener. During the third step, evaluation, the listener must decide what to try with the knowledge it receives. The choices made during the evaluation phase are a crucial a part of the listening process.
4. The ultimate step is to reply . This is often a verbal or visual response that tells the speaker if the listener has received the message and what his response.
Q6) State the importance of listening.What are the guidelines for effective listening? Explain briefly. (8)
A6) The importance of listening-
1. It helps us to understand the people and the world around us.
2. In our society, listening is essential for personal growth and survival.
3. Relationships depend more on listening skills than speaking skills.
4. A good listener is always in a better position to deal with his problems and relationships.
5. It helps a person grow in his career.
6. It keeps providing enough information to people
7. Help your organization achieve its goals.
8. Listening spells the difference between feeling accepted and paying an isolated fee.
9. Good listeners are rarely involved in controversy or misunderstanding.
10. Listening skills are important for effective leadership.
11. Good listeners are often the best speakers because they spend time finding what they are really interested in.
Guidelines for effective listening
Listening is a very important aspect of communication. Approximately 20% of all communication is listening. Therefore, you should strive to develop good listening habits.
Here are some guidelines to listen to often:
(1) Preparation before listening.
(2) Listen to understand, not refute.
(3) Focus your attention.
(4) Focus on the context.
(5) Take notes.
(6) Suppress the urge to interrupt.
(7) Ask a question.
(8) Summary and evaluation.
The details of each point are as follows.
1. Preparation before listening: As already mentioned, listening plays an important role in communication. So, you need to be prepared before you start listening. As a preparation, there are the following guidelines.
(i) Stop talking: The human brain can efficiently perform one activity at a time, so the listener does not speak while listening.
(ii) Get rid of distractions: Noisy fans, traffic noise, and unauthorized intrusions can disrupt the listening process. All these barriers need to be removed.
(iii) Good environmental conditions: There should be no unusually cold or warm environment and ventilation should be adequate.
2. Listen to understand, not refute: There may be many topics reserved by the listener. Apart from these reservations, listeners must do their best to understand the message.
3. Focus attention: There may be many objects that the listener needs to build a mental outline of where the speaker is heading in the speech.
4. Focus on context: The listener needs to remember the background and theme of the speech. This allows him to absorb the material quickly and efficiently.
5. Take notes: The listener must keep taking notes. Therefore, he should write down the idea, not the text. In this way he / she was able to keep the message safe for a long time.
6. Suppress the urge to interrupt: You should not interrupt your speech until the speaker asks a question. This habit reassures both the speaker and the listener.
7. Ask a question: Asking the right question at the right time is completely different from interrupting. The listener should have an idea to know the right time to ask question.
8. Summary and Rating: The listener should make a summary speech, but not during the listening process.
Q7) Define oral communication. (5)
A7) Oral or verbal communication” involves the transmission of commands, messages or suggestions through speech. It will be face to face or through a speaking instrument like the telephone.
Oral communication can occur directly between one person and another or in a group or indirectly through meetings and conferences. Whatever tool is used, it saves a lot of time and allows for personal contact. This fosters a friendly and cooperative spirit, ensures quick understanding and proper explanations, encourages questions and answers, and stimulates interest.
The speaker is also in a position to understand the listener's reaction. Again, it is best suited for confidential and emergent discussions. But it is not suitable if the space between the loud speaker and therefore the listener is too long. It is also not suitable if the subject to be communicated is long and must affect several people simultaneously. It also lacks recorded evidence and future references, and does not give the auditor much time to think, act and react.
Q8) What is non verbal communication? Why is it important? (5)
A8) Non-verbal communication refers to gestures, facial expressions, vocal tones, eye contact (or lack thereof), visual communication, posture and other ways in which people can communicate without using language.
Non-verbal communication is just as important as a verbal response during an interview for work or to attend a meeting. A Kinesics study conducted by anthropologist Ray Birdwhistell found that over 65% of communication was non-verbal.
Non-verbal communication skills can give a positive (or negative) impression. Arms crossed can appear defensive. Poor posture can make you look unprofessional. Avoiding downward gaze or eye contact can reduce your ability to be seen as confident.
Employers value what you do and what you say, and you'll use your nonverbal communication skills to form the easiest impression. If your skills aren't top notch, you can put them into practice to make a positive impression on everyone you meet at work and beyond.
Q9) Give examples of non verbal communication. (8)
A9) Examples of nonverbal communication skills
- Want to hone your skills? Review this list of non-verbal skills and work on areas where you think you can improve.
- Avoid crouching. Sit straight with the backrest facing the chair, or lean forward a little to convey engagement.
- Avoid smiles and laughter if the message is serious.
- An animation is displayed with facial expressions of hands and face to express a dynamic presence. (However, avoid speaking excessively by hand, as you are not an expert and may appear unsophisticated.)
- Do not bring in distracting items such as mobile phones or drinks during interviews or meetings.
- Eliminates the fidgeting and trembling of limbs.
- Establish frequent but non-continuous or sharp eye contact with interviewers.
- Focus on the conversation.
- Group interviews transfer eye contact to different speakers.
- Introduce yourself with a smile and a firm handshake. Make sure your palms are dry.
- Keep your hands away from your face and hair.
- Listen carefully and do not interrupt.
- Keep your arms open — folded arms can convey defense.
- Modulates vocal tones to express excitement and emphasize important points.
- Nod to show understanding.
- Observe the reaction of others to your remarks.
- Read other people's non-verbal signals. If it looks confusing, provide an explanation, and if you've heard enough, summarize it.
- Please refrain from forcibly laughing according to humour.
- Do not look at your watch or cell phone or display any other signs of indifference.
- We respect the amount of personal space that our communication partners prefer.
- Alternate eye contact with different speakers in group interviews and networking situations.
- Shake hands firmly without applying excessive force.
- Show that you are interested in what the interviewer is telling you.
- Smile to show that you are amused or happy with the conversation.
- Please calm down even if you are nervous.
- Avoid monotonous delivery.
- Wait for the person to finish talking to respond.
- Communication in job interviews.
Q10) Mention the barriers to effective communication. (8)
A10) The communication process presents multiple barriers. The intended release will often be disrupted and distorted, leading to a condition of confusion and communication failure. The barriers to effective communication could be of many types such as linguistic, psychological, emotional, physical and cultural, etc. we'll see all of these guys intimately below.
Language barriers
The barrier is one of the barriers that most limit effective communication. Language is the most commonly used communication tool. The very fact that each large region has its own language is one of the obstacles to effective communication. Sometimes even a thick dialect can make communication ineffective.
By some estimates, the dialects of each of the two regions change within a few kilometers. Even within the same workplace, different employees will have different language skills. As a result, the communication channels that stretch across the organization would suffer.
So, keeping this obstacle in mind, different considerations need to be taken for different employees. a number of them have a very good command of a certain language and others will be comfortable with these languages.
Psychological obstacles
There are various mental and psychological issues that will be barriers to effective communication. Some people are afraid of the stage, speech disorders, phobia, depression, etc. All of these conditions are sometimes very difficult to manage and can most certainly limit the ease of communication.
Emotional barriers
An individual's emotional IQ determines how easily and comfortably they communicate. An emotionally mature person will be ready to communicate effectively. Conversely, people who let their emotions get the best of you will encounter certain difficulties.
The perfect mix of emotions and facts is important for effective communication. Emotions such as anger, frustration, humor, can confuse the decision-making capacities of an individual and thus limit the effectiveness of his communication.
Physical barriers to communication
These are the main obvious obstacles to effective communication. These barriers are for the most part easily removable in principle at least. They include barriers such as noise, closed doors, faulty equipment used for communication, closed cabins, etc.
Cultural barriers to communication
As the world becomes more and more global, any large office can have employees from many parts of the world. Different cultures have special significance for several fundamental values of society. Dress, religions or their lack, food, drink, pets and therefore general behavior will change drastically from one culture to another.
Therefore, it is essential to take these different cultures into account when communicating. This is often what we call being culturally appropriate. In many multinational companies, special courses are offered at orientation stages that enable people to realize other cultures and to be courteous and tolerant of others.
Obstacles related to organizational structure
As we have seen, there are many methods of communication at the organizational level. Each of these methods has its own problems and constraints which will become barriers to effective communication. Most of these obstacles stem from misinformation or the lack of appropriate transparency available to employees.
Attitude barriers
Some people wish to be left alone. They are introverts or just people who are not very social. Others wish to be sociable or sometimes very clingy! These two cases could become a barrier to communication. Some people have attitude issues, like a huge ego and reckless behaviors.
These employees can cause serious strain in the communication channels in which they operate. Some personality traits like shyness, anger, social anxiety could also be eliminated through classes and proper training. However, issues like egocentric behavior and selfishness might not be corrected.
Obstacles to perception
Different people perceive a similar thing differently. This is often a fact that we must take into account in the communication process. Knowing the levels of public perception is crucial for effective communication. All messages or communications should be simple and clear. There shouldn't be room for a diverse set of interpretations.
Physiological barriers
Certain disorders or illnesses or other limitations could also prevent effective communication between the various channels of an organization. Sharpness of voice, dyslexia, etc. are some examples of physiological barriers to effective communication. However, these are not crucial as they will be easily compensated and removed.
Technological and socio-religious barriers
Other barriers include technological barriers. Technology is developing rapidly and as a result, it becomes difficult to keep up with the most recent developments. Therefore, sometimes technological progress can become an additional obstacle, at this, the cost of technology is usually very high.
Q11) What are the measures to overcome communication barriers? (8)
A11) Measures to overcome communication barriers
(1) Clarify ideas before communication:
The person sending the communication should be very clear in their mind about what they want to say. He must know the purpose of his message and, therefore, he must organize his thoughts in an appropriate order.
(2) Communicate in accordance with the needs of the receiver:
The sender of the communication must prepare the structure of the message that does not correspond to his own level or ability, but he must keep in mind the scope, understanding or environment of the recipient.
(3) Consult others before communication:
When designing the communication, suggestions should be solicited from all involved. Its main advantage will be that all those consulted during the preparation of the communication plan will contribute to the success of the communication system.
(4) Be aware of the tone, content and language of the message:
The sender must take into account the very fact that the message must be written in clear and pleasant language. The tone of the message should not hurt the feelings of the recipient. As far as possible, the content of the message should be brief and excessive use of technical words should be avoided.
(5) Convey useful and useful things to the listener:
The subject of the message must be useful to the recipient. The need and interest of the recipient must be specially borne in mind. Communication is more effective in such a situation.
(6) Provide appropriate feedback:
The purpose of feedback is to find out whether the receiver has fully understood the meaning of the knowledge received. In face to face communication, the reaction on the receiver's face is often understood.
But in case of written communication or any other type of communication, an appropriate method of feedback should be adopted by the sender.
(7) Consistency of the message:
The information sent to the recipient must not be contradictory. It must be in accordance with the objectives, policies, programs and techniques of the organization. When a new message has to be sent in place of the old one, it must mention the change otherwise it can create doubts.
(8) Follow-up communication:
In order to form effective communication, management should regularly attempt to learn about weaknesses in the communication system. In this context, efforts are often made to determine whether it would be appropriate to place more emphasis on formal or informal communication.
Likewise, suggestions are often invited regarding the communication medium (oral, written and gestural) to understand on which medium would be the most effective and the most appropriate.
(9) Be a good listener:
It is the essence of communication that the sender and receiver must be good listeners. Both need to listen carefully to the other's point of view, patience and a positive attitude. A sender can receive a lot of relevant information by being a good listener.
Q12) Why self-awareness is important? (8)
A12) There are many great ways to improve yourself. One of these methods is to look for the positive traits you have and evaluate those parts. Another important way to be a better person is to recognize your weaknesses and actively work to improve them. These two methods of self-improvement define the meaning of self-awareness. Having self-awareness helps to improve relationships with people and improve their ability to reach their goals. However, these are not the only benefits of self-awareness. There are several other reasons why self-awareness is important.
Improve your social ability
Humans are social creatures that value relationships. Self-aware people are very successful in building relationships. This is because each person you meet can understand exactly what you want. That conviction comes from knowing your own abilities and challenges. Self-awareness also promotes emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence helps us relate to the emotions of others. Without this skill, you may collide with others. The best way to improve your level of emotional intelligence is to learn your own emotional patterns.
Promotes diversity and open mind
Knowing yourself is very important to influence your approach to the problem. Self-awareness itself is the ability to actively listen to the voices of the body and mind in order to know your natural reaction to change. Therefore, this awareness helps to focus clearly when dealing with the problem. You can also accept opinions, feedback, and criticisms from others without being subjective. Ultimately, you can think of multiple solutions to a problem.
Promote productivity
A person with self-awareness is a person who thinks quickly. They can understand themselves and focus on the tasks of the day without hindrance. If you don't understand yourself, there is a big challenge that you can get caught up in uncertainty. As a result, even when quick decision-making is required, pondering different behavioral policies can be a waste of time.
Improve leadership skills
One of the most important attributes of a good leader is quick decision making. Leaders also need to be fair and confident. All of this comes from recognizing yourself. Knowing yourself allows you to get rid of your inner fears and focus on what's important.
Promote overall objectivity
Self-awareness promotes objectivity. If you are confident in yourself, you are confident in yourself. This means that you can easily make decisions without being confused by your judgment.
Body language is another means of communication. Sometimes it can send a stronger signal than words. Body language is controlled by the subconscious, so the reader can actually understand if there is a difference between what you are saying and what you think. It takes a little reading and practice for words and body language to complement each other.
What gestures should I avoid when talking to my body? Which gestures can make you sound more positive? How can I show consent / disagreement silently? Did this work? It will be interesting to know your thoughts on this.
Q13) What is formal communication? (8)
A13) Messages flowing through the organization's regulated and preconfigured channels create formal communication. The content of the communication is related to the activities of the organization, the work and everything related to it. Formal communication can consist of letters, telephone messages, radio messages, verbal messages in the form of internal printed notes and non-verbal messages. Even some gestures can consist of formal communication. The message will be sent by the authorized one. On the official channel, these reach the person or the machine that needs to react, which needs to know the content of these messages.
Normally, all formal communications are recorded and stored in organizational evidence. These copies are kept by the sender, receiver, and all offices in the organization that need to know and retain the information. Examples of formal communication are provided by work orders, financial reports and proofs, sales / inventory reports, statements referring to company policies, job descriptions, etc.
Formal communication can take place horizontally, along parallel directions of authority. The formal communication networks of organizations maintain a space for these communications and serve more purposes. Defines the channel on which important messages are sent. A transmission plan for this information is created for the sender and the receiver. It shows the direction for those who respond and the direction for those who need to be informed of these actions, their steps and their consequences. It provides the storage space for the information necessary for operational and control planning. It creates an orderly system for superiors and subordinates to keep them informed about each other.
A formal communication network is formed from formal channels created by setting up a formal accountability system according to the organizational hierarchy. A perfect network is one that contains communication channels horizontally, from bottom to bottom. In many cases, the horizontal communication direction is absent or ineffective, which reduces the accuracy of the information. The situation manifests itself in the lack of permanent dissemination of information between departments, which is essential for the organization in the existing competitive situation or lack of organizational communication specialists.
Top-down downward communication is carried out by the manager with his subordinates. The responsibilities of the employees are identified with the rules and instructions communicated. In an effective organization, this type of communication aims at continuous information on employee motivation, policies, objectives and organizational strategies. Periodicity is important to ensure constant communication. From time to time, this type of communication is seen as a priority responsibility and has gained a favorable temptation to go to employees only. Even when only the manager sends commands and instructions to employees, he can have a place without being too engrossed in their information.
When an organization changes, there is a need to use top-down communication to change opinions and attitudes, waste restrictions and fear false information to help employees comply with those changes. .. Feedback is needed for this type of communication. Therefore, it is complemented by bottom-up communication from employees to managers. They understand top-down communication and can pass the response on. Managers need to be attentive to the information they receive, thanks to employees who tend to say nothing but good things to their bosses. It may sound like intentional disinformation.
“Formal communication” is the transfer of knowledge or direction within a formal organizational structure. Formal communication maintains the relationship between superiors and subordinates. When a manager asks an assistant manager to perform certain tasks, this is an example of formal communication. Formal communication prompts workers to clearly understand what the manager is trying to do and is usually codified and expressed in writing in manuals, handbooks, newsletters, annual reports, etc.
Q14) Explain the purpose of formal communication. (8)
A14) The purpose of formal communication is to issue orders, convey instructions and achieve the goals of an organization through some pre-determined rules and regulations.
- Formal communication flows through a structured path.
- It is formal and formal in nature.
- Although primarily in writing, verbal communication may also be considered formal communication.
- Higher authority sanctions are required.
- It can be downward, upward, or bidirectional.
- Rank, status and authority are very important in such communication.
- Standards are maintained in such communication.
- Inflexible. It is generally rigid in nature.
- Formal and formal communication is binding and effective.
- Formal communication is generally written. Therefore, the possibility of ambiguity and misunderstanding is low.
- Written so you can save it and use it as a future reference.
- Formal communication is formal, so the responsibility of the sender and recipient is great.
- Formal communication takes less time than informal communication, which spends a lot of time on discussions, side talks, and even discussions.
Helps maintain overall control of employees when they arise from a relationship of authority and subordination.
Q15) What are the different types of formal communication? (8)
A15) There are two types of formal communication.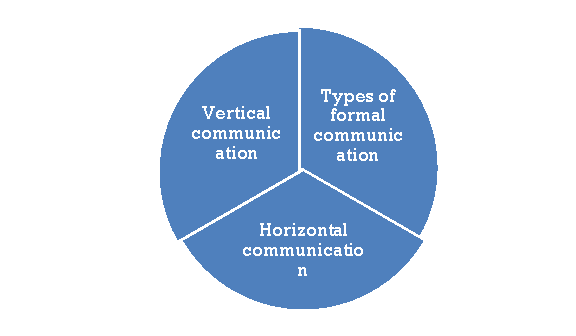
(1) Vertical communication:
(i) Downward communication
(ii) Upward communication
(2) Horizontal communication. All of these types are clarified in the following figure.
(1) Vertical communication
There are two types of vertical communication:
(I) Downward communication:
Communication between the highest level and its lower levels is called lower level communication. This communication includes commands, rules, information, policies, instructions, etc. The main benefit of top-down communication is that subordinates have access to useful and timely information to help them get the job done.
Ii) Upward communication:
It is the exact opposite of top-down communication. It goes from subordinates to bosses. The subject of this communication includes suggestions, reactions, reports, complaints and more. This type of communication helps bosses make decisions.
(2) Horizontal communication
Horizontal communication occurs when two people at the same level exchange information. Horizontal communication is used by agents of the same level to solve problems of similar nature and interests through the experience of others. The subject of horizontal communication includes information, requests, suggestions, common problems and coordination information.
Q16) What is informal communication? (8)
A16) Informal communication comes from all channels outside of the official channel and is also known as Grapevine. It is established around the social affiliation of the members of the organization. Informal communication does not follow the line of authority as it does in formal communication. The three charms of the Greek philosopher Aristotle, Logos, Ethos and Pathos, are compelling speakers and the secret to delivering the right message. Appealing to the listener's logo or logic, speaker ethics or credibility, patos or emotional appeal can help you become an effective speaker.
Adding the active listening lesson to the bouquet completes the configuration. So take advantage of this period of telecommuting and acquire effective communication skills.
Informal communication is tailored to the individual needs of members of the organization and is present in all organizations. Such communication is usually verbal and can be expressed simply by looking at it, signing it or remaining silent. Informal communication is implicit, voluntary, multidimensional and diverse. Often works in groups. In other words, when a person has interesting information organizations can effectively use informal channels to improve formal communication channels. This is a valuable goal for expressing specific information that cannot be communicated through official channels. It responds to people's desire to identify what is going on in their organization and gives them the opportunity to express their fear, concern and dissatisfaction. Informal communication also makes it easier to improve business decisions, as more people are involved in the decision-making process.
Despite many advantages, informal communication has certain disadvantages. Informal communication contains rumors, deceptions, facts and unclear data. Informal communication channels can send completely inaccurate information that can harm the organization rather than help it. In addition, we cannot determine responsibility for the source or flow of information. However, formal and informal communication is necessary for an organization to function effectively.
Informal communication refers to communication based on informal relationships between members of a group. It is essentially personal communication, not positional communication. It does not link with a formal line of authority or a formal chain of command. Yet it is not regulated by formal rules or procedures. Members of informal groups typically use this form of communication to share ideas, views, opinions and other information. There is a lack of official instructions for communication. Uncontrolled and designed by a formal organizational structure. Therefore, it is not used to convey formal messages.
Q17) Explain the types of informal communication. (8)
A17) Types of informal communication:
1. Positive strand chain
This is a type of communication in which A shares ideas and information with B, and B passes them on to C.
2. Cluster chain
Have you ever noticed how word of mouth spreads social media challenges? People start something unique and, for example, tag three friends for a challenge. They rise to the challenge and score each of the other three. In this way, the cluster chain communication is formed and continuous.
3. Gossip chain
Think about a conversation in a college cafeteria. One person listens to a group of their friends gathered around the table as they vividly explain their recent adventures. This is how the gossip chain works. One person starts a conversation, shares information with a group of people, and the group passes that information on to more people.
Today, most organizations seek to effectively integrate formal and informal communication channels. The result is increased efficiency, productivity and confidence among employees. Effective communication skills play an important role in advancing the careers of everyone from freshmen to team leaders and managers.
So start now to develop and hone your formal and informal communication skills. One way to do this is to take Harappa's “Speak Effectively” and “Write Well” courses. These courses will help you learn the PREP model and Aristotle's appeal of simple and effective communication.
The PREP method has four steps. I will briefly explain P or points, or the main points. Give a reason to prove R or a reason or a point. E or give an example or example to verify the evidence or reason, and add conclusions while re-underlining P or dots or dots.
The three charms of the Greek philosopher Aristotle, Logos, Ethos and Pathos, are compelling speakers and the secret to delivering the right message. Appealing to the listener's logo or logic, speaker ethics or credibility, patos or emotional appeal can help you become an effective speaker.
Adding the active listening lesson to the bouquet completes the configuration. So take advantage of this period of telecommuting and acquire effective communication skills.
Q18) What is a Purpose Statement (SOP)? Why is the desired statement important? (5)
A18) The Purpose Statement (SOP), also known as the Research Statement or Statement of Intent, is written on the Admissions Panel and talks about your career path, interests, professional contributions, goals, and the driving forces behind pursuing a particular program. This is usually submitted in the form of an essay. However, certain universities may also remain question-based. Determining admission to your preferred institution is the most important part of your application.
The Objective Statement (SOP) is the decision maker of the application. It helps the Admissions Board evaluate your outlook on life, your career goals, beliefs, subject knowledge, and your vision. In short, a well-written SOP depicts the overall personality of the university. This is an opportunity to suggest to the Commission your purpose and why you should choose you over other applicants. A good SOP is ideal for weak academic profiles that can be supplemented by emphasizing future goals and ambitions. Well-written SOPs also reflect how well you can use your writing skills to express your thoughts.
Q19) What should be included in the statement of purpose? (5)
A19) There are several elements that are essential to your statement of purpose. These include:
- Personal background,
- Economic background,
- Academic details,
- Professional experience (full / part-time, optional),
- Immediate and long-term goals,
- Why you want to study at this particular institution,
- Why you were interested in your chosen field,
- About extracurricular activities,
- Published work (if any),
- Submitted treatise (if any),
- Interests & hobbies.
Q20) How do you write a statement of good purpose? (5)
A20) Here are three main steps to keep in mind when creating an SOP:
1. Plan well
Create a POS overview and work accordingly. Sharing anecdotes that have developed your interest in your topic is a good way to build your SEO. Create pointers and categories to list relevant accomplishments and expertise, and most importantly, why you picked a course and college.
2. Work on the project
Focus on sharing what you have learned and what you know during your training and experience in the industry. When creating an SOP, limit the use of jargon and use the active voice. If you have a gap year or a school problem, be optimistic. Make sure the SOP has a clear introduction and conclusions. Keep in mind that SOPs should always be written from the most recent to the most recent.
3. Please check early before sending
It is important to verify what you have written. Reanalysis helps correct flow, vocabulary, sentence writing errors, long sentences, and various grammatical issues. Get a second opinion. This could be the opinion of a professor, a senior or an IDP advisor. Please proofread and reconfirm correctly before submitting.
Q21) Define Resume. What are the contents of resume? (8)
A21) The curriculum vitae or biological data may be a brief record of the candidate's personal information, degrees, specialist training, experiences, references and other relevant information. It is a summary of his personal and academic accounts. A curriculum vitae is considered an official announcement of a person's qualifications.
According to Bovee, Thill, and Schatzman, "A resume can be a structured, written summary of a person's education, work history, and professional qualifications."
Murphy and Hildebrandt said, “The curriculum vitae is a document that identifies one's qualifications and career path.”
Locker defined, "A resume can be a compelling summary of one's qualifications for the job."
Thus, a CV is a brief description of one's personal, educational and professional qualifications. The purpose of the resume is to get an interview, not to tell readers everything about you. In fact, it is a kind of advertisement. Nowadays it becomes
The content of a CV
Almost traditional to send a CV with the letter of application.
Biological data should be properly classified under certain headings or sub-headings. It includes a few people information in various fields. Usually, knowledge is presented in a bio-data under the following heading:
a. Personal Information: This section includes full name, temporary and permanent address, phone number, date of birth, parents' names, marital status, nationality, religion and cast in some cases, etc. .
b. Career Goals: Clearly state your goal or future career plan. Say what interests you and what level of responsibility you want to take on. So, the short term and future goal of your career should be mentioned here.
c. Educational Qualifications: A complete record of academic qualifications should be given during this section. It includes the name of the diplomas obtained, the name of the institution attended, the year of completion, the board or university where the diploma is obtained and the division or class or class obtained, etc.
d. Experience: This section includes the candidate's previous experience related to the work requested. The details to be included here are: the period or duration of the previous or current employment of the membership and therefore the dates of levelling, the name of the organization, the position held and a brief description of the functions or nature of work or tasks performed work.
e. Honors and Awards: : Honors and awards are given for outstanding work. This section includes fellowships and scholarship or honorary scholarship, awards given by professional associations and civic groups.
f.Extra-Curricular Activities: The applicant’s extra-curricular activities like membership in various organizations, participation in several seminar and workshops, prizes won in cultural functions etc. are to be mentioned here.
g. References: Names and addresses of the persons who known the applicant and may express a private opinion about his abilities and qualities must tend in this section. It customary to offer three references sort of a teacher, an employer and a friend of the family with high social or professional status. But if the number of referees isn't dictated by the prospective employer, it's better to mention the names and addresses of at least two references. The name, title, complete address and phone number of the referees must tend and it's preferable to point their social relationship to the applicant. The applicant should take permission from the referees to give their names or a minimum of inform them immediately after, with details of the job applied for.
h. Signature of the Applicant: At the end of the resume, the applicant should put his signature and date with the left margin. Below the signature, there must be enough space for typing the complete name of the applicant.
In concluding note, we will say that a resume must include everything relevant to the post or job applied for and must exclude irrelevant things. If the employer invites only resume, sometimes it's better to attach a recent photograph with it.
Q22) What are the types of resume? (7)
A22) Types of Resumes are: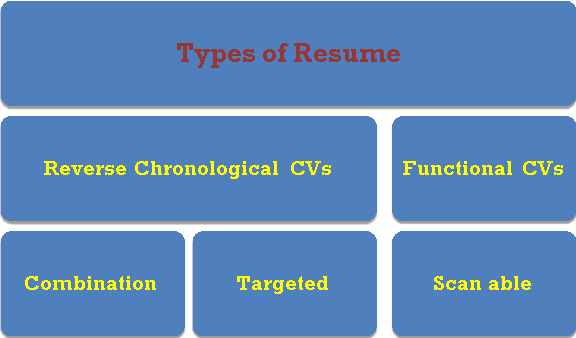
1. Reverse Chronological CVs (also called reverse time order) focus on work history. Demonstrates a Cohesive Work History . It can be difficult to highlight skills and experience.
2. Functional CVs (also known as competency-based CVs) focus on competencies. Demonstrates skills that can clearly be related to the duties or tasks of the job. It is often associated with people who have gaps in their work history.
3.Combination -A combined resume lists your skills and experience first, then your work history and education. Highlights the skills you have that are relevant to the job and provides a reverse chronological work history Some employers prefer reverse chronological order.
4. Targeted -A targeted resume is a personalized document that specifically highlights the experience and skills relevant to the position. Tells the reader how your qualifications and experience clearly match the duties of the position.
5. Scan able- A scan able CV is specifically formatted to be read by a scanner and converted into digital information. Increasingly used to facilitate search and retrieval and to reduce physical storage costs Scanners may not read CV correctly.
Q23) How to prepare for GD? (7)
A23) Over the years, the majority of B management schools have incorporated this tool into their selection process to assess the general personality traits of their applicants. GD is a test that, more importantly, determines an individual's personality, not just their knowledge. Character traits can't be shaped in a matter of days, so it's never too early or too late to start preparing for GD. Follow the prescribed procedure to start preparation.
Step 1: Self-assessment
The first step in preparing for GD is a true self-assessment to discover your inner strengths and weaknesses. For example, one should recognize the level of comfort when speaking in public. If this is an area that gives you nervousness, it may be more appropriate to build confidence through discussion and practice in mock groups.
Step 2: Create your own knowledge repository
You can speak with confidence if you have a well-prepared knowledge of relevant facts and opinions on different topics. GD topics announced today can span all fields, including economic, business, environmental and socio-cultural issues. Therefore, it is advisable to prepare important content in advance. Browse the General GK and follow the main current events. Read a lot on different topics to gather information and facts. It is also important to form your own opinion on the main issues.
Step 3: Check the GD topic from the previous year
This will help you understand and prepare for the different types of GD topics given. GD topics can be broadly divided into three categories. (1) A de facto subject based on static or dynamic knowledge of a particular concept. (2) An abstract subject that assesses your creative thinking by determining how you perceive something. (3) A case-based topic that seeks solutions to specific problems in a realistic situation with constraints and conditions. You can also see the important topics that you expect during your next GDPI session.
Step 4: Build the Required Personality Traits
You cannot acquire personality virtues such as humility or patience, but some personality traits can be taught by deliberate attempt. For example, building communication skills is essential to prepare for GD. “Good communication skills” need to be more tolerant of diverse opinions. Only those who strive to understand the whole of a problem will accept the new opposition. Likewise, when you practice solving multiple case studies using different methods, you may deliberately inherit “problem-solving skills” and “creative thinking”.
Step 5: Clarity of thought and expression
Finally, clear thinking and presenting ideas are the keys to success. There are several tools you can learn and adopt to create GD ideas and content. But the way to express your ideas is art. “Practice, practice, practice” is a mantra you swear when you want to learn the technique of structuring and presenting ideas at the right time. You can rehearse with a mock GD or with a group of friends and colleagues, but practice if you want to prepare for GD.
Q24) What to know before the job interview? (8)
A24. Points to remember before the job interview-
1. Confirmation of the job description.
2. Thoroughly investigate the company.
3. Think about what to wear.
4. Planning a trip for the interview.
5. Preparation of the question put to you.
6. Prepare your own questions for your employer.
7. Follow-up with employers.
8. Are you looking for a new role?
9. Can't find the position you are looking for? Download CV.
10. Read and confirm the job description.
Got a call for your dream job, so how do you prepare for an interview? The first step in the preparation process is to go back and review the job description. Most job descriptions follow a similar pattern and are generally categorized as follows:
1. Job title / department,
2. Tasks and tasks,
3. Skills required.
Job titles and departments help you understand a job's primary purpose, where its role fits in your organization, and who your potential supervisors are.
Carefully read and revise the job description to match your abilities with the skills required for your job. As a result, other organizations may perform similar tasks and be prepared for questions about their past experience.
Investigate the company
Organizations try to hire people with values similar to the corporate culture. A pre-interview company survey provides insight into the organization's future goals and plans, and if these points can be discussed, it seems like a long-term investment for future employers. The following interview preparation tips provide a guide to the aspects of your business that you need to study.
Business Finance:
Check out the company's website. Doing a Google search can also reveal the current state of your business. Have they experienced a merger? -Where have you expanded recently? LinkedIn is also a great source of information.
Culture:
Check out LinkedIn and Facebook, or check out Google Reviews for feedback from current or former employees.
Management:
Take a look at the company website to explore the company hierarchy and find out who the leaders are.
Competitors:
Find out about your company's main competitors and the websites of organizations in the same industry.
Planning a trip for a job interview
One of the most important things to consider when preparing for a job interview is how to get there. A failed plan is a failed plan. If you plan to go for an interview, refuel the day before. I don't want to be full when I'm wearing a costume
Make sure you arrive on time, at least 15 minutes early. Know your address, verify it and, if possible, start the trial a few days in advance. Check the traffic information the morning of the service and plan a back-up route in the event of an emergency. If you are arriving by train or bus, check the weather forecast the day before and check the public transport website for delays. Be aware of railway construction and traffic conditions that can delay your train or bus trip. Go to bed early the night before and get up early so you have plenty of time.